From this article you will learn:
- why does flux (abscess) occur?
- abscess on the gum: treatment, antibiotics,
- opening of a gum abscess: video.
Flux on the gum is a swelling of the gums associated with the development of purulent inflammation. Dentists do not use the term gumboil or abscess (only patients say so), but use terms such as “gingival abscess” or “periostitis”.
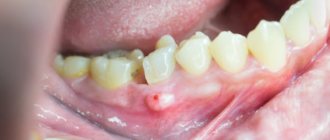
Flux on the gum: photo
Content:
- Why does it occur
- Signs
- How it proceeds
- Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
- What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
- How to remove flux
- How to speed up recovery
- Preventive actions
An inflammatory dental disease that affects the periosteum tissue is called periostitis by dentists.
It is popularly known as flux. It is easy to recognize on your own - a painful abscess forms on the gum, which does not go away for a long time. It is unwise to fight this disease without medical help. When it appears, you should definitely make an appointment at a dental clinic and, during an in-person examination, find out from the doctor how to remove the flux without negative consequences for health.
It is simply impossible to ignore periostitis. It is usually accompanied by acute throbbing pain. Sometimes it can even lead to fever and a sharp decrease in performance. When there is a lot of pus in the “bag”, it bursts. Then the purulent masses flow out, and the symptoms cease to be so bright.
Diagnostics
To diagnose flux, methods such as questioning, examination, and additional research methods are used: radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, blood test data, culture of exudate, etc. An experienced maxillofacial surgeon who treats patients with flux, can, based on the patient’s complaints and examination, carry out an accurate topical diagnosis of the disease (localization of pus) and select the optimal surgical approach to ensure sanitation of the purulent focus and adequate drainage.
Why does it occur
In order to understand how to remove flux, it is necessary to establish what led to its appearance. If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease may return. Among the main reasons for the violation:
- untreated deep caries;
- a large amount of hard plaque extending far under the gum;
- dental root cyst;
- inflammatory lesion of the gingival pocket;
- receiving mechanical injuries;
- general hypothermia of the body (especially against the background of reduced immunity);
- poor oral hygiene.
According to statistics, most often the disease occurs precisely because of advanced caries and pulpitis. If there is a large “hole,” the infection easily penetrates deep into the dental tissues, affects the surrounding structures and causes nerve destruction. Then pulpitis develops.
If left untreated, it will become chronic. The pain will become mild, but this does not mean that the disease has gone away. It’s just that now it’s happening secretly. The infection will continue to destroy the internal structures of the diseased unit. As they die, narcotic masses will begin to be released. To remove them, an abscess forms on the gum. This is flux.
If it is localized on the periosteum of the upper jaw, then the upper lip and the area under the eye swell. If inflammation progresses in the lower jaw, the chin and cheek swell, and the lymph nodes become painful.
Causes
The cause of flux is an infection that breaks through to the periosteum of the jaw and begins a purulent process. It all starts with those microorganisms that constantly live in the oral cavity and also enter with food. The putrefactive process near the tooth in the absence of hygiene leads to the breakthrough of pus through the tooth to its root.
Infection is the main factor that develops gumboil. And the supporting reasons are:
- Untreated caries.
- Injuries to the tooth and surrounding tissues that lose their integrity and give access to infection.
- Angina.
- Failure to observe and neglect oral hygiene.
- Furunculosis.
- Penetration of infection through blood or lymph flow from other infected areas.
go to top
Signs
You can understand that periostitis has developed by the following symptoms:
- tooth pain;
- swelling of the gums;
- an abscess at the base of the diseased unit;
- increased pain when pressing on the affected area;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the lymph nodes.
If these symptoms occur, you should make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated quite easily and quickly. Delay is fraught with health-threatening complications.
Forms of release of antibacterial agents used in dentistry
Dentists use drugs in the form of:
- Ointments and gels. Designed for local treatment of affected gums. Qualitatively relieve inflammation and reduce pain symptoms. As a rule, ointment and gel formulations are applied two to four times a day. It is important to use the medication regularly and strictly according to the regimen selected by a specialist. Only then will it be possible to achieve positive dynamics.
