Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Candidal stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity in which the Candida fungus begins to actively multiply in it. Normally, it, along with some other microorganisms, is always present in small quantities in the mouth of any person. If a person is healthy enough, the proliferation of the fungus is suppressed by the immune system. And if the immune system is weakened, then the fungus, multiplying, causes small red sores and white plaque, and candidiasis may appear. How to treat candidal stomatitis, what it looks like and how to prevent the onset of the disease - we will tell you in this article.
Candide solution for fungal infections in the oral cavity - principle of action and instructions for use
The appearance of a dense whitish or grayish coating on the surface of the tongue, gums and cheeks usually indicates the development of a candidal infection - thrush. Often the pathological process is accompanied by the appearance of small ulcers. After examination and confirmation of the diagnosis, the dentist prescribes appropriate antimycotic drugs. One such remedy is Candide oral solution. This is an antifungal drug, and you will learn how to use it correctly from this article.
Stages of development of candidal stomatitis
Treatment of candidal stomatitis depends on the degree of its progression. The entire disease can be divided into several stages based on its symptoms, depending on how late it is detected:
- Stage one. The mildest symptoms of oral candidiasis are the appearance of red sores on the mucous membranes: cheeks, lips, as well as on the gums, tongue and tonsils. At this stage, treatment of candidal stomatitis is difficult due to the fact that the disease is still barely noticeable and may not cause serious discomfort, which is why the patient does not see a doctor. The first stage can last quite a long time and not develop into subsequent ones.
- Stage two. A white cheesy coating appears at the sites of the ulcers, which can be removed. When scraped, red and rather painful wounds form at the site of the ulcers. At this stage, the temperature may rise, but only slightly and quite rarely.
- Stage three. The white cheesy coating becomes very difficult to scrape off, the wounds bleed and hurt a lot. This period is dangerous because microorganisms can get into bleeding wounds, which will cause bacterial stomatitis, the course of which is more severe and is accompanied by a very high temperature.
- Stage four. Severe form of candidal stomatitis, requiring immediate action. The upper respiratory tract may be affected, so only a specialist can determine how exactly to treat candidal stomatitis. At this stage, the disease is very dangerous for children.
In addition, it is also important to know that candidal stomatitis is a contagious disease that is transmitted through kissing and even through sharing utensils. We recommend that you undergo full treatment for candidal stomatitis and avoid such contact with other people during your illness.
Indications for use
An antifungal solution is prescribed for use in patients with damage to the oral mucosa and pharynx due to excessive proliferation of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and other types of fungi, including molds and dermatophytes. Thus, “Candide” is usually prescribed for the development of oral thrush and candidal stomatitis against the background of reduced immunity.
The drug is used in the treatment of thrush
Candidal stomatitis (thrush)
Treatment of candidal stomatitis includes eliminating the cause of the disease, providing a balanced diet, stimulating the immune system and improving oral hygiene. These measures may be enough to cure stomatitis in adults and children. To treat thrush in newborns, the oral cavity should be treated with the following drugs: soda solution, iodinol, 1% aniline dyes.
For moderate and severe cases, the treatment of candidal stomatitis includes oral medications, as well as antifungal ointments. Antifungal drugs are used internally to treat thrush, which are prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s age. Treatment is continued until the symptoms of thrush in the oral cavity are completely eliminated, so that there are no relapses.
The course of treatment and type of medications depends on the health of your child, as well as the form of the disease.
Infants are almost always treated with topical antifungal medications. This type of medication is not used to treat adults because their mouths are larger and it is difficult to apply the medication to all affected areas.
Mild form of candidal stomatitis Treatment of mild forms of candidal stomatitis in adults occurs at home and does not present any difficulty. Treatment of the disease involves the use of antifungal elixirs and lozenges. The course of treatment usually lasts no more than two weeks.
A mild form of candidal stomatitis in infants is treated with external medications for at least two days after the symptoms disappear.
Moderate to severe candidal stomatitis More severe forms of the infection that have entered the esophagus are treated with oral antifungal medications. External use of similar drugs is also possible.
In severe cases of the disease, the course of treatment lasts more than two weeks.
Oral antifungal drugs are almost never used to treat pregnant women because of the potential for harm to the baby. But in very rare cases, namely in severe cases of the disease, such drugs can be used for treatment, since the infection can enter the blood. In this case, mother and child are at great risk.
