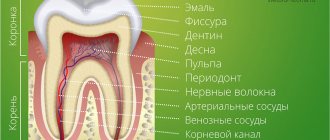
Good teeth are more than just an attractive smile. This is also an opportunity to live without major prosthetics for a long time. However, sometimes anomalies in the shape of teeth occur during growth, and the identification of these developmental anomalies is more important for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Below you will find out what violations of the correct shape of teeth are, and what methods are used for their diagnosis and treatment. You can also find out how to treat your teeth quickly and painlessly in Odessa.
Signs of developing pathology
The pathology is quite easy to detect on your own based on its characteristic signs:
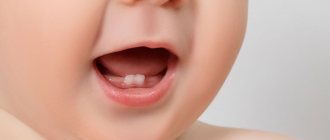
- the teeth have the shape of a cone or barrel, and their crowns become sharper towards the cutting part,
- usually they are smaller in size than all the others, that is, there is such a phenomenon as microdentia,
- they often have grooves, stripes, spots, depressions, and hypoplasia is observed.
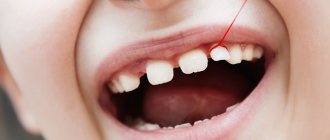
Spike-shaped teeth are also called awl-shaped. They also have another name - conical teeth. Defective units are localized in the frontal zone of the smile, most often on the upper jaw in the area of the anterior and lateral incisors. Often they are supernumerary, then they can erupt between two incisors, overlap them, causing crowding, or “break through” into the second row, like sharks.
How to prevent diastema in a child
If diastema is a common occurrence among relatives, the parents of a small child should inform the dentist about this when the child is 2-3 years old. The specialist will observe the dynamics and, if necessary, offer age-appropriate types of correction.
Among the general recommendations on how to prevent gaps between teeth in children, the main one is to ensure that the child does not develop bad habits, such as biting nails, pencils and pens, and sucking fingers.
The main reasons why pathology occurs
Conical teeth are a problem that can be noticed already in childhood. The pathology may be caused by a genetic factor, a mutation of some DNA genes, burdened by heredity. It can occur due to unfavorable conditions for the development of the child even in the prenatal period, or in the first years of life. For example, if a pregnant woman or the baby himself has had rubella, syphilis or infectious diseases, has metabolic disorders and disorders of the endocrine system.
The anomaly is usually classified as hereditary or congenital1, associated with a violation of the formation and development of tooth buds in the embryonic period. But the problem is often diagnosed in premature babies and those who have low weight or dystrophy. It can develop against the background of an acute lack of vitamin D, because it is this vitamin that the body needs, especially in the first years of life, for the proper formation of bone structures. Another reason that provokes the development of pathology is nephrotic syndrome (kidney disease).
Prevention of recurrence of diastema
Relapses in orthodontic treatment, unfortunately, occur frequently. This is especially frustrating considering how much time and money is involved in fixing the problem. In the case of diastema, its appearance can be caused by various reasons. The most common are incorrectly selected treatment and neglect of the orthodontist’s recommendations during the retention period.
Sometimes patients refuse the necessary surgical treatment or wearing braces, and insist on “simple” correction methods, for example, installing crowns or masking the gap with composite materials. But since the problem remains unresolved, the diastema will return.
Likewise, she will not keep you waiting if, after treatment, the patient decides to ignore the orthodontist’s recommendations and does not wear retention devices.
Types of pathology
Doctors distinguish several types of pathology.
Spike teeth
The tenon-like shape is characteristic of the lateral incisors located on the upper, and less commonly, the lower jaw. Such elements have a sharply narrowed cone-shaped shape. As for the length of the coronal part, it can be either shortened or, conversely, elongated. With this type of pathology, in a number of clinical situations large interdental spaces in the smile zone are noticeable, but sometimes they are absent, and the contact between adjacent units is very dense.
A child often develops a spiky tooth due to genetic disorders, DNA gene mutations, and developmental defects such as ectodermal dysplasia and cleft palate. In some cases, the development of the disease occurs against the background of congenital partial adentia or pathology of the development of tooth buds.
Hutchinson's teeth
The central incisors are barrel-shaped, and in the area of the cutting edge they have a characteristic semicircular notch. With this type of anomaly, the matter is not always limited to one problem: patients with a similar defect suffer from systemic enamel hypoplasia.
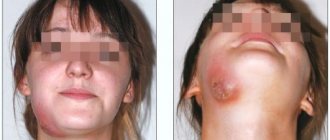
The defect develops if the child’s mother or the baby himself has had infectious diseases, rubella or syphilis.
Fournier's teeth
Fournier's central incisors differ from Hutchinson's incisors only in that they do not have a characteristic notch on the cutting edge. The reasons for their formation are infections and congenital syphilis.
