From this article you will learn:
- why is the gum around the tooth swollen,
- The gum is swollen and hurts - what to do.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
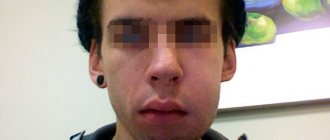
If your gums are swollen, what to do in this case will depend on the cause of the inflammation. There may be two main reasons. The first reason is associated with the development of periodontitis, i.e. inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 1-3). The development of inflammation is associated here either with poor-quality dental treatment in the past, or with the lack of timely treatment. And in this case, you can always find a carious defect, filling or crown on the causative tooth.
The second reason that the gums are swollen and painful may be the development of localized or generalized forms of periodontitis in the patient. With these forms of gum inflammation, the attachment of the gingival margin to the neck of the teeth is destroyed - with the formation of so-called “periodontal pockets” between the gum and teeth (Fig. 4-6). In such gum pockets, good conditions are created for the growth of bacteria, which can also lead to the development of purulent inflammation in the gum pocket and the appearance of gum swelling.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis –
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
A separate question in this article is what to do if the gums near the wisdom tooth are swollen. Most often this occurs in the lower jaw, and in this case the swelling of the gums is not associated with either periodontitis or periodontitis. This inflammation of the gums is called a special term - pericoronitis (which means inflammation of the “hood” over the wisdom tooth).
Why do my gums bleed?
Bleeding from the gums can occur for mechanical or pathological reasons.
The first group includes a blow to the jaw area or minor injuries due to an incorrectly selected crown or filling. In this case, bleeding goes away immediately after the problem is eliminated. Only a doctor can assess whether a crown has been chosen correctly or a filling has been installed during a face-to-face consultation, because it is difficult to see such nuances on your own. Gums can also be damaged by a brush that is too hard, intensive use of dental floss, or careless impact with other objects in an attempt to completely remove food debris. In this case, bleeding appears only after the procedure and disappears after a few minutes.
Pathological causes are associated with diseases of the oral cavity and other organs. Bleeding is a symptom:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - ulcers on the oral mucosa;
- periodontitis - inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth (localized - in several units, or generalized with damage to the entire jaw);
- leukemia (leukemia) - blood cancer with a characteristic decrease in immunity;
- intoxication with heavy metals (lead, mercury);
- diabetes mellitus, which causes weakness of the gums and blood vessels due to characteristic angiopathy.
Often gums bleed due to hormonal changes. It can be caused by pregnancy, menstrual irregularities, and puberty.
When your gums bleed when brushing your teeth
Most patients' gums do not bleed constantly. Symptoms only appear when brushing your teeth or eating hard foods. This occurs for several reasons:
- inflammation of the gums makes them more vulnerable to injury;
- the process of desquamation of the epithelium of the oral mucosa intensifies, which thins the tissue;
- capillaries located close to the gums become more permeable and bleeding occurs more easily.
The combination of all three factors leads to the fact that when brushing your teeth, your gums begin to bleed. This symptom should not be ignored. Cure the disease at an early stage is much faster and cheaper than in an advanced form. And the appearance of blood when brushing your teeth is not considered normal; it is always a sign of pathology.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
In case of poor-quality root canal treatment, due to tooth trauma, or in the absence of timely treatment of caries and pulpitis, inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, which dentists call “periodontitis.” Sometimes the terms “granuloma” or “cyst” are used to refer to periodontitis, which you may well have heard. Such names are due to the fact that the focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root in these cases has the appearance of a purulent sac.
Symptoms - usually periodontitis has a chronic asymptomatic course, or there is only slight pain when biting on this tooth. But sometimes periods of exacerbation of inflammation occur, and in this case, acute pain may first occur in the causative tooth (especially when biting on it), and a little later, swelling of the gums usually appears in the projection of the causative tooth. But sometimes pain may be completely absent, and patients complain solely that the gums near the tooth are swollen (Fig. 1-3, 7-9).
Please note that with periodontitis, the source of inflammation is located at the apex of the tooth root, i.e. quite deep in the bone tissue. Therefore, swelling of the gums during periodontitis usually develops not just in the projection of the causative tooth, but most often in the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth. And in multi-rooted chewing teeth - no less often in the projection of the bone interradicular septum. But periodontitis is not characterized by swelling of the interdental papilla or the gingival margin adjacent to the neck of the tooth.
