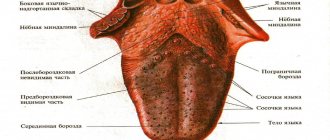
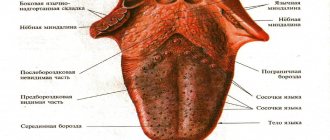
Mechanism of occurrence
Growths on the tongue are formed from epithelium, fat cells, muscle fibers, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels.
The tumor can arise against the background of embryogenesis disorders - the rudiments of foreign tissue structures get onto the tongue. Under favorable conditions, HPV begins to actively multiply and penetrates the basal cells of the epithelium. The DNA of the virus invades the DNA of cells, changes their functions, causes them to actively and chaotically divide and multiply.
Doctor about condylomas in the mouth:
Classification
Depending on the location, cancer is distinguished:
- Bodies. These include tumors of the tip, dorsum and lateral surface (most often the middle of the lateral surface). This localization occurs in 70% of cases.
- Root (accounts for 20% of all cases).
- Lower surface (sublingual area).
By growth pattern:
- Exophytic form (this includes papillary and ulcerative forms of tumors growing outward).
- Endophytic (growing inside the tissue of the tongue - infiltrative and ulcerative).
Papillary form a is a dense papillary growth of a mushroom shape. There may also be raised plaque-like growths that have clear boundaries.
Ulcerative (occurs in 50% of cases). Characterized by a superficial ulcer surrounded by a ridge. The ulcer is constantly increasing in size. At first, the ulcer does not bother the patient, but as it grows, pain and bleeding appear. The ulcer can become infected and inflamed, making diagnosis difficult.
Infiltrative form . The tumor grows into the thickness of the tissues, and they become denser. With diffuse growth, the compaction spreads to the entire tongue, which impairs its mobility.
The infiltrative-ulcerative form is characterized by thickening of the tongue with the presence of deep ulcers.
According to histological composition:
- Adenocarcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
Classification according to the TNM system.
- Tis "cancer in place."
- T1 Tumor no more than 1 cm. Not accompanied by complaints, discovered by chance during examination.
- T2 ≤2 cm. There are ulcers and areas of compaction.
- T3 >4 cm. The tumor is equal in size to half the tongue. Metastases to the occipital lymph nodes, postauricular.
- T4 Locally advanced cancer that occupies the entire tongue and invades the tissues of the mouth and face. Metastases to internal organs (brain, liver, heart) and bones.
Symbol N - the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes:
- N0 - No lymph node involvement.
- N1 One node on the side of the tumor is affected.
- N2 Metastasis: one metastasis no more than 6 cm, several up to 6 cm on one side or both sides up to 6 cm.
- N3 Metastases larger than 6 cm.
With T1 tumors, lymph nodes are affected in 40% of cases, with T4 stage in 85%. A reliable factor for metastasis is the depth of invasion - 4 mm is considered a critical value. Most often, metastases are found in the submental, submandibular and cervical nodes (upper third).
Histopathological differentiation:
- G1 High degree.
- G2 Medium.
- G3 Low.
Reasons for appearance
Growths on the tongue appear against the background of dental diseases, dysfunction of internal organs, or due to non-compliance with hygiene rules. One of the main causes is the human papillomavirus (HPV). When it is activated, papillomas are formed. The risk group includes people with autoimmune pathologies and immunodeficiency conditions, people who are promiscuous.
Provoking factors:
- taking certain corticosteroids;
- stomatitis, glossitis, periodontitis, systematic injuries of the tongue and oral mucosa;
- indulging in hot or spicy foods leads to burns on the mucous membrane, which are poorly treated in a constantly humid environment;
- candidiasis, herpes;
- intestinal infections, helminthic infestations, metabolic disorders;
- frequent stress;
- smoking, alcohol abuse, working in hazardous industries;
- avitaminosis;
- changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, menopause, and puberty;
- In children, papillomas appear due to the habit of putting dirty hands and objects into their mouths;
- contact with a sick person or carrier of infection.
