When starting treatment with an orthodontist, patients should be aware that they will then have to go through a retention stage to consolidate the result. Although this stage is much easier to tolerate than treatment (we’ll talk about that later), it is nevertheless worth remembering that at this time certain efforts are required from the patient.
Both after braces and after aligners, a period of consolidation of the result is needed
Who needs the retention stage and why?
To one degree or another, this stage is necessary for all patients, since it is necessary to secure the roots of the teeth in a new position.
Human bone tissue is constantly renewed: some cells die, others appear in their place. At a young age, this process occurs quickly, but slows down with age. In addition, the older the patient is at the time of treatment, the more years the roots of the teeth have become accustomed to the incorrect position.
If you start correcting your bite at the age of 16, it will turn out that by the start of treatment the roots of the teeth have been in the wrong position for only about 4 years (if we assume that the age of formation of a permanent bite is approximately 12 years). But many people turn to an orthodontist at the age of 30–35 and even later. Although there is no age limit, just imagine - you need to correct the position in which your teeth have been for more than 20 years!
Teeth can be in an incorrect position for 20 years or more, and the movement of individual teeth can be up to 1 cm
It is not surprising that after removing braces or stopping wearing aligners, teeth will immediately tend to return to their old place. To prevent this, a retention stage is needed.
At this time, the bone tissue around the roots is gradually renewed and compacted. The younger the person, the more active this process is.
How to consolidate the result?
The practice of orthodontists shows that relapses are most often caused by the early removal of retainers or their inconsistent wearing. If you follow all the recommendations of the orthodontist and attend routine examinations in a timely manner, the results of treatment will last for many years and your smile will remain irresistible.
When treating complex anomalies, the doctor may recommend additional observation by an orthopedist, since posture affects the bite and can “pull” it back to an incorrect position, but this is still not an ordinary case.
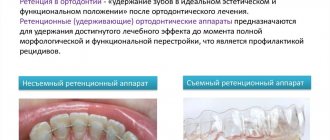
What orthodontic structures are used at this stage?
A permanent retainer is usually placed on the lower teeth. This is a thin metal wire made of the same alloy as the braces arch and about the same thickness. The retainer is installed from the reverse (lingual) side using filling material. The surface of the retainer and fastenings is smooth, does not interfere with cleaning and is not felt at all.
This is what a dental retainer looks like
But the retainer only holds the lower teeth in place. To stabilize the position of the upper ones, use a transparent mouth guard. It is made from impressions that are taken from the teeth immediately after treatment is completed. That is, the mouthguard repeats the ideal shape of the dentition that was obtained as a result. The mouth guard must be worn at night.
Signs, diagnosis and treatment
Manifestations of the disease depend on the location of the cyst. Most often, these are rounded formations that slowly increase in size, elastic and soft to the touch. They do not cause pain at first, rarely exceeding 1 cm in diameter. But in the absence of treatment, cysts begin to seriously interfere not only with eating, but also during conversation. The formation may disappear if, due to an accidental breakthrough, the contents come out. However, over time, the cyst forms again; if its size becomes very large, it acquires a characteristic bluish tint.
For diagnosis, methods such as visual inspection, palpation, and a number of hardware studies are used. Ultrasound, sialography to determine the problem with contrast, MRI and CT are more often performed. Additional examination methods may also be prescribed, for example, cystography of the bladder, probing of the salivary ducts, histology. If the diagnosis is questionable, a biopsy and puncture of samples are performed.
Conservative therapy does not bring any effect; when diagnosing a cyst of this type, surgical intervention is recommended. For this, local anesthesia is used, after which the formation is removed along with the affected gland and membrane to prevent relapses. If surgical intervention is refused, the formation often develops into phlegmon, and a tissue abscess develops.
The conservative method provides only temporary results. To do this, the membrane is punctured and the contents of the cyst are sucked out. But in all cases, the formation appears again, that is, this method of therapy is not recommended, as it is ineffective.
Surgery includes the following steps:
- inspection and surface preparation are carried out;
- local anesthesia methods are used for pain relief;
- the area with the cyst shrinks, which reduces blood flow and ensures stability of the tissue position;
- two oval-shaped incisions are made near the formation, after which the contents are husked;
- the affected lobes of the gland are removed, which helps to avoid complications or relapses in the future;
- the wound is sutured, thin sutures are applied, and self-absorbing sutures are often used.
The contents of the capsule are sent for additional research. This helps to eliminate serious risks, especially if the development of malignant processes is suspected. In case of serious intervention, plastic cystotomy is recommended. Typically, this situation occurs when removing a maxillary-hyoid formation.
How long does this stage last?
The standard period for adults is twice as long as the treatment lasted. That is, if the active stage of tooth movement has passed in 12 months, the retention stage lasts at least 2 years. But this is an average period. In each specific case, the doctor determines the duration of the consolidation stage individually.
