1970
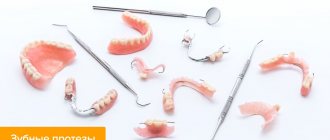
To fix the prosthesis in the mouth, preventing it from moving, clasps are used in orthopedics.
With their help, pressure is redistributed during the act of chewing. At the same time, they cover the dental unit only 2/3 of its circumference, creating support and ensuring retention of the prosthesis.
What is a clasp?
The clasp is an integral part of a removable denture and looks like specific hooks. Its purpose is to hold the denture. The fixing structure itself is assembled from several parts:
- Occlusal overlay – helps distribute the load on the supporting dental units.
- The body is a stationary area located closer to the upper pole of the chewing element. Connects all components.
- Shoulder – gives a springing effect when the denture is displaced, covers the area of the dental crown. Contains a supporting part (prevents movement to the side, imparts rigidity) and a holding part (fixing action).
- Process – connects the fixing part with the prosthesis, often covered with a base or crowns.
The task of clasps is to fix the prosthesis
To use the clasp system, you must have your own chewing elements that will serve as a support. Primary requirements:
- Sustainability.
- Functional relationship to the opposing unit of the other jaw arch. The components of the fixation will make the bite higher in the case of natural close contact during chewing or closing of the jaws.
- Classic anatomical shape. Selection with a non-standard configuration is quite risky and impractical.
- Full treatment.
Selecting a clasp system is not an easy task for a dentist. The installation is considered successful if:
- The bite does not increase.
- Rotational movements of the denture are excluded.
- The load is evenly distributed among all support units.
- The components of the retainer are practically invisible or completely invisible.
Clasps for dentures are made from wire or by casting.
The condition for strong attachment is the presence of strong supporting teeth.
Background of creation
In 1949 of the last century, American researchers (dentists, mathematicians and metallurgists) developed and implemented the Ney system. The principle of the new system was the use of clasps made by casting, which load the tooth only in the axial direction.
This technique has become a breakthrough in prosthetics, since when installing clasps there is no need to wear crowns, and its use is possible for any condition of the teeth.
In addition, the newest procedure turned out to be safe for the patient, since it does not cause traumatic damage to the surface enamel.
Manufacturing
There are several ways to make clasps. Plastic products are usually made by injection molding. First, the product is shaped using wax, then it is replaced with the base material. Stamped models are produced by stamping from metal alloys. Bent systems are made using tongs. The technician may also use pliers or needle nose pliers. With their help, the master gives the wire the desired shape.
Stages of making a clasp using the bent method:
- using pliers, one end of the wire is bent to create the shoulder of the product;
- a second bend of the wire is performed to form the body;
- the wire is bent a third time to form an appendage.
Types of clasps
Let us next consider several common types of clasps.
Material
Fixing elements for removable dentures can be made of various materials:
- Metal. Most often, products are made of medical steel, chromium-cobalt or gold-platinum alloy. These materials are highly durable and ensure maximum service life of the entire structure.
- Plastic. They are used in butterfly prostheses and nylon elastic structures. Designed to perform a holding function, since they are prone to deformation and breakage under chewing loads.
- Combined. Contains both metal and plastic elements. Most often, this type is used in orthopedic pads.
Tooth Coverage
The coverage of teeth by clasps can vary significantly in different designs. Thus, there are dentures with single-arm, double-arm, T-shaped, multi-link, double and reversible methods of covering the supporting teeth.
Each method of placement on the dental surface has both advantages and disadvantages, so the choice of a specific fixation method depends on the specific clinical situation.
Form
Depending on the cross-sectional shape, round, semicircular and ribbon clasps are distinguished.
Round clamps are the easiest to manufacture. They ensure effective fastening of the prosthesis if placed correctly and a sufficient number of support units are used.
Semicircular clasps are used when covering abutment teeth with metal crowns. They are usually made from a spring alloy.
Tape hooks are used less and less due to the difficulty of fitting them to the tooth surface.
