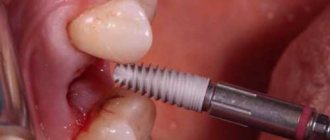
Patients often ask doctors at the NAVA dental clinic with this question.
Relatively recently, a general rule was practiced: one tooth could be removed during one visit to the doctor. Medical technology is changing dynamically, but it is still followed today.
Doctors practice simultaneous removal of several teeth when patients are diagnosed with inflammation of the periosteum, odontogenic sinusitis, there are injuries, difficult eruption of (“eights”) or loss of (baby) teeth, advanced dental root diseases and other pathologies. These procedures carry higher risks. They require the use of large doses of anesthetics, and this is unsafe for the body.
What does a dentist consider when choosing removal options?
For dental operations, 2 types of anesthesia are used: local and general. In the second case, the risks of an overdose of anesthetics and the occurrence of complications associated with them are practically absent, but the body receives an increased dose of analgesics, which can also not have the best effect on its condition.
In each case, when choosing a one-time removal of one or more teeth, the dental surgeon takes into account:
- Health group, the patient’s well-being, the presence of acute, chronic pathologies, allergic reactions to certain drugs.
- The likelihood of complications during general or local anesthesia (dizziness, disorders of the digestive system, impaired coordination of movements, functioning of the respiratory system, etc.)
- Dosage, side effects, indications and contraindications of drugs that should be used for pain relief.
- Is there a risk of damage to adjacent areas of the dentition when several teeth are removed?
- The presence of various pathologies in the oral cavity, including periodontitis, periodontal disease.
- Psychological state of the patient - if he experiences a difficult-to-control fear of medical procedures, the number of the latter must be reduced to a minimum.
It is important to know: even with general anesthesia, it will not be possible to remove a large number of diseased teeth! This approach to getting rid of damaged parts of the dentition is dangerous because it slows down the healing process of wounds and significantly increases the risk of bleeding and inflammation.
How many teeth can be removed when visiting a dentist?
If the circumstances of the operation are positive, the dentist can remove from 1 to 3 teeth at a time. It is important whether the removal is planned or critical, and how complex the operation will be. If the teeth are baby or mobile, three teeth can be removed at once without any problems. In difficult cases, more than one tooth is not removed.
There are situations in which the removal of a number of teeth at the same time is objectively necessary. For example, two adjacent teeth, the treatment of which is impossible. In such situations, the number of teeth removed is not limited and is dictated by the person’s state of health, his well-being and his own desire. Before starting the operation, the doctor assesses the situation and agrees on his decision with the patient. After the removal of a number of teeth, a serious wound immediately forms in the mouth, which is dangerous due to complications:
- introduction of infection;
- long healing;
- difficulty chewing food.
Baby teeth are easily removed, the wound heals quickly after surgery, so 2-3 of these teeth can be removed at the same time.
About indications and contraindications for multiple removals
Simultaneous extraction of several teeth can be used when they are nearby. In such cases, the load during chewing food will be on the opposite part of the dentition, and the likelihood of complications (including alveolitis) will be minimal.
Dental surgeons at the NAVA clinic perform multiple tooth extractions if:
- Extraction of part of the dentition will take place without difficulty and severe bleeding.
- Neighboring (for example: baby) teeth are loose in their sockets.
- Injuries to the dentition have been diagnosed, and the affected parts must be urgently disposed of.
Multiple extractions are practiced in cases of extensive purulent lesions and jaw fractures. The main obstacles to the simultaneous removal of several teeth are cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, and slow blood clotting. In such cases, this extraction option is strictly prohibited.
Diagnostics using a computed tomograph with ENT mode
Accurate diagnosis before extraction is a necessary condition for eliminating complications. The Center uses a Sirona Galileos dental tomograph (Germany).
- an accurate picture of the location of teeth, canals and roots
- ENT mode with the ability to diagnose sinuses
- using a 3D image of the jaw during surgery
The choice of a doctor to remove teeth, especially complex ones, should be taken extremely seriously. Average surgeons usually do not stand on ceremony during the procedure. The result of an operation carried out in a hurry, without proper preparation and adherence to gentle removal measures - bone structures of the jaw broken in pieces, wandering remains of roots, unremoved cysts growing into the maxillary sinus, perforations, fistulas, osteomyelitis and much more. Not to mention the shocking post-operative pain that overtakes the patient after such punitive surgery. Entrust removal to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. Only the maxillofacial surgeon has enough theoretical and practical skills to perform tooth extraction without complications.