In older people, growths on the tongue occur due to age-related changes in the body and improper care of dentures.
Congenital growths in children appear due to poor heredity, intrauterine development disorders, viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy, and birth injuries.
Doctors about HPV:
Methods of infection
The human papillomavirus is transmitted from person to person in different ways.
How people become infected with HPV:
- during sexual intercourse;
- in public places by domestic means - toilets, gyms, baths;
- self-infection – when papilloma is injured;
- intrauterine infection from mother to child.
For a long time, the infection does not manifest itself in any way; the virus begins to actively multiply against the background of weakened immunity.
Important! Barrier contraceptives do not protect 100% from human papillomavirus infection.
Prevention
It is not difficult to take measures to protect against this pathology. The likelihood of HPV infection should be minimized:
- avoid casual and unprotected sexual contacts, use contraception;
- use personal hygiene items;
- Get HPV vaccine
When infection has already occurred, it is necessary to prevent the activation of the viral agent due to weakened immunity:
- consume vitamin complexes;
- get rid of bad habits;
- avoid stressful situations and overwork.
You should not neglect HPV infection and leave its manifestations without proper treatment from a qualified doctor.
Papilloma on the tongue is a dangerous formation that requires a mandatory visit to a highly qualified doctor. The patient’s main task will be to timely detect the growth and seek help from a specialist.
Kinds
There are 2 types of growths :
- Reactive - appear due to constant mechanical damage to the tongue, burns.
- Neoplastic – a consequence of disorders in the body. Most often, many such neoplasms appear in various parts of the oral cavity.
By shape
Growths on the tongue can have different shapes :
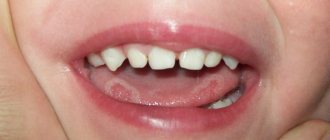
- Most often, neoplasms have clear boundaries and are colored white, pink, or red.
- The pointed formations are pink, have a stalk, cause significant discomfort, are often injured, grow quickly and occupy large areas of the mucosa.
- Flat growths have a rounded shape and resemble plaques in appearance. They grow slowly, are damaged less often, and practically do not bother.
- With stomatitis, reactions to medications, microtraumas, the growths look like pimples and blisters.
By location on the tongue
Growths can appear on any part of the tongue mucosa. The main places of localization are the tip, lateral surfaces, and root. Most often they occur on the side; less often, tumors form on the hard palate and lower surface.
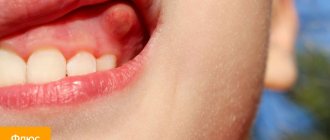
What does papilloma look like on the tongue?
Sometimes people mistakenly mistake the features of the anatomical structure of their tongue for new growths. For this reason, only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Papillomas most often have the following appearance:
- A small tumor, the maximum size of which can reach 1.5-2 cm. However, in most cases, papillomas appear on the tongue, the size of which does not exceed 0.5 cm.
- The surface virtually always has a bumpy structure.
- Sometimes papilloma is a growth that looks similar to a small papilla.
- The color almost always matches the color of the surrounding mucous membrane, but the largest papillomas may have a lighter shade.
Photo
Below is a photo of papillomas, allowing you to understand what they look like:
Papillomas can appear in many parts of the body. Look at the photo of papilloma on the neck.
