Content
hide
1 What toothpastes do dentists recommend? 1.1 Main components of hygienic pastes
1.2 The main types of therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, depending on their action: 1.2.1 Toothpastes that strengthen tooth enamel:
1.2.2 Toothpastes for gums.
1.2.3 Pastes for sensitive teeth.
Any dentist will tell you that toothpaste is not as important as a toothbrush and proper brushing technique. You can brush your teeth well without toothpaste at all. However, pastes have an additional positive effect on teeth - and what kind of effect depends on their composition. Let's take a closer look.
As you know, in order for your teeth not to be affected by caries and your gums not to become inflamed, you need to brush your teeth every day - regularly and thoroughly, so that food residues do not linger on the surface of the teeth and plaque with microbes does not have time to form.
All toothpastes are divided into hygienic (which simply help to clean teeth better) and therapeutic and prophylactic (which contain various medicinal substances that help solve certain problems).
In the beginning there was sand and chalk
Toothpaste and brush are everyday things with which our day begins and ends. However, they were once a real luxury. The ancient Egyptians were the first to think about oral hygiene and began to use sand, ash, ground stones and animal horns as a cleaning agent, and their own finger replaced the brush. In the 4th century BC. The great healer Hippocrates recommended using mixtures of pumice with the addition of wine vinegar, which are more gentle on tooth enamel, to prevent dental diseases. At the end of the 18th century, little had changed. For example, the British brushed their teeth with powders that included crushed brick, crushed bark and coal chips.
The prototype of modern toothpaste was invented by Americans in the 19th century. This time there were no stones or ash. Teeth cleaning products were a mixture of chalk powder, neutral soap and aromatic additives. It was only in 1873 that Colgate released the first toothpaste in glass jars, which replaced tubes two decades later. They were invented by dentist Washington Sheffield of New London. But Colgate beat the inventor by quickly registering a patent for itself. An interesting fact is that in Russia, most people at that time continued to brush their teeth with chalk-based powder, and only in the 50s it became possible to buy a familiar tube of toothpaste in stores.
Therapeutic pastes for tartar
Hard plaque can be completely removed only by professional ultrasonic cleaning or using a special Air Flow device. Toothpastes are used more as a preventive measure; they can lighten pigmented areas and remove small plaques.
Such products are recommended for tea and coffee lovers and, of course, smokers. Typically anti-tartar pastes contain:
- a small amount of fluorine (0.1 - 0.6%);
- antiseptics;
- minimal amount of sodium lauryl sulfate.
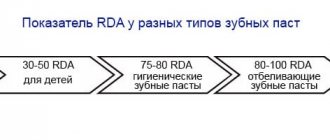
These products are highly abrasive - the RDA index is above 100. It must be remembered that abrasives increase the permeability of enamel. This means that you will need to increase your care: use floss and rinses.
Best toothpaste
Which toothpaste is better? Definitely one that meets a person’s needs and suits his indications. Until recently, the main task of toothpaste was to help the brush clean teeth from plaque. Today, modern manufacturers of hygiene products have expanded its functionality and began to offer special medicinal toothpastes, both complex and for targeted solutions to specific problems. Today you can find tubes not only for the prevention of caries, but also for bleeding gums, against the formation of tartar, paste for implants or smoker’s plaque, for fresh breath or restoring the pH balance of the oral cavity, as well as for much more. But, in fact, all pastes are divided into several varieties, which we will consider.
Application
- Hygienic. Remove dental plaque. Recommended for people with healthy teeth. Contains useful microelements and antiseptic additives.
- Fluorine-containing. Used to strengthen teeth. Fluoride-containing pastes should be used after consultation with a doctor: some filling materials are destroyed by fluoride.
- Medicinal. The composition contains antibacterial components, protects against caries, and helps prevent diseases of the teeth and gums. Natural extracts, oils, minerals, and biologically active components are used as additives.
- Whitening. Contain abrasive particles and additives to lighten tooth enamel. Recommended for occasional use. Does not eliminate the formation of tartar.
- Children's. They contain substances that have a positive effect on the health of baby teeth, strengthen gums, and disinfecting components.
- Anticarious. Active components penetrate into hard-to-reach places, strengthen enamel, and reduce tooth sensitivity. Ways to stop caries in the initial stages.
