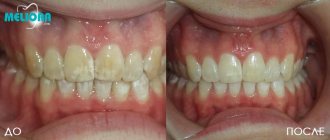
Modern dentistry is rich in drugs that effectively strengthen tooth enamel. Especially convenient are those medicinal products that you can buy and use yourself. It’s worth learning more about one of them, the Tooth Mousse remineralizing paste. Is this really a unique remedy, or just another advertising gimmick and a waste of money?
Tus Mousse was developed at the University of The School of Dental Science in Melbourne (Australia). This mousse is manufactured by the licensed trademark * RECALDENT.
Why are remineralizing agents needed?
If a person’s teeth become hypersensitive, it means that he had to face the problem of demineralization, i.e. loss of essential microelements by teeth. Dentin owes its strength primarily to three essential elements: calcium, phosphorus and fluoride. Normally, tooth enamel consists of 98% microelements and is the hardest tissue of the human body. However, due to various problems in the body (diseases, pregnancy, poor oral hygiene, whitening procedures, etc.), teeth often lose their former strength and begin to react to sweets, hot or cold.
The arsenal of remineralizing (restoring mineral composition) preparations includes many mousses, pastes and gels. One of the representatives of this series of products is Tooth Mousse gel, which dentists often recommend as a super product that can restore teeth to their former strength.
Why are dental remineralizing agents needed?
When increased sensitivity of the enamel appears, teeth begin to react sharply to temperature, acid and mechanical factors. In such cases, a diagnosis of hyperesthesia is usually made. But this phenomenon is quite common, usually associated with demineralization of the enamel layer, that is, a lack of necessary microelements. The protective layer of teeth weakens and becomes too susceptible to external influences; over time, it may darken and begin to crumble.
The drug is used for tooth sensitivity
The reason may be hormonal changes during pregnancy, some kind of systemic disease, insufficient oral hygiene or aggressive influence, for example, this is often observed after professional whitening and bite correction with braces. Remineralizing agents are designed to replenish the mineral composition of the enamel, strengthen it and provide reliable protection against thinning and destruction. One such product is Tooth Mousse dental gel.
Packaging and flavors
One tube contains 40 g of the drug. Pharmacy kits can consist of several versions of the gel with different flavors: contain 2 tubes of each flavor, have a set of one flavor or each flavor in one copy.
This mousse can have five varieties of flavors in the form of:
- Fruity (T);
- Melons (M);
- Strawberries (S);
- Mint (I);
- Vanilla (V).
Flavor variations are indicated by letters of the English alphabet and are indicated on the tubes after the batch number.
Composition and properties when used
Tooth Mousse is a water-based cream containing phosphates and calcium. RECALDEN in Tus Mousse is an amorphous or bioavailable calcium phosphate, which is perfectly absorbed by tooth enamel.
The action of the gel is based on its ability to bind dental plaque (biofilm) with CPP-ACP molecules and settle on dental tissues, promoting the most complete absorption of the calcium-phosphate complex.
Tooth Mousse paste has the following complex effect on dental tissue:
- neutralizes excess acidity in the mouth, blocking the work of acid-producing microorganisms in dental plaque;
- provides protection to teeth from the destructive effects of internal and external factors.
To maximize the effect of remineralization, it is important to combine local treatment by applying a paste with the introduction into the diet of foods containing components necessary for teeth (meat and dairy products, fish, green vegetables, legumes, nuts, etc.)
How does the product work?
Tuff Mousse is water-based and does not contain sugar. Mousse contains a patented complex Recaldent or CPP-ACP - casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate. Simply put, the main components that the Tuf Mousse remineralizing paste is rich in are minerals - calcium and phosphates, which act as the main building elements of the tooth. Molecules of calcium and phosphate, entering the oral cavity, settle on hard and soft tissues, which is how remineralization occurs.
Flavoring additives, which are also included in Tuss Mousse, stimulate salivation. And saliva, in turn, enhances the effectiveness of the CPP-ACP molecules, and also removes food debris and bacteria from the oral cavity.