Persistent and recurrent form of candidal stomatitis Persistent and recurrent form of candidal stomatitis require: • Twice as much treatment time until symptoms disappear. • Treatment with both oral and topical antifungal medications.
People with weakened immune systems can take antifungal medications on an ongoing basis to prevent thrush.
It is very important to eliminate all sources of infection, as the disease may return.
To prevent this, thoroughly disinfect toys, pacifiers, bottles and other items that the child puts in his mouth or may give to another baby. For more detailed information, read the relevant section on preventing thrush.
Diseases such as diabetes and HIV (immunodeficiency virus) increase the chances of developing thrush.
If the child has a mild form of this disease, then you just need to thoroughly wash bottles and pacifiers, and also regularly wipe the child’s mouth with a damp cloth. If you are breastfeeding, you should treat your nipples with an antifungal medication, such as nystatin (mycostatin). After feeding, dry your breasts and apply lanolin to relieve soreness.
If you wear dentures and your doctor has diagnosed you with candidal stomatitis, you need to remove them daily, wash your dentures every evening and wipe your mouth. • Remove dentures before bed. • Rinse them thoroughly using a clean toothbrush and water. • Leave them overnight in chrogexidine gluconate solution, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. An alternative is a dental and oral cleanser (Polident or Efferdent). • Rinse your dentures thoroughly in the morning. If you soaked them in a solution of chrogexidine gluconate, you should not use fluoride-containing toothpaste for 30 minutes after putting the dentures back (fluoride weakens the effect of chrogexidine gluconate).
Sometimes, for candidal stomatitis, a 1% solution of gentian violet is used, a dye that kills bacteria and is an antifungal agent. This substance can only be used by adults, so you should consult your doctor if you are going to use it on your child. If gentian violet is ineffective, the attending physician will prescribe another remedy.
Do not despair! If thrush causes discomfort, try the following tips: • Drink cold drinks, such as water, iced tea, or frozen juices. • eat soft foods that are easy to swallow, such as ice cream or sweet cream; • if the white coating causes pain, drink from a straw; • rinse your mouth several times a day with warm water (1 teaspoon of salt per glass of water).
Release forms
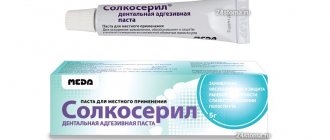
The main form of release of “Candida” is a solution in which the concentration of the active substance is 1%. The product is sold in a 15 ml polyethylene bottle. The kit includes a dropper plug, which greatly simplifies the process of treating affected areas of the mucosa. The slightly viscous substance is colorless and odorless, but after using it, patients note a slight bitter taste in the mouth. The drug is also available in other form factors: ointment, spray, suspension, gel, powder and lotion. However, not all of the listed forms are intended for treating the oral mucosa.
In dentistry, the drug is used in the form of a solution.
Stomatitis in children
Viral stomatitis
One of the most common contagious species. After the incubation period is completed, blisters form on the oral mucosa. Within a few hours they burst, turning into round or oval ulcers.
It is easy to “recognize” viral stomatitis in children: by its perfectly even shape and characteristic yellow coating on areas of erosion. Single spots often combine into larger lesions. The palate, tongue, and cheeks are inflamed and have a crimson-red tint.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
The second most common is herpetic stomatitis in children, the symptoms of which are the same as those of viral stomatitis. The onset of the disease resembles the flu: high temperature (up to 41°), aches, headache and muscle pain, enlarged lymph nodes.
First, a scattering of small bubble formations becomes noticeable (there can be quite a lot of them, up to twenty). They are grouped on the palatine arch, tongue, cheeks, and sometimes on the skin - near the lips and nose. The mucous membranes swell, the gums are also red and inflamed. In place of the burst bubbles, single or merged areas of erosion are formed, quickly becoming covered with a yellowish or whitish coating.
Recovery is long, from 10 days to two weeks. As a rule, infants who have reached six months of life and small children under three years of age become ill. During this period, the natural protection against the herpes virus obtained from the mother’s blood disappears.
Chronic herpetic stomatitis
Herpes is a virus that cannot be expelled from the body. Infection with it is also inevitable; in civilized countries, any person is a carrier of the infection. This is why herpetic stomatitis in a child with a weakened immune system periodically recurs. Provoking factors are colds, hypothermia, taking corticosteroid drugs, chronic tonsillitis, caries, microtrauma of the gums.
