1928
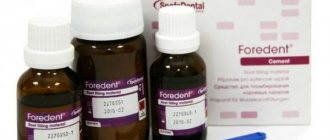
Pulposeptin is a dental paste for the treatment of bacterial root canal infections.
The drug is produced on the basis of antibiotics with bacteriostatic and bactericidal action, it stops the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora, and destroys some species. The paste is used in pediatric and adult dentistry.
Composition and properties of the product
The main active ingredients in the drug:
- Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, active against staphylococci, streptococci, Neisseria, Klebsiella, as well as those flora that are resistant to penicillin, sulfonamides, streptomycin.
- Neomycin sulfate - used exclusively topically (due to its high toxic effect on the kidneys and liver), has a bactericidal effect on cocci, protozoa, and bacilli.
- Dexamethasone is a synthetic steroid hormone that has an anti-inflammatory effect. Relieves swelling, allergic manifestations, reduces the level of intoxication.
- Polyethylene glycol is an excipient, solvent, emollient component in ointments and pastes.
- 2-phenoxyethanol is a preservative.
A balanced formula of antibiotics with a wide range of antimicrobial action quickly and effectively suppresses infection in the pulp (the loose structure that fills the tooth cavity).
The active substances do not enter the systemic bloodstream, do not have a negative effect on the functioning of internal organs, and are not addictive.
The hormone included in the composition blocks the progression of the acute inflammatory process in the periapical tissues - the soft structures surrounding the apex of the tooth root, the alveolar bone.
How does chronic fibrous pulpitis manifest itself and methods of its treatment.
Come here to learn more about the symptoms of diffuse pulpitis.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/pulpit/pri-gipertroficheskom.html we will talk about the differences between hypertrophic pulpitis and other types of pathology.
Allergy to materials used in orthopedic dentistry
Allergology studies a person’s relationship with the outside world and forms of disruption of the immune system’s response when the patient’s body becomes hypersensitive to certain substances. Allergic diseases, such as bronchial asthma, have been known since ancient times, but allergology became an independent medical and scientific discipline only in the middle of the twentieth century.
In recent decades, allergic diseases have become a global medical and social problem. There is a constant increase in incidence. Today, about 10% of the world's population is susceptible to allergies in one form or another, and this figure can vary greatly - from 1 to 50% or more in different countries, regions, and among individual population groups. Currently, there is an increase in the number of severe forms of allergic diseases, which leads to temporary disability, decreased quality of life and even disability. In this regard, early diagnosis of allergic diseases, correct methods of treatment and prevention are of great importance.
An allergen is a substance that enters the body and causes a certain type of immune response, resulting in damage to body tissue. We are surrounded by 5 million xenobiotics, many of them are allergens. The allergist's task is to identify the causative allergen.
Allergic diseases are a group of diseases, the development of which is based on damage caused by the immune reaction to exogenous allergens.
The classification of allergic reactions proposed by P. Cell and R. Coombs (1968) has become widespread throughout the world. It is based on the pathogenetic principle. The classification is based on the characteristics of immune mechanisms.
Type I - reaginic, anaphylactic. IgE-class antibodies and, less commonly, IgG antibodies participate in the development of the reaction. Clinical manifestations: bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis.
Type II - cytotoxic. It is called a cytotoxic type of tissue damage because antibodies formed to cell antigens bind to cells and cause their damage and even lysis (cytolytic action). In the clinic, the cytotoxic type of reaction can be one of the manifestations of drug allergies in the form of leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, etc. The immune mechanism of the reaction is caused by IgG and IgM antibodies.
Type III - damage by immune complexes. The damage in this type of allergic reaction is caused by antigen + antibody immune complexes. Synonyms: immune complex type, Arthus phenomenon. IgG and IgM antibodies are involved in the development of the reaction.
Type III allergic reactions are leading in the development of serum sickness, exogenous allergic alveolitis and other diseases.
Type IV is a delayed-type allergic reaction, the development of which involves sensitized lymphocytes. Allergic reactions occur in sensitized people 24–48 hours after contact with the allergen. The typical clinical manifestation is contact dermatitis.
Thus, an allergy is an immune reaction of the body, accompanied by damage to its own tissue.