According to research results, the longer the drug molecules and saliva are in the oral cavity, the more noticeable, faster and more effective the treatment result.
Indications for use
Tooth Mousse remineralizing gel is used in many European countries in situations:
- after topical use of fluoride-containing drugs;
- hypersensitivity due to tooth whitening procedures (whitening, teeth cleaning) - before and after procedures;
- for local treatment of diseases (xerostomia, erosion, Sjögren's syndrome, hypoplasia, fluorosis);
- after therapeutic dental procedures (curettage, ultrasound);
- to overcome dry mouth with problems with salivation;
- with damaged tooth enamel with symptoms of permanent plaque and white spots;
- pain due to mechanical or thermal effects on the teeth (when brushing teeth, hot or cold food);
- existing demineralized areas on the enamel from the initial stage of caries in the form of the appearance of white spots;
- if necessary, return teeth to their normal color and structure;
- for the prevention of caries due to demineralization;
- during orthodontic manipulations in the oral cavity (after wearing braces or removable dentures);
- with a repulsive odor from the mouth or an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
It is especially important to carry out preventive remineralization of teeth at times of the body’s greatest need for minerals (menopause, pregnancy, adolescence).
Indications and contraindications
Tooth Mousse, a product for strengthening enamel, is indicated both for preventive purposes and as maintenance therapy in the treatment of various pathological conditions. Among the indications for its use, dental experts highlight the following cases:
- hyperesthesia, including after professional whitening. As a preventive measure, the drug is recommended to be used not only after the procedure, but also before it,
- after using topical fluoride-containing preparations,
- as part of the treatment of dental diseases such as xerostomia, erosive lesions, fluorosis, hypoplasia,
- after carrying out certain therapeutic measures, including after ultrasonic cleaning and gum curettage,
- disorders associated with salivation, including dryness of the mucous membranes,
- the appearance of abundant plaque and caries at the white spot stage,
- presence of demineralized areas,
- desire to restore the natural whiteness and shine of enamel,
- after orthodontic and orthopedic treatment – after removing braces or installing a removable prosthetic device,
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth,
- for the prevention of caries and enamel destruction.
The drug may be needed after braces are removed.
Prevention with the use of such remineralizing compositions is especially important during periods when the teeth need additional replenishment with useful minerals and trace elements. These periods include pregnancy, menopause and adolescence.
“I once bought Tus Mus paste, my dental hygienist recommended it to me. This was after pregnancy, the enamel darkened a little and became sensitive. Then I noticed brownish spots on some of my teeth. I was prescribed ultrasonic cleaning and this product was recommended. I simply applied it with my finger, morning and evening. It was a pleasant surprise when my teeth actually became lighter and stopped reacting to hot tea. I didn’t expect much from this pasta, but it pleasantly pleased me.”
Marina, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Milk proteins are used in the production of the product. Therefore, the drug is contraindicated if you are allergic to dairy products. It is also not recommended for use in cases of hypersensitivity to benzoate preservatives and pathological conditions when fluoridation is contraindicated - diseases of the liver, kidneys and pancreas.
Benefits of using gel
Compared to other professional products, Tooth Mousse has several advantages:
- stabilizes the pH level in the mouth;
- flavoring additives allow you to choose the most acceptable aroma and taste for every adult or child;
- the drug has no age limit and is used by adults, children and the elderly;
- the gel is approved for use by women during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- perfectly remineralizes porous tooth enamel;
- does not cause any discomfort or pain when used;
- safe if swallowed;
- not only eliminates existing dental problems, but acts proactively, preventing carious and erosive lesions of dental tissue;
- allows the parallel use of fluoride-containing drugs, since it does not contain fluorides.
Tooth Mousse remineralizing gel does not replace mandatory daily oral hygiene with traditional toothpaste and brush.
How to use Tooth Mousse Gel correctly
According to the instructions, Tooth Mousse cream is used every time after meals (but at least 3 times). Be sure to use the gel in the morning and before bed.
There are 2 options for using this product: with and without an individual mouthguard.