What could it be
The most common types of growths on the tongue are lipomas, fibroids, papillomas, hemangiomas, and polyps.
| Type of growth | What does it look like |
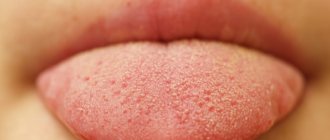
| Papillomas | Flat - noticeably rise above the epithelium, wide, light in color. They are formed one at a time. Pointed (condylomas) are light-colored neoplasms in the form of papillae with a sharp end. They often merge into groups, grow, and increase in size. Externally similar to the comb or inflorescences of cauliflower. Thread-like - thin, protruding noticeably above the surface of the epithelium, colored bright red. Form groups. |
| Polyps | The neoplasm is flat or convex in shape in the form of a lump, formed from ectopic gastric mucosa. Most often it appears on the root of the tongue. |
| Adenomas | Formed from the glands of the mucous membrane of the tongue, it looks like a small ball. Localized on the tip and root of the tongue. |
| Lipomas | Consist of fat cells. They have a soft, lobed structure, located on the root of the tongue or under it. They grow slowly and do not hurt. Flap lipoma is flat. Can grow deep into tissues. Vulgar - a small bulge on the tongue. |
| Fibroids | Consist of connective tissue. Elastic, painless neoplasms are round in shape and sometimes have a stalk. They do not differ in color from the mucous membrane, sometimes they have a pale yellow or white tint. Neurofibroma contains nerve fibers and is therefore painful. It forms on the root of the tongue and does not differ in appearance from a regular fibroma. |
| Myomas | Growths on the surface of the tongue with a dense structure, up to 1 cm in size, are covered with a mucous membrane. Formed during the proliferation of muscle cells. |
| Hemangiomas | Vascular neoplasms look like red or blue spots. Sometimes they bleed. |
| Cysts | A retention cyst consists of muscle fibers and forms on the inner surface, the frenulum of the tip of the tongue. This is a small ball with liquid inside. |
| Botriomycomoma | The tumor is flat or spherical, reaches 10 cm in size, sometimes consists of several lobules. The shade varies from red to burgundy, the surface is smooth or covered with crusts. |
| Lymphangioma | Congenital benign neoplasm. Grows from the walls of lymphatic vessels. The surface is covered with bubbles, growths are located on the upper surface and tip of the tongue. They often become inflamed and are often accompanied by problems with bite and speech. |
| Struma | It is rare and consists of thyroid tissue cells. This is a small node up to 3 cm in size, formed at the root of the tongue. |
| Sialadenitis | The tumor appears against the background of inflammation of the saliva and sublingual gland. Causes: infectious pathologies, tuberculosis, mumps, syphilis. |
Clinical case – condylomas on the tongue:
Growths on the tongue in adults and children
Neoplasms in children and adults are equally common. In adults, these are mainly papillomas, adenomas, cysts, and lipomas.
In a child, papillomas are presented in the form of epithelial hyperplasia - the tissues of the tongue mucosa grow greatly. The active growth of HPV most often begins after influenza, sore throat, or a viral disease. Lymphangioma is diagnosed mainly in children under one year of age. Hemangiomas often occur in girls.
Tongue root cancer
You should pay attention to even the slightest changes
This is one of the most difficult types of cancer, since the location of the tumor does not allow it to be removed without causing great harm to the person. In most cases, after cancer of the root of the tongue, that is, after treatment, a person loses the ability to speak, and his quality of life noticeably decreases.
Cancer of the root of the tongue is also dangerous because symptoms begin to appear only 2 or 3 months after the tumor has formed. In addition, a person cannot independently see any changes occurring at the root of the tongue, and therefore only a doctor can make a diagnosis or detect the problem. As for the symptoms of tongue cancer in later stages, these include:
Symptoms
When any growth forms on the tongue, pain and discomfort in the mouth occurs.
Problems with chewing food, speaking, and swallowing are often observed. Sometimes swelling and redness of the tissue occurs, and one or more papillae become enlarged. But all pronounced symptoms are absent in the initial stages; they appear when the tumor is of a significant size. Sialadenitis is manifested by general weakness, fever, pain and burning, swelling of the affected area, and an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth.
If the structure or color of the growth changes, it begins to grow rapidly - this may be a sign that the growth has degenerated into a malignant tumor.
Reference! In children, papillomas on the tongue occupy large areas, often the neoplasms are covered with a white coating.