It is important to note that there is no way to determine whether the teeth are securely anchored in their new location. And if you stop the retention stage too early, then there is a risk that in a month or two the teeth may move into the wrong position, and this will happen unnoticed. Most likely, not to its original state, but even a slight deviation can make the smile less ideal.
Therefore, it is much better to play it safe and wear stabilizing aligners a little longer, but maintain the result.
Currently, even the treatment process itself is quite simple and comfortable. The aligners cause minimal inconvenience and are very easy to get used to. And compared to the stage of active tooth movement, the retention period is even easier, because during the daytime there is no need to wear aligners at all.
Causes
The cyst appears as a tumor under the cheekbone, protruding from the outside. If left untreated, inflammatory processes appear, which can lead to the formation of an abscess or phlegmon. The pathology is a rare formation, usually diagnosed before the age of thirty. Place of development - on the lips, cheeks, palate, less often - in the sublingual ducts. Very rare is the pathology of the glands that develops in the parotid and mandibular areas.
The causes of this pathology are:
- injuries, wounds of the mucous membrane;
- mucus plugs that appear in the ducts;
- stomatitis and other inflammatory processes leading to obstruction;
- formation of salivary stones;
- pressure on the ducts;
- scar type narrowing.
Causes also include developmental defects, genetic predisposition, and damage to certain tissue areas. But more often the problem develops against the background of tissue injury and inflammatory processes. Wounds are formed by frequent biting of the cheek or tongue, due to the abuse of rough, spicy food, and hot dishes. In addition, such injuries can cause gland atrophy, so they cannot be ignored.
What should be done at the retention stage?
The point of this stage is to gradually strengthen the jaw tissue along with the new position of the roots of the teeth. It is impossible to speed up this process. But you can help your teeth during this period:
- Eat more solid foods - raw vegetables and fruits. This is a kind of “charging” that strengthens the gums and roots of the teeth. When teeth are stressed by chewing solid food, they perform their function to the maximum, which means that the roots receive sufficient blood supply in return. This helps maintain healthy teeth and gums.
Hard raw vegetables and fruits - as an “exercise” for teeth
- Eat foods that contain enough calcium and phosphorus. These are the main building materials for bone tissue. They are found in cottage cheese, cheese, turkey, fish, nuts, and sesame. The decision about whether you need to take additional mineral supplements in the form of tablets is made after consultation with your doctor.
- Do not forget about visiting an orthodontist once every 6 months, at least in the first year and a half after the end of treatment. It is much easier for the doctor to notice the slightest deviations in the position of the teeth from the result that was achieved. If necessary, the doctor will suggest correction methods or recommend extending the retention period.
Other articles:
- Can veneers correct crooked teeth?
- Lingual braces 2d
- What can aligners do?
Retention period
Retention period
- This is the final stage of orthodontic treatment, at which the results achieved during the therapy process are consolidated. With the help of special devices, retainers of various types, teeth are held in an anatomically correct position. The duration of the stage is about two years. This time is enough to avoid a relapse in the future - repeated curvature of the bite.
The retention part of the treatment is mandatory
, since after correction, the teeth remain mobile for a long time. Wearing retainers helps not only to completely eliminate functional and morphological disorders of the maxillofacial region, but also to normalize chewing function, “teach” the tongue to be in the correct position, and remove facial wrinkles.
Retention treatment can be carried out using removable
, as well as
non-removable installations
. The type of installation is selected by the doctor, depending on the initial problem. These can be vestibular arches, plates with clasps and inclined planes, as well as plates with an arch for the upper or lower jaw.
Fixed retainer
Removable retainer
Vestibular arches
- These are structures consisting of a base and holding elements. They are installed on the front and side teeth, ensuring they are securely held in the anatomically correct position.
the distal bite has been corrected
To consolidate the results, orthodontists use plates with an arch, clasps and an inclined plane on the upper jaw, and plates with retaining devices and a vestibular arch on the lower jaw.
Correction of mesial occlusion is secured using a maxillary plate with a dental arch held on the front teeth.
The absence of a retainer is unacceptable! Many patients mistakenly assume that they can do without retainers, especially if the correction took a long time and the result is fully consistent with expectations. In fact, the stage of treatment with retainers cannot be excluded - the bite may return to the pathological position.
Consolidating the results of open bite
is carried out using structural elements that isolate the tongue from the teeth and prevent its pressure. The units are removable devices made of plastic or wire bent in the desired direction. Wire models are more preferable, since they almost do not reduce the physiological volume of the oral cavity and are easy to adjust.
To stabilize treatment results when teeth are rotated along the axis
, non-removable structures are used that are fixed on the back surface of the teeth.
The retention stage of treatment begins immediately after removal of the main orthodontic appliance. It is believed that the patient should put on a restraint device within 24 hours to avoid relapse.
Just like braces and plates, removable retention devices require special care. The doctor will tell you what devices and medications you need to use for daily cleansing.