In general, if you have swelling on the gum in one of your teeth, pain occurs when you bite on it, and there is a crown, filling or carious destruction on the tooth, and also if, in addition to swelling on your gums, you also have swelling of soft tissues face (again in the projection of the causative tooth) - you can definitely make a diagnosis of “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.” An X-ray of this tooth will allow you to accurately determine the cause of periodontitis and the required amount of treatment.
What treatment may be required -
As we said above, if the gums are swollen and painful, then in most cases the reasons are poor-quality filling of the canals, or the lack of timely treatment of dental caries and pulpitis. Only according to official statistics, root canal fillings are performed poorly by dentists in at least 60-70% of cases. The main errors during treatment are underfilling of root canals, poor obturation of root canals with filling substances, breakage of instruments, perforation of the tooth root...
As a result of this treatment, a focus of purulent inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root. Moreover, in the absence of timely treatment of the tooth for caries and pulpitis, exactly the same focus of inflammation will appear at the apex of the tooth root, but only against the background of unsealed root canals. In Fig. 10-12 you can see how the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root looks like during periodontitis (on the diagram, x-ray and on the root of the extracted tooth) -
Below we describe several treatment options that may be possible for patients with gum swelling due to dental periodontitis. In any case, the doctor will first be forced to take an x-ray. The image will allow us to determine whether this tooth can be saved at all, the size of the inflammatory focus at the apex of the root, and whether root canals have been filled in this tooth previously. The treatment tactics will depend on the latter, and below we will tell you how to cure a tooth and remove swelling from the gums so that it does not appear again.
1) If the channels are not sealed -
If root canal treatment has not previously been carried out on this tooth, then standard treatment of periodontitis is carried out with mechanical treatment of the root canals and treatment of the source of inflammation behind the root apex. On your first visit, they will open your tooth, expand the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them, and leave the tooth open for several days, prescribing antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If necessary, your dentist may then refer you to an oral surgeon to make a small incision in the gum to allow additional drainage of pus. After about 3-5 days, the doctor makes an appointment for a second appointment and, if the inflammation subsides, completes the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seals them - either first with a temporary medicinal paste, or immediately with gutta-percha (the latter depends on the size of the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root). You can read more about the treatment of periodontitis at the link above.
How the gum incision is made - significant swelling of the gums, or if your gums and cheek are swollen at the same time - indicates the formation of a large purulent abscess, which will require not only opening the root canals of the causative tooth, but also making an incision in the gums to release the pus. The incision is made under local anesthesia, the wound is then washed with antiseptics and a drain is inserted into it (see video below).
2) If the channels are sealed poorly -
If an x-ray shows that canal treatment has already been carried out previously and the cause of inflammation was incomplete filling of the root canals to the apex of the tooth root, then there are 2 treatment options: either standard conservative therapeutic treatment, or an option associated with resection of the root apex.
- Conservative therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the filling/artificial crown is removed from the tooth, poorly filled root canals are unsealed, washed with antiseptics, and antibiotics are prescribed.
If necessary, the patient is referred to a dental surgeon to make an incision along the gum. Thus, to the treatment we described in the previous section, only 1 point was added here (unsealing the root canals). Then everything is the same - after the inflammation subsides, temporary or permanent filling of the root canals is carried out. If the source of inflammation is small, the canals are usually filled immediately and permanently with gutta-percha, and a permanent filling is placed at the next visit. If the inflammation is large, the canals are sealed with temporary medicinal paste for 1-3 months, and a temporary filling is placed. And only after this time the canals are filled with gutta-percha + a permanent filling or crown is placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This surgical method is much simpler and much cheaper than conventional therapeutic treatment, and it allows you to avoid removing the crown from the causative tooth in order to unfill and reseal the root canals.
However, this method is only suitable for those teeth in which the root canal was poorly filled only at the very apex of the root (and throughout the rest of the length the canal should be filled normally). This simple surgical operation is carried out within 25-35 minutes and consists of cutting off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal using a drill. To do this, an incision is made along the gum and a flap of the mucous membrane is moved back to give access to the bone tissue in the projection of the apex of the tooth root. Next, a small hole is made in the bone with a drill, through which the apex of the root is cut off and removed from the wound along with the granuloma/cyst at the apex. The wound is sutured and antibiotics are prescribed. Pros: cheap, simple, no need to remove the crown and re-treat the tooth.→ How is root resection surgery performed?
