- About the method
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Diagnostic stages
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Which is better - MSCT or CBCT
- Prices
- Doctors
- Reviews
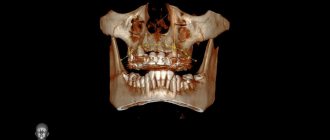
Dental computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic procedure in modern dentistry. Its result allows the therapist to reliably assess the condition and anatomical features of the root canals and localize the inflammatory process. An orthopedist can see the exact location and structure of the TMJ, and an implantologist can evaluate the parameters of the jaw bone, structure, density and volume. A 3D image is an accurate diagnostic method; the doctor receives complete information about the condition of the patient’s maxillofacial apparatus and maxillary sinuses. The images obtained as a result of scanning allow the dentist to enlarge, rotate and examine at an angle the areas of interest, which is not possible with X-ray examination. Computed tomography also measures the height, width of the bone, and determines the type. This is necessary to select the size and type of implant when planning the operation.
Computed tomography – technologies of the future for the health of your teeth!
Do you know what complex diagnostics is? What modern diagnostic methods allow you to obtain the most accurate data and the best results?
In modern dentistry, not only treatment methods are being improved, but also diagnostic methods. Any competent treatment begins with a full comprehensive examination of the patient. Dental computed tomography of the teeth has long become a mandatory and priority method for examining the jaws.
Improved devices provide unmatched accuracy and reduce the X-ray burden on the patient's health. This improves the quality of the examination and its safety.
Is dental CT harmful to the health of pregnant women?
Often women are interested not only in how often dental CT can be done, but also whether this diagnostic procedure is available for pregnant women. Experts give the following answers to this question:
- First half of the term . Computed tomography is indicated only if absolutely necessary. For example, if there is an urgent need to identify tumors.
- Second half of the term . During this period, there are no restrictions or prohibitions on computed tomography and the resulting radiation exposure for expectant mothers.
It is worth understanding that an experienced doctor will never send a patient for a tomography unless necessary. But, if when collecting a clinical picture or during treatment it is necessary to see what a CT scan of the teeth and jaws shows, you cannot do without an X-ray scan. Be sure to tell your doctor that you are pregnant (if this is not obviously noticeable) so that he can reschedule a CT scan or prescribe a suitable alternative diagnostic test that will not be harmful to the health of the expectant mother and fetus.
What are CT scans and CT scans?
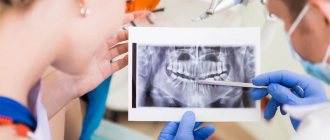
Previously, as part of a standard examination, patients were given a targeted X-ray of the tooth and an orthopantomogram. The latter is a panoramic image of the dental system, where you can see all the teeth, but this image has distortions.
With the advent of computed tomography, diagnostic options for doctors have expanded significantly. This is a method of x-ray examination that allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the object under study. A computed tomogram (CT) is the result of an examination, a finished layer-by-layer image.
Radiation exposure during CT scan of the jaw
Clinics of the Smile Factor network use new generation tomographs, the radiation from which during scanning is reduced to a minimum.
While the exposure time of standard (outdated) X-ray machines is about 2-3 seconds, the equipment we use operates with a exposure time of 0.05 seconds (this is the time of direct exposure to radiation). To understand the size of the radiation exposure and find out for yourself how often you can do a CT scan of your teeth so that it is not harmful to your health, you need to do more than just familiarize yourself with dry data figures. It would be more clear to consider a comparison of radiation from a tomograph with radiation in everyday life:
- Watching any TV at a distance of less than 2.5 meters from the screen for 3 hours gives 0.5 millisievert (mSv). Accordingly, five days of watching TV for 3 hours is equal to the same radiation exposure that can be obtained with 1 x-ray of the jaw.
- Working on a computer/laptop for more than 3 hours is 1 µSv, which is equal to 1 targeted photograph of a tooth.
- A plane flight from St. Petersburg to Omsk, Surgut or Turkey takes 3.5 hours. During this time, a radiation dose of 10 mSv will be received, which is equivalent to 5 CT images.
And this is without taking into account the daily exposure of your body to radiation from the refrigerator, microwave oven and other regularly used appliances. The examples given are enough for you to understand that the radiation exposure from a CT scan of the jaw is small and its effect is not as harmful to health as it might seem. But the results of the study will help not only to correctly diagnose diseases, but also to correctly carry out some dental operations, for example, implantation.
What are the advantages of CT?
