What is a nylon prosthesis
Removable nylon dentures are soft orthopedic structures made of a pink, gum-colored nylon base with invisible clasps that hold it in the mouth. The fixation is on the adjacent teeth; the hooks wrap around the supports, keeping the prosthesis stationary on the jaw. Artificial crowns are placed on an elastic frame.
A person can take off and put on a nylon prosthesis without assistance. They are used in dentistry as a temporary solution during implantation (during the process of osseointegration) or as a permanent prosthesis according to indications.
Nylon is a polymer that has the quality of flexibility, and under certain conditions, in the patient’s mouth, softness increases. As a denture material, it has come as an alternative to dental acrylic, to which some people are allergic.
Partial nylon prosthesis RUR 40,000. for all!
The price includes: diagnostics, impressions, manufacturing, installation, fitting and 1 year warranty! Complete denture Akrifri 1 jaw - 47,000 rub.!
Consequences of a loose prosthesis
Dentures are installed in order to restore the dentition, restore the previous functionality for high-quality chewing of food, and restore the beauty of the smile. The best solution is to install fixed dentures and implants. But sometimes you cannot do without removable, conditionally removable dentures. A well-installed structure is reliable and does not require grinding of adjacent teeth, which is one of the biggest advantages. However, a poorly installed prosthesis leads to many serious problems;
- Constant rubbing of the gums, which can even develop into cancer;
- Distortion of speech and even facial expressions;
- Pieces of food getting under the prosthesis, which leads to inflammatory processes;
- Accidental loss of the prosthesis during a conversation or even during sleep;
- Psychological stress leading to decreased self-esteem and the emergence of self-doubt.
If your denture becomes loose in the first days after installation, you should discuss this with your doctor. Perhaps there are anatomical features that make it difficult for the doctor to achieve ideal fixation of the prosthesis. However, in many cases it is possible to improve fixation through adjustment.
Stages of manufacturing a flexible prosthesis
To create nylon dentures, you must first treat the teeth, perform removal according to indications, and then proceed to the following steps:
- taking impressions of jaws in a clinical setting;
- plaster models are made in the laboratory;
- a wax prototype of the prosthesis is cast, tried on, and finalized;
- a nylon final version is created, matched to the color of the gum. The equipment used is a heat press, in which polymer granules are melted and an individual mold is poured in a liquid state. After hardening, the structure is polished.
Clasps are a continuation of nylon dentures and are therefore completely invisible on the jaw even when smiling and talking.
How to manage without dentures?
Alas, you cannot do without prosthetics. The loss of even one tooth disrupts the harmony in the oral cavity. In place of a lost tooth, the skin becomes less elastic, the correct oval of the face is lost over time, and signs of aging appear. The load on the remaining teeth increases. The jaw bone becomes thinner and the gum structure changes.
After tooth extraction, less blood flows into this area of tissue, and the number of blood vessels in the area where the tooth is missing decreases. As a result, the structure of the jaw bone is disrupted. All these processes then lead to displacement of the dentition, to an incorrect bite. And this, in turn, affects the quality of chewing food and disrupts the digestion process.
Even a person’s speech is impaired. Due to the absence of individual teeth, it is impossible to pronounce some sounds correctly. Especially if the problem affects the front teeth. Moreover, the absence of the front row of teeth leads to changes in the nasolabial fold. It lengthens, the corners of the mouth droop, and the person begins to look older than his age.
Indications for installation
Indications for removable nylon dentures can be:
- loss of one or more teeth in a row;
- scattered defect;
- absence of all teeth;
- allergy to metal, acrylic;
- if you do not want to grind the supporting teeth for dentures, for example, clasp ones with locks;
- periodontal disease of 1st and 2nd degrees to keep teeth in place (but 3.4 degrees will already be a contraindication);
- patient refusal or medical contraindications to implantation;
- childhood, if necessary, hide early tooth loss;
- as a temporary solution for implantation with delayed loading.
Sometimes nylon dentures can be installed to treat bruxism, involuntary grinding in the mouth, which damages tooth enamel and increases wear. And also for athletes and people involved in traumatic sports, a flexible design is the best option, better than acrylic, which can easily break in case of injury.
Prosthetics
Contraindications
What may be a contraindication to a nylon prosthesis in dentistry:
- periodontal diseases (grade 3-4 periodontal disease), loose teeth, their displacement;
- recession;
- the height of the supporting teeth is not enough, the clasps will not be able to securely fasten;
- inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane and gums;
- tooth mobility;
- significant bone atrophy.