- Tablets and capsules. The most popular types of antimicrobial agents intended for oral administration. The daily dosage is determined by the doctor. When deciding which antibiotics to prescribe, the doctor must take into account the patient’s health condition. It is unacceptable to include in therapy drugs that can aggravate the course of existing diseases of internal organs.
- Solutions for injection. Injections are given intravenously or intramuscularly. This is the most effective option for antibacterial therapy. It is used for complicated and advanced forms of dental disease.
How it proceeds
The disease progresses through several successive stages:
- Acute serous. Spreads quickly. In just two or three days, a large, painful “bump” forms, with pus inside. The cheek tissues swell.
- Acute purulent. The pain becomes more pronounced, the person feels an unpleasant pulsation. The mucous membrane in the area of the affected unit turns red and swells. Body temperature rises.
- Acute diffuse. The swelling becomes voluminous. It can go under the eye or onto the nose. The patient's appearance changes significantly for the worse.
- Chronic. The painful process fades away and is replaced by a chronic one. The patient may mistakenly think that the problem has disappeared without a trace. In fact, it only calmed down for a while. Periodically, the disease will recur.
The sooner a sick person consults a doctor, the higher his chances of a speedy recovery.
Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
In adults, the disease usually has vivid symptoms. Most often it is caused by bad habits and ignoring the rules of oral hygiene. The tissues surrounding the root become inflamed. Persistent pain forces a person to seek dental care.
In children, flux usually progresses with mild symptoms. This is due to the fact that in children the immune system reacts less actively to abnormal processes in the oral cavity. Even if the purulent “bump” does not hurt the child, a consultation with a dentist is still required.
What undesirable effects are possible during the course of medication?
Side effects depend on the active compound of the particular drug and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Common complications caused by long-term antibiotic therapy include :
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis. The conditions are manifested by nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and flatulence.
- Decreased performance, muscle weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Allergic reactions. Usually these are skin rashes and itching. Swelling also often develops.
If the antibiotic is poorly tolerated, a repeated consultation with the dentist is indicated. It is possible that the doctor will replace the medication with a safer analogue.
What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
It is unacceptable to treat purulent gum lesions as a minor dental disorder. It is very insidious and rarely disappears without a trace on its own. Often, if treatment is refused, the following occurs:
- Abscess. It is a consequence of a long-term presence of a pus-filled sac in the area of the tooth root. The abscess grows and then ruptures.
- Phlegmon. Represents an extended lesion. It usually occurs after a rupture of a purulent sac, if the patient does not comply with the dentist’s instructions, does not rinse the mouth with a special antiseptic solution, or apply anti-inflammatory gels.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. It occurs if the gums are not treated for a very long time. The pathological process spreads to the jaw bone, which is very dangerous.
- Inflammation of individual sinuses of the skull. It is also diagnosed with advanced periostitis. The maxillary, frontal and sphenoid sinuses are affected.
It is extremely rare that the disease affects brain tissue. Then the person may even die.
Which antibiotic to choose
It is impossible to name one medication that would suit everyone. Only a doctor can determine the drug that is effective for a particular patient. To do this, he conducts a survey, examines the oral cavity and performs some diagnostic manipulations.
Among the antimicrobials most often used in dentistry, it is worth highlighting:
- Ciprofloxacin. Broad-spectrum composition. Belongs to the group of second generation fluoroquinolones. Effectively destroys Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans - a gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacterium that causes periodontitis and periodontal disease. It is noteworthy that the medicine practically does not change the microflora of the oral cavity. Therefore, dentists classify it as safe.
- Metronidazole. It is used in the relief of pathologies caused by protozoa, oral bacteria and Trichomonas. Helps with damage to tooth roots, purulent processes, phlegmon, periostitis, abscess, alveolitis and many other diseases of the mouth.
- Doxycycline. Prescribed by specialists at the dental center if severe inflammation of soft tissues, gingivitis, granuloma, or damaged tooth roots are diagnosed.
- Tetracycline. Allows you to cope with the destruction of the periosteum and periodontitis. It has a unique ability to accumulate in the gingival fluid of periodontal pockets, due to which it quickly destroys pathogenic microorganisms.
- Azithromycin. Used in the treatment of inflamed periosteum in patients allergic to beta-lactam compounds. Drink once a day for three days. Moreover, its therapeutic effect persists for several days after the end of the course.