This examination gave rise to the study of the dental system not only externally, but also internally.
The most important aspect here is the ability to see the jaw from all angles, to objectively assess the size of any parts and objects, be it a tooth or an implant. CT also allows you to plan and simulate various situations in the oral cavity, for example, you can simulate dental implantation and see what size implants are exactly suitable for a particular patient.
Often, a computed tomogram can detect cysts and neoplasms, as well as foreign bodies in the canals of teeth or see supernumerary teeth located in the jaw. Often, timely identification of such objects preserves the health of patients. If any deviations are detected, it is possible to prescribe targeted, adequate treatment as quickly as possible.
Experts highlight the following advantages of computer diagnostics:
- High level of quality and detail of the resulting image. Allows you to objectively assess the size of any formations, which affects the choice of treatment methods.
- The ability to create a three-dimensional model on a computer for further diagnosis and treatment planning. With this model on the computer, the doctor can at any time once again examine the analyzed area in detail from all sides.
- Identification of hidden inflammatory phenomena, foci of infection and foci of the pathological process, which may become a contraindication to one or another treatment method.
- More opportunities for implantation planning; implants can be placed on a 3D model and the required size and length can be calculated based on the individual characteristics of the jaw structure
- Expanded capabilities for orthodontists to assess occlusion and jaw relationships. This is very important for competently drawing up a treatment plan and selecting the necessary orthodontic treatment methods.
How to prepare for a dental examination and what should you take with you?
The cone beam computed tomography procedure is absolutely painless and no special preparation is required. To prevent optical effects from forming in the image, before starting the study it is necessary to remove jewelry and metal objects located in the head area - earrings, chains, hair clips, etc.
So that the laboratory technician knows which area should be examined during CBCT, it is necessary to take with you a doctor's order indicating the examination protocol.
What types of CT scans are there in dentistry?
Depending on the type of device, CT diagnostics is divided into:
- Cone beam
- Multispiral
- Sequential processing of layers
Only the doctor chooses which device to perform the diagnostic procedure on. This depends on the planned manipulations, since in some cases, diagnostics on another device can provide the doctor with all the necessary data for an accurate assessment of all possible risks.
Is it dangerous to take pictures?
According to SanPiN1, when performing X-ray procedures for preventive purposes, radiation exposure should not exceed 1000 microsieverts (µSv) per year. We are talking specifically about prevention, since for medicinal purposes the indicator can be much higher.
In terms of the number of shots it looks like this:
- 500 targeted shots (1-3 µSv),
- 80 OPTG (13-17 µSv),
- 20 digital CT scans (50-60 µSv).
For comparison, here is a table that shows the radiation doses that a person receives during diagnostic procedures in dentistry, in other areas of medicine and in life in general. The last table shows parameters that are truly dangerous to the body and can be fatal.
| In dentistry | In other areas of medicine | In life | Dangerous indicators |
| 1-3 μSv – one targeted shot | 30-60 µSv – one digital fluorography, 150-250 µSv – old type film FOG | 5 µSv – 3 hours in front of a computer or TV | 750 thousand µSv – minor changes in blood composition |
| 13-17 μSv – one panoramic image (OPTG) | 500-700 µSv – one mammography procedure | 20-30 µSv – one 2-3 hour flight | 1 million µSv – mild radiation sickness |
| 50-60 μSv – one CT procedure in dentistry | 2000 μSv – one head CT procedure | 2000-3000 μSv – natural dose of radiation per person per year (food, solar radiation, air) | 7 million µSv – lethal dose of radiation |
As can be seen from the table, irradiation can cause harm (minor and short-lived) only when a dosage of 750 thousand µ3V is reached, while only one thousand µ3V is allowed for diagnosis. Therefore, 20 CT images or 80 panoramic images will not cause any harm to the body.
When is a CT scan performed?
Diagnosis of a specific area or the entire jaw depends on the purpose of the study and the suspected disease. Most often, CT is done in the following cases:
- Studying the structure of bone tissue before implantation
- Identification of hidden inflammatory processes in the peri-root zone of teeth
- Detection of hidden foci of inflammation and infection in the bone tissue of the jaws
- Diagnostics of soft tissues for neoplasms
- Determining the location of the injury
- Complete diagnostics of the dentofacial apparatus before starting orthodontic treatment
With the advent of new diagnostic methods, treatment methods have also improved. With the help of computed tomography of the upper and lower jaw, simultaneous implantation surgery became possible, and the risks of complications were reduced to a minimum. Accurate calculations and a clear vision of the actual situation allows complex operations to be performed with the lowest risks of complications both during and after the operation.
