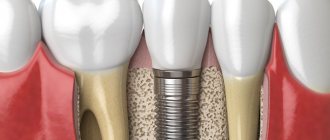
An allergy is a reaction of the body's immune system to a specific substance, an allergen (antigen). The first time, the immune system simply “remembers” the antigen; upon repeated interaction, some people begin to have an inadequate, exaggerated reaction. After the antigen enters the body, antibodies are produced: histamines and cytokines. Redness, swelling, hives, and difficulty breathing appear.
An allergy to dentures can be:
- instant;
- postponed.
The first is very rare, the second is more common.
WITH 99% ACCURACY!
“Bionic Dentis” is the only dental clinic in Moscow where you can undergo an analysis of the survival rate of dental implants (Titanium intolerance TEST). Our European partner guarantees diagnostics for implant rejection at the highest level.
______________________________________________________________________
Our clinic is the exclusive representative of the German laboratory IMD Institut für Medizinische Diagnostik Berlin-Potsdam GbR in the Russian Federation and CIS countries, which works with a unique technique for determining intolerance to titanium implants (Titanium intolerance TEST).
The laboratory is accredited by DAKKS Certificate D-ML-13142-01-00, as well as Certificate D-PL-13142-01-00, which guarantees the highest level of molecular diagnostics according to European standards.
We will help you determine in advance whether your implants will take root or not, which will help you avoid such a painful complication as implant rejection and spend money wisely on dental services without the risk of losing them.
_____________________________________________________________________
IMPORTANT!
If you are planning to install dental implants, you need to find out in advance whether they will take root with you.
______________________________________________________________________
The installation of dental implants is associated with large financial costs for the patient, which is why it is necessary to know in advance that allergies to implants will not occur.
According to European statistics, 26% of the population has a genetic intolerance to titanium , from which dental implants are made.
Search strategy
A PubMed search was conducted to obtain all available literature on allergy and orthodontics. The search revealed a total of 114 articles on the topic. A total of 106 articles focused on nickel allergies in orthodontics. Of these, 14 were directly devoted to Nickel allergy, and 92 were case studies. 4 articles were published in languages other than English. These were excluded and 10 articles were reviewed. Five articles examined the relationship between allergy and root resorption, and three examined the relationship between allergy and hypodontia.
Get laboratory diagnostics for titanium intolerance in Germany:
- if you want to insure yourself against implant rejection
- if you want to know that you are not paying for implantation in vain
- if you want to correctly and individually select the material for dental implants
Implantologists at German and Swiss VIP implantology clinics recommend diagnosing titanium tolerance in 100% of patients, thereby insuring themselves and their patients from severe complications after the installation of dental implants and rejection of dental implants.
_______________________________________________________________________
IMPORTANT!
IN THE RF AND CIS COUNTRIES, TESTS FOR TITANIUM INTOLERANCE AND REJECTION OF TITANIUM IMPLANTS ARE NOT CONDUCTED!
_______________________________________________________________________
There are 2 types of studies that predict implant failure:
1. Type of determination of intolerance to titanium implants (Titanium intolerance TEST)
This study is recommended for all patients before installing even 1 dental implant.
The cost of Titanium intolerance TEST is 19,800 rubles 00 kopecks.
The analysis is carried out directly in a laboratory in Germany.
The price includes blood collection and transportation of blood samples to Germany.
1. The type of study includes determination of intolerance to titanium implants (Titanium intolerance TEST) and determination of genetic polymorphism of interleukins (Degree of inflammation IL-1, IL-1RN, TNF-alpha-genotype).
This study is recommended for patients to undergo before installing 4 or more dental implants and especially when installing zygomatic implants. This test, with a positive conclusion, indicates not only the possibility of early implant rejection, but also indicates late implant rejection.
Cost Titanium intolerance TEST + Degree of inflammation TEST
38,800 rubles 00 kopecks.
The analysis is carried out directly in a laboratory in Germany.
The price includes blood collection and transportation of blood samples to Germany.
