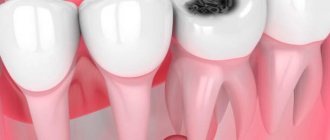
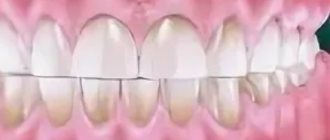
Symptoms of caries
Diagnosis of the disease should only be carried out in the dentist's office. But the person himself can determine the presence of this pathology by very characteristic symptoms:
- the appearance of dark spots on the teeth: most often they appear on the chewing surface, but often inflammation develops between the teeth (but it is usually not possible for the patient to see this - special equipment will be required),
- there is a roughness of the surface of the teeth,
- When eating food, aching pain appears, teeth react to sweet and sour, as well as cold and hot. But the unpleasant sensations subside immediately as soon as contact with the irritant ceases - this is how caries, even deep ones, differs from pulpitis - inflammation of the dental nerve,
- Breath odor may become unpleasant,
- a carious cavity can even be felt with the tongue; food debris often gets clogged into it, which causes discomfort or even swelling of the tooth - for example, if a small gap appears under a filling.
Possible complications due to improper treatment of caries and pulpitis in children
When performing a number of manipulations, some dentists with a low level of qualification may perform them insufficiently carefully or completely incorrectly. This can cause serious complications after treatment of caries of primary teeth, as well as its next stage, pulpitis.
The presence of such complications in a baby can be determined by the following signs:
- lack of positive dynamics;
- the presence of symptoms that do not correspond to the diagnosis;
- the occurrence of severe pain after treatment;
- deterioration of indicators of objective methods of examining the condition of the child’s oral cavity.
To avoid these unpleasant consequences, you should initially seek help from competent specialists who not only have a high level of professionalism, but also know the specifics of working with young children. These are the professionals who work in our dental clinic “Prodental”, located in Dolgoprudny (Moscow region).
Reasons for the development of the carious process
The development of caries largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body. For example, in women with hormonal imbalances, plaque accumulates on the teeth more often, which leads to an increased attack from bacteria. In general, caries is caused by pathological microorganisms, which become much more numerous in the oral cavity than good bacteria. And their appearance is caused by the following reasons:
- lack of proper hygiene: brushing your teeth for 20-30 seconds in the morning and evening is very little. Dentists' recommendations are at least 2 minutes twice a day, as well as removing food debris that accumulates in narrow spaces after eating. Gradually they transform into plaque, which is a provocateur of many dental diseases, including caries,
- poor nutrition: excessive consumption of sweet foods and changes in the PH composition of saliva - all this again contributes to the formation of plaque and an increased attack of bacteria,
- age: it has been established that the destructive processes of primary teeth actively develop in the first years of children’s lives. As you get older, the likelihood of developing dental diseases decreases. This is influenced by the fact that adults pay more attention to oral hygiene. In old age, the risk of caries increases again - this is the result of various diseases of the body and insufficient oral hygiene,
- pregnancy and lactation, that is, during those periods when a woman loses many vitamins and minerals, in particular calcium and fluoride,
- lack of vitamins and, as a result, increased fragility of tooth enamel,
- genetics: a predisposition to many diseases of the gums and teeth is passed on from parents.
Our advantages
Our pediatric dentists always have innovative equipment at their disposal, which allows them to treat caries in children using the most modern methods - painless and effective.
At the same time, the prices for treatment of caries in young children in our clinic are quite affordable, as you can see by reading the price list for services.
And most importantly, we know how to approach children, and therefore it is almost impossible to see a crying child in our offices and corridors. All manipulations are carried out very carefully, the baby does not experience pain and does not begin to be afraid of dentists, and goes to the preventive examination recommended twice a year with pleasure!
Make an appointment any day of the week - we work 7 days a week, without lunch breaks.
Treatment methods
Cure caries, especially at the initial stage, is not difficult - this involves removing the inflamed tissue and then filling it. In the presence of deep lesions, binoculars and a microscope can be used, which allow you to increase the working space and remove even the smallest inflamed cells, while preserving healthy tissue. Depending on the situation, it may also be necessary to restore the coronal part if it has been severely damaged.