- Anti-inflammatory. For sensitive gums. Contains components with antibacterial, antimicrobial, hemostatic effects. Activate the processes of restoration of tissues and mucous membranes.
Pastes for the prevention of dental caries
Toothpastes for the prevention of caries are recommended for increased susceptibility to the formation of caries bacteria, as well as as restorative therapy after teeth whitening. They saturate dental tissues with useful minerals, prevent the growth of carious bacteria, and also fight the formation of plaque. To strengthen teeth, fluoride compounds are added to such pastes. It is contained in such pastes as “Day and Night” Swiss Smile, Enzycal 950 CURAPROX, Mirafluor C Miradent, “Power of a Smile” Jason and others. Fluorine is an important microelement, since it is the one that participates in the metabolism of calcium, and, therefore, ensures its presence in the enamel. But it is worth remembering that it is extremely toxic, so its amount entering the body should not exceed the established norm. People living in areas with fluoride-saturated water (more than 1.2 mg/l) are advised to use fluoride-free toothpaste. You can find out about the fluoride content in the water in your area by calling the nearest Sanitary and Epidemiological Station.
Toothpaste
Theodent Classic
Features of the composition: active substances
- Ammonia - added to toothpastes in past decades due to its good whitening properties. A number of manufacturers continue to add amines - organic components that are derivatives of ammonia, obtained from animal fats. In large doses, ammonia and its components cause irritation to the oral cavity.
- Dibutyl phthalate is a substance used as a solvent in the manufacture of toothpastes, perfumes, and cosmetics. Dibutyl phthalate is toxic and prohibited for use in the USA and Europe: the permissible concentration is no more than 0.1%.
- Camphor - the essential oil of the bark of the camphor tree is famous for its whitening properties, but the high percentage of the substance makes the paste unsafe for tooth enamel.
- Dyes - used to give the paste a rich color. Manufacturers use pigments based on natural, artificial components; They produce toothpaste without adding coloring additives.
- Mineral oils strengthen dental tissue, prevent gum disease, and have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Odorless and colorless mineral oils obtained from petroleum refining are added to toothpastes; undergone multi-stage cleaning. The component is harmless, but production does not meet environmental standards.
- Fragrances - give the paste a pleasant aroma. The basis is natural mint oils, menthol, cloves, eucalyptus, anise and other plant extracts. Used together with a sweetener: sodium saccharinate.
- Parabens are components based on ethyl, propyl, methyl bases. Serve as a preservative, a means to extend the shelf life of products. They accumulate in the environment and are not environmentally friendly substances.
- Silicones - liquid silicone is harmful to the body; in some types of toothpastes the substance is added in a minimal dose as a binding component.
- Alcohol kills germs, but has an irritating effect on the mucous membranes of the mouth. Pastes with alcohol are contraindicated for children; persons who have undergone a medical alcohol coding procedure; people with intolerance to the component; managers of vehicles, machinery, etc.
- Sulfates are surfactants added to toothpaste as a binder. Sodium lauryl sulfate is toxic in high doses; it is added to toothpaste in safe proportions.
- Toluene - methylbenzene is used as an organic solvent. Exceeding the concentration causes irritation of the mucous membranes and poisoning of the body.
- Formaldehyde is a substance that kills bacteria in the mouth. This is a dangerous component: a serious dose if ingested leads to poisoning and serious health consequences.
- Fluoride strengthens enamel and prevents the development of pathogenic bacteria. Fluoride-containing toothpastes are used to prevent caries. Not suitable for people with fillings; receiving fluoride from other sources (drinking water, medications, etc.).
- Xylitol is a sweetener that is good for teeth. Strengthens enamel, supports immunity.
- Calcium - The calcium carbonate in toothpaste is a chalk, an abrasive ingredient used to whiten enamel.
- Urea peroxide is a bleaching component based on urea and hydrogen peroxide. A gentle brightening agent.
- Colloidal silver is a natural antibiotic, a useful microelement that strengthens teeth and gums; killing bacteria.