In recent years, an increase in life expectancy, new opportunities that have appeared in ordontology - all this makes us think about the mechanisms of occurrence of certain complications when using materials for dentures.
Metal and plastic dentures can cause not only allergic, but also toxic stomatitis, as well as mechanical irritation.
There are certain requirements for materials used for dental prosthetics. Among other things (hardness, aesthetics, etc.), materials must be chemically resistant to the environment in the oral cavity, created with the participation of saliva, nutrients and microbes. These factors can enhance the processes of metal dissolution and oxidation.
Dentures should not have a harmful effect on the oral mucosa and the body as a whole. Materials that are electrochemically neutral relative to each other should be selected.
For the manufacture of metal prostheses, about 20 metals are used - stainless steels, cobalt chrome, silver-palladium alloys, alloys based on gold and platinum. For metal-ceramics - nickel-based alloys, which include iron, chromium, titanium, manganese, silicon, molybdenum, cobalt, palladium, zinc, silver, gold and other metals.
To join dental alloy parts, solders containing silver, copper, manganese, zinc, magnesium, cadmium and other elements are used.
Low-melting alloys used for dies contain lead, tin, bismuth and some other substances.
The development of allergies is facilitated by the severity of electrochemical processes (corrosion) in the oral cavity, which depends on the structure of alloys, heterogeneity of metals, temperature conditions during the manufacture of metal prostheses, the chemistry of saliva and other factors.
Nickel is a component of stainless steel used for orthopedic treatment. In the oral cavity, nickel corrodes under the influence of saliva, causing allergic reactions.
For patients with a history of developing nickel dermatitis from wearing watch bracelets, clothing parts (zippers, clasps), jewelry, the use of this material is not indicated.
Chromium is used for dental prosthetics in the form of cobalt chromium and other alloys. It can have a wide range of effects on the human body, including causing allergic reactions.
Allergic complications can occur when using manganese and cobalt. In patients with allergic stomatitis caused by stainless steel dentures, antihapten antibodies to manganese are found in the blood.
An insoluble aluminum compound, kaolin (aluminum silicate), is used in dentistry as a filling material.
Iron is a metal characterized by corrosion resistance. Does not cause allergic complications.
Copper is an integral part of gold alloys of 750 and 900 samples, solders, and copper amalgam. Electrochemical processes between metal structures in the oral cavity lead to an increase in copper content in saliva, gastric juice and blood. Toxic reactions are possible.
Zinc oxide is part of dental cement, dental amalgams, solders, and brass. Zinc is more active than iron. In the presence of moisture, these metals form a microgalvanic couple in which zinc is the anode, therefore, when metal dentures corrode in the oral cavity, zinc dissolves first. The toxicity of zinc compounds when ingested is low.
When using metal prostheses, the lead content in saliva is increased. Lead is a corrosive metal and has a toxic effect.
Tin is part of low-melting alloys for models used for making crowns. Tin compounds are toxic and are not used in medicine.
Titanium is a component of stainless steel for dentures. The biological role of titanium has not been sufficiently studied.
Molybdenum is low-toxic and is included in stainless steel as an alloying additive.
Indium is a component of solder for stainless steel and is low-toxic.
Arsenic, which is used in dentistry for dental treatment, has significant toxicity.
Silver is part of alloys (silver-palladium, 750 gold, etc.) used in orthopedic treatment. Considering the bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect of silver, silver-palladium alloy is recommended for use in chronic diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract.
Gold has high corrosion resistance and is included in gold alloys and solders for dentures.
Platinum metals (palladium, platinum, etc.) are not poisonous. Palladium is part of the silver-palladium alloy for dentures. Platinum group metals, including palladium, are allergens.
Currently, superelastic materials with shape memory have been created. This direction is very promising and determines the future of orthodontics. An example is titanium nickelide (Ti, Ni, Mo, Fe).
The greatest role in the occurrence of sensitization to metal prostheses is played by the haptens they contain (nickel, chromium, cobalt, manganese). They become antigens only after combining with proteins of body tissues. As a result, so-called conjugated antigens are formed.