Is CBCT examination dangerous?
Despite the relative safety of the method, it is still associated with a small radiation load, so it can be carried out not thoughtlessly, but only if there are indications for this, as prescribed by a doctor.
However, CBCT is not recommended for children under 3 years of age, pregnant women (1st trimester) and people who are unable to remain still during the examination. But if there is an urgent need for research, it is carried out even during pregnancy. To protect the fetus, the woman wears a lead apron to protect her stomach and chest from exposure to radiation.
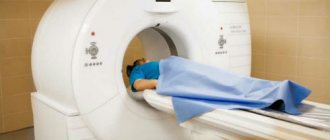
How is CT diagnostics performed?
Diagnosis begins with patient preparation. The specialist asks to remove all metal objects and jewelry to avoid interference and distortion of the results obtained. To protect internal organs from radiation, a special lead apron is worn.
To obtain the best image, keeping the patient still during the examination is very important. The chin is fixed on a special stand.
Then, after starting the device, a scanner with an emitting tube rotates around the patient’s head. At this time, the image begins to be transferred to the computer.
This procedure does not require any special preparation on the part of the patient.
CT diagnostics in Dr. Lemberg’s dentistry means there are no contraindications, including for pregnant women and children. Doctors carry out diagnostics using the Planmeca device - this is 3D imaging with a lower radiation dose to the patient than with standard two-dimensional panoramic imaging.
How to make a 3D tomogram
Usually the procedure is performed standing, the patient bites a small flat plate with his teeth and stands without moving for 15 to 30 seconds. The device makes several rotations around the head, managing to take about two hundred pictures in various projections.
In 10-15 minutes, the information is processed and transferred to electronic media.
We invite you to make a three-dimensional tomogram in our clinic using the latest generation dental tomograph. Sign up for the procedure online or by phone at a time convenient for you.
Interpretation of computed tomogram
The doctor can evaluate and interpret the results immediately. Initially, the specialist evaluates the overall picture based on images of 3D models of the jaws. Then moves on to the area of interest. It is important to assess the condition of the tooth and adjacent tissues if a CT scan of one tooth was performed. Determine the number of roots and their condition, the structure of the bone tissue near the tooth, and also consider the presence of inflammation around the roots of the tooth. This determines treatment tactics and helps assess possible risks.
Before starting orthodontic treatment, the doctor evaluates the occlusion on a computer model, and also selects the necessary angles of layer-by-layer images and makes calculations to select an orthodontic apparatus or system.
The quality of the images obtained directly affects the objectivity of the assessment of the actual condition of the oral cavity. And it can radically change the intended treatment plan.
Prescribing a CT scan of the upper and lower jaw before installing implants
Diagnosis of teeth and jaw structures
3D X-rays make it possible to examine areas of the maxillofacial system - from one tooth to a complete set of cross-sectional sections of the jaw and maxillary joint. Tomography before implantation allows:
- identify hidden carious cavities of neighboring teeth, curvature, length of canals, number of broken tooth roots to draw up a treatment plan before implantation;
- detect impacted, supernumerary teeth that may interfere with the installation of implants;
- evaluate bone septa, areas of pathological reorganization of bone tissue;
- visualize inflammation, cysts, granulomas, dental abscesses near the planned implantation area, which must be treated before surgery;
- identify inflammation in the maxillary sinuses and lacrimal ducts, which can become a temporary obstacle to implantation;
- evaluate bone tissue parameters - volume, density, degree of resorption, alveolar process inclination, thickness of cortical plates in order to correctly select the size and shape of the implant;
- clarify the anatomical structure of the maxillary sinuses, mandibular canal and other bone structures in order to plan the angle of inclination when installing an artificial rod;
- identify anomalies of the dentofacial system, pathologies of the temporomandibular joint for the correct modeling of the orthopedic structure for the implant;
- control the quality of implant and crown installation;
- assess the bone density around the installed implant;
- clarify the severity of the injuries received if the dentition is being restored after an injury
The information received in digital format is recorded on a medium (disk, flash drive) and sent by e-mail.
3D modeling of the operation CT results allow you to simulate the installation of implants of the required size, determine the angles of implementation bypassing the anatomical structures and simulate the final result of implantation.