When applying Tooth Mousse cream using a mouth guard, you must:
- The oral cavity is treated after eating in the usual way: teeth are brushed and then rinsed. Additionally, you can use dental floss.
- The mouth guard for individual use is washed with water (running).
- A little mousse is squeezed into the mouthguard to fill its entire interior with the drug.
- The mouthguard is placed on one (right or left) or both rows of teeth, and after 2-3 minutes it is removed. Keeping the gel longer will allow it to remain in contact with the dental tissue longer and restore it better.
- After removing the tray, a certain amount of product remains on the gums, which is distributed onto the teeth. After this, the mouth is kept slightly open for several minutes. You should not spit or swallow saliva.
- After the procedure, saliva and remaining gel are spat out, but without rinsing the mouth.
- For half an hour after using the mousse, no impact on the oral cavity is allowed (chewing gum, drinking, eating).
- After the procedure is completed, the mouth guard is washed and dried again.
It is also possible to carry out the teeth remineralization procedure without a tray.
The technique for direct application of Tooth Mousse on teeth is as follows;
- The teeth are cleaned and blotted with a clean napkin to remove moisture.
- A small ball of paste is squeezed out of the tube, which is applied with a dry gloved finger or a cotton swab to the upper row of teeth, and then to the lower row. In hard-to-reach places, the gel is applied with a brush.
- The gel is distributed over the entire tooth surface and gums.
- With your mouth slightly open, the product is kept for about 2-3 minutes. The longer the Tus Mousse and saliva are in the mouth, the better the result of the treatment.
- Then the remaining gel with saliva is spat out. There is no need to rinse your mouth, as the remaining gel will quickly dissolve.
- For another half hour after such a procedure, it is forbidden to eat, drink, brush your teeth or rinse your teeth.
Assessing the effectiveness of remineralization –
The effectiveness of the remineralization course is easy to assess if your teeth have caries in the white spot stage. But it is very important to distinguish white spots during initial caries from white spots of non-carious origin, which can occur with enamel hypoplasia or fluorosis. To check this, you need to apply a dye (1-2% solution of methylene blue), which is sold at any pharmacy, to the surface of the stains. If the white spots are areas of demineralization, they will temporarily turn blue. With hypoplasia and fluorosis, staining of the spots does not occur, because The enamel in these diseases is very dense and is not able to absorb dye.
Therefore, the disappearance of white spots is an excellent indicator of the effectiveness of remineralization. However, it is not always possible to achieve this, and in some cases we can only count on reducing the size of spots and reducing their visibility, which also allows us to talk about the positive effect of the remineralization course. Minimal effectiveness will also be indicated by the fact that there will simply be a stabilization of the number and size of white spots (this is not a very good result, but still a result). If the patient does not have white spots, a criterion for the effectiveness of remineralization can be a decrease in the frequency of caries development (relative to previous periods).
Expected effectiveness of white spot remineralization:
The effectiveness of caries therapy in the spot stage depends on two criteria: 1) the clinical size of the white spot, 2) the level of its permeability to the dye. In turn, the level of permeability for the dye clearly correlates with the degree of destruction of the hydroxyapatite crystal lattice, i.e. the higher the destruction, the higher the permeability for the dye.
If the size of the spots is up to 3.0-5.0 mm2 inclusive, and the spots demonstrate a low degree of permeability to the dye (up to 3 points inclusive on a 10-point printed scale of blue color) - we can most likely hope for their complete disappearance after a course of remineralizing therapy + normalization of hygiene. By the way, according to some authors, small spots in 50% of cases can disappear without a trace – just after normalization of oral hygiene (in this case, only the remineralizing potential of saliva will be involved).
But the situation is completely different if the white spots show a high degree of permeability to the dye, and also if the white spots have dimensions greater than 5.0 to 30.0 mm2. In these cases, you can only count on a reduction in the size of the spots (foci of demineralization), as well as a decrease in their visibility - this is due to a decrease in the brightness of the spot and restoration of the shine of the enamel. But if left untreated, white spots are highly likely to simply turn into carious defects over time.