Precancerous conditions
We should also talk about those diseases that are classified as precancerous conditions. It is they who need to pay more attention and treatment, since any factor can provoke the degeneration of simple cells into cancerous ones. Such diseases include:
- Leukoplakia. This is keratinization of the mucous membrane in the mouth, most often a red stripe appears on the lips. The main reason for the appearance of this disease is a decrease in the stability of the mucous membrane in the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to the penetration of harmful microbes and viruses into it, which can provoke cell mutation
- Papilloma. This is a benign formation, which consists of papillary growths of connective tissue. In themselves, such formations are painless, but they pose a great danger associated with the possibility of the tumor degenerating from benign to malignant
- Ulcer. It often happens that a person damages the oral mucosa. This can occur as a result of biting the cheek, tongue, cut, or thermal burn. In the event that no antibacterial treatment is carried out, the likelihood of ulcers on the mucous membrane increases, and as a result, in the future, the formation of cancer cells
- Glossitis. This is a very rare disease, but still encountered in medical practice, which is characterized by pain in the tongue, as well as increased salivation.
- Bowen's disease. This disease is characterized by the appearance of a small spot on the tongue, which has a rough surface. Over time, erosion may appear on it
If a patient is diagnosed with one of the above diseases, then close attention is paid to its course, as well as treatment. Due to the fact that some of these diseases cannot be completely cured, a person is recommended to visit a specialist every six months or year for a full examination and examination in order to control the situation.
Diagnostics
The dentist diagnoses and treats growths on the tongue.
Sometimes additional consultation with a dermatologist, endocrinologist, virologist, immunologist and otolaryngologist may be required. Examination and diagnostic methods:
- Anamnesis collection, examination of the oral cavity and skin. The doctor notes the color, shape and consistency of the growth on the tongue, its surface, and location.
- A general blood test shows the presence and intensity of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Tissue biopsy - biomaterial is sent for histological examination.
- PCR diagnostics – identifying the type of causative agent of the pathological process.
- Analysis for thyroid hormones.
- Digen test.
The methods allow us to identify the characteristics of the disease with high accuracy. But at the initial stage of HPV development, there are often false positive and false negative results.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies is possible only after consultation with your doctor. Typically, such treatment acts as an additional method, but it is not recommended to use it as an independent method of therapy, since complications such as oncology may develop.
Together with medications, the patient can use herbal infusions and decoctions to increase the body's defenses. Infusions can be prepared from rose hips, lemon balm, chamomile, plantain and other herbs.
You can drink 100 milliliters of red potato juice every day.
Celandine has a good effect. Its juice is applied to the affected areas if the growths are small. The procedure is repeated three times a day, the full course of treatment is about one month.
Can growths be malignant?
At any moment, the growth can degenerate into a malignant tumor. Causes: constant damage to the tumor when talking or chewing food. Tongue cancer is classified as squamous cell; other forms, such as basal cell carcinoma or carcinoma, are rarely diagnosed.
Types of malignant tumors:
- An ulcer is a dense neoplasm that turns into an ulcer; it often hurts and bleeds. Located on the lower surface of the tongue.
- Infiltrative - a seal on the tip or back surface of the tongue, covered with a white coating. Constantly and severely painful.
- Papillary - a solid tumor on a stalk, formed on the lateral surfaces. Characterized by slow growth.
The prevalence of tongue cancer is 5 cases per 100 thousand population . The disease is easy to diagnose. But people often do not notice or ignore the symptoms of the pathology and go to the doctor with already advanced forms of the disease.
Formation of tongue cancer
Stages and symptoms of tongue cancer:
- Initial . Whitish spots appear on the tongue, most often on the lateral surfaces. These are papillary growths that look very similar to plaque. During examination, doctors often mistake formations for manifestations of glossitis and stomatitis. There is no pain or discomfort.
