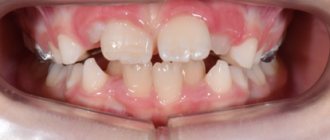
A small chin (medically called inferior micrognathia, or microgenia) is an incredibly common problem.
However, most people who can be confidently diagnosed with this have not only not heard such words, but also do not suspect that there is anything wrong with them. They are healthy, everything is in place. But no matter how hard they try to achieve an ideal appearance, it doesn’t work!
Neither losing weight, nor taking care of your face, nor changing your hairstyle helps. It's not clear what's going on! As a result, people either come to terms with the fact that everyone is imperfect, or they suffer all their lives because the ideal is unattainable for them personally.
Reasons for the development of micrognathia
Anomalies of jaw development can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital ones include:
- Severe acute illnesses of a woman during pregnancy,
- Anomalies of intrauterine development of the fetus,
- Congenital pathologies of the development of the dental system,
- Genetic predisposition.
An acquired anomaly can result from:
- Maxillofacial trauma,
- Artificial feeding and improper sucking in infancy,
- Diseases of the endocrine system,
- Past infectious diseases and inflammatory processes,
- Early loss of baby teeth,
- Problems with nasal breathing.
Which prosthetics are better for complete edentia?
Classic removable dentures are affordable, but they are not able to provide everything necessary for a high quality of life:
- functionality;
- comfort to wear;
- quality of chewing food;
- healthy load on the jaw;
- restoration of the natural shape of the face.
This is a half-measure that does not allow us to fully restore a decent quality of life. This is why dental implantation is the best solution for complete edentia. Computer modeling methods allow you to understand what your smile and overall face will look like even before implants and prostheses are installed. At the same time, computer programs help to accurately determine the location of future implants to restore the natural shape of the face, eliminate deep wrinkles, hollow lips and cheeks caused by missing teeth.
In case of complete absence of teeth, two concepts of implantological treatment are provided: classical and mini-implantation.
With mini-implantation, which is considered a temporary solution, the prosthesis is installed immediately after implantation. With mini-implantation, only removable prosthetics are available, and the design is inferior to classical prosthetics in terms of reliability and durability.
In the classic version, the patient undergoes the procedure of engrafting several implants - artificial roots made of titanium, which will serve as support for the future prosthesis. To securely attach the prosthesis, a minimum of 4 implants are required in the upper jaw and 3 in the lower jaw. But in a number of clinical cases, to achieve better stability, it is recommended to use a larger number of implants. After 6 months, when the implants have finally taken root, a permanent prosthesis is installed on them.
Diagnosis and treatment of narrow jaw
Deformed dentition, crowded teeth, malocclusion, unerupted teeth are consequences of an underdeveloped dental system. The earlier these abnormalities are diagnosed, the more effective the treatment will be. To expand the lower and upper jaws, therapeutic methods, mechanical expanders and plates are used. In rare cases, only surgery helps.
In children under 10-11 years old, jaw expansion gives the best results. This is a time of active growth and formation of bone tissue, so the defect can be corrected with the help of orthodontic structures.
Micrognathia - symptoms and treatment
Almost every type of dysgnathia and micrognathia is accompanied by very specific and noticeable functional and aesthetic disorders. These include all cases of malocclusion: from mesial, when the lower teeth protrude forward relative to the upper ones, to any variants of distal occlusion, in which the lower row of teeth is much behind the upper row. Such malocclusions are always accompanied by certain negative manifestations:
- from the teeth: abrasion, carious lesions, periodontal diseases;
- from the dentition: crowding and compensatory disorders (narrowing of the dentition and its curvature);
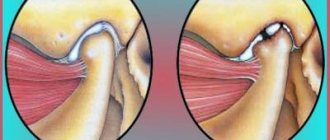
- from the temporomandibular joints: pain, clicking, crepitus (crunching sound), limitation of movements.
With skeletal disorders associated with a decrease in the upper respiratory spaces due to the small size of the supporting structures of the upper and lower jaws, a frequent manifestation of the pathology is breathing obstruction syndromes during sleep, for example sleep apnea.
Obstructive sleep apnea is a potentially life-threatening condition. It is characterized by snoring and repeated cycles of cessation of breathing during sleep. Most often, the pathology is associated with a narrowing of the respiratory space caused by improper bite and position of the jaw bones. In addition to snoring with pauses in breathing and night pain in the chest area, sleep apnea is accompanied by a decrease in oxygen levels in the blood, severely fragmented sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, migraines and irritability.
Despite the listed functional disorders, the most significant clinical manifestation of dysgnathia and micrognathia is the aesthetic component . It is dissatisfaction with the smile and face that forces patients to seek medical help. While the intervention of an orthodontist and/or orthopedic dentist is often sufficient to correct a smile, the help of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon is necessary to restore the aesthetic balance of the face [11].
The main signs of severe underdevelopment of the jaw can usually be seen with the naked eye. These include:
- disproportionate features, distortion of facial contours;
- malocclusion;
- retraction of the upper or lower lip;
- a slanted (“bird-like”) or protruding chin;
- wrinkled skin of the chin, etc.
