Causes of caries
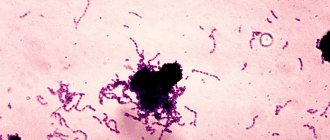
Caries occurs “thanks” to microorganisms living in the thickness of dental plaque. These bacteria - primarily streptococci, lactobacilli and actinomycetes - process food debris that remains on the teeth and produce acids that corrode the tooth enamel, leaching calcium from it. The tooth enamel begins to deteriorate.
The activity of bacteria varies from person to person: it is higher if a person brushes their teeth irregularly or not thoroughly enough, since soft interdental plaque is an excellent nutrient medium for them.
Possible causes of caries in children
- Poor dental hygiene.
- Poor nutrition. Bacteria multiply more actively in the mouth of people who prefer foods with a high content of easily digestible carbohydrates and sugars.
- Insufficient production of saliva, its increased viscosity.
- Lack of solid foods in the diet, which helps remove soft plaque.
- Lack of calcium and phosphorus in food.
- Lack of fluoride in water (below 1.5 mg/l).
- Crowding of teeth, since it is impossible to clean plaque from the interdental space in this case.
- Some diseases predispose to increased activity of the carious process: diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease.
Proper nutrition
One of the preventive measures for dental diseases is a balanced diet - one in which the daily diet contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins that are necessary for the formation and proper growth of dental tissues. In infants, this is breastfeeding. Older children need to include in their diet all the necessary types of complementary foods that are recommended for this age. Additional sources of fluoride can also be water and fluoridated salt; their use does not require special indications. The main sources of calcium are fermented milk products (cottage cheese, milk, cheese, etc.), buckwheat, gooseberries, potatoes, peas, oats, mineral water (some of its types).
Clinical picture of caries
The first stage of the carious process
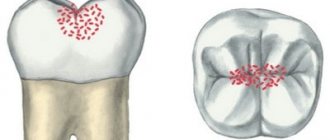
Caries occurs in the spot stage and in the superficial layers of enamel. Then we observe a stain on the surface of the tooth, which gradually becomes more dull, rough and porous.
The second stage of the carious process
If the enamel is chipped and a defect is formed, the tooth becomes more sensitive to irritants. Transient pain appears after eating cold, sweet and sour foods.
The third stage of the carious process
A carious cavity in dentin (tooth tissue located under the enamel). In this case, toothache appears depending on the situation, for example, when chewing on a diseased tooth or when there is a sudden change in the temperature of food, air, or when food gets into the cavity of a damaged tooth.
The fourth stage of the carious process
With further destruction, a deep carious cavity appears in the tooth, which gradually increases in size, so that eventually the tooth is destroyed and the pain appears spontaneous and constant. At this stage, an urgent visit to the dentist is necessary, as this indicates damage to the nerve of the tooth. In this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
Meet our tooth fairies and find out prices
First visit to the dentist
A child’s first visit to the dentist is most often necessary for the following reasons: for a preventive examination upon admission to a preschool or if complaints arise. Don't wait until after the age of four to visit the dentist for the first time. Subsequently, the child needs such visits twice a year. If the baby has already begun the carious process, then during this time it will not be able to spread deeply, caries complications such as periodontitis and pulpitis will not arise, and the tooth can be saved. The sooner the doctor can detect caries, the more successful and painless the treatment will be. Sometimes, in the initial stages of superficial caries, treatment can be carried out without instrumental intervention using mineralizing agents. In this case, medicinal solutions of calcium and phosphorus are applied to damaged areas of enamel. The dentist’s task is not only to provide dental treatment, but also preventive measures that will help keep teeth and gums healthy:
- professional oral hygiene (removal of dental plaque);
- treatment of teeth with calcium and fluoride preparations
- prescribing general treatment if necessary (internal intake of vitamin and mineral complexes);
- teaching your child how to properly brush their teeth;
- correction of the composition and diet, identification of bad habits together with parents;
- sealing fissures (grooves that are located on the chewing surface of the tooth) is a prevention method that is aimed at preventing caries from affecting permanent teeth.
Diagnosis of caries in children
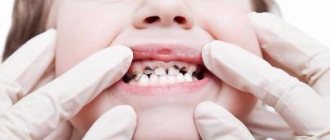
How to recognize caries in a child? A parent cannot always do this, since caries in children becomes noticeable only when there is already a hole in the tooth. Often a child is brought to the dentist “just to check his teeth,” and the doctor finds several caries after examining him with instruments.
