The order of eruption of baby teeth
Everyone is different, but it is still important to know how most babies develop. Children's first teeth usually erupt almost simultaneously on the right and left. The sequence is as follows: first the anterior ones (incisors, canines), then the posterior ones.
It is important to understand that this pattern of teething in children is average, and in your case it may happen in a different order or at a different time. This does not necessarily indicate any violations.
Doctors have compiled an approximate, average diagram of teething in children:
Don't worry if you don't meet these standards for several months. If the parents got teeth late, most likely the children will have the same. Heredity has a very strong influence on development. The teething pattern should not become an unnecessary source of parental anxiety. This is just a guideline, like all other norms.
Both the sequence and timing of teething in children can vary greatly. Only if you are “late” by more than 6 months (for example, nothing appears until a year), it is worth discussing this with your doctor. There are genetic disorders when the rudiments of teeth do not develop at all. However, this is extremely rare. Some diseases also affect the timing of teething, but these conditions in children always manifest themselves with some more obvious symptoms.
In any case, there is no remedy that would “cut teeth” - we won’t pull them out of the jaw. We also do not regulate the cutting order. All that remains is to observe the process in children and take care of their health in general.
How long do permanent teeth grow?
There are no exact dates for the growth of permanent teeth; in each case, individual characteristics of the body and hereditary factors play a role.
Time frame for the final formation of the root system of molars:
- incisors located in the center - climb by 10 years;
- lateral incisors - by 10 years;
- fangs - by the age of 13;
- first premolars - emerge by age 12;
- second premolars – 1 to 12 years;
- first molars – by 10 years;
- second molars are cut by the age of 15.
The rate of tooth growth is different for each group. Rapid eruption is observed in the second premolars; in six months they rise by 8 mm. The incisors located in the center rise by 12 mm per year, and the canines grow to 13 mm in two years.
If there is a slight increase over a long period of time, you should see a doctor. Perhaps the child has problems related to the replacement of milk units.
What problems may arise during teething in infants?
Difficulties do not always arise. But sometimes, about 3 days before and 3 days after teething, the baby’s condition changes:
- gums swell;
- saliva flows more strongly (although a lot of it can be released without connection with teething);
- the temperature rises slightly;
- mood deteriorates (child is less active, cries more often);
- sleep becomes restless;
- stools become slightly looser and more frequent;
- your cheeks turn slightly red (no need to immediately look for allergens and change your diet).
These symptoms may not all appear, in any combination.
The difficulty is that the same symptoms, but usually stronger, can also occur in children with infections. Therefore, if your condition has changed significantly, consult your doctor.
Red flags (tell your doctor if your child has):
- temperature above 38 degrees in the absence of cold symptoms;
- a rash that is unfamiliar to you, which appeared along with a high fever;
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- lethargy;
- mouth ulcers or other sores.
- Eruption cyst (hematoma).
Assess how much the child's condition has changed. If he begins to clearly feel unwell, there is no need to attribute this to the teething of baby teeth. In this case, you need a doctor to rule out more serious problems.
Intramaxillary development
The permanent bite is formed on the basis of dental plates, which are formed inside the pits of stratified squamous epithelium. At approximately the 5th month of the child’s embryonic development, an enamel organ appears along the lower edge of the primordial teeth. As mesenchyme grows into it, dental papillae and sacs are formed.
In total, each child has 20 rudiments in two jaws for the development of replacement permanent teeth, 16 of which are present at the time of birth, and the remaining 4 appear at 1-5 years of life. Being in the same alveolus with the milk sacs, after a while they are separated from them by a bone septum and are placed in separate sockets. The dental plates grow in a posterior direction. The main dental tissues are actively developing - dentin, pulp, enamel, as well as blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Medicines for teething in children
When your baby is in pain, you would like to have a reliable, effective medicine that you can give and sleep peacefully. As in the case of colic, when teething, the pharmacy will offer you a variety of remedies. Pediatric experts do not advise giving any medications without a doctor's permission.
Why? Homeopathic medicines are divided into true homeopathic (containing no active substance at all, and therefore ineffective) or pseudo-homeopathic. The latter contain some amount of plant components (usually chamomile and other, more exotic plants). The first ones do not work under any conditions, including teething in children, but at least they are harmless. Homeopathic remedies for pain containing belladonna (which was not even always listed in the composition) caused many deaths and were therefore strictly prohibited in developed countries.
In our country, the Commission of the Russian Academy of Sciences recognized homeopathy as a pseudoscience, but, unfortunately, there is no strict ban on potentially dangerous drugs. Since manufacturers do not always indicate belladonna in the composition, we recommend that you generally refrain from using any homeopathic remedies for teething pain in children.
Another case is gels with a local anesthetic drug (their name ends in “-caine”: usually benzocaine or lidocaine). Medicines like these are “freezes” that are injected into the gums when treating teeth. Although these drugs are obviously effective, they have also caused many child deaths. Substances of this group affect the functioning of the heart, because the gel is quickly washed off with saliva, and the child swallows it. It is especially dangerous if the parent uses a higher dose than recommended in the instructions. This happens often because these drugs only relieve pain for a few minutes. When the baby starts crying again, the parents apply more, often exceeding the dose. Now professional communities of doctors do not recommend the use of products with local anesthetics, but this does not stop their widespread advertising.