Connection to base
There are three options for connecting the clasp to the prosthetic structure:
- Rigid fixation involves a fixed attachment of the hook to the base, as a result of which the chewing load is transferred to the teeth through the clasp.
- The spring connection is ensured using a spring extension. The pressure of the prosthesis is only partially transferred to the teeth.
- The articular connection is made using a hinge. In this case, there is completely no pressure on the supporting teeth, and the load is placed on the mucous membrane of the alveolar ridge.
Functions
According to the variety of functions they perform, clasps can be supporting, holding, or combined.
This is interesting: How long after tooth extraction can you get dentures?
Support products are attached to the canines and molars using hooks and participate in the process of redistributing the chewing load.
Retaining elements are designed to secure the prosthesis to the elements of the jaw arch when performing vertical movements.
In combined support-retaining clasps, various types of load are redistributed between periodontal tissues and the prosthetic bed.
Overview of modifications
Clasps have different functional features and are used in accordance with the individual structural characteristics of the patient’s jaw arches and the current clinical situation.
Support-holding
Support-retaining structures were an improved model of a simple wire hook, fixed directly in the neck area of the support unit.
Through technological developments, support structures have been modernized:
- two types of retaining clasp were designed: alveolar and dentoalveolar;
- The classic system of support-retaining structure is represented by its components: two arms, a process and an occlusal pad.
Ney system
The system can be classified as a standard version of a support-retaining clasp, and the materials are highly wear-resistant during operation. Design features of the Ney system:
- the thickened body and the upper shoulder area are modeled with a sufficient level of rigidity to eliminate frequent fractures directly in the area of articulation with the base;
- the upper part is positioned above a given centerline: this position provides stable support for the frame and creates an obstacle to lateral displacement;
- the lower part is specially thinned and placed below the boundary line, its functionality lies in reliable fixation of the prosthesis, preventing displacement;
- has a wedge-shaped shape: the hard thickened shoulder becomes thinner towards the bottom.
The system is universal, because when fixing there is no need to use a crown for any condition of natural teeth.
The Ney system is designed in such a way that the load on the jaw mechanism is distributed as evenly as possible, without damaging the enamel.
Roach clasps
The use of this type is not possible in all clinical situations, but they are a universal option for anatomically short crowns.
Design Features:
- the design consists of a long rod body and long arms; due to this structure, the element becomes elastic and springs well, which reduces the horizontal load on the teeth;
- rod elements can be used on both sides;
- ensures a highly aesthetic smile.
The Roach model, with all its apparent advantages, cannot be used in case of anatomical violation of the dentition. This also applies to high upper gums that open when smiling.
Acker clasps
This type of model is considered the most effective in its functionality. Acker design features:
- the rigid and durable composition of the system allows it to be fixed to molars;
- the use of the design is justified in the absence of one or two teeth in a row, provided that the supporting units are intact;
- a rigid frame blocks the displacement of clasp dentures;
- practical accessibility.
However, the rigidity and strength of a structure is not always the only guarantee of stability. When using Acker clasps, low elasticity is noted, which limits the possibilities of their use.
Bonneville
The Bonville design guarantees high fixation and stabilization of the prosthesis in the oral cavity, but only if there is sufficient space between the antagonists.
Item Features:
- the design has four arms that perform a holding function, while two of them can also perform a stabilizing function;
- equipped with two occlusal pads, fixed on premolars and molars, prevents food from entering during the act of chewing.
Clasps of this type are used to fix corrective devices for small unilateral anomalies, as well as to preserve elements of the jaw arch on the opposite side.
Jackson
This model belongs to the support-retaining systems of the flip-over type and is visually visible as a kind of loop. Peculiarities:
- placed in the interdental space, encircling the supporting unit, and located below the equator on the vestibular surface;
- support is provided by those parts of the loop that lie in the interdental zone;
- elements responsible for fixation are located below the equator;
- This type of model is available in three options: wire, elastic, and cast.
The Jackson model does not injure the enamel and ensures high stability of the prosthesis in the oral cavity.