- Stage of clinical manifestations . The spots gradually become denser and transform into a tumor. Pain appears, which often radiates to the neck, ears, and temporal region; the tongue, neck, and face swell. When the formation becomes infected and suppurates, unpleasant odor from the mouth is disturbing. Problems arise with swallowing, articulation, and some areas of the tongue become numb. Metastases often spread to the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
- Launched . Necrosis and tissue decay begins, the tumor penetrates deep into the tongue.
- Terminal . Metastases extend beyond the oral cavity - lungs, liver, bones. Treatment at this stage is ineffective, and the prognosis is disappointing.
Specific diagnosis involves examining a smear of the fingerprint to identify cancer cells. A biopsy of the tumor is required. Additional research methods - ultrasound of the tongue, lower jaw and neck, x-ray or CT scan of the skull are prescribed to identify metastases.
Video about tongue cancer:
Treatment methods:
- Surgical . To radically remove a malignant tumor, partial resection or complete removal of the tongue is performed. When the tumor grows into the surrounding tissue, complete resection is performed, down to the bones of the lower jaw.
- Radiation therapy . The tumor is irradiated with X-rays. Radiotherapy is carried out before and after surgery.
- Polychemotherapy . A method of treating advanced forms of the disease, used in the presence of distant metastases. Drugs – Cisplatin, Methotrexate.
Surgery
Radio rays
Polychemotherapy
Attention! One of the main differences between malignant and benign neoplasms is that cancerous tumors are very dense. They rise somewhat above the mucous membrane and have an uneven surface.
Survival prognosis
Each type of cancer has its own prognosis, but it can be roughly represented as follows:
- If a cancerous tumor is detected at the first or second stage, the survival rate is 75 percent
- If a cancerous tumor is detected at the third stage, the survival rate is 50 percent
- When a cancerous tumor is detected at the fourth stage, the survival prognosis is less than 30 percent. It should be noted that a period of time equal to five years is taken.
Those who promptly consult a doctor for medical help have every chance of recovery, since the earlier tongue cancer was detected, the easier it will be to cure.
Tongue cancer is one of the most dangerous diseases that develops rapidly. That is why, if you detect at least a few symptoms indicating cancer, you should not immediately contact a specialist in order to avoid the possible transition of the disease to the most severe stage.
Treatment methods
Drug therapy is carried out at the initial stage of the formation of papillomas in the mouth. All other growths are removed surgically. Folk remedies will help strengthen the body's defenses, prevent the growth of formations and the development of complications.
Until complete removal of growths from the diet, you need to exclude hard, sour, spicy, salty, hot and cold foods.
Medicines
The choice of medications depends on the type of growth, the cause of its appearance, the general condition and age of the patient.
How to treat growths:
Antiviral ointments and tablets - Acyclovir, Panavir, Altabor. Prescribed for papillomas to suppress HPV activity.
Acyclovir
Panavir
Altabor
Solutions for injections – Ferrovir, Immunomax, Cycloferon. More effective against HPV than pills.
Ferrovir
Immunomax
Cycloferon
Rectal suppositories with antiviral and immunostimulating effects - Galavit, Kipferon, Genferon.
Galavit
Kipferon
Genferon
Immunomodulators – Likopid, Neovir.
Lycopid
Neovir
Local antiseptics – Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt. Eliminate inflammation, bleeding, prevent the spread of infection.
Chlorophyllipt
Vitamin A oil solution – prevents tumor growth. Treat the growth daily.
Vitamin A
Vitamin complexes – Supradin, Complivit, Ascorutin.
Supradin
Complivit
Askorutin
If growths are detected during pregnancy, immunostimulating drugs - Viferon, Reaferon. Safe immunomodulators for children - Amiksin, Viferon.
Viferon Reaferon Amiksin
Folk remedies
Non-traditional methods will not help cope with growths on the tongue.
But folk remedies have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effects and help strengthen the immune system. They can be used to enhance the therapeutic effect of drugs. When removing growths surgically, folk remedies are not used.
Recipes:
- Pour 500 ml of boiling water over 20 g of dry plantain leaves and leave in a sealed container for 15 minutes. Drink the strained infusion 100 ml twice a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days. The product increases the body's resistance to viruses.