The external manifestation of the disease does not differ from the acute form of this type of stomatitis: the same blisters and ulcers. However, with a chronic course of the disease with periodic exacerbations, there is no acute period: there is no jump in temperature, the child remains active, although the lymph nodes enlarge.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis in children
The disease often develops against the background of food or drug allergies, so children with identified allergopathology are at risk. The treatment of stomatitis in children with this feature is also carried out together with the dentist by an allergist, and sometimes by a gastroenterologist.
Outwardly it manifests itself as the formation of painful round lesions covered with a dense grayish coating - aft. All aphthae have a clear shape and a bright rim. They are much larger in size than ulcers: they can reach 5-10 mm.
Unlike herpetic manifestations, with aphthous stomatitis the rise in temperature is slight, although there is weakness, the gums do not swell or redden. Aphthae are few in number (sometimes one lesion appears on the tongue or under the tongue, on the cheek), touching them causes severe pain.
The disease is provoked by staphylococcus, a microbe that lives in carious teeth and dental (soft) plaque. The disease appears more often if the child has congenital, acute or acquired pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, or some kind of immune disorder.
Bacterial stomatitis
Painful areas of bacterial stomatitis are small in size, uneven, and covered with a dense yellow coating. Sometimes yellowish dense crusts form on the baby’s lips, there is a clear putrid smell of breath, and drooling occurs. Mucous membranes are inflamed, dark or purple-red. It can be seen that the gums are loose and bleeding. The general condition also suffers: there are complaints of aches, headaches, and nausea.
Bacterial stomatitis in children is caused by staphylococcal and streptococcal bacteria. Treatment must be specific, fast and correct.
Candidal stomatitis
Candida fungi cause this type of disease that affects newborns. A characteristic sign of the disease is the formation of a cheesy, homogeneous milky coating over the entire area of the tongue and cheeks, on the gums, and sometimes on the lips. If this layer is removed, a painful, bleeding ulcer will be exposed.
A characteristic sign is the appearance of a sour odor from the infant’s breath. The baby does not take the breast and bottle and is capricious.
General approaches to the treatment of childhood stomatitis
Depending on the type of stomatitis in children, treatment will vary significantly. Nevertheless, there are general principles, the observance of which will alleviate the baby’s condition and will not aggravate the course of the disease.
- Careful oral care is necessary: antiseptic rinsing before and after meals, mandatory but careful brushing of teeth with a brush with the softest bristles. Infants can wipe the inside of their cheeks with a special napkin soaked in an antiseptic composition.
- Food for a sick child should be warm, so as to cause as little pain as possible when chewing. Spicy, sour, irritating mucous membranes and solid foods are prohibited. Purees, broths, and pureed porridge are preferred. Whole milk and juices should be excluded for a while.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, you can apply an anesthetic gel or spray to the gums and mucous membranes before meals.
- To recover faster, your baby needs to drink plenty of fluids.
The dishes of a sick child should be kept separately and carefully handled, especially if there are other children in the house. It is important to provide him with a separate towel and toys. If a newborn is sick, nursing mothers should definitely take care of the cleanliness of their breasts, nipples, and bottles.
The most important point, common to all types of disease, is not only timely and correct, but also sufficient treatment. This means that even with significant relief of the condition, you need to complete the course of taking medications prescribed by your doctor. If treatment is interrupted earlier, pathogenic pathogens will form a persistent defense against drugs, and it will become difficult to fight them.
Treatment of acute and chronic herpetic stomatitis
The acute form is treated with antiviral drugs that are effective against herpes. If the disease has become chronic, then additional immunomodulatory drugs will be required. To relieve the first acute symptoms, the doctor will prescribe an antipyretic, but only if the temperature is above 38.5°. At a lower temperature, you need to give the baby’s immune system the opportunity to work - the immunity will be stronger.
The main drug used to combat viruses in the oral cavity in dental and pediatric practice is Acyclovir. It successfully destroys herpes, but only at the first stage, when a vesicular rash forms. From the moment the ulcers form, ointments and gels are used for local treatment.
Viferon restores immunity well and destroys viral infection. Thanks to interferons and a vitamin complex in its composition, it quickly alleviates the condition of a sick child, especially if used in the first hours of illness. Available in convenient forms: candles are suitable for newborns and one-year-old babies, gel and for older children.