Plastics used in dentistry for orthopedic treatment are high-polymer organic compounds. Acrylic plastic can cause allergic and toxic stomatitis. The main etiological factor in the development of allergies to acrylic is considered to be the residual monomer contained in plastic in an amount of 0.2%. If the polymerization regime is violated, its concentration increases to 8%.
Allergies can also be observed to dyes used in aesthetic dentistry.
Ceramics does not cause allergic complications.
Let us note a number of nonspecific factors that contribute to the penetration of hapten from the oral cavity into the blood, increasing its dose and thereby increasing the risk of developing an allergic disease.
- Disruption of heat exchange processes under removable acrylic dentures. An increase in temperature promotes loosening and maceration of the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed, increasing vascular permeability, which, in turn, creates conditions for the penetration of hapten (monomer) into the bloodstream.
- Mechanical trauma to a removable denture during chewing leads to the development of inflammation of the prosthetic bed.
- Electrochemical (corrosive) processes in the oral cavity between metal dentures contribute to an increase in the amount of metal haptens in saliva and mucous membranes.
- A change in the pH of saliva towards increased acidity leads to the development of corrosion processes in metal and plastic structures. At the same time, the release of haptens (metals, monomer, etc.) into saliva and mucous membranes increases.
- The processes of abrasion of dental materials lead to an increase in the content of their components in saliva, and the risk of sensitization increases.
During inflammation, the barrier function of the mucous membrane is disrupted. The permeability of the mucosa is directly dependent on the chemistry of saliva.
It is necessary to differentiate between allergic stomatitis caused by the prosthesis, stomatitis of gastroenterological origin, as well as candidiasis.
Stomatitis can be a manifestation of a disease of the endocrine system (diabetes, pathological menopause), skin (lichen planus) or systemic disease (Sjogren's syndrome).
Complaints may be caused by a decrease in occlusal height (Costen syndrome), manifestations of galvanism, and toxic reactions.
Galvanism occurs after the first contact of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity with irritants. Such stimuli are a variety of potentials (microcurrents) between dissimilar materials.
Allergic stomatitis should be distinguished from toxic reactions to metal prostheses. Toxic stomatitis is characterized by rapid development after orthopedic treatment (stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis).
A qualitative and quantitative assessment of the spectrogram of saliva is carried out to identify the toxic dose of heavy metals. Assessing the quality and correctness of the designs of removable dentures in the oral cavity helps to differentiate between mechanical irritation and toxic and allergic stomatitis.
To diagnose the nature of complications, it is necessary to collect a dental and allergy history. An allergic history includes identifying the patient’s hereditary predisposition to allergic diseases. It is necessary to find out whether the patient suffers from allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, eczema, drug and food allergies, i.e., in other words, whether he has an allergic constitution.
An examination of the patient, including the oral cavity, is necessary. Elimination and exposure tests are widely used in orthopedic dentistry. When the denture is removed, i.e. during elimination, the number of clinical symptoms sharply decreases or disappears for a period of time (3–5 days).
To confirm the allergic nature of the disease, it is necessary to conduct additional immunological tests and, in particular, for the presence of antibodies to plastic and metals. The achievements of today's immunological laboratory diagnostics include examination using 8 tests to identify the true mechanism of allergy:
IgE a/t - antibodies in blood serum; IgE b - antibodies on basophils; IgG a/t - antibodies in blood serum; IgG n - antibodies on neutrophils; TlS - T-lymphocyte sensitization in the IL-2 stimulation test; AGT - platelet aggregation under the influence of allergens; IPLA—inhibition of leukocyte adhesion by allergens; RGML is a reaction of inhibition of lymphocyte migration under the influence of allergens.
If the content of haptens - nickel, chromium, cobalt, manganese - increases in saliva by more than 1x10-6%, the dentures should be removed. An increase in the content of microelements that have a toxic effect (copper, cadmium, lead, bismuth, etc.) is also a reason for removing the prosthesis.
To diagnose allergies, you can use skin tests (drop tests, prick tests, etc.). In order to identify contact allergies to nickel and chromium, alcohol solutions of metal salts are used. You can use a skin patch test, as well as conduct a patch test on the oral mucosa. It should be noted that skin and provocative tests should be carried out only in an allergy office by an allergist with the necessary experience.