_______________________________________________________________________
This cost is tens of times less than the cost of implants and prosthetics in Moscow. For example, the average cost of the popular Nobel Biocare implant, gum former, abutment and zirconium dioxide crown in Moscow is 130,000 rubles turnkey. What if 3-12 such implants are installed?
_______________________________________________________________________
Correctly diagnose implant failure in advance, spending 19,800 or 38,800 rubles, rather than lose health, time and tens of hundreds of thousands of rubles on useless implantation and subsequent reworking of prosthetics.
Ozerov Petr Vladimirovich
Chief physician. Dentist, implantologist, orthopedist, surgeon. Laser dentistry specialist
More details
Braces
Stainless steel braces are generally considered safe. However, alternatives to nickel-free stainless steel braces include:
- Ceramic brackets made of polycrystalline aluminum oxide, monocrystalline sapphire and zirconium dioxide;
- Plastic braces;
- Titanium braces;
- Gold plated braces.
Clarity Advanced ceramic braces.
Extraoral metal products, including metal decorations on headdresses, deserve special attention due to the greater sensitivity of the skin on them. For these patients, plastic-coated jewelry is a better alternative.
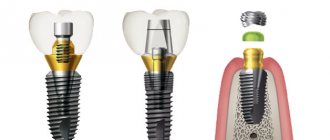
TITANIUM INTOLERANCE - TITANIUM INTOLERANCE. ALLERGY TO TITANIUM.
Titanium has outstanding properties, which means that, compared to other metals, it is well tolerated immunologically.
However, it is known that in 26% of patients, implants cause adverse signs of inflammation, which lead to:
- lack of bone integration of implants,
- failure to engraft a dental implant,
— rejection of dental implants in the first 6 weeks after implantation
— rejection of dental implants within one to five years after installation
- peri-implantitis.
True cellular allergies of type IV to titanium are rare compared to other metals. The reason is that titanium ions have a high affinity for oxygen and therefore form oxides immediately after their release, and unlike free ions, these oxides cannot form protein bonds and therefore allergic effects cannot develop.
The often heard statement that “there is no allergy to titanium” is quite likely true from an immunological point of view. However, allergies are not the only cause of immunologically related intolerance. The most common cause of individual hypersensitivity to titanium is excessive proinflammatory reactivity of tissue macrophages. Macrophages are special cells of the body that are responsible for protecting humans from foreign substances and bacteria.
Titanium particles in the tissue cause an inflammatory response, which leads to implant rejection.
Studies have shown that titanium particles are always found in the bone and soft tissues surrounding the implant. Tissue macrophages ("scavenger cells") phagocytose (ingest) these titanium oxide particles (particulate matter). As a result, a physiological response of the patient's tissues to the implantation occurs, such that macrophages react to contact with titanium oxide particles by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, in particular TNF-α and interleukin-1.
However, the extent of this immune response is very individual.
The intensity of cytokine release depends on the genetic variants (polymorphisms) of the proinflammatory (IL-1 and TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (IL-1RN) mediators involved.
Therefore, titanium intolerance usually results from an increased propensity of tissue macrophages to become inflammatory in response to titanium oxide particles. Titanium-specific lymphocytes do not play a role here, which explains the negative results of LTT and the results of the skin test.
Links
- Hensten-Pettersen A, Jacobsen N. Disintegration of orthodontic appliances in vivo. In: Eliades G, Eliades T, Brantley WA, Watts DC, editors. In VivoAging of Dental Biomaterials. Chicago: Quintessence; 2003, p. 290‑296
- Namikoshi T, Yoshimatsu T, Suga K, Fujii H, Yasuda K. The prevalence of sensitivity to constituents of dental alloys. J Oral Rehabil 1990;17:377‑81.
- Counts AL, Miller MA, Khakhria ML, Strange S. Nickel allergy associated with a transpalatal arch appliance. J Orofac Orthop 2002;63:509‑15.
- McDonagh AJ, Wright AL, Cork MJ, Gawkrodger DJ. Nickel sensitivity: The influence of ear piercing and atopy. Br J Dermatol 1992;126:16‑8.