It is necessary to have healthy teeth on both sides of the prosthesis as supports for clasp fixation.
Methods of prosthetics of the anterior upper units
- Veneers. They are thin porcelain plates with a shade completely similar to the color of natural teeth. Veneers are made to fit the contour of the patient’s teeth, so they fit him perfectly. Thin plates are installed on the front of the units and solve the following problems:
- Filling interdental gaps.
- Leveling tooth enamel.
- Concealing dark spots and yellowed tooth enamel.
- Masking cracks and chips.
- Alignment of teeth.
Veneers can be:
- Composite (direct) - the veneer material is applied and formed directly on the tooth.
- Ceramic (indirect) – made from pre-made impressions of the patient’s teeth, formed in the laboratory, and then attached to the teeth. Ceramics has high aesthetic properties and is as similar in appearance and properties as natural tooth enamel.
- Lumineers. These are ultra-thin veneers, the thickness of which is only 0.2 mm. Considering the fact that lumineers are installed without grinding the tooth enamel, they do not always fit tightly and have a risk of coming off. The disadvantage of lumineers is the fact that the teeth covered with them protrude slightly forward compared to units without dentures. Therefore, when prosthetics is applied to one tooth, it will stand out strongly against the background of the rest of the units.
Lumineers and veneers have the following advantages:
- Painless installation.
- Long service life.
- The prosthetic procedure takes little time.
- Lumineers can be installed without grinding the enamel.
- Teeth under veneers and lumineers are protected from the harmful effects of oral microorganisms.
- Crowns. Artificial crowns are installed in cases where teeth are severely damaged. Such dentures allow you to preserve the tooth root. In this case, before prosthetics, the specialist carries out the necessary treatment of the affected tooth. Under the crown, the remaining part of the dental unit will remain intact. The crowns are fixed with special dental cement.
- Dental bridge. This design allows you to simultaneously restore several lost teeth in a row. A bridge is a structure consisting of a false tooth sandwiched between two dental crowns. These crowns are placed over the teeth on either side of the gap and are secured. The benefit of dental bridges is that they prevent surrounding teeth from shifting.
Varieties
There are:
- mini dentures for 1-2 teeth;
- partial (in the absence of three or more teeth);
- complete (replacing the dentition of the entire jaw).
Many people mistakenly believe that all flexible prostheses are nylon. This is wrong. They are very similar to the touch and in some characteristics. However, they should be considered separately.
Quadrotti prosthesis
A special modern type of prosthesis, which stands somewhere between clasp and nylon. It is more durable than the latter, has a little flexibility, and the fasteners are also not visible, unlike the clasp design, where, perhaps, this is the only drawback. The material of manufacture is monomer-free plastic.
Immediate prosthesis “butterfly”.
This is just a type of nylon prosthesis. It is used in cases where one, or less often, two teeth are missing. Small design, good replacement for a lost dental element. Produced quickly. The supporting teeth are not affected, that is, the doctor does not grind them down, they remain healthy and serve their term.
Ceramics on zirconium
Such metal-free crowns for the front teeth are an opportunity to combine strength, reliability, and aesthetics. Indistinguishable from natural teeth, do not cause allergic reactions, and can withstand severe loads.
But the price of such products is quite high, so they have not yet gained universal popularity.
Rules of care and wearing features
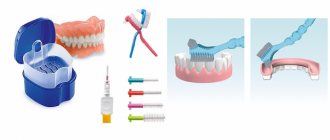
In order for the prosthesis to look aesthetically pleasing throughout the entire period of use, you should adhere to simple rules for caring for it:
- brush your teeth and teeth 2 times a day;
- the toothbrush should have soft bristles and the toothpaste should be non-abrasive;
- After each meal, also clean the product or rinse your mouth with water if it is not possible to remove and thoroughly wash the denture;
- take it to the dentist for professional cleaning twice a year;
- do not store in a dry place;
- periodically use a special solution to disinfect and clean removable dentures.
Reasons for poor fixation
- Incorrect fit of the prosthesis initially;
- Over time, the size of the gum and jaw have changed;
- Prosthesis care violations.
In rare cases, it happens that even a fixed prosthesis begins to wobble. The reason is that the cement on which the crown was fixed may lose its strength after a few years. In this case, you should immediately contact a specialist who knows how to fix the denture without damaging it. The crown can be carefully removed and reinstalled with new cement. More often, this problem affects those who installed crowns many years ago. Modern cement for fixing the prosthesis is much more durable.