To determine the permeability of white spots for dye, the Okushko V.R. test is used. (synonyms: enamel resistance test or TER test). Sensitivity to the dye is determined by a 1% solution of methylene blue. The interpretation of the results is carried out based on the intensity of coloring of the white spots, for which a 10-point blue scale is used. Coloring of only 1-3 points indicates a high probability of disappearance of white spots after a course of remineralization. A color score of 6 or more indicates that you should only count on reducing the size and improving the appearance of the spots.
Precautionary measures
When using Tus Mousse, you need to know the following:
- It is important to close the tube tightly after each use. Before this, you need to remove any inclusions from the inside of the neck (remains of paste, drops of moisture, cotton fibers).
- If the drug gets into the eyes, it is necessary to immediately rinse them with plenty of water. If necessary, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
- If symptoms of drug intolerance or angioedema appear, the drug should be discontinued immediately and medical attention should be sought.
- If the drug gets on clothing, it should be washed off immediately with water.
Reviews
On the Internet you can find many reviews about the use of this tool.
Veronica, 32 years old
I bought tooth mousse gel for my youngest son. Already at the age of 2 he started having problems with his teeth, although I don’t give sweets to children. I smeared his teeth after brushing, although the baby was unable to withstand the gel according to the instructions. However, my son’s teeth have really gotten better. The disadvantage of this product is that it is too expensive.
Olga, 28 years old
I bought tooth mousse paste on the advice of my dentist. After pregnancy, dark spots appeared on the enamel, which even ultrasound did not remove. I was skeptical about the prescription of the cream, but I bought it. I smeared my teeth with my finger morning and evening. It’s surprising that the teeth actually turned white and stopped reacting to hot and cold.
Oleg, 39 years old
I had incredibly sensitive teeth. I was amazed that already on the second day of use the sensitivity decreased, and on the third it stopped. The effect of the gel also pleased my wife. The teeth became harder and stopped crumbling. The downside is that I drool heavily when using it.
Natalya, 22 years old
I didn't like the vaunted Tooth Mousse at all. I tried to use it during pregnancy, but gave up: every time I burned my tongue and lips from the inside. Then for 3 days I felt like my mouth was scalded with boiling water.
Tooth Mousse gel is a professional dental restoration product with a minimum of contraindications, which is easy to use on your own. Its huge advantage is the ability of the gel to quickly eliminate tooth sensitivity and fight caries in the early stages.
On the Internet, Tooth Mousse gel has the maximum number of positive reviews from patients whom it really helped. It is important that this product can be used by people, regardless of their age. Take care of your teeth!
Sources used:
- https://www.dentsplysirona.com
- Oral hygiene / Yu.A. Fedorov. — M.: Medicine
- General hygiene/Bolshakov A.M., Novikova I.M.//Textbook for medical universities. M.: Medicine, 2002.
Chemical basis of tooth remineralization:
In the oral cavity, the processes of demineralization or remineralization constantly replace each other. The critical pH at which the demineralization process begins is pH 5.5, but with a sufficient amount of fluoride ions in the oral fluid, demineralization begins at a much more acidic pH of 4.5. To begin the remineralization process, a pH of 6.2 and above is required, but more or less intensive remineralization will occur only when the pH of the oral fluid is neutral (from 7.0 and above).
Tooth enamel consists of hydroxyapatite crystals. Its formula, as well as the dissociation of this substance into ions, is as follows: Ca10(PO4)6OH2 ↔ 10Ca2+ + 6(PO4)3- + 2OH−.
How does enamel demineralization occur?
During the fermentation of carbohydrates, cariogenic bacteria produce organic acids (lactic, acetic and propionic), which serve as sources of hydrogen protons (H+). It is hydrogen protons that play a key role in the processes of enamel demineralization. As a result of ion exchange, they penetrate the enamel, but at the very beginning they only cause decalcification. The latter occurs without destruction of the enamel structure, and it consists in changing the ratio of calcium and phosphorus in hydroxyapatite crystals (calcium ↓, phosphorus ↑).
