Indications for the drug Lidocaine
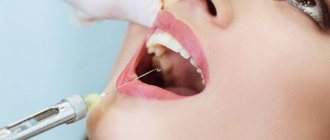
Local anesthesia: in dentistry (anesthesia of the injection point before local anesthesia, suturing the mucous membrane, extirpation of baby teeth, removal of tartar), otorhinolaryngology (surgery on the nasal septum, electrocoagulation, etc.), obstetrics and gynecology (episiotomy and incision treatment , removal of sutures, interventions on the vagina and cervix, etc.); during instrumental and endoscopic examinations (insertion of a probe, rectoscopy, intubation, etc.), radiographic examination (elimination of nausea and pharyngeal reflex), minor surgical interventions on the skin.
Permanent makeup. How to choose an anesthetic cream?
In the permanent makeup industry, application anesthesia is widely used, which can be divided into primary and secondary. Primary anesthesia is applied exclusively to intact skin during the preparation stage. The secondary one is used only after the first punctures. Choosing an anesthetic is an important task for a permanent makeup artist. Together with laser pigment removal expert Vitaly Mikryukov and Akriol Pro project manager Anna Meyendorff, the specialized magazine iColor Magazine has prepared a special material about anesthetics. Chistovye thanks its partners for the information provided.
ADVANTAGES OF APPLICATION ANESTHESIA
- The anesthetic can remain effective for up to 4 hours
- The effect of the drug occurs 10-15 minutes after application
- The anesthetic will not enter the patient’s blood, but only deep into the skin
- The anesthetic does not interfere with control of the depth of needle insertion
ATTENTION! The speed of action of the anesthetic depends on the part of the body to which it is applied, the thickness of the skin and the speed of blood flow. It makes no sense to keep lidocaine + prilocaine cream on the patient’s face for more than 30-40 minutes, since the anesthetics will begin to wash out.
SYSTEMIC TOXICITY OF APPLICATION ANESTHESIA
Despite the ease and safety of using topical anesthesia, there are contraindications to this method of pain relief. Barriers include: acute skin diseases, lactation and pregnancy, elevated body temperature, individual intolerance to the drug, open inflammation and damaged skin areas. Also, the specialist should always keep in mind that topical anesthesia can cause systemic toxicity, which is accompanied by symptoms: from trembling, muscle twitching, nausea, impaired consciousness, orientation to apnea (stopping breathing).
What increases the risk of developing symptoms of systemic toxicity?
- Elderly age
- Heart failure
- Cardiac ischemia
- Low plasma protein concentration
- Metabolic diseases
- Liver disease
- Metabolic or respiratory acidosis
- Prescribing drugs that inhibit sodium channels
All local anesthetics have a systemic effect on the central nervous and cardiovascular systems. For example, lidocaine in small concentrations increases blood pressure and has an anticonvulsant effect. However, as the dose of the drug increases, the pressure begins to drop, and the risk of developing convulsive seizures becomes possible.
EXPERT OPINION
“An allergic reaction can occur to absolutely any ingredient in an anesthetic, so when choosing an anesthetic, preference should be given to drugs that have been registered in the Russian Federation. These products include EMLA and ACRIOL PRO. Both drugs have the same composition – 2.5% prilocaine and 2.5% lidocaine, which is the optimal ratio,” says Vitaly Mikryukov.
HOW TO CHOOSE AN ANESTHETIC?
PRIMARY ANESTHESIA Primary anesthesia drugs are available in the form of a cream, emulsion or gel. The main active ingredient is lidocaine. When choosing an anesthetic, pay attention to the fact that the lidocaine content in the composition is no higher than 5-6%, since exceeding this value will make the skin harder. Most masters use products with a lidocaine concentration of up to 10%, which is acceptable.
SECONDARY ANESTHESIA Secondary anesthesia preparations must have a liquid consistency. The watery structure of the anesthetic makes it easier for the anesthetic components to penetrate deep into the skin and provide instant “freezing”. A good indicator would be the content of vasoconstrictor substances. They reduce lymph production, which has a positive effect on the distribution of pigment in the skin. To select the optimal anesthetic, you should take into account the area and technique of applying permanent makeup. When working in the eyebrow area, it is better to use water-based anesthetic creams and gels. The liquid consistency of the drug will ensure deep penetration of the anesthetic into the layers of the skin. To work with the upper eyelid, preference should be given to anesthetic agents with a thick texture. They are more suitable for this delicate area, as they do not spread and do not get into the eyes.