- Park HY, Shearer TR. In vitro release of nickel and chromium from simulated orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod 1983;84:156‑9.
- Grimsdottir MR, Gjerget NR, Hensten-Pettersen A. Composition and in vitro corrosion of orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 1992;101:525‑32.
- Fors R, Persson M. Nickel in dental plaque and saliva in patients with and without orthodontic appliances. Eur J Orthod 2006;28:292‑7.
- Fischer LA, Menne T, Johansen JD. Experimental nickel elicitation thresholds—a review focusing on occluded nickel exposure. Contact Dermatitis 2005;52:57‑64.
- Emmett EA, Risby TH, Jiang L, Ng SK, Feinman S. Allergic contact dermatitis to nickel: Bioavailability from consumer products and provocation threshold. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988;19:314‑22.
- van Loon, LA, van Elsas PW, Bos JD, ten Harkel-Hagenaar HC, Krieg SR, Davidson, CL. T‑lymphocyte and Langerhans cell distribution in normal and allergically‑induced oral mucosa in contact with nickel‑containing dental alloys. J Oral Path 1988;17:129‑37.
- Rahilly G, Price N. Nickel allergy and orthodontics. J Orthod 2003;30:171‑4.
- Janson GR, Dainesi EA, Consolaro A, Woodside DG, Freitas MR. Nickel hypersensitivity reaction before, during, and after orthodontic therapy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1998;113:655‑60.
- Lindsten R, Kurol J. Orthodontic appliances in relation to nickel hypersensitivity: A review. J Orofac Orthop 1997;58:100‑8.
- Starkjaer L, Menné T. Nickel allergy and orthodontic treatment. Eur J Orthod 1990;12:284‑9.
- Lamster IB, Kalfus DI, Steigerwald PJ, Chasens AI. Rapid loss of alveolar bone association with nonprecious alloy crowns in two patients with nickel hypersensitivity. J Periodontol 1987;58: 486‑92.
- Bishara SE, Barrett RD, Selim M. Biodegradation of orthodontic appliances. Part II. Changes in the blood level of nickel. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1993;103:115‑9.
- Genelhu MC, Marigo M, Alves-Oliveira LF, Malaquias LC, Gomez RS. Characterization of nickel induced allergic contact stomatitis associated with fixed orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2005;128:378‑81.
- Smith-Sivertsen T, Dotterud LK, Lund E. Nickel allergy and its relationship with local nickel pollution, ear piercing, and atopic dermatitis: A population based study from Norway. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999;40:726‑35.
- Mattila L, Kilpeläinen M, Terho EO, Koskenvuo M, Helenius H, Kalimo K. Prevalence of nickel allergy among Finnish university students in 1995. Contact Dermatitis 2001;44:218‑23.
- Schafer T, Bohler E, Ruhdorfer S, Weigl L, Wessner D, Filipiak B, et al. Epidemiology of contact allergy in adults. Allergy 2001;56:1192‑6.
- Blanco-Dalmau L, Carrasquillo-Alberty H, Silva-parra J. A study of nickel allergy. J Prosth Dent 1984;52:116‑9.
- Janson GR, Dainesi EA, Pereira AC, Pinzan A. Clinical evaluation of nickel hypersensitivity reaction in patients under orthodontic treatment. Ortodontia 1994;27:31‑7.
- Jacobsen N, Hensten-Pettersen A. Changes in occupational health problems and adverse patient reactions in orthodontics from 1987 to 2000. Eur J Orthod 2003;25:591-8.
- Schuster G, Reichle R, Bauer RR, Schopf PM. Allergies induced by orthodontic alloys: Incidence and impact on treatment. J Orofac Orthop 2004;65:48‑59.
- Kerosuo H, Kullaa A, Kerosuo E, Kanerva L, Hensten-Pettersen A. Nickel allergy in adolescents in relation to orthodontic treatment and piercing of ears. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 1996;109:148‑54.