Advantages
An undoubted advantage is the aesthetic appearance, better than that of acrylic and clasp structures. And:
- light weight, which is a significant factor for the upper jaw, where a person feels every gram of a foreign body;
- small basis. There is no wide part blocking the sky, like the plate analogue, which is much more comfortable;
- quick addiction is due to the two points above;
- “invisible prosthesis”, invisible to others, a person can laugh and talk without hesitation. Nylon, in this sense, is a good material; it perfectly imitates gums. And since the clasps are a continuation of the base and are of the same color, they are attached directly to the gums behind the supporting tooth, so they are not visible. What is an advantage over metal visible hooks of clasp structures and acrylic ones;
- hypoallergenic. The production does not use toxic monomers that are added to the plastic mass of acrylic prostheses. They are the ones who cause allergies in patients. By the way, other alternatives to prosthetics have appeared for such sensitive people - Acry Free;
- there is no metallic taste in the mouth due to the absence of metal in the composition;
- The next plus will be felt by people who have a small mouth. Opening it wide to install a large prosthesis is not very comfortable. But not in this case. Nylon bends easily and does not require such sacrifices from patients.
Flaws
It cannot be said that all the disadvantages that we describe below apply to mini-prostheses. They are the ones who receive the least number of complaints. But larger designs definitely have the following negative nuances:
- uneven load when chewing and discomfort when chewing food. The base is flexible and when bitten it bends even more, all the pressure goes to one area, which causes pain. Since the load is not distributed over the entire prosthetic bed, the tissues underneath it atrophy;
- rapid atrophy. Under any removable denture this process occurs and the height of the alveolar ridge is lost. You can find figures about 1mm per year. Loss of tissue leads to subsidence of the prosthesis;
- damage to the gums in the area of clamp fixation. Unlike the clasp type and the plate type, where the hooks wrap around the neck of the supporting tooth, nylon dentures have a gingival attachment. Therefore, the load when chewing is transferred not to the tooth, but to the gum, which over time injures it;
- a fairly rapid decline in aesthetics. Nylon scratches, becomes sticky over time, and attracts dirt;
- beyond repair;
- short service life - up to 5 years and at the same time the need for frequent corrections.
What types of removable dentures are there?
Removable dentures are classified according to the material of manufacture, method of attachment and indications. In addition, they are:
- completely removable;
- partially removable;
- conditionally removable.
These varieties can be used as permanent or temporary, for example, in preparation for implantation.
Fully removable
This option is equally good for cases of partial and complete edentia. Such an orthodontic appliance consists of a base (plastic, acrylic, metal-plastic or nylon) on which the teeth (acrylic, nylon or polyurethane) are located. Two types are considered popular and best among analogues (according to a number of characteristics):
- Acrylic.
- Acrylic-free.
Both of them have a number of features and indications that you should familiarize yourself with before choosing the best option.
Acrylic
They represent a complete or partial imitation of the dental system (depending on the number of missing units). Indicated for prosthetics of both jaws. Considered a budget option.
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
In addition, patients who have installed such orthodontic products are strictly prohibited from eating sticky and hard foods, as they can damage and render the prosthesis unusable. It is also worth knowing that acrylic is an excellent environment for the development of bacteria. Irregular or careless care of such dentures can lead to allergies or bacterial contamination. At night, acrylic dentures must be removed and stored in special solutions.
Acrylic-free (AcryFree)
AcryFree is innovative and superior to other full dentures. They are elastic and flexible, but at the same time durable and provide the necessary rigidity during operation. The manufacturing material used is acrylic resin, the quality characteristics of which are several times higher than medical nylon and plastic.
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
The main distinguishing feature is the translucency of the prosthesis base. The biocompatibility of the material ensures hypoallergenicity. In addition, high aesthetics makes AcryFree invisible to others.
Completely removable dentures are made taking into account all the physiology of the patient’s oral cavity (after taking impressions).
Partially removable
Partially removable dentures include those that require some effort to remove. You can remove them from the oral cavity yourself, but you need to know how the structure chosen for prosthetics works - how it is attached. This type of orthodontic appliances includes the following:
- clasp;
- QuattroTi (Quadrotti);
- without sky.
Each type has its own characteristics and requires a more detailed consideration.