INGREDIENTS IN ANESTHETICS How do popular ingredients in local anesthetics work?
Lidocaine
It forms the basis of almost all anesthetic creams. Rarely causes allergic reactions, acts quickly and for a long time, does not cause local irritation, is well absorbed and dilates blood vessels. Not recommended for patients with liver disease, as well as for patients using beta-blockers due to the risk of developing hypotension.
Prilocaine
Unlike lidocaine, it has less analgesic effect. Rarely causes allergies, low toxicity. In case of overdose (more than 400 mg at a time), it can increase methemoglobin in the blood. As part of anesthetic creams in the Russian Federation, it is registered only in combination products with lidocaine.
Benzocaine (Anestezin)
It has minimal absorption and is suitable for use on mucous membranes. Insoluble in water. For superficial anesthesia, it is used in the form of a 5-20% oil or glycerin solution, 5-10% ointment. There are no registered drugs with benzocaine for skin pain relief in Russia.
Novocaine
Once in the body, it is hydrolyzed into diethylaminoethanol and para-aminobenzoic acid. Because of this, it often causes allergies. It has low toxicity and is contraindicated in patients with anemia and liver diseases. Intoxication is expressed in nausea, decreased blood pressure, and dizziness. The effect is short-lived and weak – 15-20 minutes. The product does not have a registered indication for superficial anesthesia.
Tetracaine
Highly effective local anesthetic from the ester group. It is often used for tattooing the eyelids, since when it comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye, it does not affect intraocular pressure. It is highly toxic (2 times more than cocaine, 10 times more than novocaine). Due to its vasodilatory properties, it is supplemented with vasoconstrictors to reduce the risk of intoxication. Not a single solution of tetracaine is registered in the Russian Federation.
Epinephrine
Epinephrine constricts blood vessels, making the master’s work bloodless. Also, it has an antiallergic effect.
Adrenalin
Adrenaline is added to anesthetics to prolong the effect. It causes vasospasm, due to which the anesthetic is carried more slowly by the bloodstream. The substance is already present in the body, so it does not cause allergies.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO MAKE ANESTHETIC DRUGS YOURSELF?
Recently, the practice of independently producing anesthetic preparations for the permanent makeup procedure from ingredients available for purchase in pharmacies has begun to gain popularity among permanent makeup artists. Experts strongly recommend refraining from such an initiative due to the risk of harm to the client. In the conditions of “non-pharmaceutical” production, it is impossible to fully comply with all the subtleties of manufacturing: the accuracy of the formulation, the quality of mixing, and sterility. Use only certified products for work!
EXPERT OPINION
Interview with the head of the Akriol Pro project, Anna Meyendorff.
How do you feel about the fact that beauty industry professionals make their own anesthetic cocktails from ingredients purchased at the pharmacy?
Anna:
Extremely negative, because now even dermatologists, who are well versed in skin problems, are moving away from prescription production towards industrially produced drugs in pharmaceutical factories, since there they can maintain precise dosage, good mixing of ingredients, as well as aseptic and antiseptic rules .
How dangerous is adrenaline in its pure form as an anesthetic?
Anna:
Adrenaline added in therapeutic doses promotes greater vasoconstriction, which means it can increase the duration of action of the drug and reduce its systemic toxicity. It began to be added to local anesthetics at the beginning of the 20th century. Most local anesthetics also have a vasoconstrictor effect, and the addition of epinephrine may not greatly affect the effect. In addition, when using anesthetics registered as cosmetics, you cannot always count on the fact that they contain adrenaline, even if it is indicated on the box.
What ingredients should be included in a numbing cream?
Anna:
The composition of the anesthetic cream should be as pure as possible: without preservatives and ether anesthetics that increase the risk of developing allergies (novocaine, tetracaine, benzocaine). An example of the composition of an anesthetic cream per 100 g: lidocaine - 2.5 g, prilocaine - 2.5 g; PEG-54 hydrogenated castor oil – 1.9 g; carbomer – 1.0 g; sodium hydroxide – 0.52 g; purified water – up to 100 g.
Why is lidocaine 2.5% + prilocaine 2.5% emulsion considered the standard in skin anesthesia?
Anna:
Lidocaine and prilocaine enhance each other's effects. When the concentration increases above 5%, the power does not increase, and the risk of developing toxic reactions increases. Clinical trials have proven that the emulsion lidocaine + prilocaine 5% anesthetizes 2 times better than single-component lidocaine, even at a concentration of 40%. In the lidocaine + prilocaine emulsion, the concentration of anesthetics in each fat drop reaches 80%. It is important that the ratio of lidocaine and prilocaine should be 1:1.