Let's find out why the denture rubs and what to do in such a situation.
In this publication you will find useful information about the T Crystal removable denture.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/zubnyie-na-prisoskah.html all the most important things about dentures with suction cups
Design features
Retaining type clasps consist of the following elements:
- The shoulder performs the function of holding the clasp on the tooth surface. This element ensures the spring properties of the structure and the transfer of pressure to the support unit. The shoulder should not have sharp protrusions to avoid injury to the gum tissue and cheek.
- The body is an element of the product placed on the surface of the tooth and connecting the shoulder and the process of the clasp.
- The process performs the function of fixing the fastening in the prosthetic structure. Placed under the plastic components of the hook.
In support-retaining clasps, in addition to the shoulder and body, there is an occlusal pad that prevents tooth displacement when pressure occurs on it, and an anchor part - an element connecting the clasp to the metal base.
Roach design
This design is also known as a split clasp, which is due to the peculiarity of its structure. The clasp has two T-shaped arms. In addition, the product has one occlusal pad. Most often used for clasp prosthetics.
Due to the reduced contact of the shoulder with the tooth surface, stabilization of the prosthesis is ensured. Practicing orthodontists recommend using the structure in combination with anchor mechanisms of increased rigidity.
Pros:
- good retention of supporting elements;
- aesthetics;
- minimal risk of developing caries due to the lack of impact on the enamel;
- can be used for short teeth, as well as for units that are inclined;
- Relatively simple adjustment of the retinal edge.
Minuses:
- inability to use with pronounced bone protrusions;
- lower efficiency compared to the anchor mechanism;
- limiting use for teeth located in the smile zone;
- risk of damage due to improper use.
Boundary line
The location of the boundary line is of great importance when choosing the type of clasps to be installed.
There are 5 options for its placement:
- The boundary line originates from the contact point of the row element on the side where the pathology is located and descends to the center of the proximal region of the adjacent tooth. In this case, the use of clasps with long holding arms is effective.
- The equator line is located in the center of the approximal surface and is directed towards the contact point of the adjacent tooth along the lingual or buccal side. The situation requires the use of support and retention mechanisms.
- The boundary line is placed diagonally on the surface of the supporting element - from the chewing area in the defect area to the neck of the element on the reverse side. Experts prefer to use Ney clasps for this pathology.
- The boundary line is located low, the equator passes in the area of the tooth neck . To fix the prosthetic structure, the use of support clasps is required.
- A high location of the equator occurs in cases of increased tooth abrasion. To restore their functionality and appearance, artificial crowns are required.
Retention clasp
It is a subsequent invention after the conventional wire clasp. The wire structure was a hook, which is installed on the tooth itself near its neck. Later this clasp was modernized and at the moment it has several varieties. Retaining types of clasps include: alveolar and dentoalveolar.
A classic support-retaining clasp consists of two arms, a process and an occlusion pad. One of the best representatives of this type of clasp is the Ney system. Since the clasp fracture mainly occurs near the base of the prosthesis, the upper shoulder part and the body itself were created thick and rigid. Since the upper part became rigid, it began to be positioned higher than the center line. As a result, such a placement of the clasp began to provide a supporting installation and at the same time prevent the lateral displacement of the prosthesis itself. In addition, the lowest thin part is located slightly lower than the boundary line. As a result, it serves as a supporting element and does not allow lateral displacement of the prosthesis. The lower part securely fixes the prosthesis itself. The upper part is located higher than the boundary line.
Ney system
The methods were introduced into orthodontics by Ney in the middle of the last century. These are classic support-retaining clamps. They contain a process, two shoulder elements and an occlusal type overlay.
To minimize fastener fracture, the areas located closer to the base were made thicker and stronger, while the distant sections gradually became thinner, and the product took on the shape of a horn.
Ney devices include the following options:
- Single-armed.
- Forked Roach.
- Acker with two shoulders.
- Ring single-arm.
- Combined.
General characteristics include practicality, wear resistance, and high aesthetics.