Predisposing factors
Bleeding gums can be caused by injury or disease. But there are a number of factors that make the risk of this symptom appearing higher.
Gums bleed in patients:
- with chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- with xerostomia - dry mouth;
- with reduced immunity, including HIV and AIDS;
- with vitamin deficiency, especially C and K;
- with mouth breathing;
- with poor or irregular oral hygiene.
These factors cannot be called the cause, but they contribute to the development of bleeding gums. Those for whom none of the points apply have a much greater chance of not learning about such a problem.
If your gums bleed in the morning or at night
Peak bleeding at night or in the morning indicates an unsuitable toothbrush. During brushing, the gums are injured. In this case, you need to visit the dentist and take a hygiene lesson with the selection of personal hygiene products.
Bleeding gums may not be normal. It is definitely worth finding out the cause and treating it before the disease reaches a chronic stage.
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the dental surgeon cleans the wound and applies a sterile swab. The patient is asked to tightly clamp the tampon with his teeth and hold it for about half an hour. If the tampon quickly becomes saturated with blood, it should be changed.
If the bleeding does not stop after 20-30 minutes
, the dry swab is replaced with one moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A cold compress can be used to constrict blood vessels. Ice is applied to the cheek, after wrapping it in a towel so as not to freeze the skin. Keep the compress for 10-15 minutes
, then take a break and repeat the procedure.
After surgery, the dentist recommends painkillers. You should follow these recommendations to avoid accidentally taking a product containing aspirin, which thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
If after all the manipulations there is still bleeding from the tooth socket, you need to contact a dental clinic.
Bad breath due to bleeding gums
Bleeding from the gums is often accompanied by bad breath. There are several reasons for this:
- proliferation of bacteria against the background of inflammation;
- accumulation of soft and hard dental plaque;
- the presence of deposits under the gum that are not visible to the naked eye.
An unpleasant odor is a formidable symptom, since it does not appear immediately. This means the disease is already progressing. It is impossible to find out the cause and eliminate it on your own (without a dentist); The pathology will become chronic and it will be more difficult to cure.
What complications are possible?
When, in addition to bleeding, there is an unpleasant odor coming from the mouth, you should immediately visit the dentist. At home, you can only rinse your mouth with an antiseptic. If such symptoms are not followed by treatment, complications will not be long in coming.
Many bacteria increase the risk of cyst formation; cystic formations can only be removed surgically.
The pathological process will cause destruction of the filling and crown, inflammation of the gum tissue. Treatment includes the use of medications and surgical removal of the infection.
The lack of timely treatment of pulpitis and caries aggravates the situation and ongoing inflammation completely destroys the teeth.
To eliminate the risk of complications, it is necessary to carry out a course of treatment in a timely manner.
A lump with pus on the gum against the background of bleeding
The appearance of a tumor on the gum can frighten anyone. The presence of a round swelling against the background of bleeding gums indicates one of the diseases:
- periodontitis - destruction of the soft tissue around the tooth with the formation of a characteristic lump;
- periodontitis - the presence of a capsule with pus on the gum due to destruction of the tooth root;
- intragingival fistula - a lump with pus inside, the contents of which, when ruptured, come out, significantly facilitating the patient’s well-being;
- periostitis (flux) - a red spherical formation on the gum, the appearance of which is accompanied by swelling of the cheeks and enlargement of the nearest lymph nodes;
- epulis is a neoplasm that does not contain pus, resulting from mechanical damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Gingivitis is a painless lump on the gum.
Most of these conditions require urgent medical attention. If pus gets into the bloodstream or into the internal tissues of the tooth, it not only leads to severe pain, but also poses a fatal danger. If a lump appears on your gum, you should immediately go to see a dental surgeon. He will determine the cause of its formation and select treatment.
If the gums are swollen due to periodontitis -
No less often, complaints that the gums around the tooth are swollen are associated with the patient having an inflammatory gum disease, which is called periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, due to which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue. As a result of these processes, periodontal pockets are formed between the gum and tooth (Fig. 14).
There are a lot of pathogenic bacteria in such pockets, and therefore serous-purulent exudate is always released from them. When the pocket becomes deep enough (more than 4 mm), the drainage of exudate from the gum pocket may be disrupted, which leads to the formation of a purulent abscess in the depths of the pocket. Dentists usually use the term periodontal abscess in this case (Fig. 15-16).