- Thyssen JP, Linneberg A, Menne T, Johansen JD. The epidemiology of contact allergy in the general population—prevalence and main findings. Contact Dermatitis 2007;57:287‑99.
- Naranjo AA, Trivino ML, Jaramillo A, Betancourth M, Botero JE. Changes in the subgingival microbiota and periodontal parameters before and 3 months after bracket placement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2006;130:17‑22.
- Pazzini CA, Junior GO, Marques LS, Pereira CV, Pereira LJ. Prevalence of nickel allergy and longitudinal evaluation of periodontal abnormalities in orthodontic allergic patients. Angle Orthod 2009; 79:922-7.
- Gursoy UK, Sokucu O, Uitto VJ, Aydin A, Demirer S, Toker H, et al. The role of nickel accumulation and epithelial cell proliferation in orthodontic treatment‑induced gingival overgrowth. Eur J Orthod 2007;29:555‑8.
- Pazzini CA, Pereira LJ, Carlos RG, de Melo GE, Zampini MA, Marques LS. Nickel: Periodontal status and blood parameters in allergic orthodontic patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2011;139:55‑9.
- Pazzini CA, Marques LS, Ramos-Jorge ML, Júnior GO, Pereira LJ, Paiva SM. Longitudinal assessment of periodontal status in patients with nickel allergy treated with conventional and nickel‑free braces.
- Angle Orthod 2012;82:653‑7.
- Wataha JC. Biocompatibilty of dental casting alloys: A review. J Prosthet Dent 2000;83:223‑34.
- Menné T, Brandup F, Thestrup-Pedersen K, Veien NK, Andersen JR, Yding F, et al. Patch test reactivity to nickel alloys. Contact Dermatitis 1987;16:255‑9.
- Marigo M, Nouer DF, Genelhu MC, Malaquias LC, Pizziolo VR, Costa AS, et al. Evaluation of immunologic profile in patients with nickel sensitivity due to use of fixed orthodontic appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2003;124:46‑52.
- Toms AP. The corrosion of or thodontic wire. Eur J Or thod 1988;10:87‑97.
- Kim H, Johnson J. Corrosion of stainless steel, nickel titanium, coated nickel‑titanium, and titanium orthodontic wire. Angle Orthod 1999;69:39‑44.
- Kurol J, Owman‑Moll P, Lundgren D. Time related root resorptions after application of a controlled continuous orthodontic force. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 1996;110:303‑10.
- Davidovitch Z, Lee YJ, Counts AL, Park YG, Bursac Z. The immune system possibly modulates orthodontic root resorption. In: Davidovitch Z, Mah J, editors. Biological Mechanisms of Tooth Movement and Craniofacial Adaptation. Boston, MA: Harvard Society for the Advancement of Orthodontics; 2000. p. 207‑17.
- McNab S, Battistutta D, Taverne A, Symons AL. External apical root resorption of posterior teeth in asthmatics after orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1999;116:545‑51.
- Nishioka M, Ioi H, Nakata S, Nakasima A, Counts A. Root resorption and immune system factors in the Japanese. Angle Orthod 2006;76:103‑8.
- Owman-Moll P, Kurol J. Root resorption after orthodontic treatment in high- and low-risk patients: Analysis of allergy as a possible predisposing factor. Eur J Orthod 2000;22:657‑63.
- Symons AL, Stritzel F, Stamation J. Anomalies associated with hypodontia of the permanent lateral incisors and second premolars. J Clin Pediatr Dent 1993;17:109‑11.
- Larmour CJ, Mossey PA, Thind BS, Forgie AH, Stirrups DR. Hypodontia—a retrospective review of prevalence and etiology. Part I. Quintessence Int 2005;36:263‑70.
- Yamaguchi T, Tomoyasu Y, Nakadate T, Oguchi K, Maki K. Allergy as a possible predisposing factor for hypodontia. Eur J Orthod 2008;30:641‑4.
ALLERGY TO TITANIUM. ALLERGY TO IMPLANTS.
