Why your tongue burns: the most common reasons
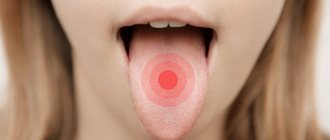
Fans of spicy food know firsthand how the tongue bakes.
As soon as spicy food touches your tongue, your taste buds instantly react to the pepper. Sometimes this condition is not associated with eating peppered foods. According to statistics, about 1% of people suffer from burning mouth syndrome. This is when the tongue and oral cavity “burn” for no apparent reason. Moreover, when carrying out diagnostic procedures, doctors often shrug their shoulders without understanding the cause of such a symptom.
The most plausible explanation for burning mouth syndrome is the theory of a pathological change in the nerve endings of the tongue. Most likely, the burning sensation on the tongue in this case is a consequence of a change in the polarization of nerve cells. For reasons that are still unclear, burning tongue and oral cavity syndrome occurs 5-7 times more often in women than in men.
In most cases, doctors are still able to determine the cause of this symptom. Let's look at the most common types of diseases and conditions that cause a burning tongue:
- Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity . The most obvious reason is dental pathologies. For example, these are gingivitis, periodontitis, advanced forms of caries and others. The causes of burning and soreness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue are inflammation, which occurs against the background of infection or a non-infectious inflammatory process.
- Action of chemical and physical agents . Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity develop when exposed to chemical or physical aggressive agents. For example, this is gastric juice in gastroesophageal disease, stomach ulcers or vomiting. In this case, the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus and oral cavity, where it has an irritating effect. Some types of treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation, also have a negative effect on the condition of the oral mucosa.
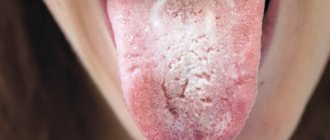
- Fungal infection of the mouth . A common reason for a burning tongue is a fungus. Typically, this is an infection with yeast-like fungi from the genus Candida. Accordingly, this disease is called candidiasis. It is popularly known as thrush. This name is due to the characteristic external manifestations, namely, a white cheesy coating on the tongue. It is noteworthy that candida are representatives of the normal human flora. A certain amount of these fungi is always found in the mucous membranes and skin. However, as soon as the immune system fails or the balance of microflora is disturbed (for example, when taking antibiotics), the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably. This is how thrush occurs. In rare cases, oral candidiasis occurs without a white coating on the tongue, but a burning sensation is present.
- Stomatitis . Often a burning sensation of the tongue is observed with aphthous stomatitis. This is a type of stomatitis in which rounded aphthae (or pockets of erosion) form on the tongue. Such formations appear not only on the surface of the tongue, but also on the cheeks, palate and other parts of the oral cavity.
- Allergic reaction . A burning sensation on the tip of the tongue or other parts of it is sometimes triggered by an allergic reaction. Typically, this is a reaction to a food allergen. In this case, you should be especially careful with some exotic fruits. Often it is overseas fruits that become a source of allergens.
- Medicines . The instructions for some medications state in black and white that a burning sensation in the mouth is possible as a side effect. This effect often occurs with blood pressure medications, antidepressants, sedatives, and some antibiotics.
- Diabetes . It is known that high blood sugar levels have a toxic effect on the body. First of all, blood vessels suffer (angiopathy develops) and nerve fibers (neuropathies develop). Diabetic neuropathy sometimes affects the nerve endings of the tongue, resulting in a burning sensation, changes in taste, tingling or numbness. Accordingly, such symptoms are also possible in some neurological pathologies, for example, multiple sclerosis and others.
- Glossitis . A common cause of burning sensation or pain in the tongue is glossitis. These are inflammations of the tongue that occur due to infectious and non-infectious causes. Often the cause of this symptom is the so-called “geographical tongue” or migratory glossitis. In this case, the tongue becomes covered with spots, and its external outline resembles a map of the world.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals . A burning sensation in the mouth is also possible due to a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, in particular B vitamins, iron or folic acid. In this case, hypovitaminosis may be caused by various diseases that prevent biologically active substances from being absorbed in the small intestine. For example, this is celiac disease, a disease in which gluten intolerance is noted.
- Other diseases . Soreness and burning in the oral cavity is also possible with some other diseases - autoimmune disorders, scarlet fever, tumors and other pathologies.
Geographic language
What is dystonia?
Dystonia of the tongue muscles causes involuntary movements of the tongue and uncontrolled mobility of structures adjacent to the tongue, which can lead to problems with chewing food and articulating sounds. As experts note, this may result in weight loss and loss of the ability to speak. In particularly severe cases, for example, when a patient may suddenly choke on food, tongue dystonia can provoke the development of more serious health problems.
According to observations, musicians who play wind instruments are more susceptible to spasms of the mouth muscles.
Risk factors
For a symptom such as burning of the tongue or mouth, it is quite difficult to determine the risk factors. Fair will be those risk factors that contribute to the development of the above-described diseases and conditions. These factors include:
- poor oral hygiene;
- untimely treatment of dental diseases;
- improper care of dentures (this contributes to the occurrence of infections);
- eating disorder;
- long-term use of antibiotics or improper use of these medications;
- long-term use of medications that regulate blood pressure;
- hereditary and acquired pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- lack of control of sugar levels in diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2;
- hormonal changes, such as menopause;
- lack of preventive examinations at the dentist.