Swelling of the gums in the projection of the periodontal pocket –
Why gums swell during periodontitis: reasons
Periodontitis can be local and generalized. Local periodontitis differs in that it occurs only in one or several teeth exposed to a traumatic factor. For example, the formation of a periodontal pocket can be caused by trauma to the gums due to the overhanging edge of a filling in the interdental space, or by an incorrectly made crown or removable denture. Also very often the cause is traumatic occlusion, when some teeth are subjected to increased chewing load (for example, due to the loss of part of the chewing teeth).
If the teeth that have swelling on the gums do not have fillings or crowns, and you do not have long-term chronic inflammation of the gums, then you can immediately say that the reason is the presence of premature closure of the teeth in this area of the dentition. As a result, an increased mechanical load is placed on the tooth, which leads to the onset of destruction of the bone around the tooth and the formation of a periodontal pocket (24stoma.ru).
But in chronic generalized periodontitis, the causes of gum swelling are completely different. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you periodically experience bleeding when brushing your teeth, there is constant low-grade inflammation of the gingival margin in the area of all teeth (which is accompanied by swelling of the gingival papillae, their redness or cyanosis). The cause of this form of periodontitis is the accumulation of soft microbial plaque on the teeth, as well as hard dental deposits.
Microbial plaque and tartar bacteria produce toxins that destroy the dental-gingival attachment and bone tissue around the teeth, and also destroy the periodontal attachment of the tooth to the bone. With this form of periodontitis, periodontal pockets can be found in almost all teeth, and not 1-2 teeth as in the local form of periodontitis. When the discharge of serous-purulent discharge in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess is formed in the projection of the pocket.
Symptoms - if periodontitis, swelling of the gums occurs mainly in the projection of the apex of the tooth root or the bone interradicular septum, then with periodontitis the gums always swell in the projection of the formed periodontal pocket. Sometimes you may notice that thick pus spontaneously secretes from under the gums in the area of swelling, or it may appear when you gently press on the swelling (such symptoms clearly indicate that the cause is periodontitis, not periodontitis).
Also, the fact that the cause was local or generalized periodontitis can be indicated by the presence of mobility of the causative tooth, especially if mobility was present even before the swelling appeared. Let's now figure out what to do if the gums are swollen due to periodontitis... Treatment of the local and generalized forms of this disease will differ, because their development is caused by various reasons.
Treatment of local periodontitis –
When you see a doctor, the doctor, based on an examination and analysis of an x-ray, will determine the presence of a periodontal abscess and the amount of tissue destruction around the tooth (the depth of the periodontal pocket). Treatment immediately begins with eliminating the traumatic factor - removing the overhanging edge of the filling, grinding the contacts on the chewing surface of the causative tooth. At the same time, under anesthesia, the periodontal abscess is opened to allow the pus to drain out.
Next, the pocket is washed with antiseptics, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed, as well as a home course of anti-inflammatory therapy, consisting of antiseptic rinses and treatment of the gums with an anti-inflammatory gel. At the same time, the issue of the need to depulpate the tooth can be resolved, i.e. removal of the nerve and filling of the root canals (this is necessary if the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches more than 1/2 the length of the tooth root).
Removal of the nerve in such a situation is required because infection from a deep pocket can penetrate through the bloodstream into the tooth pulp (through the apexes of the roots). And then in this case, the tooth pulp itself becomes a source of infection. But this is all just basic treatment! The main treatment will be an open curettage operation of the periodontal pocket, which will remove the inflammatory granulation tissue from under the gums that has formed at the site of the destroyed bone, as well as fill the pocket with special bone material, which will partially restore the level of inert tissue.
Progress of open curettage operation –
Please note that in the first stage of the operation, the gums are peeled off from several teeth to create good access to the periodontal pocket. In the photo above you can see a deep periodontal pocket between the canine and lateral incisor (at this point all inflammatory granulations have already been cleared from the pocket). Next, the pocket is filled with bone material, which can also be covered on top with a special membrane, after which the gum is returned to its place and sutures are applied. Please note that an x-ray 5 months after the operation shows an increase in bone tissue level of about 2.5-3 mm.