Risk of titanium dental implant loss in healthy patients with titanium intolerance:
THE FOLLOWING VALUES SHOULD BE CONSIDERED AS THE CRITERIA FOR THE TEST FOR INTOLERANCE OF DENTAL IMPLANTS:
Titanium intolerance TEST
negative titanium stimulation test there is no risk of rejection positive titanium stimulation test the risk of rejection is 12 times greater
Degree of inflammation IL-1, IL-1RN, TNF-alpha-genotype
genetic degree of inflammation 0 risk of rejection no genetic degree of inflammation 1 risk of rejection 1.5 times greater genetic degree of inflammation 2 risk of rejection 2.4 times greater genetic degree of inflammation 3 risk of rejection 3.8 times greater genetic degree of inflammation 4 risk of rejection greater 6 times
Comment: A patient with a positive titanium stimulation test has a 12-fold increased risk compared to the normal population.
If he or she also has a genetic grade 4 inflammation, the risk increases sixfold, IN THIS CASE TITANIUM IMPLANTS CANNOT BE INSTALLED.
What does a positive titanium stimulation test or increased genetic inflammation mean?
A positive test result (titanium intolerance) in one of the two tests indicates the presence of a significant predisposition to the development of titanium-related inflammation, which may be associated with primary or secondary implant loss.
This is not the same as an allergy, which requires that the allergen be avoided as a matter of course.
Therefore, a positive titanium stimulation test or inflammation grade of 2 to 4 is not an absolute contraindication for a titanium implant.
However, in these cases, alternatives (eg, ceramic implants, removable bridges, coated titanium implants) should be critically evaluated and preventive measures should be increased (prophylaxis, use of reduced rotation speeds, avoidance of titanium periodontal probes, immediate implants, removal of sources of infection, smoking cessation , optimal correction of other predisposing diseases (diabetes mellitus), absence of multiple implants, avoidance of immunostimulation for up to 4 weeks after implantation).
Should an implant allergy test be performed before implantation or in cases of suspected titanium intolerance?
An allergic reaction to titanium, as mentioned earlier, is extremely rare, due to titanium's strong tendency to oxidize. Thus, LTT is much less important for dental problems compared to the titanium stimulation test.
However, even dental implants from the most famous manufacturers contain elements such as nickel, vanadium and aluminum.
These metals are super allergens.
From the point of view of type IV sensitization, metal contaminants are of greater importance in the development of implant rejection.
For this reason, an LTT screening profile in addition to the titanium stimulation test has been developed, in which these three metals are tested in addition to titanium.
By undergoing laboratory diagnostics in our clinic for intolerance to titanium implants , you will protect yourself from severe complications associated with implant rejection and save your money.
How is the disease diagnosed?
To diagnose the disease, you may need to consult an allergist, immunologist, or dermatologist. Diagnostics is accompanied by the following stages:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity . The doctor will note the moisture content of the mucous membrane, its condition, the type of saliva, and the presence of defects. Receive information about the composition of the implant and time of use. Oxide films indicate the development of allergic reactions.
- Allergy tests . They are prescribed to identify allergens. There are several types: cutaneous and provocative. The first type of test involves introducing a drop of allergens into skin incisions. Provocative tests are done only in a hospital, when other diagnostic methods turned out to be uninformative.
- Elimination and exposure test . Used in the presence of removable dentures. Elimination - removal of the prosthesis for a period of one day to 7 days, until allergic symptoms disappear. Exposure - installation of a prosthesis after the disappearance of negative manifestations.
- Isolation of the prosthesis from the mucous membrane. It is performed by fixing gold foil to dental glue and cement. Used for fixed dentures.
- Analysis of venous blood for antibodies responsible for the occurrence of an allergic reaction.
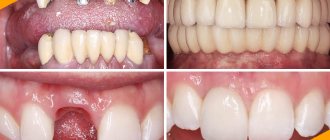
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
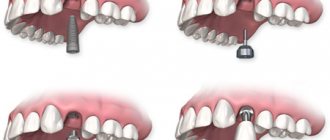
SURVIVAL OF IMPLANTS.