How to prevent complications?
The healing of the sockets, the risk of diseases in the oral cavity, and infection of the body directly depend on compliance with medical recommendations after tooth extraction.
To prevent complications from occurring, you should:
- Hold the cotton swabs that the dental surgeon placed in the sockets for at least 20 minutes.
- The first day after extraction, stop rinsing your mouth.
- From the second day, rinse it with water-salt solutions, decoctions of calendula, chamomile, oak bark, chlorhexidine and similar preparations.
- Avoid physical activity for several days, control your facial expressions, and do not touch the site of the operation with your hands.
Food and water can be consumed at least 3 hours after extraction (hot, cold, spicy, coarse foods are prohibited). As for alcohol and alcohol: you should abstain from the first for 3 days, from the second - for 48 hours.
General recommendations
High-quality compliance with the postoperative period will help to avoid complications and unpleasant consequences. Let's take a closer look:
- With such manipulation it is necessary to use a double dosage of an anesthetic substance. Therefore, it is not recommended to drive any transport during the day.
- At the end of surgery, time 4 hours. During this time, try not to eat food, then start with liquid meals.
- For 7 days, do not go to the bathhouse or lie in a hot bath.
- Limit physical activity to a minimum, try not to lift weights more than 1 kilogram.
- Rinse only from the third day as prescribed by the doctor.
- In the first two days, you can take painkillers if you experience discomfort. The specific drug and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician.
- If bleeding occurs, pain continues for more than three days, or other problems arise, visit your doctor immediately.
- If you take any medications on a regular basis, be sure to tell your doctor. Some pills may be limited for a couple of days, as some groups of medications thin the blood.
Each clinical case is individual!
At the same time, the question arises: is it possible to brush your teeth in the days after surgery? Only partially, and a number of precautions should be observed: do not touch the sockets with a brush, significantly reduce the usual amount of toothpaste, rinse the oral cavity slowly. After extraction, it is necessary to take painkillers, and in difficult cases, antibiotics and antihistamines. To ensure that procedures and medications do not harm the oral cavity and the body, they must be agreed upon with the specialists of the NAVA clinic. It is important to know: each treatment case is individual. And what helps one patient may be dangerous for another.
This article was checked and approved by the doctor Eduard Gennadievich Reunin.
There are two types of extraction
Planned removal is prescribed if:
- A diseased tooth cannot be cured;
- The patient has a growth pathology - the tooth is positioned incorrectly, injures the tissues in the oral cavity or interferes with nearby teeth;
- The crown of the tooth is completely destroyed.
Emergency extraction is performed if the patient:
- Purulent periodontitis – acute inflammation develops in the periosteum;
- There is a process of bone destruction due to jaw osteomyelitis.
Signs of periostitis are:
- Throbbing sharp pain;
- Temperature increase;
- Edema.
In such cases, you cannot take measures on your own. Rinsing and warming up will not only not help, but will also worsen the situation.
Modern anesthetic drugs allow tooth extraction to be performed without pain. Anesthesia can be carried out in stages: first, the surface of the gums is covered with gel, and only after that the main anesthetic is administered.
Removal varies in difficulty. In any case, the tissues of the oral cavity are injured and complications are possible. Manipulation requires the professionalism of a dentist.
Treatment of complications with the growth of figure eights
The most common complication with the growth of figure eights is pericoronitis
(formation of a gum hood). When a molar erupts, it is forced to overcome many obstacles: the jaw bone, periosteum, and periodontal tissue. During long, complex eruption, a specific mucous canopy (hood) is formed over the molar. Bacteria and food particles penetrate under it, which causes inflammation.
If coronary artery disease is not treated, the consequences will be serious, the inflammation will spread to the periosteum and jaw bone. This is fraught with the development of periostitis, osteomyelitis, tissue suppuration with the formation of phlegmon, cysts, and fistula tracts. Nearby tissues may be affected, and inflammatory ENT pathologies (otitis media, sinusitis) may occur.