In addition, if a tooth is mobile, it may be necessary to splint it with adjacent teeth using fiberglass and filling material. You can read more about these treatment methods in the articles linked below:
→ Open gum curettage operation, → Teeth splinting technique
Treatment of generalized periodontitis –
In the generalized form of periodontitis, periodontal pockets occur not in just a few teeth, but in almost all teeth. Such periodontitis usually has a chronic course with sluggish symptoms, usually manifested by bleeding and soreness of the gums when brushing, and swelling of the gingival margin. Periodically, an exacerbation of inflammation may occur, and then abscess formation may occur in the area of one or more periodontal pockets (i.e., the formation of a purulent periodontal abscess).
Treatment of the generalized form of periodontitis is very complex, and therefore a separate article is devoted to this problem on our website, which you can read at the link above. But the main stages of treatment in this case will be removal of dental plaque and anti-inflammatory therapy, after which splinting of mobile teeth and/or gum curettage can be additionally applied.
Gums bleed in pregnant women
While carrying a child, a woman’s body undergoes restructuring: special hormones begin to be produced, and the body changes. This also applies to the oral cavity. Every second pregnant woman is diagnosed with hypertrophic gingivitis. It is manifested by an increase in gingival papillae and the appearance of bleeding.
The cause of this condition in a pregnant woman can also be the accumulation of bacteria due to an increase in the depth of the gum pockets. Bacteria accumulate in them, causing inflammation. Proper brushing helps to avoid the development of bleeding gums. It is better to use an irrigator and mouth rinses for this.
Children's gums bleed
Young children enjoy brushing their teeth the least. If parents do not control the quality of oral hygiene, gingivitis occurs. In this case, the main symptom of the disease is bleeding gums.
The physiological cause of this condition in children is the process of teething. In this case, the integrity of the gum is compromised and it can bleed.
Problems with the gums are also caused by an incorrect bite. In this case, soft tissues are injured by teeth that are incorrectly positioned relative to each other.
Wearing orthodontic appliances can damage the integrity of the gums. This especially happens when wearing braces with uneven edges. To prevent injury, locks must be treated with special wax. But children often forget to do this; as a result, braces damage soft tissues, causing bleeding.
“Disease of dirty hands” - stomatitis, also more often affects children. They take less care of hygiene, which provokes the appearance of characteristic ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Some parents believe that children do not need to treat their baby teeth, because they will still be replaced by molars. This opinion is erroneous, because caries is caused by bacteria, and their constant presence in the mouth leads to periodontitis. The disease is characterized not only by bleeding gums, but also by the appearance of bumps with pus. This condition requires immediate medical intervention, otherwise serious complications arise.
Folk remedies
They are sometimes included in the overall treatment strategy, and sometimes used as a temporary measure before going to the dentist.
If your gums bleed, the following folk remedies are usually used:
- Oak bark decoction. They rinse the mouth with it several times a day, as it strengthens the gums and helps eliminate the inflammatory process. The preparation is simple - you need to brew 1 tbsp. l. crushed oak bark in 1 glass of water. The product should be allowed to brew until it cools, decant, and then you can use it;
- Camomile tea. This plant is an effective antiseptic with healing and anti-inflammatory effects. Pour 1 tsp into a glass of boiling water. plants, after which the infusion should be left to cool. Next, it is expressed and used to rinse the mouth. The procedure must be performed several times/day;
- Sage tea. The plant is an excellent antiseptic that has a healing, anti-inflammatory effect. It is brewed at the rate of 1 tsp. for 1 cup boiling water. Cooled to room temperature and strained, the infusion is used for rinsing;
- Water pepper infusion. This is something you can rinse your mouth with to reduce bleeding. The plant helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels, thereby normalizing blood clotting processes. To prepare the product, add 1 tsp. raw materials 1 cup boiling water, let it brew. It is then expressed and used as a mouthwash;
- Horseradish or black radish juice. It must be freshly squeezed, and its properties are that it helps eliminate plaque and tartar. You need to mix 2 tsp. juice of one of the vegetables with wine (200 ml). You can not only rinse your mouth with it, but also use it as an immunomodulator, taking it orally in small portions.
Traditional medicine suggests using sauerkraut and freshly squeezed carrot juice as ways to combat the problem. Please note that the methods listed above only help eliminate the symptom, but do not help cope with the cause of its occurrence. Therefore, visit your dentist, and only with his permission, use or discard them.
Which doctor will help if my gums are bleeding?
If you have bleeding gums, you should consult a dentist. In the absence of complications, the doctor’s specialization does not play a role.