The survival rate of implants depends on several factors:
- tolerance to titanium and lack of macrophage polymorphism.
- absence of allergies to impurities: nickel, vanadium and aluminum.
- compliance with the technique of installing a dental implant.
- absence of bone burn during implantation.
- compliance with the rules of septicism and asepsis in the clinic during implantation.
- correct choice of thickness and length of the implant.
If points 3, 4, 5, 6 depend only on the qualifications of your implantologist, then points 1 and 2 from this list depend on genetic changes in the patient’s body. This is why it is necessary to conduct laboratory diagnostics of implant survival before implantation.
Preventive measures after installation of an implant or prosthesis
Implants must be installed after a thorough examination of the medical history, the absence of contraindications and allergy tests. Then there will be no exacerbation of the allergic reaction. After implantation, you must adhere to the following rules:
- avoid stress;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- Healthy food;
- reduce the consumption of spicy, sour foods;
- exclude strawberries, citrus fruits, coffee, eggs from the diet;
- quit smoking.
Even ordinary mineral water provokes allergies because it accelerates electrochemical processes in the oral cavity.
IMPLANT REJECTION. REJECTION OF DENTAL IMPLANT.
Implant rejection is the lack of growth of bone tissue to the surface of a dental implant, or the destruction of this connection, which was formed earlier.
An inflammatory process begins in the bone tissue, which leads to implant rejection and peri-implantitis.
Implant rejection is classified:
- implant rejection in the early stages, up to 4 weeks after implantation.
- implant rejection in the later stages, after 6 months after implantation.
Implant rejection is a serious treatment complication that must be prevented!
First aid
At home, to reduce the intensity of unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to do the following:
- Take an antihistamine tablet, Zodac or Zyrtec will do.
- If the denture is removable, remove it and rinse your mouth with an antiseptic.
- Do not wear dental appliances until the cause of the discomfort has been identified.
There is a great way to avoid trouble and protect your health. Before choosing a material for making a dental structure, take an allergy test. This is especially true for those who are prone to similar problems and have encountered adverse reactions when in contact with various materials or metals.
SYMPTOMS OF IMPLANT REJECTION. SIGNS OF IMPLANT REJECTION.
Signs of implant rejection may be completely absent. Sometimes the patient does not notice any symptoms of implant rejection. Only when the dentist begins to check whether the implant has grown to the bone tissue or not, he discovers that the implant is not fixed to the bone.
However, most often the patient experiences the following symptoms of implant rejection:
- redness of the mucous membrane in the area where the implant is installed.
- change in color of the mucous membrane in the area of implant installation to bluish.
- discharge of pus from the gums in the area of implantation.
- pain when pressing on the gums in the area of implantation.
- proliferation of granulation tissue in the area of implantation.
- not a significant increase in body temperature.
- mild pain in the implantation area.
- loosening and mobility of the implant.
- a change in a clinical blood test indicating inflammation in the body.
- acceleration of ESR in clinical blood tests.
If these symptoms of implant rejection are detected, it must be urgently removed.
Diagnostic measures
Timely assistance from a specialist will help prevent the worsening of the condition and the development of complications. Initially, the doctor will perform bimanual palpation and determine the need for subsequent laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Making a diagnosis may require:
- orthopantograms (dental x-rays);
- tests and samples in the laboratory (Müllemann test, Schiller-Pisarev test);
- computed tomography;
- examination of biomaterial from the affected area (determination of the type of pathogenic microflora).
The specialist also performs a differentiated analysis of signs to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms: cystic suppuration, mucositis, periostitis.
CONSEQUENCES OF IMPLANT REJECTION
If a dental implant fails, it must be removed immediately. After removal of the implant, bone grafting is necessary. After removing the implant, you must wait 4 months and reinstall the implant.
If you do not remove the rejected implant, serious complications will arise:
- destruction of bone tissue in the area of the rejected implant.
- periostitis.
- osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
- abscess.
- phlegmon.