- Amoxiclav. Its active compound is amoxicillin supplemented with clavulanic acid. It is in such a “bundle” that the connection manifests itself best. If you use it in the fight against gumboil in the form of monotherapy, you are unlikely to be cured.
- Lincomycin. It has a pronounced bacteriostatic effect - quickly stops the proliferation of harmful bacteria, which is very important for periosteal pathologies. Destroys streptococci, staphylococci.
Most of the medications listed are available in pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. This once again proves that it is impossible to try to overcome toothache without ever visiting the dentist.
How to remove flux
To avoid purulent damage to the pulp zone and periosteum, you need to receive qualified dental care in a timely manner. In the early stages of the disease, in order to prevent further progression of the inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. It is mandatory to open the abscess. The wound is then cleaned and washed with an antiseptic.
In some cases, to prevent re-accumulation of pus, drainage is installed for several days. All surgical procedures are always performed under general anesthesia so that the patient does not experience pain.
To support the patient’s body, he is additionally prescribed a vitamin and mineral complex. If necessary, physiotherapy is included in the treatment course. Good results can be obtained using UHF and electrophoresis.
It is important to strictly follow all medical recommendations and under no circumstances interrupt antibiotic therapy. Treatment is considered successfully completed if pus is no longer released, pain does not occur, and the entire wound has healed. In some cases, after healing, a small bluish scar remains on the gum. You shouldn't worry about it. This means that the defeat was very deep. Over time, the gums will return to their normal appearance.
Danger of overdose
Some patients believe that by using higher doses of medication they will be able to recover faster. This is wrong. In the case of any medications, it is important to adhere to the dosage and regularity of use.
If you deliberately increase the number of tablets consumed per day, an overdose will develop. This is an insidious condition that is harmful to health. In the case of incorrect antibiotic therapy, it manifests itself:
- vomiting, nausea;
- dizziness;
- loss of strength;
- discomfort in the abdomen, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases (if any);
- allergic rashes.
If an overdose occurs, you should immediately interrupt treatment and consult a doctor.
How to speed up recovery
To make healing go faster, it is important not only to follow the dentist’s instructions, but also to remember the rules:
- do not heat the area where the pus was located;
- do not take antibiotics or any other medications unless prescribed by a doctor;
- do not use any folk recipes without consulting your doctor;
- Until the wound is completely healed, do not use aspirin or any medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid.
If the “bump” appears again, it is recommended to immediately contact a dental clinic.
Preventive actions
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you need to take care of your teeth and visit the dentist at least once a year. You can't start caries. As soon as a dark spot appears on the surface of the dental crown, it needs to be treated.
After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To make hygiene as high as possible, it makes sense to use not only a brush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and irrigators. It is very important to remove tartar every year at the dentist's office.
An important place in the issue of prevention is given to diet. You should eat as much fresh fruits, vegetables, and plant foods as possible. They require more thorough chewing and thus have a positive effect on the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. They also provide natural cleansing of crowns from soft plaque.
If you have any questions about how to remove flux, please contact the doctors at the Line of Smile dental clinic for help. We specialize in the treatment of this disease and know how to quickly rid our patients of it.
Anti-inflammatory pills
Anti-inflammatory drugs for flux have a strong analgesic effect, relieve swelling and reduce inflammation. Some of the medications used can relieve high fever, which sometimes accompanies the symptoms of periostitis.
Nimesil
Flux tablets with a pronounced analgesic effect actively eliminate inflammation at all stages of the disease. The daily dose of the drug is 200 mg (1 tablet of 100 mg twice a day). The duration of treatment depends on the clinical picture of periostitis and the need for treatment of toothache.
Diazolin
A drug for flux from the group of antiallergic drugs. It has a strong anti-edematous effect, reduces the production of biologically active inflammatory substances at the site of abscess development. Diazolin is taken depending on the severity of swelling of the gum and cheek tissues, 1 tablet (100 mg) 1-3 times a day until the condition improves.
Diclofenac
An anti-inflammatory drug that has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect, significantly reduces toothache. To eliminate pain, use 25-50 mg 1-2 times a day.