The completion of tooth root formation occurs at approximately this age:
| Teeth | Upper jaw, age | Lower jaw, age |
| Central incisors | 9-13 | 7-11 |
| Lateral incisors | 9-12 | 8-11 |
| Fangs | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| First premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| Second premolars | 11-13 | 11-13 |
| First molars | 9-12 | 9-12 |
| Second molars | 14-15 | 14-15 |
Since the eruption of third molars does not occur at a specific time, it is impossible to establish a clear age at which their roots are formed.
X-ray results confirm the completion of the process of tooth root formation. The key signs are the absence of an opening at the apex, as well as a pronounced periodontal contour.
Thus, completion of dental growth, including full maturation, usually occurs only between the ages of 15 and 18 years. It is at this time that the maxillofacial apparatus already has the same dimensions as in adults.
What to do when children are teething?
The most natural and one of the most reliable ways to reduce pain is cold. Pick up an item - a “rodent” that can be put in the refrigerator. Freezing them is not recommended because it can damage the baby's delicate gums.
Often children prefer to gnaw on their parent's finger or, unfortunately, on their mother's breast. But parents may not have enough patience for a long time, so it is better to find a suitable teether.
It should be:
- whole and durable (the child should not bite off pieces that could cause choking);
- without ropes and beads (the rope can pinch the neck or break, creating a risk of choking on a bead);
- without paint with toxic components;
- just clean (no need to disinfect it).
You can refrigerate the fruit puree or put a few wet cloth toys in the refrigerator so you can replace them.
Of course, children chew not only objects that are ideal for this. But if with a teether made of one piece of silicone or a mitten with a silicone pad the child can be left alone in the playpen for some time, then with a bunch of small objects on a string around the neck or a bracelet made of beads, the same as with some fruit or vegetable, you need to look after it.
If cooling does not help, and the stress of teething is very severe, discuss taking pain relievers and fever reducers (ibuprofen is most often used) with your pediatrician. To be on the safe side, consult your doctor, but a single dose by weight (for ibuprofen is 10 mg/kg), given once at night for 3-4 days of active teething, will not cause harm.
What can cause delays in teething?
Reasons for deviation from normal timing:
- heredity;
- smoking or drinking alcohol by the mother during pregnancy;
- illnesses of the mother suffered during pregnancy or the presence of chronic diseases in one or both parents;
- toxicosis;
- prematurity or postmaturity of the baby (birth earlier or later);
- congenital hypothyroidism;
- rickets;
- diseases suffered by a newborn in the first months of life.
Interesting facts: according to statistics, first-born children develop teeth earlier than subsequent children; in babies from late-bearing mothers - earlier than in babies from young parents; for boys - later than for girls.
Should I brush my newly erupted teeth?
Dentists strongly recommend starting to take care of oral hygiene from infancy. For newly emerging teeth, they offer special silicone brushes or wipes. A simpler option is a finger wrapped in gauze. You can simply moisten it with water or use toothpastes for children under 3 years of age (they are marked 0+ and can always be swallowed). The main thing when brushing your teeth is no violence! A little more cleanliness isn't worth the stress.
| Author Fedor Katasonov | Scientific editor Maria Gantman |
At what age does a permanent bite form?
Permanent elements of the dental series begin to appear even before the temporary ones fall out. The first teeth to appear (at about 6 years old) are the “sixes” (first molars). At 8, the incisors erupt, at 9–10, the canines and premolars, then the second premolars and molars. Well, wisdom teeth (aka “eights”) – after 20 years, and not for everyone. The principle of paired appearance of teeth is preserved during the formation of a permanent dentition. In this case, the molars on the lower jaw grow first, then on the upper jaw. Next, the elements of the lower dentition are replaced, then the upper ones. The surest sign of the early appearance of a permanent tooth is the loss of a temporary one.
Eruption pathologies
What parents should be wary of when primary or permanent dental elements appear:
- delay in the eruption of the first teeth by 2 - 3 months. This may be a sign of the absence of primordia or a genetic predisposition;
- abnormally early dates. Possible disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- excessively dark enamel color. May be a consequence of chronic diseases or high iron levels in the blood;
- pathology of the bite or incorrect vector of tooth growth (rotation, tilt, displacement to the side). These signs indicate deformations of the dental system.
Possible problems
Permanent teeth have just appeared, but this does not mean that there will not immediately be any problems associated with them. Parents should be aware of possible dental problems:
- lack of molars;
- pain in the molar area;
- crooked position of molars;
- molars fall out;
- injuries.
For any of these problems, it is important to contact a specialist in time to receive qualified help.
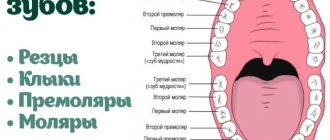
What does a dental formula look like?
To make it more convenient to describe teeth and their number, special formulas are usually used. Each tooth has its own number, which is used to decipher its location.
When describing a milk bite, Roman numerals are used:
- incisors – I, II;
- canine – III;
- molars – IV, V.
If we talk about the formula for adult teeth, here the teeth are counted starting from the center:
- incisors – 1.2;
- fang – 3;
- molars (small) – 4.5;
- molars (large) – 6,7,8.
8 is a wisdom tooth; not every person has it.