Galvanic intolerance is observed in 6% of people using stainless steel dentures. The disease occurs 3 times more often in women than in men. Clinically, the disease was manifested by a sensation of “current passing” and a taste disorder that developed in the first days after prosthetics. In the presence of an allergic process, irritation of the oral mucosa, redness, swelling, as well as distant manifestations of allergy (skin rash with nickel dermatitis) occur.
PH-metry of saliva and potentiometry (measurement of electrode potentials of dentures) are not very informative.
When treating electrogalvanic intolerance, metal inclusions should be completely removed, followed by replacement with appropriate structures made of noble alloys. Similar tactics should be adopted if an allergy to chromium or nickel is detected.
Elimination of allergies can be achieved not only by removing the prosthesis from the oral cavity, but also by shielding (chemical silvering of the prosthesis) and gold electroplating of solid-cast devices.
Diagnosing intolerance of an allergic nature can only be done through a thorough analysis of complaints, anamnesis and the results of clinical and allergological examination of patients.
In the presence of allergic complications (stomatitis, eczema), antihistamines and symptomatic drugs are used. For severe allergic reactions, glucocorticoids are used.
If allergic stomatitis develops, it is necessary to prescribe the patient antihistamines in injection or tablet form. The priority is the intramuscular administration of first-generation antihistamines - suprastin and tavegil, since the development of the allergic process can cause pain in the oral cavity and make it difficult to take both food and medications.
Antihistamines that block H1 receptors are quite safe. First-generation H1 blockers are rapidly absorbed both when taken orally and when administered by injection. Their pharmacological effect appears after 30 minutes. Most drugs are excreted in the urine after 24 hours in an inactive form. The disadvantage of these drugs is the fact that many first-generation drugs cause dry mouth, which can increase the symptoms of oral discomfort.
The activity of H1-blockers is approximately the same, therefore, when choosing a drug, they are guided by its side effects, experience with use and effectiveness in a given patient. First-generation H1 antagonists, at least in the near future, will remain in the arsenal of drugs that are in wide clinical use. This is facilitated by 50 years of experience in the use of these drugs, and the availability of injectable dosage forms that are absolutely necessary for the treatment of acute allergic conditions. In addition, it should be noted the relatively low cost of this group of drugs.
Since the late 70s. Second generation antihistamines began to be used in widespread medical practice. It should be noted that they are highly selective in blocking H1 receptors and lack blockade of other receptors. The effect of the drugs begins to appear 20 minutes after administration and lasts for quite a long time - up to 24 hours. These drugs are produced only in tablet form. They are used 1 or 2 times a day, which is preferable to taking 1st generation antagonists 3 times a day. Second-generation antihistamines do not cause addiction, as well as sedative and cholinergic effects.
Thus, second-generation antihistamines (Telfast, 180 mg; Claritin, Erius, Zyrtec) are considered an alternative to drugs for parenteral administration in the absence of severe pain in the oral cavity. Considering the fact that fexofenadine (Telfast) is a final metabolite and does not undergo further transformations in the liver, it can be prescribed to patients with pathology of this organ.
If chewing and swallowing food is difficult, you can use toothpastes containing anesthetics. Soda rinses are used as a softening agent.
Since the oral cavity contains many microbes (up to 400 species), oral care is very important. It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with furacillin solution. You can use KMnO4 (weak pink solution).
When a secondary infection occurs, broad-spectrum antibiotics should be prescribed. Second-generation macrolides (sumamed, rulide, rovamycin) have proven themselves well in clinical practice. Rovamycin can be used in injection form. In severe cases, quinolone drugs (Tarivid, Maxaquin, Tsiprobay, etc.) are prescribed. It is advisable to do a culture of the oral cavity for bacterial flora and fungi to determine the sensitivity of the microflora to various antibiotics in order to prescribe etiotropic treatment.
In case of severe erosive processes in the oral cavity, glucocorticoids are administered for health reasons. It should be noted that prednisolone is considered the shortest-acting glucorticoid and should be administered at least 4 times a day. More preferable is the use of dexamethasone 4-8 mg 2-3 times a day or the drug celeston, 1.0-2.0, twice a day for 5-7-10 days. Positive experience has been accumulated in the use of long-acting drugs, such as diprospan, 1.0-2.0, which is administered once.