Retainers, like other orthodontic devices, require specialist supervision. At each scheduled appointment, the orthodontist checks the fixation. If the element has come off, you need to go to the clinic as soon as possible. In general, during the control period, it is recommended to visit the doctor two to three times a year.
If, after bite correction, the patient experiences periodontal disease, standard appliances may not be suitable. In this case, a cast splinting retainer is used. It is installed directly on the crowns and covers half of their height.
Expert opinions
Most experts believe that retention is a mandatory phase of treatment, and its duration should be determined depending on the clinical picture.
At the same time, recent studies have led to the conclusion that teeth after certain types of correction are generally characterized by instability due to physiological reasons.
For example, it was found that a recurrence of crowding of lower resources cannot be dealt with by performing a one-time retention. This is due to the fact that with age, the intercanine distance decreases, and as a result, its forced increase in order to prevent crowding is unstable.
In this regard, experts express the opinion that the only solution to the problem in this and similar cases is lifelong retention, that is, wearing the device until the end of your days.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Estimated timing
The time it takes to consolidate the result depends on a number of factors:
- Type and severity of the anomaly. In particular, treatment of severe crossbite, deep bite, open bite and distal bite should result in long-term retention.
- Structures of rebuilt bone tissue. For example, correction of the temporomandibular joint requires longer retention than correction of dental misalignment.
- The speed of movement of teeth or dentition during treatment. It is believed that the slower it is, the lower the risk of relapse.
- Achieving conditions for stability of teeth and rows. For example, if during the correction of crossbite it was possible to ensure a stable illusion (multiple tubercular-fissure contact), then relapse is unlikely.
- Depending on the patient's age.
The standard ratio of the duration of consolidation of the result to the treatment time is considered to be 2:1. That is, the retention period should be 2 times longer than the treatment time. If a small correction force was used and the movement speed was low, a 1:1 ratio can be used.
There are also supporters of the point of view that when moving slowly and ensuring stable occlusion, retention is not required at all.
In some cases, if it is impossible to achieve stable stabilization, it is necessary to resort to lifelong wearing of devices.
Indications for orthognathic surgery and possible complications.
In this publication we will tell you what you should not eat with braces on your teeth.
Here https://orto-info.ru/ortodonticheskoe-lechenie/podgotovitelnyiy-period/konsultatsiya.html find out how much an orthodontist consultation costs.
The importance of consolidating the result
From all of the above, it follows that for a successful, predictable result of correction, the active treatment stage must be followed by a retention period.
The importance of consolidating the achieved results during orthodontic treatment is obvious. In the absence of retention, the likelihood of relapse is very high. According to some studies, it reaches 60%. There was no relapse in only 20% of the analyzed cases.
Even a partial return of teeth to their previous position negates the time and money spent on treatment. To avoid this, the doctor must properly plan and carry out the final phase of treatment, and the patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
The latter is especially important if a removable device is used, which can be removed by the patient himself.
Strict adherence to the wearing regimen is the main condition for the successful stabilization of teeth after treatment.
How is laparoscopy performed on the right and left ovaries?
After a complete preliminary examination and receipt of the results of clinical tests, provided there are no contraindications, surgery is prescribed. Its duration is short, the trauma is minimal, however, like any surgical intervention, it requires attention and accuracy on the part of the surgeon, since the integrity of healthy ovarian tissue depends on his professionalism and correct actions. Therefore, you should approach the choice of a specialist who will perform laparoscopy with all responsibility.
The most important and interesting news about infertility treatment and IVF is now in our Telegram channel @probirka_forum Join us!
cyst
Causes of retention cysts of the left and right ovary
The causes of this disease can be of various types. One of them is dysfunction of the endocrine system of the woman’s body, hormonal imbalance. Female sex hormones, called estrogens, thicken the secretion secreted into the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the uterus itself. Sometimes clots of this mucus can disrupt their own flow from the gland, clogging its duct. The fluid (secret) that accumulates in the cavity of the gland leads to an increase in its volume and the formation of a cyst. Numerous terminations of pregnancy, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, early puberty, and other endocrine diseases can also be the causes of cystic ovarian formations.
Symptoms of ovarian retention cysts
There are common symptoms with existing retention cysts in the right and left ovaries. These are changes in hormonal levels, reproductive dysfunction, disruption of the menstrual cycle, pain in the lower abdomen and an increase in its volume. However, there are some differences in the symptoms of retention cysts in the right or left ovary.
Retention formation of the left ovary, symptoms
With an existing retention cyst of the left ovary, palpation of the left iliac region can determine the presence of a tumor-like formation, the rupture of which causes tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, otherwise called a clinic of acute abdomen and causing acute pain in the left half of the abdomen.
Retention formation of the right ovary, symptoms
The retention mass of the right ovary is also a space-occupying mass palpated on the right in the iliac region. The patient may experience aching pain in the lower right abdomen. This formation of the right ovary, greatly enlarged in size, often leads to indigestion and problems of the gastrointestinal tract.