If the condition is complicated by the appearance of a lump with pus, you should immediately go to a dental surgeon. He will determine the type of tumor, choose treatment tactics and, if necessary, perform urgent surgery. At the Matisse Dent clinic, you don’t need to make an appointment several weeks in advance, endure pain and wait for help. With an acute condition, doctors will accept and perform surgery on the day of treatment.
Content
- Causes of bleeding
- Possible complications
- Treatment regimens
- Prevention
If your tooth is bleeding, gum disease may be the cause. Inflammatory processes develop as a result of gingivitis and periodontitis, in the absence of proper oral hygiene. If there is pathology, bleeding can be caused even by regular brushing of teeth.
To fix a problem, you need to understand the cause of its occurrence. In some cases, it will be enough to eliminate the source of the problem; sometimes the approach to treatment should be complex, using medications.
PROMOTION
Dental restoration, installation of fillings
from 2200 rub.
SOS remedies against bleeding gums
Sometimes it’s impossible to get to the doctor and you need to wait 1-2 days until the appointment. In this case, several SOS tools will help.
- Rinses: chlorhexidine, oak bark decoction, LACALUT Aktiv rinses with aluminum lactate and sodium fluoride, PRESIDENT Antibacterial with plant extracts - relieve inflammation, prevent bleeding.
- Gels: Cholisal, Parodontocid - reduce pain, remove signs of inflammation.
- Pastes: Forest balm - contains oak bark, stops bleeding, strengthens gums.
All means must be used comprehensively. First, brush your teeth, then rinse (1 minute). After this, the solution is spat out and the gums are dried with gauze: this way the gel is better fixed. Then use ointments, applying with your finger to the entire inflamed surface. If saliva comes out during treatment, you should not swallow it, you need to spit it out.
After the procedure, you should refrain from drinking for 30 minutes and from eating for 2 hours. Treatment is carried out twice a day: after breakfast and at night.
The most effective remedy for diseases in which the gums begin to bleed is antibiotics. They help to quickly relieve inflammation and improve well-being. But they are available with a prescription and are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Therefore, you won’t be able to buy and prescribe antibiotics yourself. It is better to immediately make an appointment with a specialist so as not to waste time and money on something that will not solve the problem, but will only delay the inevitable.
The treatment regimen includes:
- systematic professional teeth cleaning – removal of plaque and tartar;
- a course of physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve inflammation;
- sanitation of the oral cavity.
The next stage of treatment is home therapy: rinsing with disinfecting solutions (salt and soda, chlorhexidine).
For a purulent infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
At home, you can independently use traditional medicine methods, including decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants:
- oak bark;
- chamomile flowers;
- sage herbs.
You can use these decoctions and calendula tincture as lotions on problem areas of the mouth.
Use of pharmaceutical products:
- fluoridated toothpastes with the addition of medicinal herbal extracts;
- dental anti-inflammatory gels (Cholisal);
- vitamin complexes.
Mistakes in self-medication
When trying to get rid of bleeding gums on their own, patients make a number of mistakes. Never worth it:
- start taking antibiotics without a prescription - they may not be needed, but the blow to the body will be dealt;
- Stop brushing your teeth - this will only lead to a worsening of the condition;
- getting too carried away with oral hygiene - this will not save you from complications and will not cure, but will only aggravate the situation due to systematic injury to soft tissues;
- be afraid to go to the dentist - modern treatment methods are painless and do not cause discomfort, unlike purulent complications.
Lack of timely and competent treatment of bleeding gums leads to the spread of inflammation to bone formations. As a result, teeth become loose and fall out, requiring implants to be inserted. This is much more expensive than contacting a specialist in time to solve a gum problem.
You should not let the disease progress and self-medicate; come to the Matisse Dent clinic and receive competent medical care.
Classification of bleeding
Bleeding is divided into primary, which begins immediately after surgery, and secondary, when bleeding begins after some time.
The intensity of bleeding is determined depending on how much the hole bleeds after removal:
1st degree
– blood flows
for 20-30 minutes
, saturates the tampons and colors the saliva.
2nd degree
– bleeding continues for more than 40 minutes, blood and saliva mix intensively.
3rd degree
– the bleeding does not stop for more than an hour, the patient spits blood.
With prolonged bleeding, the patient's general condition worsens. Weakness, dizziness appear, and the skin turns pale. Blood pressure drops, the heart begins to beat less frequently. In case of bleeding, dentists advise not to delay a visit to the doctor so that he can take measures to stop the bleeding and prevent the condition from worsening.