Associated symptoms
This symptom manifests itself in different ways. The tip of the tongue often burns, but sometimes the entire tongue or just the base burns. Often, with a burning sensation in the mouth, other accompanying symptoms are also noted. These include sore throat, dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, the appearance of white spots on the tongue, and others. The patient may also experience tingling, tingling, or rawness in the mouth. The nature of pain can be acute or chronic. If a symptom bothers you irregularly, then it is important to understand under what circumstances it develops. For example, if your tongue begins to burn whenever you eat pineapples, mangoes or other allergenic foods, then the cause is most likely food.
Diagnostics
With complaints of tingling of the tongue, first of all, contact a dentist, who carries out an examination and identifies the most common causes of this condition. If there are no obvious factors, a comprehensive examination is prescribed with the participation of a therapist, neurologist and other specialists. To detect the etiology of tongue tingling, the following are used:
- Instrumental diagnostics
. For dry mouth, ultrasound of the salivary glands and sialography are recommended. To identify gastrointestinal diseases that cause tingling, EGD and radiography with oral contrast are performed. Electromyography is informative to determine areas of paresthesia in glossodynia. - Laboratory research
. A general blood test determines the level of hemoglobin, the presence of macrocytes or megaloblasts, indicating B12-deficiency anemia. Additionally, the content of cyanocobalamin in the blood is examined. For differential diagnosis, a saliva test is performed to measure the pH value. - Microbiological analysis
. To confirm candidiasis, microscopy of plaque on the tongue is performed, during which pseudomycelium and budding cells are detected. Confirmation of the diagnosis requires inoculation of the biomaterial on nutrient media. To exclude syphilitic glossitis, microscopy of the scraping is done for Treponema pallidum.
Examination of the tongue and oral cavity
When to see a doctor
If this is not the first time a burning sensation in the mouth has occurred, and the culprit is NOT spicy food, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Based on the above reasons, doctors of various specialties can deal with this problem. First of all, these are therapists. A general practitioner, based on the history taken, will be able to exclude a number of pathologies and refer the patient to the right specialist. Among them are dentists, endocrinologists, infectious disease specialists, gastroenterologists and others.
Important! During the interview, the doctor should tell you about all concomitant diseases, lifestyle and medications you are taking. This information will help the doctor rule out a number of diseases and quickly identify the cause of the symptom.
Burning tongue: treatment methods
After diagnosing and establishing the cause of burning tongue, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. The extent of therapeutic intervention mainly depends on the underlying cause of the symptom. For this symptom, the following treatment options are used:
- Analgesic, symptomatic treatment . Anesthetic drugs are used for these purposes.
- Antibacterial therapy . Prescribed when a bacterial infection of the oral cavity is detected.
- Treatment at the dentist . The patient is given a set of therapeutic measures to eliminate caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, periodontitis and other dental diseases.
- Antifungal therapy . It is used for fungal infections of the oral cavity (candidiasis).
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus . Antihyperglycemic drugs are prescribed, as well as a special diet that limits the consumption of simple carbohydrates.
- Antiallergic treatment . Used for allergic reactions. The most effective way in this case is to avoid contact with the allergen. And to relieve an allergic reaction, antihistamines are used.
- Treatment of neurological and mental disorders . Depending on the root cause of the burning sensation in the mouth, the patient is prescribed antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants and other drugs that improve the functioning of the nervous system.
- Psychotherapy. Sometimes psychotherapy helps with this symptom. In particular, this works if the symptom is associated with increased stress levels or a mental health disorder.
- Other types of treatment . An individual treatment regimen is selected for each patient.
Home methods and traditional medicine
To treat this symptom, various traditional medicines are used that have a calming effect on the oral mucosa. Let's look at the most popular means:
- Rinsing with decoctions of medicinal plants . For these purposes, sage, chamomile flowers, aloe, linden flowers and other medicinal plants that have a calming effect are used.
- Rinsing the mouth with a salt solution . Salt has a mild anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect.
- Sucking ice cubes . This procedure will not only soothe the “burning” tongue, but also strengthen the throat.
To maintain oral health, it is important to drink enough fluids. This will avoid dry mouth and a number of problems that are associated with this circumstance (in particular, oral infections).
Preventive measures
Preventive measures against a “burning” tongue include the following:
- Proper dental and oral hygiene.
- Clean your tongue daily with a special cleaner (but not with a brush!).
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Avoiding allergens, in particular food ones.
- Controlling blood sugar levels.
- Timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Compliance with the principles of balanced nutrition.
- Regular preventive examinations with a dentist (at least 2 times a year).
Is my tongue my doctor? What diseases can be identified by the organ of taste?
The tongue is one of the most important organs in the body. It contains receptors that allow you to recognize all shades of taste of products entering the oral cavity.