Clasp
A classic version of conditionally schematic prostheses. There are four types:
- On clasps
. The most budget option. The design contains claw-shaped hooks. The main nuance that can be considered a disadvantage is the visibility of the fixing elements when smiling. Such orthodontic devices are chosen by those who do not care about high aesthetics. - Telescopic
. This type is characterized by the presence of two telescopic crowns - internal (metal, covering the supporting teeth) and external (made of metal-ceramics or plastic), attached to the prosthesis. The peculiarity of this type of prosthetics is the need for depulpation and turning of supporting units. - On attachments (locks)
. It consists of two parts, the first is on the tooth, the second is in the prosthesis. The parts of such an orthodontic apparatus are connected using special locks. The result looks very aesthetically pleasing. The main disadvantages are that installation requires depulpation and strong turning of the supporting units. - Splinting
. It solves two problems at once - restores the dentition and prevents loosening of movable units. The peculiarity of the fastening is a hook-shaped shape that completely follows the shape of the tooth. This option is better than others for patients with diseases such as periodontitis, gingivitis and periodontal disease.
The design of the clasp prosthesis itself consists of the following parts:
- metal arc (clasp), which is a support;
- base - a base that imitates gums on which artificial teeth are mounted;
- teeth (or crowns) made of metal ceramics, zirconium or ceramics;
- fastenings
An orthopedic dentist will tell you which partial removable dentures are best for you after collecting/studying the clinical picture and identifying possible contraindications.
QuattroTi
This is a type of clasp dentures, but modern dentistry distinguishes them separately as orthodontic devices of a new generation. The manufacturing material used is biocompatible Dental D plastic, which does not cause allergies. The design does not contain metal, has high strength and flexibility.
Other features include the following facts:
- imitates natural dentition as much as possible (manufacturing technology allows parts of the denture to be painted in different shades);
- installation does not require turning of support units;
- cheaper in cost than clasp analogues;
- does not rub the gums;
- does not affect diction;
- after fixation, no long adaptation period is required;
- the chewing load is distributed evenly.
With all the positive qualities, there is one caveat - the service life, even with proper use and care, is no more than 3-5 years.
Without sky
Invention of domestic specialists. The second name is sandwich dentures. Indicated for use in partially edentulous patients. The design consists of three parts:
- Base (made of acrylic).
- Artificial teeth (acrylic).
- Fastenings – clamps or telescopic crowns (made of polyurethane).
When installed, the clamps are pulled onto natural units and, due to the flexibility of polyurethane, fit tightly, holding the structure well. This type of prosthesis received the name “without palate” precisely because of the method of fixation. It is worth noting that these orthodontic products are better than their analogues in terms of their effect on healthy teeth - they do not deteriorate or become loose.
At the same time, there are several nuances that you need to be aware of:
- this option is not suitable for people allergic to acrylic and polyurethane;
- the use of this orthodontic apparatus does not allow the jaws to close completely (due to the thickness of the original material);
- most often the prosthesis is visible when speaking.
If aesthetics is not in the first place and there are no contraindications, then sandwich dentures will be an excellent solution for restoring lost units.
Conditionally removable
These include orthodontic appliances, which can only be removed by a dentist in a clinic (you cannot remove them from the oral cavity on your own). The most popular type is dentures on implants. Installation takes place in three stages:
- Preparing the oral cavity
. At this stage, thorough sanitation and treatment of problem areas is carried out. - Implantation
. As a rule, with complete edentia, 4 implants are sufficient to support the artificial jaw. After this stage, an adaptation period is required, which lasts until the gums are completely healed. - Installation of the prosthesis
. Special two-part clamps are used, which can be push-button or beam. The fasteners, clinging to the prosthesis, seem to snap into place, providing the most reliable fixation.
The technique is indicated for complete edentia, as the best way to restore the dentition. The service life of an orthopedic product depends on the choice of material and averages 10 years.
You might be interested in:
Removable dental prosthetics
New generation removable dentures
Conditionally removable prosthetics
Fixed dentures
Overdenture
Nylon dentures
Acrylic dentures
Denture “Butterfly”
Clasp prosthetics
Expert opinion
Roman Borisovich Alekperov
orthopedic dentist
Experience: 24 years
The choice of flexible prostheses is based mainly on the patient’s desire to receive maximum comfort from wearing an orthopedic structure. Nylon or silicone prostheses do not require long-term adaptation - made from an individual cast, they immediately sit comfortably and allow you to chew food and speak normally. It is important to remember that long-term wearing of flexible prostheses can lead to the development of atrophic processes in bone tissue, since these structures do not have a rigid base. Do not use flexible dentures for more than 6-9 months if you are planning to have implants. If such a situation occurs and the bone is “gone,” it will be necessary to pre-build it or perform basal implantation.