Fissure sealing A method that allows you to stop the carious process. Essentially, this is the prevention of inflammation. Fissures or depressions (grooves) on the surface of the enamel are filled with a special sealant, which evens them out and thereby prevents the accumulation of bacteria and plaque.
Price:
from 2500 rubles more details about the solution
Treatment of caries If the doctor notes caries at the spot stage, then the main procedure is remineralization (restoration of the required mineral content) using a special solution. If the caries is superficial, medium or deep, then the resulting cavity will need to be treated, followed by filling using composite materials. When the carious process penetrates into the deep layers, it is advisable to use medicated pads containing calcium hydroxide - this way additional protection is created to preserve the dental nerve.
Price:
2500 rubles more details about the solution
Installing an inlay In a number of situations, when the tooth is quite badly damaged and a large filling will not hold, you can develop an individual inlay made of ceramic or zirconium dioxide. It will accurately follow all the curves of the tooth and be securely fixed inside the cavity. At the same time, it will last many times longer than a large filling.
Price:
from 20,000 rubles more about the solution
Instrument fracture in the root canal
The risk of instrument fracture is very high in case of file deformation (bending, unwinding of turns) and most often occurs when passing and expanding narrow, curved, previously sealed canals (Fig. 8). The main reasons for this complication may be the lack of adequate access to the mouth of the root canal; violation of the sequence of use of endodontic instruments; use of instruments without taking into account indications; non-compliance with operating mode and rotation speed; application of significant force during manual or machine endodontic treatment; metal fatigue caused by repeated use of the tool.
Rice. 8a. Introduction of a curved file.
Rice. 8b. Broken instrument in the root canal.
Prevention of tool breakage consists in strict adherence to the operating mode and use of the tool according to indications. The sequence of use of tools must be taken into account. During machining, the use of endolubricants is recommended.
Incomplete and insufficient obturation of the root canal is mainly due to incorrect determination of the working length, incomplete passage of the canal (Fig. 9), the use of the technique of one gutta-percha or silver pin in canals that have an oval, dumbbell-shaped, slit-like (irregular) shape that does not correspond to the shape of the pin, and also using liquid-mixed paste for filling (using a channel filler). As a result, shrinkage is inevitable, as well as dissolution of the paste some time after filling.
Rice. 9a. Obturation of root canals: high quality.
Rice. 9b. Obturation of root canals: incomplete.
The removal of filling material beyond the apical foramen is often observed after excessive mechanical treatment of the root canal. The result is destruction of the physiological apical constriction. It can also be disrupted due to a chronic inflammatory process in the tissues of the apical periodontium. In addition, there is a real possibility of removing material beyond the apex when using a machine channel filler. The risk of complications increases sharply when filling a root canal without taking into account the working length (Fig. 10).
Rice. 10. Removal of a significant volume of sealer beyond the apex.
The removal of the filling material beyond the apical foramen is observed in the case of using a large amount of sealer, as well as as a result of excess pressure during the condensation of the filling material in the root canal.
Pushing the gutta-percha pin beyond the apex may be a consequence of incorrect determination of the working length and/or incorrect selection of the size of the main pin (Fig. 11).
Rice. 11. Removing the gutta-percha pin beyond the root apex.
Removal of gutta-percha beyond the root apex is possible during the process of lateral condensation of gutta-percha (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12. Lateral condensation of pins.
Preventive measures: control of working length at all stages of endodontic treatment; competent formation of the root canal; maintaining the integrity of the anatomical (physiological) narrowing.
If removing a small amount of sealer beyond the apical foramen may not cause problems, since it is quickly resorbed, then gutta-percha removed beyond the apex, which itself is biologically inert, can maintain inflammation in the apical periodontal tissues for a long time, being a mechanical irritant.
Longitudinal root is possible during the process of lateral condensation of gutta-percha pins and is a consequence of excessive thinning of the walls of the root canal during mechanical treatment. In addition, a longitudinal root fracture can be observed with strong lateral pressure on the sprider during the condensation of gutta-percha pins.
Prevention measures include assessing the condition of the hard tissues of the tooth root, their thickness, as well as improving manual skills and applying adequate efforts in the process of condensation of gutta-percha pins.