Pflueger's teeth
This anomaly most often develops on premolar teeth. It is characterized by underdevelopment of the masticatory tubercles. The enamel in this pathology has various microdefects; it is covered with spots, tubercles, and grooves. The disease is also characterized by the fact that without treatment, hard tissues quickly wear out; they are very sensitive to various types of influences and temperature changes.
On a note! Anomalies of Hutchinson, Fournier and Pfluger are closely related to systemic hypoplasia caused by insufficient development of enamel. Therefore, in patients with this diagnosis, not only the aesthetics of the smile suffers. They experience pain and discomfort; hard tissues are very sensitive to spicy, cold and hot foods, to mechanical stress, and are susceptible to fragility and abrasion, as well as the development of caries.
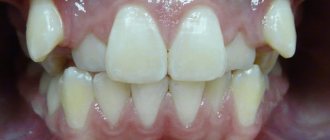
Malocclusions
Malocclusions are deviations from the normal relationship of the dentition of the upper and lower jaws. These deviations can be considered in three directions:
Sagittal
Prognathia (distal bite) - characterized by a mismatch in the relationship of the dentition due to the protrusion of the upper teeth or distal displacement of the lower jaw. Distal occlusion may be partial or total; jaw, skeletal or dental; with or without displacement of the lower jaw. Etiology: congenital structural feature of the facial skeleton, childhood diseases affecting the development of the skeletal system, inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, etc.
Progenia (mesial bite) - characterized by inconsistency of the dentition due to protrusion of the lower teeth or mesial displacement of the lower jaw. It may be partial or complete; jaw, skeletal or dental; with or without displacement of the lower jaw. Etiology: congenital structural feature of the bones of the facial skeleton, incorrect method of artificial feeding, early loss of primary molars, etc.
Transversal
Transversal narrowed dentition - discrepancy between the width of the upper and lower dentition
Vertical
- deep bite - a closure of the dentition in which the front teeth are largely overlapped by the antagonists. Depending on the vestibular or oral inclination, two types of deep bite are distinguished - vertical and horizontal. Etiology: congenital structural feature of the facial skeleton, childhood diseases affecting the growth and development of bones, early loss of primary molars. The main goals of treatment are to separate the bite, expand the narrowed dentition on the jaw that is lagging behind in development, and, if necessary, move the lower jaw.
- open bite - characterized by the presence of a gap between the teeth with central occlusion. This gap occurs more often in the area of the front teeth. There are two forms of open bite - vertical and horizontal. Etiology: rickets, difficulty in nasal breathing, early loss of frontal teeth, wide diastema.
- crossbite - characterized by the reverse closure of the teeth of the right or left half of the bite. Etiology: delay in the replacement of milk teeth by permanent ones, incorrect position of the tooth buds and subsequent incorrect eruption of these teeth, uneven development of the jaws and dental arches.
Problems that pathology leads to
An awl-shaped tooth in a child or adult is not only an aesthetic and psychological problem. A person with this defect can constantly injure the oral mucosa, which in turn is fraught with stomatitis, gingivitis and periodontitis, the formation of painful and poorly healing ulcers and their degeneration into malignant tumors.
An abnormal form can become a prerequisite for the formation of malocclusion, as well as the cause of poor-quality chewing of food, dysfunction of the maxillofacial apparatus, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
On a note! If spike-shaped teeth are supernumerary, then they provoke a phenomenon called crowding. When overcrowding occurs, high-quality hygienic oral care is difficult; small pieces of food are poorly removed from the spaces, which leads to increased accumulation of bacterial plaque, the appearance of halitosis, caries and gingivitis.
The defect is often accompanied by enamel hypoplasia, which means that hard tissues are very vulnerable and sensitive to any external influences and bacteria. The enamel in patients with this problem is quickly destroyed and is susceptible to caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis).
How does a wedge-shaped tooth defect manifest?
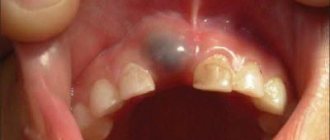
When teeth are affected by a wedge-shaped defect, as a rule, the enamel does not change its color or darken. The surface of the affected tooth remains smooth, smooth, and shiny. The main symptom of a wedge-shaped tooth defect is the appearance of increased sensitivity of teeth to external irritants: cold, hot, sweet and sour foods, as well as an acute reaction of teeth to brushing and chewing solid food. Sometimes a wedge-shaped tooth defect is accompanied by a slight exposure of the neck of the tooth.
A change in the color of the enamel when it is affected by a wedge-shaped defect can occur if the disease affects not only the surface layers of the tooth, but also the internal ones, for example, dentin.