As scientists noted back in ancient times, human language has a connection with various organs of the body. When diagnosing, they divided it into conventional parts: basal, middle and tip. And they believed that in case of pathology of a particular organ, the lesion would be observed strictly in one of these areas. AiF.ru looked into what diseases leave their mark on the language together with Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, head of the laboratory for the development of an interdisciplinary approach to the prevention of chronic non-infectious diseases of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine of the Ministry of Health of Russia", expert of the National Health League Mehman Mamedov .
Color spectrum
When examined by a doctor, you are often asked to show your tongue. And they do this not out of idle curiosity. After all, even by the color of the tongue it is quite possible to determine whether there is a particular disease. For example, the tongue of a healthy person should be pale pink: this is what is accepted as the norm. If there is a white coating on the tongue, we can talk about fungal infections of the body or disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. A gray tongue is usually the result of chronic pathologies. Bright red - will indicate infectious and inflammatory processes in the human body; if the red color has a shade of scarlet, doctors will suspect problems with the circulatory system. A burgundy tint is a clear sign of an acute infectious process. The tongue is part of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also connected with the respiratory system, because located in the oral cavity. With stomach and duodenal ulcers, problems with the gallbladder, liver and intestines, there may be changes in the color of the tongue. Each disease has its own manifestations - in some places it can be more contrasting, in others it can be lighter.
It also happens that the color of the tongue changes to blue and purple. In this case, they talk about problems with the lungs or severe kidney ailments. Yellowing of the tongue is not only a characteristic feature of a heavy smoker, but also a signal of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If there is a lack of vitamins in the human body, the tongue may completely lose color.
It is worth considering that a shade that is too dark and saturated is a sign of problems that require immediate medical intervention, or even hospitalization.
Additional factors
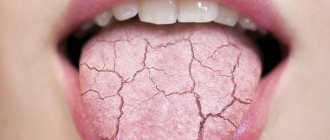
However, not only color matters. If the tongue is too dry, the following diagnoses may be made: dehydration, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis. Often, dry tongue is observed with an increase in body temperature. If the situation approaches critical, the taste organ may even crack due to dryness. In this case, an additional threat is created: it is easily infected with bacteria, resulting in suppuration and severe inflammation.
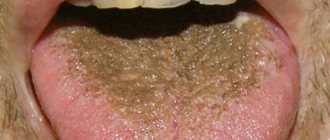
The type of coating on the tongue is also of particular importance. So, if it is thin, it means that the disease is in the initial phase, and if it is frankly fatty and thick, then the problem most likely lies in pathologies of the gastrointestinal system: this usually happens if mucus has accumulated there and food stagnates. A spotted and purple coating indicates the development of blood stagnation. Malfunctions in the digestive system will cause the tongue to become slightly swollen and wet. In this case, it is recommended to be checked for gastritis, cholecystitis, ulcers and even appendicitis.
Doctors pay special attention to the place where plaque accumulates. So, if it is more adjacent to the root of the tongue, then problems are noted in the large intestine: most likely, many human waste products have accumulated there and cannot find a way out. Plaque in the middle indicates problems in the small or duodenal intestine or stomach. If the plaque is so thick and the tongue is so swollen that you can see teeth marks along the edge, you need to reconsider your diet: with a high degree of probability it can be said that the intestines cannot cope with the food that a person eats.
The presence of deep wrinkles and cracks located transversely should alert you and send you to a neurologist - as a rule, this problem manifests itself with a predisposition to vascular disorders of the brain.
The tongue can even indicate serious cardiac and vascular problems, which may occur without any symptoms for some time. For example, a tongue that is slightly shifted to the side or slightly bent will indicate a hemorrhagic stroke, cerebrovascular accidents, or problems with the functioning of the cerebellum.
An increase in the volume of the taste organ may be a consequence of problems with the thyroid gland, malfunction of the pituitary gland, or mental disorders.
Shaky and grainy
Sometimes a person may notice that his tongue... trembles. This condition indicates nervousness and problems with the central nervous system. In such a situation, doctors recommend changing the psychological environment, as well as working on your lifestyle. It is also worth checking with a doctor if your sense of taste begins to decrease. After all, it does not develop out of the blue: there must be a reason why a person no longer feels the tastes to which he is accustomed. Moreover, it is important to understand that there are certain zones and areas on the tongue that are responsible for the reaction to different tastes: spicy, salty, sweet, etc. If a malfunction is noted in any of the parts, this may indicate that the nervous system is suffering. or endocrine system. Loss of taste in the taste buds of the tongue manifests itself as a result of metabolic disorders in the human body, as well as malfunctions of the central system of various etiologies, the development of anemia and the presence of cancer.
Also, people often begin to notice that the tongue has become rougher: this is due to an increase in the size of the papillae on the surface of the organ. When swollen papillae are localized at the tip, it is worth being examined by a cardiologist. If the tongue becomes “spiky” around the edges, you need to check the liver. An affected middle part of the tongue indicates problems in the stomach and intestines. At the same time, you should not rejoice when the tongue becomes smooth and “mirror-like”. After all, this is also a pathology. This happens with anemia, exhaustion or severe pathologies of the stomach.