Treatment of pericoronitis is surgical and involves excision of the mucous hood. The operation opens access to the growing eight. The doctor removes the affected tissue, carefully treats the surgical area, and evaluates the clinical picture. According to the situation, he decides whether to remove the eights or help the molar to erupt completely, taking the correct place in the row.
Possible consequences after removal
Complications can occur after any surgical procedure. These include: bleeding from the wound, suture dehiscence, inflammation of the socket (alveolitis), increased body temperature over 38 degrees, numbness of the jaw, bone fragments or tooth remains in the socket.
A normal reaction of the body in response to surgery is the appearance of pain, discomfort, unpleasant sensations in the surgical area, a slight increase in temperature, swelling of the angle of the jaw, and facial asymmetry. These symptoms occur due to soft tissue injury, damage to blood vessels and nerve endings. The pain should subside over time and disappear after 5-10 days.
If after 3-4 days the pain does not decrease and the symptoms of inflammation increase, you should consult a dentist. The most unpleasant complication is alveolitis - inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth. It manifests itself as acute pain, redness and swelling of the gum tissue, a significant increase in temperature, and general symptoms. The wound may discharge purulent contents or necrotic plaque. In this case, treatment by a dentist is necessary.
The problem of medical errors in dental treatment without pain
Many experts argue that when treating teeth under sedation or anesthesia, the likelihood of medical error is greater than when using local anesthesia. It all depends on the professionalism of the doctor and anesthesiologist. The latter must quickly put the patient into a state of sedation or anesthesia and quickly remove it from it, and the dentist must have time to do everything necessary during this time. If the team is well-coordinated, and before the procedure the patient is properly interviewed, fully examined, and planned what they will do, then errors are minimized. We already have legal proceedings, as is customary in America and Europe. A doctor is unlikely to risk his job, position, diploma just to do something wrong while the patient is sleeping.
Phobia or simply fear of dentists
A common fear of a drill can always be distinguished from such a serious problem as dental phobia. If a person goes to talk to a doctor, then most likely he is simply afraid. In this case, the specialist’s task is to find an approach to the patient and choose the right words. When a person realizes that there is nothing to be afraid of, he relaxes and may even fall asleep during the appointment. This happens only because he found contact with the doctor and trusted him. A patient suffering from dental phobia is non-communicative, he can faint only at the sight of a syringe, during the treatment he begins to interfere with the doctor with his hands or feet, he develops shortness of breath, his blood pressure rises sharply... In such situations, it becomes obvious that the person is really not able to control your fear, and this is a serious psychological problem.
When you need to remove the bottom "eight". Indications
Wisdom teeth are distinguished by late eruption, which occurs at 20-30 years of age. During this period, the dental system is practically formed and the third molars often do not have enough space in the dentition. Eruption causes various complications and in most cases requires removal of the molar. In addition, in humans, with evolution, a decrease in the size of the jaws occurs, since, due to the nature of nutrition, the chewing load is constantly decreasing.
Most people do not take good hygienic care of their last teeth. They are located at the end of the dentition, and it is often technically impossible to clean them well. This leads to the accumulation of plaque, damage to the enamel by the carious process and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis). Root canal treatment is very difficult due to difficult access. Therefore, eights must be removed in 90% of cases.
Removal of a fully erupted wisdom tooth
Removal of the lower wisdom tooth is indicated in the following cases:
- Excessive pressure on neighboring teeth, which can lead to their destruction;
- Injury to surrounding tissues;
- Constant biting of the mucous membrane of the cheek;
- Carious lesion that cannot be eliminated due to difficult access;
- Complications of caries: pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis;
- Dystopia – location of the molar outside the dentition;
- A tooth that is a chronic source of infection;
- Formation of perihilar cysts, granulomas;
- Malocclusion and displacement of other teeth.
Do patients who are afraid of dental treatment always need sedation?
Sedation is not a panacea in the fight against fear, it is simply an emergency measure. It very effectively helps to level it out or get rid of it altogether. The fact is that the big advantage of sedation is the absence of memories. The man remembers sitting in a chair, but nothing more. This means that even if there was discomfort during treatment, no unpleasant emotions will remain. It turns out that after having his teeth treated several times under sedation, a person understands that nothing bad is happening to him, and before his next visit to the dentist he no longer experiences such strong fear as before, which means he can try treatment without sedation. At first, of course, the patient may remain tense, but then a feeling of relaxation sets in.