A dentist will be able to diagnose the disease in a timely manner during a routine examination. It is very important to come for a consultation at the dental clinic every six months. If you are looking for where to get effective treatment for dental defects, we invite you to Dentistry on Shchelkovskaya “Diamed”. Our clinic employs experienced doctors with a large practical base in treating a wide variety of dental diseases. You can make an appointment by calling 8 or through the website - just fill out the appointment form.
Treatment methods
You need to understand that if teeth have grown in an irregular shape, the defect is irreversible. Therefore, all the methods that modern dentistry offers will be aimed at visually concealing and eliminating the defect, restoring the correct anatomical shape for the normal functionality of the maxillofacial system, improving the appearance and beauty of the smile.
Composite restoration
Artistic restoration, namely changing the shape of a tooth and its color using a light-curing composite and photopolymers, is the least invasive technique that quickly allows you to get results in just 1 visit to the clinic. Composite restorations are good because their cost is low, and the patient, if necessary, can remove filling materials in the dentist’s office or replace them with new ones, renew his smile, or choose a different treatment method at any time.
Important! Irregularly shaped teeth are a consequence of internal pathologies and diseases of the body. Therefore, patients often require complex treatment: not only a visit to the dentist, but also constant monitoring by specialized specialists (endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist).
Installation of veneers or lumineers
Lumineers and veneers for spiky teeth are a good way not only to comprehensively transform your smile for a long time (hide irregular shapes, unsightly shades, gaps, crevices, cracks and fillings), but also protect hard tissues from food temperature changes, bacteria and premature destruction. The method is suitable only for adults when the milk bite has completely changed to a permanent one.
Prosthetics with crowns
This method is radical, since the installation of crowns is preceded by large-scale preparation of hard tissues. However, patients whose tenon-shaped teeth have begun to deteriorate severely due to hypoplasia or carious diseases, or when the defects are not amenable to other, less radical methods of restoration, cannot do without it.
Prosthetics with crowns can be performed on both adults and children. For young patients, temporary plastic solutions are used, as well as strip-crowns made of acrylic and light-curing composites, which allow preserving the anterior elements of the row (in this case, the incisors) with various malformations and do not interfere with the correct growth and formation of a permanent bite.
If installing a crown is not possible, then doctors perform removal. Next, the defect is eliminated using implantation, bridge-like fixed or removable dentures.
Why is an unclosed diastema dangerous?
The large distance between the teeth cannot be ignored. You need to visit an orthodontist, who will tell you what caused the pathology and whether it needs correction. At ORTHODONT CENTER clinics, the first consultation is free. If the doctor suspects serious changes in the structure of the jaws, he will conduct a detailed examination using X-ray equipment or a CT scanner.
If the situation is unfavorable, the specialist will offer various types of correction that can remove the cleft and at the same time eliminate the problems associated with it. Untreated diastema can lead to gum disease, the formation of “pockets” in the periosteum, and premature tooth loss. Due to the diastema, incorrect pronunciation of hissing and whistling sounds may occur.
When is orthodontic treatment necessary?
Orthodontic treatment of patients with splintered teeth is carried out in cases where their presence has provoked the development of malocclusion and crowding. And also when there is not enough space on the jaw to create a beautiful and proportional restoration. Orthodontics in this situation allows you to expand the space in the area of defective elements, create gaps in order to subsequently carry out high-quality and functional prosthetics, or artistic restoration.
On a note! If there are ugly or irregularly shaped teeth, then patients most often turn to an orthodontist, although this doctor cannot influence this defect in any way. But in some clinical situations (crowding, lack of space on the jaw), it creates conditions for subsequent beautifully shaped restorations. If you are going to install veneers, lumineers or crowns, then an orthopedist will help with this, if you are carrying out an artistic restoration, a dentist-therapist.
For pathologies such as overnumeration and crowding, the doctor may first recommend the removal of irregularly shaped incisors.
Anomalies of the dentition
Anomalies of the dentition are characterized by a change in the shape of the typical dentition of the upper or lower jaw, which is caused by their narrowing or expansion in various areas and is expressed by crowding of the teeth, their rotation along the axis, vestibular or oral teething, partial edentia, the presence of supernumerary teeth, diastemas and etc. The following irregular forms of dentition are distinguished when they are narrowed:
- acute-angled, when the narrowing is localized in the canine area;
- saddle-shaped, when the narrowing is more pronounced in the premolar area;
- V-shaped, when the dentition is narrowed in the lateral areas, the frontal area acts as an acute angle;
- trapezoidal, when the frontal area is narrowed and flattened;
- common, when all the teeth - frontal and lateral - stand closely together;
- asymmetrical, in which the narrowing is more pronounced on one side of the dentition of the upper or lower jaw, resulting in a crossbite.
The main etiological factors of anomalies in the shape of the dental arches are underdevelopment of the jaws and their deformations caused by diseases of early childhood.