- Grind the peeled pink potatoes and squeeze the juice through cheesecloth. Drink 100 ml before breakfast. Duration of treatment – 3 weeks. The drink has a pronounced immunostimulating effect.
- Pour 500 ml boiling water 1 tbsp. l. dry chamomile or calendula inflorescences, leave for an hour. Use the strained infusion to rinse your mouth twice a day for 10 days. This remedy is a natural antiseptic and accelerates the healing process of damaged tissue.
- Mix 4 parts hemp oil with 1 part honey. Treat the growths with the mixture 5 times a day.
- Lubricate the new growths 2-3 times a day with fresh juice of sour apples.
- Treat the growths with raw chicken protein. Apply every 15 minutes for an hour. Do the procedure three times a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
- Mix 100 g of chopped beets, 200 g of carrots. Add 1 lemon, twisted in a meat grinder along with the peel, 30 ml of olive oil, 100 g of walnuts. There are 1-2 tbsp. l. in a day. This vitamin complex strengthens the immune system.
Important! It is often recommended to use fresh celandine juice to treat growths on the tongue. This method is dangerous, the plant is poisonous, you can get poisoned. If the juice gets on healthy tissue, it will cause a severe burn. Papillomas in the mouth cannot be cauterized with hydrogen peroxide, vinegar, or removed with thread.
Removing growths
There are several methods for removing growths on the tongue. The choice depends on the location of the neoplasm and the presence of contraindications in the person.
Methods for removing growths:
| Surgically | Excision of the tumor with a scalpel under local anesthesia. The wound is disinfected, sutured, and the stitches are removed after a few days. The method is affordable, but causes a lot of discomfort during and after the operation. Contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, exacerbation of herpes, acute infectious and inflammatory processes in the body. |
| Laser | The most popular method of removing growths. The tumor is removed quickly and without pain - the procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes. There is no infection in the wounds, relapses are rarely diagnosed, and the rehabilitation process is short. Laser therapy can be used to remove tumors in children over 2 years of age. Contraindications – tumor size more than 3 cm, diabetes mellitus, pregnancy and breastfeeding, diseases of the circulatory system. Disadvantages: high cost, inability to send tumor tissue for histology. |
| Cryodestruction | Before the procedure, it is necessary to cure all infectious diseases. The affected area is exposed to liquid nitrogen, which stops the growth of the growth. During the session, the risk of infection and bleeding is reduced to zero. The duration of the procedure is 30 seconds. Cryodestruction is safe for children over 1 year of age. But this method is painful, often scars form at the site of exposure to cold, and it is difficult to control the depth of freezing. The method is not used to remove multiple tumors. After the session, immunity sharply decreases, so after removing the growth you should immediately start taking immunostimulating drugs. Contraindications – epilepsy, convulsions, arterial hypertension, vasospasm, pregnancy and lactation. Cryodestruction is not suitable for removing growths on the uvula and sublingual frenulum. |
| Electrocoagulation | A special loop is placed on the growth, which transmits electric current deep into the tissue. The tumor is cut off, and the vessels are sealed at the same time, which prevents bleeding. The method is painful, recovery takes a long time. But scars do not form, relapses are rare, and several tumors can be removed at once. After an incorrect procedure, scars may remain. |
| By radio waves | Non-invasive, bloodless procedure. After removing the growth, tissue samples can be sent for histology. The method is rarely used, since radio waves negatively affect healthy tissue, and relapses often occur. Contraindications: pregnancy and lactation, exacerbation of chronic pathologies, acute forms of infectious diseases, heart disease, diabetes mellitus. |
| Sclerosis | Used to remove vascular growths. The vessels are cauterized; when the blood supply is cut off, the growth stops growing and developing. |
| Galvanocaustics | A small growth is cauterized with platinum wire, preheated under the influence of current. The method is fast, without the risk of infection and bleeding. |
| Ultrasound | Ultrasonic waves of high intensity destroy damaged cells, but do not affect healthy tissue. The method is safe and effective, but has a high cost. |
Before any surgical intervention, a complete sanitation of the oral cavity is performed.