Roach
It is a rod type of fixer. Has a springy effect due to its long arms.
The advantages include:
- uniform pressure distribution,
- aesthetics.
- retainer of choice in case of short teeth,
- good holding characteristics.
Roach clasps
- Limited choice of material; this type is made exclusively from chromium or nickel. Therefore, it is not prescribed for patients with metal allergies.
- Not applicable for anatomical features of the jaw arch and teeth, when the gums of the upper jaw are exposed when smiling
- High load on the alveolar processes
Adams clasp
Versatile and durable fastener. Capable of fixing both to single chewing elements and to a full row of teeth. Adams are installed on the first premolars and molars.
Acker's clasp
One of the most effective and affordable fasteners. Installed on molars in the absence of one or more chewing elements and intact supports. Simple in design, it reliably keeps clasp dentures from moving.
The rigidity of the model’s frame can be considered both a plus and a relative minus, depending on the situation.
Various types of clasps
Jackson
Jackson clasp is a combined design of a flip-over type. It has the shape of a loop; the supporting part is considered to be the part that is located in the interdental spaces. Made from wire or casting.
Bonneville
A modification of the Acker clamp is the Bonville clasp. This type is based on two occlusal overlays. They are placed in an anatomical gap located on the chewing surface of the abutment tooth. Additionally, two shoulders are used.
The purpose of the design is to retain and provide stability for unilateral dentition defects. The peculiarity of the structure prevents food from entering the interdental spaces, reducing the risk of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Schwartz
A type of arrow-shaped fastening of a point configuration, it can be one- or two-link. This type is widely used in orthodontic practice due to its high fixation ability. The product is only available in wire.
Multi-link clasps
Consists of humeral processes connected to each other. This fixation is adjacent to each tooth and is shaped like a semi-oval. Manufactured in the following form:
- Wide stripes are a type of Cross-Shredder.
- Narrow stripes are a variation of Kennedy.
Multi-link clasps
They play the role of combining the parts of the denture and fixing them.
The choice of clasp system is individual in each case. The basis for preference is the volume of prosthetics and the initial state of the dentition.
Combined
Clasps of the third type combine elasticity and pronounced rigidity of the first two types. It is allowed to use the product for any part of the jaw row; the location of the product on the row is oral or vestibular. On the lingual side, clasps are placed for the lower jaw if the tooth acts as a supporting one. For the upper jaw, a structure of the second type is placed on the side of the cheek, and an anchor on the side of the palate.
Single shoulder ring
Products of type 5 have 3 options for use, on the upper or lower jaw and a clasp with one lining. This type of clasp connection is installed on molars.
In this case, it is allowed to tilt towards the oral side on the mandibular row. On the upper row, the design can be used if the tooth is tilted in the opposite (vestibular) direction.
The peculiarity of the clasp is that it consists of one or two occlusal pads, and an elongated arm that covers the surrounding dental unit. This attachment creates rigidity, strength and stability of the prosthesis.
Due to the large length of the ring clasp, the likelihood of its deformation increases. Therefore, the structure is strengthened by connecting the rod to the shoulder and the distal pad to the arch on the maxillary row.
The same sequence of connecting elements with the base on the mandibular row allows you to significantly increase the strength of the orthopedic product.
This type of construction has a complex structure, which is why food debris can accumulate under its surface. This can cause the development of caries or inflammatory diseases of the gum tissue.
Need to know! Practitioners initially place crowns on single molars, after which clasps are installed. This ensures proper hygienic care.
The video presents the principle of creating clasps.
Arrow-shaped
Most often, this option is used to strengthen orthodontic plates. For installation, the interdental space is used, located below the equator line of the tooth.
conclusions
Despite the fact that Ney clasps were developed in the middle of the last century, their use is still relevant today.
The simplicity of the design ensures high practicality, wear resistance, and, importantly, after installation a high degree of aesthetic value is noted.