The third mandatory component of the treatment of stomatitis in children is frequent antiseptic rinsing. It is important that only the drug that is active against herpes viral infection will work. Miramistin is usually prescribed. There is no point in rinsing your mouth with herbal infusion.
It is good to treat ulcerated areas with Cholisal gel, which both heals and relieves pain for several hours. Sea buckthorn oil, Aekol, and wild rose (rose hip) oil have a strong healing effect. They are used topically, applied to the mucous membrane.
If the disease returns, that is, becomes chronic, then immunomodulatory drugs are included in the treatment regimen. You cannot use them on your own or violate the recommendations of the instructions: this is fraught not with an increase, but with an even greater decrease in immunity. Effective immunomodulators, for example, Immunal, Imudon, Amiksin.
Additionally, special pastes enriched with enzymes will enhance immunity in the mucosal area.
pharmachologic effect
The main active ingredient in the drug "Candide" is clotrimazole. It is a derivative of imidazole, a broad-spectrum active component in the treatment of fungal infections. The therapeutic effect in this case is due to the ability of clotrimazole to interfere with the synthesis of ergosterol, which is present in the membrane of fungal cells. As a result, the structure of the cell itself is deformed, and it is deprived of the ability to function normally, which leads to the destruction of microorganisms1.
Instructions and dosages
As for how to use the drug, you need to carefully check the instructions. The solution should be applied to problem areas using a cotton ball or two. "Candide" is used to treat exclusively affected tissues - it does not need to be applied to the entire mucous membrane.
For infants with candidal stomatitis
Answering the question about at what age can Candide be used, it should be noted that the drug in the form of a solution is approved for use from a very early age, that is, for newborns. But before you start treating your baby’s oral cavity, you should definitely consult a doctor. The procedure is performed as follows:
- a cotton ball should be moistened in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and carefully wipe the mucous membrane with it,
- Apply 3 drops of solution to a new clean ball or cotton swab and spot treat the affected areas.
Frequency of treatment for infants - no more than 2 times a day.
The instructions for the drug indicate the maximum frequency of treatment for infants - no more than 2 times a day. The first results will become noticeable after 2-3 days of therapy. Treatment usually takes about a week, but if stomatitis is severe, complete recovery will take 10-14 days. Moreover, therapy should be comprehensive, with the use of other antifungal agents prescribed by a specialist.
For children from 3 years old
For children aged 3 to 18 years, the dosage and frequency of use of the solution is determined by the attending physician. First, you will have to undergo appropriate diagnostics so that a specialist can determine the type of pathogen and assess the extent of the damage. The standard single dosage for children is 2-3 drops. It is usually recommended to carry out such treatment 3 times a day after meals.
Pregnancy and lactation
While there is no confirmed clinical data on the safety of using the solution during pregnancy and lactation, this product cannot be used without a doctor’s prescription. And even if necessary, a specialist may suggest the use of Candida with increased caution only in the 2nd trimester, if the benefit outweighs the potential risk.
During pregnancy you should use the drug with caution
Adults and elderly people
The dosage for adult patients is usually 10-20 drops. It is recommended to carry out the procedure 3-4 times a day. As practice shows, a noticeable effect occurs on days 3-5 of therapy. If relief does not occur during this time, you need to visit the doctor again and, as prescribed, begin more intensive complex treatment. For elderly patients, the dosage should be adjusted by a specialist taking into account the current state of health.
“And I had candidiasis in my mouth. When they put the denture on my upper teeth, about a couple of months later I started getting thrush. Terribly unpleasant sensation, I didn’t even expect it... I can’t say that something hurts, but everything itches, there’s always this plaque, smell, and burning ulcers in my mouth. Then the doctor prescribed Candide solution to me, a normal remedy, it helped me. But it’s better not to use it so easily; it’s still worth talking to the doctor.”
Valentina V.D., from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
The dosage for adult patients is usually 10-20 drops.
The instructions indicate that it is best to treat problem areas at the same time, preferably after eating. You should first rinse your mouth thoroughly and remove any remaining food. It is also important to complete the course of therapy completely. Even if acute symptoms have passed in the first days, premature cessation of treatment can lead to relapse. In the future, it will be more difficult to combat the spread of the fungus, since microorganisms become resistant to clotrimazole. And one more important point: after treating the mucous membrane, you should refrain from eating for at least half an hour.