The absence of pain and discomfort during an appointment with a permanent makeup artist is 50% of the success of the work result. Relief of pain with the help of anesthesia is mandatory when applying tattooing to the lips and eyelids, because these parts of the face belong to hypersensitive areas. Eyebrow tattooing is not such a painful procedure, therefore, at the request of the client, it can be performed without the use of anesthetics. In this case, the master must take into account that a sudden wince of the client can negatively affect the result of the work.
Directions for use and doses
Locally. Before use, remove the protective cap, put the nozzle on the rod and bring its end to the place of use. When pressed all the way, 0.04–0.054 g of the drug (4–5.4 mg lidocaine) is released. The dose is determined by the size and nature of the surface being treated. The minimum dose is 1–3 doses. Number of doses: in dermatology - 1-3, dentistry and otorhinolaryngology - 1-4 doses, endoscopic and instrumental studies - 2-3, gynecology - 4-5, obstetrics - 15-20 (maximum 40 doses per 70 kg body weight).
In children, in dental practice it is preferable to use it as a lubricant.
Lidocaine
Regional and local anesthesia should be carried out by experienced specialists in an appropriately equipped room with the availability of equipment and drugs necessary for cardiac monitoring and resuscitation, ready for immediate use. Anesthesia personnel. must be qualified and trained in anesthesia techniques and must be familiar with the diagnosis and treatment of systemic toxicities, adverse events and reactions, and other complications.
It should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis, epilepsy, chronic heart failure, bradycardia and respiratory depression, as well as in combination with drugs that interact with lidocaine and lead to increased bioavailability, potentiation of effects (for example, phenytoin) or prolongation of elimination ( for example, in hepatic or end-stage renal failure, in which lidocaine metabolites can accumulate).
Patients receiving class III antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, amiodarone) should be closely monitored and ECG monitoring, since the effect on the heart may be potentiated.
There have been post-marketing reports of chondrolysis in patients who received prolonged intra-articular infusion of local anesthetics after surgery. In most cases, chondrolysis was observed in the shoulder joint. Due to the many contributing factors and the inconsistency in the scientific literature regarding the mechanism by which the effect is realized, a cause-and-effect relationship has not been identified. Long-term intra-articular infusion is not an approved indication for the use of lidocaine. Intramuscular administration of lidocaine can increase the activity of creatine phosphokinase. which may complicate the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
Lidocaine has been shown to cause porphyria in animals and should be avoided in persons with porphyria.
When injected into inflamed or infected tissues, the effect of lidocaine may be reduced.
Before starting intravenous lidocaine, it is necessary to eliminate hypokalemia, hypoxia and acid-base imbalance.
Some local anesthetic procedures may cause serious adverse reactions, regardless of the local anesthetic used.
Conduction anesthesia of the spinal nerves can lead to depression of the cardiovascular system, especially against the background of hypovolemia, so caution should be exercised when administering epidural anesthesia to patients with cardiovascular disorders.
Epidural anesthesia can lead to hypotension and bradycardia. The risk can be reduced by pre-administration of crystalloid or colloid solutions. Arterial hypotension must be stopped immediately.
In some cases, paracervical blockade during pregnancy can lead to bradycardia or tachycardia in the fetus, which requires careful monitoring of the fetal heart rate (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
Administration to the head and neck area may result in inadvertent arterial entry leading to cerebral symptoms, even at low doses.
Retrobulbar administration may rarely result in entry into the subarachnoid space of the skull, resulting in serious/severe reactions including cardiovascular collapse, apnea, seizures, and temporary blindness.
Retro- and peribulbar administration of local anesthetics carries a low risk of persistent oculomotor dysfunction. The main causes include injury and/or local toxicity to muscles and/or nerves.
The severity of such reactions depends on the degree of injury, the concentration of the local anesthetic and the duration of its exposure in the tissues. In this regard, any local anesthetic must be used in the lowest effective concentration and dose. Lidocaine injection solution is not recommended for use in newborns. The optimal serum concentration of lidocaine to avoid toxicities such as seizures and arrhythmias has not been established in neonates.