In addition, to minimize the occurrence of breakage, areas located closer to the base are made thicker and more durable, and distant sections tend to gradually thin out, taking on the shape of the oral cavity.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: removable dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Aquasplint is an innovative method of treating and diagnosing TMJ abnormalities
Next article
How to effectively and quickly remove plaque?
Pros and cons of nylon
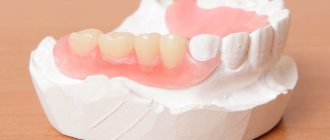
There are also nylon - one-piece dentures with clasps for attaching to abutment teeth
The main positive quality of nylon is the ability to create any shade, so it is easy for the dentist to choose the color of the base. Clasps for nylon dentures are poured simultaneously with the base, so they merge and do not stand out when you smile. The thin layer of plastic is not felt when chewing and talking.
But some patients are dissatisfied with nylon prostheses with clasps:
- atrophy of gum tissue and its subsidence are possible;
- dentures deteriorate faster and become deformed;
- sometimes there is pain when biting and chewing;
- you have to visit the dentist more often for correction;
- the likelihood of developing infections, stomatitis, and gingivitis increases.
More modern versions of Acry-free from an Israeli manufacturer are manufactured using software and scanning of the oral cavity. They are distinguished by high aesthetics, perfectly follow the contours of the gums, therefore they are invisible and practical. Suitable for full or partial dentures, replacement of dentures with metal clasps.
Requirements for the location of clasps
To successfully install clasps you must:
- So that the tooth itself is very stable. If the doctor identifies pathological mobility, he will attempt to block it in order to ultimately obtain a stable system. If the patient’s teeth have inflammatory processes at the apex of the tooth, then before installing the support they must be sealed.
- So that the teeth have the correct anatomical shape. Teeth with a rather low crown along the cone, with an incorrect ratio of the length of the root and the clinical crown itself, as well as teeth with an exposed neck, are not suitable for installing clasps. The listed symptoms are relative. They can be eliminated and you can safely proceed to installing clasps.
- So that the supporting tooth has the correct relationship with the antagonist. Relationships can be very close. In this case, even a very small pad, which is placed in the fissure itself, greatly disrupts the bite. In such a situation, a completely different tooth is chosen to install the supporting element. Another solution is to install a protective crown on the initially selected abutment tooth.
Other types of fasteners
Bonneville flip design
Bonneville is a variation of Acker, but the shoulders are directed in opposite directions. The retainer is designed for a continuous row of teeth. The design reliably fixes the prosthesis and creates high-quality support for it. The fastener also masks the gaps located between the teeth.
Other advantages of the Bonneville flip-over design:
- prevents food from getting stuck in areas considered difficult to reach;
- prevents the occurrence of certain pathologies of the oral cavity;
- prevents the development of an inflammatory process in the gums.
Swenson
Swenson - a clasp used on fangs
The product creates a reasonable load on the supporting teeth, which is especially important when they are mobile
Disadvantage: Some space between molar and premolar is required to secure the anterior shoulder of the product.
Double single arm design
There are two types of products:
- For the upper jaw - used from the side of the entire dentition and for two molars located next to each other.
- For the lower jaw - used in the presence of two converging molars.
Jackson
Jackson is a reversible clasp. This is a type of support-retaining device. The design has two branches and two bodies, is made in the form of a loop, and is also made in two ways - bent and cast.
Video: denture with and without clasp.
Adams
Adams is a universal clasp. The design fits tightly to the support, which ensures high-quality fixation of the prosthesis.
Dentoalveolar clasp
Dentoalveolar clasp - plastic is used for production. Used on front teeth in aesthetically significant areas of the oral cavity. For reliability, the plastic is reinforced with wire. This increases the strength of the structure, but negatively affects the quality of the material.
Flaws:
- the lip is slightly deformed, protruding forward, which negatively affects the appearance;
- cannot be used for supports with a low crown;
- records are not reused;
- cannot be used for the alveolar process.
The reliability of fixation of the prosthesis and the aesthetics of the smile depend on the clasp. For this reason, it is recommended to approach the choice of design with all responsibility.