Candidal stomatitis in children, symptoms and treatment
Candidal stomatitis, or fungal stomatitis, or thrush is the most common type of inflammation of the oral cavity in children. Although it is more common in young children, children of all age groups are not immune from the development of a cheesy coating with a rather unpleasant odor on the mucous membranes and tongue.
The causative agent of this type of inflammation is the Candida fungus, which is present in the microflora of the oral cavity, but some unfavorable factors can provoke its rapid proliferation and, as a result, candidiasis - inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Candidiasis is stomatitis on a child’s tongue and on the inside of the cheeks and lips, which is accompanied by severe pain and itching. Sometimes hyperemia (redness) and plaque spreads to the pharynx. Candida plaque is easily removed, revealing brightly colored erosions underneath. There is one popular misconception that if you take a bandage with powdered sugar (or honey) and remove the plaque, the thrush will go away. Yes, the plaque is removed, but the sharp microparticles of sugar injure the mucous membrane in new places and the microwounds immediately become infected with fungus. After some time, stomatitis returns in an even greater volume, since sweets serve as an excellent breeding ground for fungus, as well as various bacteria, so such self-medication can also result in infectious stomatitis in addition.
If your baby has inflammation in the mouth, immediately contact the experienced specialists of the Utkinzub clinic and they will determine the type of stomatitis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. And now we will tell you how to quickly cure stomatitis of fungal origin under the supervision of our doctors.
How to treat oral stomatitis
Treatment of candidiasis is carried out in two directions - local therapy and general treatment. It is known that all fungal diseases actively develop in an acidic environment, which means that in order to limit the spread, the pH in the mouth should be changed. You can alkalize the environment in the oral cavity using a soda solution or a 2% boric acid solution. Often, for children over 3 years old, lubrication with aniline dyes, in particular methylene blue, is used. of candidal stomatitis in infants has its own characteristics, which you can read about in the article “ Treatment of stomatitis in infants . You should rinse your mouth with alkaline solutions several times a day, or wipe the gums of the necks of your teeth, where harmful fungus is most often hidden in plaque. The doctor will prescribe a special solution for the treatment of Candide stomatitis, which destroys the fungus. The duration of use of the drug is strictly 10 days; you cannot stop treatment, even if there is no longer visible thrush, since the fungus may not be completely eliminated, and if it returns, it will be resistant to the drug and difficult to cure.
Older children can be prescribed Diflucan, but in a strictly individual dosage, determined by the doctor. The use of special antifungal ointments is also mandatory; vitamin complexes and immunomodulators will be prescribed to enhance immunity. After treatment, the teeth will be sanitized and the child will be taught the rules of oral hygiene. If thrush persistently returns, then other family members who can constantly infect the child should be examined. A sick child must be immediately isolated from other children, given a separate room, dishes and a towel, because candidal stomatitis is quite contagious. Complex forms of candidiasis are treated with antifungal medications, sometimes in the form of injections. The prognosis is good and a complete cure is possible.
How long does therapy last?
According to reviews of experts in the field of dentistry, with early diagnosis of a fungal infection, the use of the solution gives a rapid therapeutic effect, which can most often be noticed already on the 3-4th day from the start of use. However, for adult patients, the duration of therapy is usually at least 2 weeks.
As mentioned above, this antifungal agent is intended for systemic use. This means that premature cessation of its use in the future will seriously complicate the treatment process. In this case, mild stomatitis can be cured in a week, but only a doctor can determine the exact timing of treatment.
What are the contraindications
There are no categorical contraindications to the use of the solution, but before starting a therapeutic course, you should definitely consult a doctor and study the composition in order to exclude the possibility of developing allergic reactions to the components. You should also avoid using Candida during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The advisability of using the drug during these periods remains at the discretion of the treating specialist.
Before using the drug, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in adults
How to treat the disease “candidal stomatitis”?
First of all, at the first signs of the appearance of red sores, it is necessary to contact a specialist who must correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment. Quick and timely diagnosis is the key to successfully overcoming the disease and eliminating discomfort.
Most often, in the treatment of candidal stomatitis, drugs from the group of antifungal agents are prescribed. Depending on the stage and form of the disease, they are taken 4-7 times a day until any signs of thrush completely disappear. Be sure to consult your doctor before using any medications!