Removal of the dental nerve before prosthetics
If the tooth often bothers the patient with severe pain, a procedure to remove the dental nerve will be performed before prosthetics. This will eliminate the source of discomfort and save the patient’s budget. If the nerve is not immediately removed and a crown is installed on the painful tooth, the patient will soon turn to the dentist for help again, which will entail additional costs.
Other indications for nerve removal:
- caries on the root system of the tooth;
- low landing of the dental crown;
- uncharacteristic anatomical features of the tooth, for example, strong axis tilt;
- periodontitis;
- pulp inflammation.
If no indication for nerve removal is identified, crowns are installed on a living tooth.
Why remove wisdom teeth
Third molars are rarely preserved - they are destroyed early or removal is necessary for the proper functioning of the dentition. Most dentists prefer to remove pathological 8 even before they can seriously harm the health of the jaw (especially the lower one) of the entire row.
Cannot be deleted
wisdom tooth in the absence of the 6th and 7th molars. A contraindication to extraction is inflammation of the periodontium, root, bone or gum, since there is a danger of spread and aggravation of the pathological process against the background of a postoperative wound. The limitations to surgical extraction of third molars are:
- location 8 in the area of malignancy;
- pregnancy;
- hypertension stage II-III;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke less than 3 months ago.
All operations, including dental ones, in these cases are carried out after consultation with the patient's attending physician.
How often can teeth be treated using sedation therapy?
Until now, many patients and even doctors are afraid of everything that is in one way or another connected with anesthesia, because previously heavy drugs with a lot of side effects were used for this. But since then, everything has changed dramatically: a huge amount of research has been carried out, many new medicines have been released. Today, anesthesiologists use the latest generation of drugs that have virtually no side effects; their contraindications are limited to the third and first trimester of pregnancy, lactation, as well as banal intolerance, which can even occur with aspirin.
Removal of the lower impacted figure eight
A common complication is wisdom tooth retention, which is incomplete eruption. It can erupt above the gum as part of the crown or as one or two bumps. In this case, the second part of the crown will be covered with a gingival hood. With insufficient hygienic care, food accumulation, gum inflammation, and pericoronitis (inflammation of the hood) occur. In the case of pericoronitis, the dentist excises or cuts the gingival hood. But if the situation is constantly repeated and bothers you, then it is better to remove such a tooth. Chronic inflammation of the gums is a source of infection that spreads throughout the body and can provoke an exacerbation of other diseases.
The reception is being conducted
Nazaryan Aram Samvelovich
Dentist
Head of the Dental Department. General dentist
Sadoeva Irina Aslanovna
Dentist
Dentist
Konyaeva Elena Vladimirovna
Pediatric dentist, Dentist-therapist
Pediatric dentist, dental therapist
If you are concerned about one or more symptoms, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor, since failure to contact a specialist in a timely manner can lead to irreversible processes.
7
Difference between sedation and anesthesia
Sedation is simply a sleeping pill that puts the patient into a shallow sleep. At the same time, he breathes on his own, he retains all vital reflexes, he can respond to the doctor’s requests, and after the procedure he can calmly go home. Anesthesia is more global. The patient is put into deep sleep, undergoes mandatory intubation, and during the treatment, his breathing and cardiovascular activity are supported and controlled by devices. After recovering from anesthesia, he must be under the supervision of a doctor for at least 30 minutes, and to return home he must be accompanied by someone close to him. Therefore, use general anesthesia only because the patient is afraid. In addition, there are sad statistics according to which, after dental treatment under anesthesia, fear not only does not go away, but intensifies even more.
Types of dental treatment and sedation
Almost all types of dental treatment can be performed under sedation, but the question here is whether it is appropriate. It is reasonable to use sedation during global long-term treatment, lasting more than 3-5 hours, when it is simply uncomfortable for the patient to lie with his mouth open. It is also used in cases of implantation or during open and closed sinus lifts, where it is important to reduce excessive patient activity for safety reasons. In addition, sedation is used in the treatment of children under 3 years of age diagnosed with bottle caries, when it is necessary to treat 6 - 8 teeth. It is important to note that sedation is not anesthesia in dentistry and is used in conjunction with local anesthesia.