The usual methods for diagnosing caries are inspection and probing. As a rule, this is enough to determine the presence of caries. The depth of the lesion can be assessed based on the child’s complaints and by x-ray examination.
Deep caries in a child is visible to the naked eye. At the same time, deep carious lesions on a tooth will almost always require x-rays so that the doctor can understand how far the carious process has gone, whether it is possible to save the tooth or whether removal is necessary.
Special offer
Participate in the promotion
Promotion “1+1”: child and parent
You have entrusted NovaDent with the treatment of your child’s teeth, as a token of gratitude we are giving you a free consultation with any specialist (surgeon, implantologist, therapist, orthodontist, hygienist), as well as an orthopantomogram (panoramic photograph of the teeth) sent by email.
Take time for your health and take advantage of this great offer! Participate in the promotion
Expert of the article you are reading: Lapshina Maria Aleksandrovna Dentist, pediatrician
21 years
Clinical experience
Krasnogorsk
Moscow region, Krasnogorsk, Podmoskovny Boulevard, 5
+7
Free consultation with this specialist
Caries of primary teeth in children
Caries in young children can occur immediately after the first teeth erupt. There are many reasons: the course of pregnancy, illnesses in the first years of life, the rules and regimen of feeding, and the nature and composition of early complementary foods.
Bottle or “circular” (circular) caries in children affects the necks of the upper incisors and canines, since in these areas the enamel is usually the least durable.
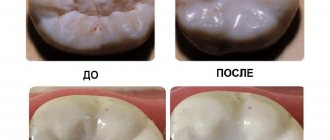
Caries of primary teeth in children at the initial stage manifests itself in the form of a chalky or white spot on the tooth. If you visit the dentist frequently, such caries can be stabilized. However, the enamel of baby teeth with stains can be damaged and destroyed very quickly. First, the stain becomes grayish or brownish, then softens and falls off, and after 2-3 months the carious process already damages the dentin. A cavity forms on the tooth - a clearly visible dark depression. If you see a cavity with a pigmented bottom (“hollow”) on a child’s tooth, do not put off going to the dentist, since at this stage the tooth already needs surgical and restorative treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
A child cannot always point out the source of pain and discomfort, so parents need to be especially attentive to their child’s behavior and monitor the condition of the oral cavity. The following symptoms should alert you:
- Refusal to eat, tearfulness while eating;
- Chewing food on only one side of the jaw;
- Painful sensations from hot, cold and sweet;
- Yellow or white spots, dark streaks on tooth enamel;
- Bad breath.
If you observe one or more of the signs listed above in your child, contact your dentist immediately.
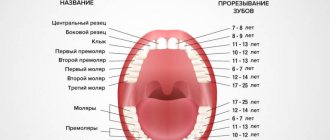
Caries of permanent teeth in children
Newly erupted teeth have lower mineralization, which is finally completed only by 4-5 years after eruption. Young permanent teeth are especially vulnerable in the first year of development. The enamel on them is easily permeable to caries bacteria, so a junior schoolchild should be helped to brush his teeth and be sure to consult with a dentist about the need to seal the fissures and make a protective coating for the enamel.
Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
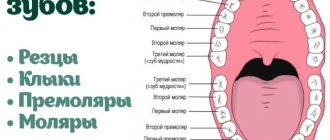
Types of caries
According to the place of manifestation
- Fissure caries affects the grooves and grooves on the surface of the chewing teeth - fissures. Food debris accumulates inside the fissures, which means bacteria that cause caries.
- Approximal (interdental) caries occurs between adjacent teeth, especially often when teeth are crowded. It is very difficult to clean out food debris from the interdental spaces, so plaque often accumulates there.
- Cervical caries destroys the enamel next to the gum, since it is in this place that it has lower mineralization and minimal thickness.
- Root caries characterizes the destruction of the tooth root under the gum. To diagnose root caries, additional methods are needed, since it is difficult to detect visually. In children, it occurs when there is severe destruction of baby teeth.
According to the speed of development
- Compensated caries proceeds slowly; many months can pass from the spot stage to the development of deep caries. In some cases, the process may even be reversible, but only by restoring the mineralization of the enamel in a tooth with caries in the stain stage.