Treatment methods
Allergies cannot be cured. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can be relieved. There are two ways to solve the problem of allergies to fixed structures . The doctor can:
- Remove the implants and install structures that do not cause allergies. The method requires identification of the allergenic component. A new structure can be installed no earlier than a month after the first one is removed.
- Metallize the surface of the implant with hypoallergenic materials. Usually gold and platinum are used.
Drug therapy is not always required. Initial symptoms following surgery usually go away on their own. If this does not happen, the following may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines (Loratadine, Fenistil, Zodak, Claritin).
- Antiallergic - antihistamine (Fenkarol, Diphenhydramine, Tavegil).
- Adsorbents (Smecta, Polysorb).
- Hormones.
- Ointments for the oral cavity (Cholisal, Metrogyl Denta, Vokara).
Additionally carried out:
- plasmapheresis - filtration of blood plasma through special membranes;
- immunosorption is a method of blood purification (extraction of antibodies or antigens from complex mixtures using immunosorbents);
- cricothyroidotomy - ensuring patency of the upper respiratory tract in case of obstruction.
When using removable dentures that cause an allergic reaction , the doctor can replace them with structures made of hypoallergenic materials.
To what components of structures can an acute reaction of the body occur?
The above symptoms occur when the body does not “read” certain substances contained in the structures as homogeneous to it. Since they are made from artificial materials, some elements contained in the material or unwanted chemical reactions that occur under the influence of certain conditions can cause allergies. The following materials/components can act as an allergen and cause an inflammatory reaction:
- various metals in the composition: the use of cobalt, chromium, nickel and their combinations in production somewhat reduces the cost of construction, which makes them popular. They are used to create budget crowns and bridges made of metal-ceramics, as well as the basis for removable clasp dentures. The presence of these metals in dentures becomes a common problem for allergy sufferers due to spontaneous corrosion processes - destruction of the metal. It occurs under the influence of the chemical components of saliva, due to the “hostile” interaction between different metals in one prosthesis. Temperature changes during the manufacture of structures also have an impact, causing instability of the material,
- toxic elements such as copper and manganese. Under the influence of electrochemical processes in the oral cavity, these metals are released from the supporting material and enter the blood, saliva, and gastric juice. Thus, they increase the undesirable concentration of antigens and provoke allergies,
- dyes in dentures can also trigger an immune response. They are used to provide aesthetics, but are not always biocompatible,
- Some types of plastics (most often inexpensive acrylic) can provoke stomatitis or, again, acute allergies. The residual monomer must be contained in the prosthesis in a certain concentration - no more than 0.2%. Exceeding this proportion in case of violation of production technology causes an inflammatory process in the mouth,
- galvanic currents that arise due to the heterogeneity of metals incompatible with each other and have an irritating effect on tissue. Different metals can act as electrodes in relation to each other, saliva serves as an electrolyte, and the entire system produces microcurrents. The so-called “galvanic syndrome”, or galvanism, is manifested by a number of symptoms, such as a metallic taste in the mouth, increased salivation, sleep disturbance, distortion of the sense of taste, and more.
Interestingly, acrylic, which is used in orthopedics, is a high-polymer compound of a non-protein nature. Namely, it is to foreign proteins that allergies mainly occur. But the monomer contained in acrylic, which is called methacrylic acid methyl ester, can combine with body proteins as a potential hapten and turn into an antigen.
REPROSTHETICS WITH ACRYLIC PROSTHETICS - RUB 150,000. instead of 180,000 rub. until January 15, 2022!
Re-prosthetics with an acrylic bridge on a metal frame (all included) up to 12 units.
Call now or request a call
Modern prosthetics have developed several new composites that are more biocompatible. New technologies are being used in this area. Now designs made of safe plastics have come into use, for example, soft and durable nylon. Allergies to nylon dentures are extremely rare. Ceramics, from which a large proportion of structures are made, are also safe for the body. It is reliably known that metals such as gold, silver, titanium, and iron are resistant to corrosion and do not cause allergic reactions. But the tolerance of the components is individual for everyone, so it is impossible to say with one hundred percent certainty that the prosthesis will not cause rejection.