When symptoms of dermatitis in various parts of the body appear, which is often observed when installing prostheses containing nickel and chromium, antihistamines are also prescribed. Treatment with local and systemic glucocorticoids follows general principles. It should be noted that there are various forms of glucocorticoids used externally: ointments, creams, lotions. In recent years, the drugs Elokom and Advantan have been widely used in clinical practice. These glucocorticoids can also be used on the face. When the skin becomes infected, combined agents are prescribed: Triderm, celestoderm with garamycin. In the presence of a purulent infection, antibiotics in tablet or injection form are indicated.
When the acute allergic process subsides after 7–10 days, you can switch to local non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. A good effect is observed when using Elidel cream. In the third or fourth week of the disease, you can use moisturizers: toleran, lipicar, cold cream, etc. For lips, use a balm with cold cream, ceralip. Aevit, complexes of vitamins with microelements, is also prescribed.
It should be noted that allergic diseases caused by the use of materials for dentures are highly curable and have a favorable prognosis with a full course of treatment adequate to the severity of the patient’s condition.
Yu. V. Sergeev , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor T. P. Guseva Institute of Allergology and Clinical Immunology, Moscow
Indications
Pulposeptin is used in endodontics to eliminate the source of infection. Medicinal dressing of root canals (paste injection) is done for the following pathological conditions:
- Periapical periodontitis is an infectious or traumatic inflammation of the periodontium with a violation of the integrity of the ligaments (secure the tooth in the alveolus), internal and external alveolar processes (cortical plate).
- Periapical abscess is a local limited accumulation of pus on the surface of the alveolar process (externally or internally). It develops against the background of advanced caries, periodontal diseases, and chipped teeth.
- Periapical granuloma is a clearly limited inflammation of an infectious nature, proliferation of soft tissues with the formation of nodules (granulomas).
- Gangrenous pulpitis is purulent inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth, followed by tissue death.
- A fistula is a canal from the root of a tooth through the jawbone, which is formed during the disintegration of an inflammatory focus for the release of pus. After the inflammation has stopped, the wound heals and heals.
- Odontogenic radicular cysts – arising in a chronic inflammatory focus of periodontal tissues. The neoplasm is located at the apex of the tooth root. An inflammatory infiltrate and hemorrhages are found in the cavity.
Pulposeptin paste is also used for prophylactic purposes to prevent the proliferation of pathogenic flora after endodontic manipulations (removal of canal contents, preparation for the filling stage).
Instructions for use
Before applying the paste, the root canal is thoroughly prepared. For endodontic treatment, EDTA (acid) is used to expand the canal and improve the permeability of Puloseptin into the walls.
The treatment is carried out several times alternately with sodium hypochlorite (disinfector, antiseptic irrigation solution). After completing the preparatory procedure, the dental canal is dried.
The paste is injected to the apex (the very apex of the root) using a canal filler - an endodontic instrument in the form of a conical spiral, a helical rod with a tail for rotation. The resource of one filler is 3 cycles of filling one channel.
After filling with paste, the canal is closed with a sealed bandage (temporary filling) made of indifferent material (which does not affect the surrounding tissue). This allows you to quickly restore the anatomical shape of the crown. The temporary filling can be easily removed.
The required dose of Pulposeptin paste is determined individually. The maximum amount for filling a root canal in an adult patient is 20 mg.
The duration of the treatment course is 5-7 days. This time is enough to destroy the infection, relieve swelling, reduce inflammation, and stop an allergic reaction.
On a second visit, the dentist removes the filling material and any remaining drug. Cleans and carries out antiseptic treatment of the canal, thoroughly dries the cavity.
Then the root is filled with filling material (two-component paste based on epoxy resins, radiopaque material based on zinc oxide and eugenol).
Attention! Pulposeptin paste is intended exclusively for professional use in dental offices. Self-treatment of purulent inflammation of the oral cavity at home is unacceptable.
Signs of chronic gangrenous pulpitis and treatment of pathology.
In this article you will find instructions for using Pulpotec in pediatric practice.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/pulpit/slozhnosti-vyiyavleniya-nachalnogo.html all the most important things about initial reversible pulpitis.
Warnings
Subject to storage conditions and proper transportation, the drug does not cause side effects.