Pastes against tooth sensitivity
There are special toothpastes for sensitive teeth. They contain potassium chloride, potassium citrate (Twin Lotus Recipe for Sensitive Teeth, Mirasensitive hap+) or strontium chloride. These substances “clog” the dentinal tubules and reduce hyperesthesia. They also saturate the tooth enamel with minerals, the deficiency of which is most often the cause of increased sensitivity of enamel and dentin. But the most progressive substance today is considered to be hydroxyapatite (Sensitivity Control Biorepair). Its crystals are similar in composition to tooth enamel, so they effectively combine with it, restoring the natural protection of teeth. Pastes for sensitive teeth should not contain a drop of chemical bleaches and, instead of coarse calcium carbonate, should contain gentle abrasive substances with a smaller particle diameter, for example, silicon oxide. Such pastes are recommended for hypersensitive teeth, as well as for use during and/or after teeth whitening procedures.
Sensitivity Control Biorepair toothpaste
Anti-caries pastes that restore enamel
Such products are designed to combat enamel demineralization and prevent the development of caries at the white spot stage. Pastes are based on calcium compounds or fluorides. You should not use products that contain both types of compounds. The fact is that fluorine and calcium react and form an insoluble residue, which means that during cleaning no active ions are released and no recovery occurs.
Calcium-containing pastes can be used every day. They are designed to correct mild thinning of the enamel.
Fluoride-containing pastes are designed to restore seriously damaged enamel. They can only be used with the permission of a doctor, as there is a risk of getting excess fluoride in the body. This can lead to brittle bones and teeth. Such products are used no more than twice a week. For greater effectiveness, they can be alternated with calcium-containing pastes.
Pastes for strengthening gums
Toothpastes aimed at preventing and reducing periodontal inflammatory processes reduce bleeding gums, help strengthen them, have an astringent effect, and also destroy harmful microbes. They most often contain antibacterial substances, for example with chlorhexidine, as in Curaprox ADS 712 paste, together with plant extracts that have an anti-inflammatory effect, such as edelweiss and echinacea in the SWISS SMILE vitamin herbal paste or witch hazel and calendula in the Plus Parodontgel BioRepair paste. Some of them also contain chlorophyll and vitamin E. All of these substances have a beneficial effect on gum tissue, accelerating the healing process and the formation of new cells. Such pastes are recommended for diseases of stomatitis, gingivitis and periodontitis.
Toothpaste Curasept ADS 712 CURAPROX
Therapeutic pastes for bleeding gums
These products contain extracts of various medicinal plants. They soothe sore gums, relieve swelling, reduce bleeding when brushing, and eliminate itching, bluishness and redness. In addition, these pastes relieve pain. They can be used in the treatment of periodontitis or gingivitis. But we must remember that in case of serious diseases, pastes are effective only with dental treatment.
In the absence of serious measures, such pastes can temporarily hide the symptoms, but, unfortunately, they will not cure the disease.
Pastes against bad breath
The action of toothpastes that help fight halitosis is aimed at restoring the normal balance of oral microflora, the disruption of which is usually accompanied by excessive proliferation of anaerobes. These substances emit volatile sulfur-containing products that have a pungent odor. Anti-bad breath pastes contain components that suppress pathogenic microflora and act on viruses. In addition, such pastes eliminate dry mouth syndrome, which can also cause halitosis. Antihalitic hygiene products are recommended for bad breath caused by microflora disturbances and dry mouth.
Enzymatic toothpaste gel
Jason Enzyme Brightening
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of Asept toothpastes has been clinically proven:
- it has been proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33%;
- It has been confirmed that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce the sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%.
- It has been proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION after 4 weeks improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
Composition of toothpaste - which is better?
A dental hygienist can help you figure out which toothpaste is best for specific oral problems. When purchasing a product yourself, you need to pay attention to whether it contains substances potentially harmful to teeth. For example, coarse abrasive substances that negatively affect tooth enamel. These may be chalk or calcium carbonate, as well as aluminum oxides, which are prohibited in some countries. Nowadays, silicon dioxide is considered the best abrasive; it gently removes all dental plaque without having a negative effect on the enamel and gums. You can also find other safe abrasive substances in paste compositions—dicalcium phosphate or sodium metaphosphate.