Severe micrognathia is clearly visible from the outside, but in the early stages only a doctor can diagnose underdevelopment of the jaw bones.
Expansion of the lower jaw
A narrow lower jaw, or microgenia, can be corrected in childhood with special devices - distractors. This is a device that gradually stretches the bones of the lower jaw. New bone and soft tissue grows at the site of the sprain. When installing a distractor, first increase the distance between the canines of the lower jaw. Every day the device allows you to increase the lower jaw by 1 mm. When the jaw is wide enough to accommodate tooth growth, the distractor is placed in place for at least two weeks to stabilize the sprain.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
In adult patients, the lower jaw bones are fused and cannot be stretched, as in children. Therefore, to enlarge the lower jaw, the surgeon cuts the bone in several places with an ultrasonic knife. On the fourth day after surgery, an expansion device is installed. The first adjustment of the stretching is carried out by an orthodontist, then the patient himself controls the stretching process, which can take up to six months.
After expanding the lower jaw, braces are installed on the lower front teeth to correct the bite. Crowded teeth gradually occupy the resulting space.
The photo below shows a narrow jaw before and after expansion.
Diagnosis: complete absence of teeth
Partial edentia means that the patient is missing several teeth. Multiple edentia is a condition in which more than 10 teeth are missing. If the patient has lost the entire dentition - on one or both jaws, then the doctor diagnoses “complete edentia”. As a rule, people in adulthood face this problem, but in exceptional cases, this diagnosis can occur in young people and even children.
There are two types of edentia.
- With primary adentia,
a person is born with dead/undeveloped tooth rudiments. Even partial primary adentia occurs in only 1% of cases of all dental anomalies, and complete primary adentia is an extremely rare diagnosis. The congenital absence of tooth buds is caused by various hereditary factors or diseases that provoke disturbances in the development of the dental plate. Thus, the cause of congenital adentia can be ichthyosis, hypothyroidism, pituitary dwarfism, and infectious diseases. - Secondary complete adentia
is most common in adulthood, affecting about 20% of people over 65 years of age. This form is considered acquired; it is provoked by:
- metabolic disorders;
- age-related changes;
- injuries to teeth and jaw;
- gum disease;
- caries and its complications.
Periodontitis, periodontal disease, periostitis, pulpitis, periodontitis without high-quality and timely treatment can lead to complete or partial adentia even at a young age.
What is secondary edentia
Why, with partial edentia, teeth cannot fully perform the chewing function?
What does partial adentia lead to?
In dental practice, a situation often occurs when a patient is missing several teeth and one could say that this is partial adentia, BUT the remaining teeth are in such a deplorable condition that they cannot perform their natural functions, and in this case it would also be complete edentia, i.e. lack of teeth for chewing food.
On the picture
- partial edentia
Causes of edentia
The first cause of adentia is periodontitis.
The second cause of edentia is caries.
The third reason for tooth loss is pulpitis
The fourth cause of adentia is periodontitis.
The fifth possible cause of adentia is hypoplasia
The most common thing is the lack of proper oral hygiene and care.
There are three diseases that provoke tooth loss - periodontitis (soft tissue diseases), caries and its complications (pulpitis and periodontitis) and hypoplasia (underdevelopment of tooth tissue, most often enamel).
There are other reasons for tooth loss - due to a blow or some complex disease - but such cases are exceptions to general practice, so we will not dwell on them in detail.
The main reason leading to tooth loss is, after all, a lack of proper attention to one’s health and letting the first signs of illness take their course.
There is no consensus or single way to prevent caries or periodontitis; the occurrence of these diseases can be influenced by various factors - genetic predisposition, poor nutrition, poor hygiene and even the area of residence. But timely diagnosis and proper treatment always save the patient from many further health problems.
Features of treatment
Complete dentures on implants can be removable or conditionally removable. Removable ones are used for mini-implantation. Conditionally removable dentures are removed only in the dentist's office.
In classical prosthetics on implants, different fastening methods are used.
- Push-button fixation
is carried out using abutments - equatorial or spherical. When the prosthesis is fixed, the lock is activated. With some force, the prosthesis can be removed for inspection and hygiene procedures. - Another method is beam fixation.
First, a beam is made to connect the already installed implants. The prosthesis itself is attached to it. Prosthetics using this method are more reliable, but more expensive. From a technical point of view, it is more difficult to carry out.
Micrognathia and macrognathia: treatment
Since a child is often born with this anomaly, doctors recommend using special pacifiers and nipples in the first year of life.
For the treatment of micrognathia and macrognathia in adults, different orthodontic structures are used:
- Katz guide crown;
- chin sling;
- corrective mouthguards;
- special plate with a pull-out.
If treatment with this method does not produce results, surgical intervention is possible: the bone is cut and reconnected, the jaw is fixed with a splint so that the bones grow together correctly. This operation can be performed by either a surgeon or an orthodontist. Some dental clinics are engaged in correcting underdevelopment of the lower jaw and other pathologies described above.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!