At a pH below 5.5, hydrogen protons also begin to react with the phosphate group in hydroxyapatite crystals, which leads to the conversion of “phosphate tones” into “hydrogen phosphate ions”, i.e. (PO4)3- → (HPO4)2-. As a result of this process, the balance of bonds in the crystals is disrupted, and hydroxyapatite crystals are destroyed. Also, hydrogen protons (H+) neutralize the “hydroxide ions” (OH−) formed as a result of the breakdown of hydroxyapatite crystals, resulting in the formation of water (H2O).
Ca10(PO4)6OH2 + 4H+ ↔ 10Ca2+ + 6(HPO4)2- + 2H2O.
As a result of this process, there is a sharp drop in the concentration of hydroxide ions, which actually play a very important role in remineralization processes.
How does enamel remineralization occur?
The formula of hydroxyapatite is Ca10(PO4)6OH2, and thus to create it we need the following ions - 10Ca2+ + 6(PO4)3- + 2OH−. We have highlighted the hydroxide ions (OH−) in the composition of hydroxyapatite - in blue, because their concentration during remineralization processes will play a key role. But the concentrations of Ca2+ and PO43- (calcium and phosphates) in the oral fluid change little, and therefore natural fluctuations in their concentrations will not have a significant effect on the remineralization process.
The lack of hydroxide ions (OH−) leads to the fact that, against the background of a lower pH, remineralization is impossible even at the highest concentrations of Ca2+ and PO43- ions in saliva. But there is an interesting loophole here too. The fact is that fluoride ions (F−) are capable of providing remineralization of enamel with Ca2+ and PO43- ions contained in saliva - even at a lower pH of 5.5-4.5.
This occurs due to the fact that F− ions can partially replace OH−. And in this case, instead of the formation of ordinary hydroxyapatite, fluorohydroxyapatite and fluorapatite are formed (these are types of apatite crystals in which hydroxide ions will be completely or partially replaced by fluorine ions). Moreover, the resulting fluorapatite is much better than ordinary hydroxyapatite, because it is much more resistant to organic acids.
Hydroxyapatite, fluorohydroxyapatite or fluorapatite: Ca10(PO4)6OH2 ⇔ Ca10(PO4)6(OH F) or Ca10(PO4)6F2
Important: thus, remineralization occurs much faster - precisely in the presence of fluorides. Fluorine acts as a catalyst for the growth of hydroxyapatite crystals in areas of enamel demineralization, ensuring its remineralization even at a more acidic pH of 5.5-4.5 (i.e., when normally, on the contrary, demineralization should already occur). This shows why varnishes and gels with a high concentration of fluoride alone can be effective for remineralization, even if the preparation does not contain sources of Ca2+ and PO43-. After all, our saliva always contains its own calcium and phosphate ions.
In this case, fluoride interacts with calcium dissolved in saliva, forming a layer on the enamel surface consisting of calcium fluoride globules (which in turn are surrounded by a hydration shell of phosphates). During subsequent acid attacks, calcium fluoride slowly dissolves, releasing active calcium and fluoride ions, which are involved in the remineralization of enamel.
Conclusions: therefore, if we are talking about initially poorly mineralized temporary and milk teeth in children and adolescents, as well as in the presence of initial caries in the white spot stage, you need to use either a remineralization drug with calcium and phosphates, or even better, a combined drug with calcium, phosphates + fluorides. In addition, combined preparations (due to the fluoride content) will have a more pronounced caries-preventive effect.
If your main goal is to protect teeth from caries, then it is optimal to carry out remineralization with varnishes and gels with a high fluoride content (but it will be even better if the varnish, in addition to fluoride, contains CPP-ACP or tricalcium phosphate). Teeth treatment with fluoride varnish is carried out once every 3-6 months - the frequency is set depending on the quality of the patient’s oral hygiene. When using varnishes with 5% sodium fluoride, the risk of developing caries is reduced by approximately 63%.