The tomograph data is loaded into a computer program, and a 3D model of the jaw is created. The implantologist creates a virtual operation plan - selects the shape and size of artificial roots, their number, determines the installation location and angle of inclination. This allows you to take into account the nuances in advance.
A customized surgical template is printed using a 3D printer. This is an overlay with guides for future implants, which accurately determine the location and angle of installation of artificial roots. During the operation, the template is tightly applied to the gums, and the implants are installed with maximum precision.
How much does a CT scan of teeth cost in Moscow dentistry?
At Dr. Lemberg's Dentistry, the service of cone beam tomography of teeth costs 4,000 rubles. When conducting such diagnostics, the quality of diagnostic equipment and the professional knowledge of the medical personnel performing this examination are very important.
When thinking about where else you can get a dental CT scan in Moscow, you should mention specialized diagnostic centers. If diagnostics are carried out outside the clinic, the time required to transfer the results to the doctor and interpret them increases significantly. If you carry out the diagnosis immediately in the clinic, you can develop a competent treatment plan during the consultation and make a correct diagnosis.
Read also
What is dental restoration
If the aesthetic properties of teeth are lost, a person experiences certain discomfort.
What to do if your tooth aches
Sometimes aching pain in a tooth can appear for no apparent reason at first glance.
How often can a CT scan be done?
The radiation dose for this type of research reaches only 70 μSv. While the figures for established standards for adults reach 1000 μSv, for children under 15 years of age it is 300-400 μSv. Thus, this procedure can be repeated up to 14 times a year. Most often, CT scans are performed for dental implantation at the planning stage and then after surgery. And it is completely harmless to health. The radiation dose is very low, allowing multiple examinations to be performed in short periods of time.
In order to prevent the development of complications and inflammatory processes after operations, CT scans are performed 1-2 times a year. Observation in dynamics makes it possible to evaluate the course of healing processes and see changes in the structure of the bone tissue of the jaws.
Thus, computed tomography as a diagnostic method is often mandatory. It allows you to make the correct diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin adequate treatment. Allows the doctor to see more detailed information about the health of specific teeth and the dental system as a whole. It also helps to identify inflammatory and tumor processes at the initial stages and minimizes their harm to the patient’s health.
At Dr. Lemberg's Dentistry, multidisciplinary specialists with extensive experience will not only conduct a full-fledged comprehensive diagnosis, but also draw up a professional treatment plan with the involvement of doctors of all necessary specialties to ensure that your treatment is as effective as possible.
Unique visualization method
A computed tomograph produces a high-quality three-dimensional image of an individual tooth, maxillary sinuses, one or both jaws. Unlike standard panoramic images, a 3D tomogram allows the doctor to see the desired anatomical structures in a virtual section, from any angle.
During the procedure, the doctor can enlarge, rotate and study the maxillofacial area of interest at the required angle, which is unrealistic with conventional radiography.
Computed tomography is an integral and primary stage of examination before implantation. It allows you not only to assess the condition of bone tissue, but also to measure its height, width and density. Moreover, three-dimensional beams help to choose the optimal method for installing implants through preliminary virtual surgery.
3D CT is a multi-purpose and indispensable diagnostic tool that makes it possible to avoid many medical errors and complications. Thanks to this examination, the quality of treatment increases significantly and eliminates unnecessary traumatic operations.
Online consultation with a doctor
If you are concerned about the condition of your teeth. Painful sensations arise, gums bleed for a long time, and seals have appeared on the jaw. You are concerned about previously installed dental implants. And there was a need to take a 3D photo of the teeth. Then, after receiving three-dimensional visualization, it is better to go for an examination or consultation with a dentist to interpret the images and compare the results with your current complaints. It is impossible to independently understand the nuances of a 3D image, much less make a diagnosis. The specialist will explain the situation and give recommendations before the in-person appointment.
What equipment is used
To carry out 3D diagnostics, a three-dimensional computed tomograph SOREDEX Scanora 3D with advanced functionality is used. This is the latest generation equipment, which allows you to obtain three-dimensional images of the anatomical structures of the maxillofacial region in a few seconds, with the least radiation exposure for the patient.
The program analyzes the obtained multiplanar sections and builds them into a 3D model, thanks to which the specialist is able to accurately assess the condition of the dental system, detect all pathological processes occurring in this area and competently plan a treatment regimen.
A virtual 3-dimensional model of the scanned area can be recorded on any digital media (CD, flash drive), which allows the attending physician, if necessary, to view diagnostic data or involve related specialists in the analysis of the received information.