Intravascular administration should be avoided unless directly indicated. Use with caution:
- in patients with coagulopathy. Therapy with anticoagulants (eg, heparin), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or plasma expanders increases the tendency to bleed. Accidental damage to blood vessels can lead to severe bleeding. If necessary, check bleeding time, activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and platelet count;
- patients with complete and incomplete block of intracardiac conduction, since local anesthetics can inhibit AV conduction;
-Patients with seizure disorders should be carefully monitored for CNS symptoms. Low doses of lidocaine may also increase seizure activity. In patients with Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, allergic and toxic reactions from the nervous system in response to the administration of local anesthetics may develop more often; -third trimester of pregnancy.
Lidocaine, solution for injection, 10, 20 mg/ml is not approved for intrathecal administration (subarachnoid anesthesia).
Publications in the media
(Lidocainum) INN
Synonyms. Xycaine, Xylocaine.
Composition and release form. 1% solution of lidocaine hydrochloride in ampoules of 10 ml; 2% solution in ampoules of 2 and 10 ml; 10% solution in ampoules of 2 ml; an aerosol can containing 790 doses of lidocaine hydrochloride, 4.8 mg each.
Indications. Infiltration, conduction, epidural, spinal anesthesia; local anesthesia in dentistry, otorhinolaryngology, surgery (tracheal intubation, bronchoesophagoscopy, removal of polyps, etc.); arrhythmia, prevention of ventricular fibrillation.
Pharmachologic effect. Lidocaine has a strong local anesthetic effect and antiarrhythmic activity. Lidocaine is used in different concentrations: for infiltration anesthesia - 0.025-0.5% solution; conductor - 1-2% solution, terminal - 10% solution. Compared to novocaine, it acts faster, stronger and longer. In low concentrations (0.5%) it does not differ significantly in toxicity from novocaine; with increasing concentration to 1-2%, toxicity increases by 40-50%. The drug blocks the occurrence and conduction of nerve impulses, reducing the permeability of neuronal membranes to sodium ions, which leads to stabilization of the membrane and inhibits depolarization. The antiarrhythmic effect of the drug is due to its stabilizing effect on the cell membranes of the myocardium. It blocks the slow flow of sodium ions into myocardial cells and is therefore capable of suppressing the automaticity of ectopic foci of impulse formation. In this case, the conductivity function is not inhibited. The drug promotes the release of potassium ions from myocardial cells and accelerates the process of repolarization of cell membranes, shortens the duration of the action potential and the effective refractory period.
Pharmacokinetics. The rate of absorption is affected by the site of administration and the rate of administration of the drug. With resorptive action from the surface of the mucous membranes, the maximum concentration of lidocaine in the blood is achieved after 10-30 minutes; with intravenous administration of the drug - after 5 minutes. 50% protein bound. Metabolized in the liver to form two pharmacologically active metabolites. T 1/2 is from 1 to 3 hours. A small part of the drug undergoes enterohepatic circulation and is excreted in the feces; 10% is excreted unchanged in urine.
Side effects. Headache, dizziness, drowsiness, anxiety, euphoria, ringing in the ears; bradycardia, conduction disturbances; decrease in blood pressure; collapse.
Contraindications. Increased individual sensitivity to lidocaine, weakness of the sinus node in elderly patients, AV block of II-III degree, severe bradycardia, cardiogenic shock; severe liver dysfunction.
Adverse reactions when interacting with other drugs. When beta-blockers are used together with lidocaine, the metabolism of lidocaine slows down due to a decrease in blood flow to the liver, which leads to an increased risk of lidocaine toxicity. Antagonism was noted in the effects of antimyasthenic drugs and lidocaine due to inhibition of neuronal transmission under the influence of the latter.
Information for the patient. When using an aerosol form of lidocaine, it should be remembered that the amount of the sprayed drug depends on the surface to be anesthetized. In adults, the dose should not exceed 200 mg. The aerosol should not come into contact with the eyes. Various types of local anesthesia are administered by medical staff.
No pain – anesthesia in modern dentistry
General dentist Lelekov Alexander Mikhailovich tells.
Dentists don't like to hurt. Civilized dentistry strives for complete painlessness at all stages of treatment.
The most unpleasant procedures, such as treatment of deep caries and pulpitis, tooth extraction, are unthinkable without effective anesthesia.
There are many everyday myths and outdated ideas associated with anesthesia. I’ll tell you more about this useful tool, which makes treatment comfortable, without suffering, pain and tears.
Why is it painful to be treated in some clinics, but not in others?
The patient’s sensations depend on many factors, but the most important is the anesthetic drug itself. At the beginning of the twentieth century, dentists began to use novocaine, and from the middle of the century - the more powerful lidocaine. At one time, this was a real breakthrough in medicine. The treatment became tolerable, but the pain could not be completely eliminated.