In rare cases, symptoms of a local allergic reaction can be observed in people with high sensitivity to antibiotics:
- burning, irritation of the gums in the area of the diseased tooth;
- pathological swelling of the oral mucosa and tongue;
- local increase in temperature, hyperemia of soft tissues;
- rashes, both on the mucous membrane and on the outside of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
There are no contraindications to the use of the drug; no incompatibility with other drugs has been identified.
Pulposeptin does not penetrate the hematogenous (blood) and placental barrier. Does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus (does not disrupt embryonic development through toxic effects). Therefore, the paste can be used in the treatment of pregnant women in any trimester.
The drug does not pass into breast milk and does not affect the physical and mental development of the baby. Pulposetin is harmless for nursing mothers.
Release form, price, analogues
The drug for topical use is available in the form of a paste of dense consistency in aluminum tubes with a volume of 10 g. The medicine can be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of at least 4°C or at room temperature up to 20°C.
Important! At higher temperatures, the paste separates, making it unsuitable for use for medicinal purposes.
Before use, to ensure the plasticity of the material, the preparation can be slightly warmed up. It is enough to hold the tube in your clenched palm for no more than half a minute.
The cost of Pulposeptin in online pharmacies varies from 940 to 1146 rubles. for one unit of goods. Manufacturer – Russia.
Antiseptic analogues for filling root canals (therapy of pulpitis, periodontitis):
- Yodent (iodoform paste) - available in a 25 g darkened glass bottle. Manufacturer - Russia.
Cost – 162 rubles. Non-hardening paste is used for acute and chronic periodontitis. The main active ingredient is chlorophenol, iodoform. A side effect is pain during the first 1-2 days after filling the canal with paste. - Abscess Remedy - creson-based paste (disinfector) with dexamethasone. Available in plastic or glass jars. Manufacturer – Switzerland. Price – 2150 rub. Indicated for pulpitis, purulent periodontitis, abscesses.
- Tempofor is a paste based on creosote, thymol, camphor, and iodoform. Manufacturer – France. Cost – 1980 rubles. Indications: treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis, baby teeth in children, including those with absorbable roots.
- Septomixin is a broad-spectrum antiseptic paste with dexamethasone.
Active ingredients: neomycin sulfate, polymyxin sulfate, tyrothricin. Available in 7.5 g tubes. Manufacturer: France. Price – 4988 rub. It is used to treat severe forms of periodontitis that occur with complications. - Ledermix is a paste based on demeclocycline and triamcinolone (synthetic hormone). Produced in aluminum tubes of 5 g. Manufacturer – Germany. Cost −4500 rub. Indications: treatment of gangrene, acute periodontitis, pulpitis.
- Grinazol is a drug based on metronidazole for the treatment of gangrenous pulpitis. Tube volume – 4.5 g. Manufacturer – France. Price – 4230 rub.
Indications for use and purposes of use
As mentioned above, the paste is used for inflammatory processes, periodontitis, gangrenous pulpitis, tooth and gum cysts.
The drug is placed into the inflamed cavity for the following purposes:
- to eliminate severe pain;
- to destroy pathogenic microflora of the root canal and dentinal tissue;
- to reduce the inflammatory process of periodontium;
- to stimulate regenerative processes in bone tissue.
What you need to know about pulpitis, its symptoms and treatment:
Reviews
If you have had root canals treated with Pulposeptin, please share your experience using this remedy. Tell us if you had any complications, how quickly the infection and symptoms such as toothache, inflammation, swelling resolved, and how quickly you returned to your normal eating regimen.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags pulpitis
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Purpose of the Coffin spring in orthodontic appliances
Next article
Impression of teeth during treatment with braces, why can’t you do without it?
What to do if a pulpless tooth hurts?
First, a diagnosis is made and the causes of pain are found out. To do this, the dentist conducts an examination and takes a control x-ray. If the pain appears due to the re-development of infection, an allergy to the filling material, or due to errors in the primary treatment, retreatment is performed: the root canals are opened, re-processed and filled. If the pain is associated with caries or pulpitis in an adjacent tooth, treat it. In case of injury to the trigeminal nerve, treatment should be comprehensive, with the participation of a neurologist.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7