How clasps are made
The hook with which the denture is fixed can be made only using existing theoretical knowledge and concepts of a particular specialty. To make the right clasp, you need to know what types of prostheses will be attached with its help. The manufacturing technology of any clasps has the same sequence of actions. Here it is very important only to correctly follow the stages of the entire process and select the right material.
The clasp is always bent with pliers. Any dental technician has them in his arsenal. You can also use round nose pliers and pliers to make a clasp, with which you can make only three bends.
To obtain the clasp arm itself, designed to cover the tooth, one end of the cast wire is bent. The next bend is made using round nose pliers. Using these tools, the body of the clasp is also formed.
Requirements for making a shoulder
- Firstly, the design of the shoulder itself must be made so that it can cover the tooth from the cervical or labial side. It should be located behind the convexity line or otherwise between the gum and the equator.
- The shoulder should not create pressure on the supporting tooth itself, that is, it should be passive.
- Regardless of whether the shoulder is flat or round, it should touch the entire surface of the tooth as much as possible. If the fit is carried out only at one point, this means that increased pressure will be created on the tooth and, over time, the enamel will be erased.
- After the main stages of shaping, the shoulder must be rounded and polished. This is necessary in order to prevent possible injury to the mucous membranes.
- The shoulder must be elastic. The best in this case are wire clasps, not so good - cast ones. However, cast ones more accurately replicate the features of the tooth relief.
Execution of the contact process
In order to fix the created clasp shape, you must use round nose pliers. It is best to bend to the ridge using pliers. Next, the resulting process is crushed on an anvil and notches are made on it so that it is more firmly attached to the base.
Only single-arm clasps are made using the described method. In the case of double-arm execution, the sequence of actions is the same, only two elements are involved in the manufacturing technology.
Manufacturing Basics
Clasps are made by technologists who focus on the prosthesis that will be installed on the patient. The manufacturing technology goes through the following sequence of actions:
- the clasp is essentially a hook that secures the prosthesis, so it is given the desired shape using specialized forceps, round nose pliers or pliers;
- first, a shoulder is formed that covers the dental crown;
- then the body itself is formed.
Dental technicians make the necessary bends to form clasps quickly and accurately, in just a few bends.
Features of the production of the shoulder and contact process
The desired shape of the clasp is formed using round nose pliers. The contact process and the shoulder are formed as separate elements using different tools.
The contact process is first formed with pliers and then flattened on an anvil. This procedure is necessary to apply special notches that promote tight bonding of the process to the base.
A number of rules apply to the manufacture of a shoulder:
- the shoulder must have a sufficient level of elasticity, which is more typical of wire elements than cast ones;
- the shoulder is designed in such a way that its parts lie between the gum and the equator;
- when fixed to an abutment tooth, the material should not cause discomfort;
- the element must adhere to the tooth surface at all points of contact in order to prevent excessive pressure and thinning of the enamel;
- After rounding the shoulder, it must be thoroughly polished to avoid possible trauma to the mucous systems.
The video shows the manufacturing process of Jackson clasps.
Side effects from clasps
Denture clasps can cause:
- To the abrasion of the tooth enamel itself due to constant load and micro-movements.
- This leads to a significant deterioration in the hygienic condition of the mouth due to the fact that the clasp is a separate structure and various food debris can accumulate under it. As a result, carious processes begin to develop very quickly. And this destroys the supporting teeth.
- Clasps can cause teeth to become very loose. This happens due to the movements of the prosthesis in a horizontal position. As a result, there is a functional overload of the teeth, which serve as support.
Sources:
- https://youstom.com/protezirovanie/klammer.html
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/klammerov-sistemyi-neya.html
- https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/sovremennyie-vidyi-klammerov.html
- https://CreateSmile.ru/klammer/
- https://dentaclass.ru/protezirovanie/klassifikaciya-klammerov.html
- https://my-ort.ru/novosti/klammery-neya/
- https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/klammeryi-sistemyi-neya.html