- Decompensated caries develops quickly and on several teeth at the same time; sometimes from the stain stage to deep caries it can take less than 2-3 months. Numerous foci of carious lesions, increased sensitivity of teeth to irritants, deterioration of the enamel structure are signs of decompensated caries.
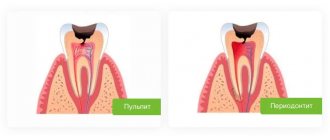
Complications of caries in children: pulpitis and periodontitis
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of a tooth (where its nerve endings and blood vessels are located). Pulpitis can develop from caries very quickly - within 3-4 months. Up to three years of age, pulpitis of primary teeth in children usually develops on the front teeth, after three years - on the chewing teeth. In acute pulpitis, the pain in the tooth is very severe, the temperature may rise, and the child refuses to eat.
Chronic pulpitis in children can occur asymptomatically or be similar in symptoms to deep caries. Such pulpitis develops under fillings or in teeth with advanced caries. If a child of any age develops pulpitis, he must be treated immediately, since pulpitis, in turn, is fraught with serious complications.
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues located near the root of the tooth. Acute periodontitis in children develops quickly and leads to severe pain in the affected area, especially when pressing or touching hot food. The general condition deteriorates sharply, the body temperature can rise to 39 degrees, the child cannot eat. Chronic periodontitis in children can develop slowly and is characterized by mild pain when pressing on the tooth or chewing on the affected side. The mucous membrane next to the tooth swells and becomes bright red.
How to brush your teeth correctly?
It happens that trying to brush your teeth can sometimes cause a negative reaction. But you don't need to get upset about it. Better be patient and play. Remember that a child under three years of age, and older children too, learn about the world through play. Therefore, do not insist on brushing your teeth; it is unlikely that the baby will understand that this is important. Just play. For such games, a battery-powered brush and a toy on the handle are perfect. The movements performed by the brush for different groups of teeth should differ from each other. Cleaning the front teeth should be done from the gums with unidirectional vertical movements. Move the brush behind the cheeks in a circular manner, while the teeth should be closed. Cleaning the chewing surface of the teeth is carried out with horizontal movements from the inside (from the palate and tongue), back and forth, sweeping upward like a “broom”. But not only the movements that are performed are important, but also how much time is devoted to it. There are two ways to check whether your teeth are being brushed adequately:
- – in terms of time (you need to spend about 7-10 minutes brushing all your teeth), for this you can use an hourglass or any other clock
- – by the number of movements (for each area occupied by the bristles of the brush, 5-6 movements are needed).
Treatment of caries of primary teeth in children
Preservation of primary teeth is very important for the growth of the facial skeleton and for the subsequent development and correctness of permanent teeth. If baby teeth have to be removed, chewing food, diction, and the development of the rudiments of permanent teeth suffer. Therefore, treatment of caries in children must begin in a timely manner. Treatment methods for caries in children may vary depending on the stage of the process and the age of the child.
Fluoridation and mineralization
We have already written above that in order to treat caries at the stain stage, it is sometimes sufficient to remove the stain and ensure the restoration of the enamel composition. For this purpose, there are solutions, gels and resins containing calcium and fluorine. Remineralization of enamel is also a good prevention of caries.
Fissure sealing
This procedure is recommended to prevent the development of fissure caries on primary and permanent chewing teeth. The dentist cleans the fissures and seals them with a special liquid sealant that penetrates the enamel fissures and then hardens under the influence of special light. A sealant containing fluoride or calcium fills the recesses of the tooth surface and protects this surface from damage for several years, creating a mechanical obstacle to the penetration of plaque and microorganisms into these physiological recesses of the tooth.
Sealing
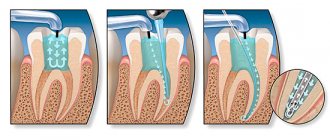
The traditional technology for treating medium and deep dental caries in children is filling. Under local anesthesia, the dentist opens the cavity and cleans it. If a child’s caries is not very deep, sometimes you can do without a bur, using only hand tools. The dentist then places a filling.
Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Treatment of caries in a child under anesthesia
Sometimes we suggest parents treat their child’s teeth under general anesthesia, in medicated sleep. If the child is small and cannot sit with his mouth open, if several teeth need to be treated at once, if we are talking about a special child, then treatment in medicinal sleep will be the only opportunity to provide him with full dental care.
We also have a video in which we filmed the treatment process in medicated sleep. Look