How to remove papilloma on the tongue using electrocoagulation:
Drug therapy
Interferon
Treatment of papillomas should be comprehensive, which includes drug and surgical therapy. Before prescribing medications, the doctor cleans the oral cavity, eliminating white plaque and pockets through which infection can enter the body.
For this purpose, the oral cavity is sanitized, and then treated with ointment, which has an antiviral effect. This could be, for example, “Bonaftone”, “Adimal” or “Megosin” ointment. It is necessary to treat the oral cavity from below and from above.
Then the doctor prescribes antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, for example, Interferon or Panavir, and vitamin complexes. Their action is aimed at increasing the body's defenses. The doctor selects medications based on the individual characteristics of the body, taking into account contraindications and side effects.
Treatment prognosis
With timely detection and proper treatment, tumors can be completely eliminated. Problems may arise in older people, people with immunodeficiency conditions, and chronic diseases.
Possible complications
Negative consequences are most often associated with frequent injury to growths.
Why are growths on the tongue dangerous?
- abscess;
- infectious processes in the oral cavity;
- sepsis;
- severe intoxication;
- tissue necrosis;
- frequent relapses;
- degeneration into a malignant tumor.
If the cyst ruptures, the tongue may shift, speech, breathing and swallowing may be impaired.
Important! Hemangiomas and lymphangiomas most often recur.
How to avoid relapse of the disease?
After the growth has been removed from the patient's tongue, the person should not relax. Typically, single papillomas do not recur, but with multiple formations, the reappearance of growths on the body occurs quite often.
Therefore, after surgical removal of papillomas from the surface of the tongue, you should:
- Take precautions and limit risk factors (see above).
- Take a course of antiviral treatment as recommended by your doctor.
- Seasonally take immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes, which your doctor will also help you choose.
- Maintain oral hygiene and avoid tongue injuries.
One of the main conditions for achieving a favorable outcome in the fight against papillomas is choosing the right medical center, since much in the procedure for removing a tumor depends on the actions of the doctor. We hope that the recommendations of specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics helped you clarify the picture of the growth that has developed on your tongue, and now you can solve this problem without unnecessary emotional distress.
Preventive measures
The main methods of prevention are strengthening the immune system and maintaining good hygiene.
How to prevent growths from appearing:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- exercise regularly, spend more time outdoors;
- avoid stressful situations, learn to relax, master meditative techniques;
- wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after going outside or visiting the toilet;
- Always use only your own towels and personal items;
- adjust your diet - give up unhealthy and heavy foods, eat more vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, cereals, lean meat and fish;
- observe the drinking regime - you need to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean still water per day;
- promptly identify and treat dental diseases and pathologies of internal organs.
An effective method for preventing the formation of papillomas on the tongue is HPV vaccination. The Cervarix and Gardasil vaccines have contraindications and side effects, so they are not suitable for everyone. Vaccination does not completely protect against infection, but it does promote the production of antibodies that help the body fight infection more quickly.
It is advisable to vaccinate up to 26 years of age. The protective effect is designed for 8 years. Contraindications: pregnancy and breastfeeding, any gum problems.
Danger
When papillomas occur on the tongue, the patient experiences some discomfort. So, during eating, the growth can easily come off. In addition, the formations are visible when speaking and contribute to changes in speech.
Pointed-type formations cause not only physical, but also psychological inconvenience. Against the background of this condition, a person may experience embarrassment at an appointment with a dentist or ENT specialist. Complexes also appear when communicating with other people.
The localization of growths on the inside of the oral cavity poses a serious danger, since they can provoke the penetration of another infection, resulting in an increased risk of blood poisoning. All this often leads to cancer, which often ends in death.