Modern clinics use anesthetics based on articaine.
Before treatment, be sure to ask what drug is used to relieve pain:
- Based on articaine, it shouldn’t hurt.
- Lidocaine, novocaine - most likely get ready for a test of patience.
For comfortable and safe treatment of my patients, I use:
- Articaine Inibsa (Spain),
- Ultracaine Sanofi (France),
- Scandonest Septodont (France).
I use Articaine in most situations. Ultracaine D, Scandonest, which do not contain adrenaline - if the patient has health problems. They can be used in elderly people, patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and bronchial asthma. The listed anesthetics do not penetrate the placental barrier and are approved for pregnant women.
Do anesthetics contain adrenaline?
Many patients are afraid that they will be injected with adrenaline along with the anesthetic. Adrenaline (epinephrine), indeed, is contained in anesthetics; dentists value it for its vasoconstrictor effect:
- The removal of anesthetic from tissues is slowed down, so the anesthesia lasts longer.
- Bleeding is reduced, which is important when removing a tooth, treating gums or caries in the gingival area of the tooth.
But there are also undesirable effects: adrenaline can increase your heart rate and increase your blood pressure. A healthy person, as a rule, does not even notice this. But for children and patients with cardiovascular diseases, drugs with adrenaline are contraindicated.
They are given an anesthetic with reduced or no adrenaline. Earlier I mentioned the drugs Scandonest and Ultracain D - they do not contain adrenaline at all.
A mosquito is about to bite
Whether the injection will be unpleasant depends on several factors:
- Which tooth are we treating: anesthesia can be very sensitive when placed in the area of the upper and lower incisors. Mandibular anesthesia is unpleasant: an injection into the area of the mandibular nerve.
- Doctor's manual skills. If the doctor has “trained his hand” properly, is not in a hurry and has set himself the goal of making the treatment as pleasant as possible for the patient, then the injection may not be felt at all.
- The equipment of the clinic: for the patient’s comfort, thin needles and special carpule syringes were invented. For children, topical anesthesia is used - the gel is applied to the gum and “freezes” it before the injection.
Carpule syringe
You may have noticed the unusual but recognizable shape of an anesthesia syringe. It has rings on the sides to make it fit more comfortably in the doctor's hand.
But the main thing about it is a mechanism that allows you to carry out anesthesia quickly, effectively and safely in absolutely sterile conditions. The capsule with the drug is opened by this mechanism right inside the syringe. Fewer hands means fewer germs.
The needles for the carpule syringe are thin and flexible, they are easy to bend at the desired angle. With them you can get close to awkwardly located teeth and provide pain relief in the best possible way.
If anesthesia is contraindicated
In most cases, anesthesia is not completely contraindicated, but only requires a more careful, balanced approach. The doctor takes into account the patient’s age, health characteristics and selects the optimal drug and dosage.
Be sure to tell your doctor if you have the following diseases:
- Heart diseases: arrhythmia and tachycardia, previous heart attacks and heart surgery.
- High blood pressure.
- Problems with the endocrine system: diabetes and thyroid lesions.
- Glaucoma.
- Liver failure.
- Psychoneurological diseases, including epilepsy.
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Allergy to local anesthetics deserves special attention. If you have ever had an allergic reaction to an anesthetic, be sure to remember its name.
In diagnostic laboratories you can order an allergy panel - an analysis of the body's reactions to various drugs. This way you will find the anesthetic approved for you. There is no need to buy it or bring it to your appointment! When making an appointment with a dentist or for a consultation, check whether the clinic can purchase the required anesthetic for you.
General anesthesia
If it is impossible to use any local anesthetic, we will not torment the patient with pain anyway. In such cases, anesthesia is used - dental treatment during sleep.
The procedure is carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, who monitors the patient’s condition using special equipment.
To make the anesthesia work better
A few tips for maximum pain relief:
- Don’t be nervous before your appointment; you can take a mild sedative;
- Do not drink alcohol or liters of coffee, they can reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia;
- Don't delay treatment. If pus forms near the tooth, it will prevent the anesthetic from working.
High-quality anesthesia is not only about the comfort and peace of mind of the doctor and the patient.
Most patients who are afraid of dental treatment are actually afraid of the pain, not the treatment itself. And the fear goes away when they come to the clinic, where reliable pain relief is used.
Having got used to good anesthesia, the patient does not delay treatment and keeps his teeth healthy!