Also during treatment it is necessary to use local antifungal agents, such as:
- A solution of baking soda in water (a teaspoon per glass of water). For better dissolution, the water should be warmed up a little.
- Drops with nystatin.
- Lotions with potassium permanganate. Potassium permanganate dissolves at a rate of 1 to 10,000.
- Asepta rinse solution. It contains an anesthetic component that relieves discomfort. The rinse aid is convenient because it does not require preparation and is immediately ready for use. You can take it with you to work and periodically rinse your mouth with it throughout the day. The solution has an excellent disinfectant effect and relieves burning sensation.
Side effects
In extremely rare cases, the drug provokes the appearance of adverse reactions, mainly associated with the body’s increased sensitivity to the active substances included in its composition. In this case, the mucous membrane may noticeably redden at the site of application of the drops; in other situations, urticaria appears, and a slight tingling and burning sensation occurs within the treated area.
If such symptoms appear, you should rinse your mouth and consult a doctor. A specialist can suggest alternative medications to combat fungal infections. It should also be noted that a slight bitter taste in the mouth causes gagging in some patients. If a significant amount of the product enters the stomach, diarrhea and abdominal cramps may develop.
What causes the development of the disease?
Before you begin treatment for candidal stomatitis, you need to know what affects its appearance. This will help you better understand what to avoid to prevent illness.
So, the main reasons:
- Weakened immunity that does not fully suppress the growth of the fungus.
- Any allergy (the appearance of which can also be influenced by a weakened immune system).
- Long-term use of medications that cause dysbacteriosis.
- Dehydration due to severe diarrhea.
- Lack of vitamins, especially vitamins A, B, C, E.
- Hormonal changes in the body (for example, during pregnancy in a woman) or other problems with hormonal levels.
- Oral health problems: diseases of the gums and teeth (gingivitis, caries, tartar).
- Toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulfate, which is designed to clean the oral cavity and freshen breath, but leads to dehydration and the rapid development of stomatitis.
- Long stressful loads.
- Hereditary predisposition to diseases of the oral cavity often requires almost constant treatment of candidal stomatitis.
- Long-term chemotherapy associated with malignant neoplasms, which also weakens the immune system.
Due to one or more of the above factors, a favorable environment is created for the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida.
There is also a systemic cause of candidal stomatitis, which requires treatment from several medical specialists at once - this is thrush affecting the entire body or its occurrence on the vaginal mucosa of a woman.
A child becomes infected with a fungus of the genus Candida as a result of passage through the birth canal or due to non-compliance with hygiene standards.
Drug interactions
Advanced forms of fungal infections require complex treatment. However, interactions with certain medications may affect the effectiveness of Candida. For example, in combination with Nystatin and Amphotericin, the activity of clotrimazole is noticeably reduced.
Interactions with certain medications may affect the effectiveness of the drug
Analogs of Candide
There are other means with a similar effect. So, for example, among analogues of “Candida”, experts in the field of dentistry identify the following drugs with an identical active ingredient in their composition:
- "Canesten" - presented in the form of a spray, the cost of a 30 ml bottle is approximately 350 rubles,
- “Clotrimazole” is a 1% solution with the same active ingredient in its composition, the cost of a 15 ml bottle is approximately 180 rubles,
- “Kanizon” is a cream with a 1% concentration of clotrimazole in its composition, a 20 g tube costs about 75-80 rubles,
- “Candibene” - a cream with a concentration of 1% costs around 130 rubles for a 30 g tube.
Together with Candide, the same pharmacological group also includes such products as Miconazole cream and Mycoseptin ointment. Micogal cream and Binafin oral tablets have pronounced antifungal properties. All of the above drugs are allowed for use only as prescribed by a doctor.
How much does the drug cost?
The cost of Candide depends on the form of its release and the pricing policy of the retailer. The price for a bottle of solution for treating the oral mucosa (15 ml) is approximately 350-400 rubles in Moscow pharmacies.
Candide solution is an effective remedy, which often becomes the best option in terms of price and quality ratio. The drug is non-toxic and does not cause dangerous reactions even if the recommended dosage is exceeded. At the same time, it demonstrates high efficiency in the fight against fungal infections of oral tissues, which is confirmed by numerous positive reviews from doctors and their patients.
1According to data at the office. manufacturer's website: glenmark-pharma.ru.