You should be careful with toothpastes that contain triclosan or chlorhexidine. Brushing with such pastes may be necessary to treat inflammation in the gums or to eliminate bad breath. However, long-term use (more than 3 weeks) of paste with antibacterial substances can lead to disruption of the beneficial microflora of the oral cavity. If sodium lauryl sulfate is in one of the first places in the description of the composition (that is, its percentage is large), then it is also better not to buy such a paste. The fact is that this surfactant is responsible for foaming, but does not in any way affect the quality of cleaning. In addition, it has long been proven that even in small doses, sodium lauryl sulfate can negatively affect the body. This component is contained in all pastes from Blend-a-med, Colgate, Oral-B, Aquafresh, Karimed, Forest Balsam, some pastes from Lacalut, SPLAT, PresiDENT, and New Pearl.
Composition features: paste categories
- Pharmacy cosmetics - this type of toothpaste belongs to a special category and is sold through pharmacy chains. Products are rarely offered for sale in supermarkets and retail stores. European brands prefer to sell products through city pharmacies.
- Vegan and vegetarian cosmetics are a category of toothpastes that do not contain organic fats or components of animal origin.
- Aqueous toothpaste - contains purified water and is sold in economical bottles with a dispenser. This is a composition in the form of a gel for cleaning teeth.
- Not tested on animals.
- Organic cosmetics - contain natural ingredients grown without chemicals. Cosmetics do not harm the environment.
- Availability for daily use - this is how toothpaste is labeled for regular use.
- Dermatologist Tested - The product has been dermatologically tested.
- Edible toothpaste is a type of composition that is harmless when ingested.
- The category of eco-products includes toothpastes made from environmentally friendly ingredients in recyclable tubes.
How much does toothpaste cost and where to buy it?
The price of toothpaste varies from 50 to 1,000 rubles per tube, and sometimes can exceed this threshold. Some people think that expensive pastes are the best, others don’t see the difference in all the variety and buy the cheapest one. In both cases, the buyers are wrong. A high price does not always indicate the quality of a product, and buying cheap pastes is simply dangerous - they may turn out to be a fake or a product not manufactured in accordance with GOST. Where to buy toothpaste? This is best done in pharmacies and specialized stores, such as Startsmile Shop. You should not buy pasta in underground passages, at the market, on the train, or from “distributors.”
The choice of toothpaste determines many things - the appearance of teeth and gums, the condition of the enamel and its saturation with essential microelements. However, even the best toothpaste is not able to protect teeth from caries and gums from inflammation if cleaning is carried out quickly, poorly, incorrectly and irregularly.
To summarize: what criteria should you use to choose a toothpaste?
In addition to the above classification parameters, toothpastes also differ according to the category of users for which they are intended. Moreover, the division occurs not just “for adults and for children,” but also taking into account different periods of growing up (puberty), changes in health (pregnancy), etc. Specialists at the Amel Dental dental clinic recommend that before you buy toothpaste, make an appointment make an appointment with a dental hygienist or your own dental therapist and receive professional recommendations based on the actual condition of the teeth and mucous tissues, and individual characteristics. Only a specialist can choose the right toothpaste, especially for patients with certain dental problems.
Knowing which type of paste suits you best, you can choose the right product. When choosing, you should also take into account the general parameters of toothpastes:
- composition (absence of harmful substances, allergens, components that can cause irritation of the mucous membrane);
- abrasiveness of toothpaste;
- deodorizing properties and duration of fresh breath effect;
- individual preferences (for example, for people who cannot tolerate the menthol aroma, an odorless and tasteless paste is ideal).
Dental brushes
If you have gaps between your teeth or your teeth are slightly diverging due to the initial stage of periodontal disease, then be sure to use brushes .
The brush needs to be selected according to the size of the gap between the teeth - so that it fits tightly into the gap. TePe has them ) and empirically choose the one that suits you.
For the convenience of patients, brushes with long handles are produced so that they can clean the spaces between the far teeth.
Important: the brush should be changed every 1-2 weeks as it wears out.
Dental brushes
What kind of toothbrush should you have?
First recommendation. A toothbrush must have synthetic bristles . Nowadays it is important to be eco-friendly, but this is not the case when you should give preference to natural things. Any natural fiber (be it boar bristles or bamboo) has a porous structure, and inside it there is a channel that quickly fills with bacteria from dental plaque. There is no way you can clean the plaque from inside such bristles, so after the first uses, your eco-friendly toothbrush becomes a breeding ground for microorganisms.