Implants
Strong fixation occurs due to the fact that they are installed as artificial analogues of living roots. Removable structures can be attached to implants and can be removed at home.
The best and most popular of those offered are implants and telescopic crowns. But for each patient they are selected individually by a highly qualified orthopedic dentist.
Due to the fact that the oral cavity is constantly mobile, displacement or loss of the structure often occurs. Therefore, there are additional means of fixation.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Partial restoration of teeth on both jaws
Case: partial absence of teeth on both jaws.
Complete prosthetics of the upper and lower jaws
Case: absence of teeth in the upper jaw (completely), absence of an orthopedic structure in the lower jaw on existing implants (installed in the USA two years earlier) Work: production of a complete removable denture in the upper jaw as a temporary structure until the installation of one-stage implants with subsequent prosthetics.
Installation of plate dentures with complete edentia (April 2012)
Case: complete absence of teeth in the upper and lower jaws, weak fixation of the removable denture in the lower jaw.
Complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw
Case: Completely edentulous upper jaw Work: Complete removable plate denture - acrylic Number of visits: 4 Time: 2 weeks Cost: 25,000 rub.
Correction of an incorrectly manufactured complete denture base
During the delivery of complete dentures, errors are possible, caused in some cases by incorrect determination of the central relationship of the jaws or violations in the process of laboratory production of dentures, in others - by incorrect determination of the lower third of the face or the boundaries of the prosthetic field.
However, one of the most serious and most common disadvantages of complete dentures is their poor fit. The tissues under such prostheses are often subject to mechanical trauma, which leads to pathological changes. The reasons for poor fixation of complete dentures are: shortened or elongated edges of the denture base; discrepancy between the base of the prosthesis and the relief of the hard palate or alveolar process of the lower jaw; lack of space for the torus palatinus and other bony protrusions; the tissue of the soft palate is not pressed upward with an individual spoon before and during the impression; anatomical formations on the lower jaw (sublingual and retroalveolar spaces, mandibular tubercles) are not used to hold the lower denture; the edges of the prosthesis do not correspond to the edges of the obtained functional impression; poor quality prints; the edges of the prosthesis cover the frenulum and folds; there is not enough space for the free functioning of the language, etc.
Heringer compasses
If the edges of the prosthesis are elongated, then hyperemia appears in places of increased pressure, and then pressure sores occur. In this case, during contraction of the muscles on which the edges of the prosthesis are located, the prosthesis is displaced from its bed.
Correction of the prosthesis should be made when hyperemia appears, since subsequently, when bedsores form, accompanied by pain and inflammatory infiltration of surrounding tissues, the boundaries defining the area of the elongated edge of the prosthesis are erased.
To accurately determine the elongated boundaries of the prosthesis, dentin or gypsum powder is applied to the hyperemic areas and the prosthesis is applied to the jaw. The areas marked on the prosthesis with white powder are the places of correction. If the edges of the prosthesis are shortened, they are lengthened with wax, formed in the patient’s mouth, and the wax is replaced with plastic.
Functional overload of teeth
M.A. Napadov and V.Yu. Kurlyandsky (1955) recommend correcting the base of the prosthesis and its edges directly in the patient’s mouth using quick-hardening plastic. There are other ways to reline dentures. However, using them, we did not always obtain satisfactory results.
The following method of correcting the base of the prosthesis on the lower jaw turned out to be more reliable.
Using fast-hardening plastic, areas of the prosthesis extending into the retroalveolar and sublingual spaces are supplemented, and if the base is narrowed, it is expanded from the vestibular side in the area of the lateral teeth. Excess plastic on the inner surface of the prosthesis base, which restricts the movements of the tongue, is cut off, and a recess is made between the molars and premolars on the vestibular surface of the prosthesis base for applying a retainer. After this, an orthocore plate is applied to the base of the prosthesis, the edges of which end on the vestibular and lingual surfaces. Excess orthocore is cut off in such a way as to form a smooth transition to the base of the prosthesis. Orthocor is heated in hot water, the prosthesis is placed on the lower jaw and secured with a retainer. Then the patient is asked to carry out the full range of chewing, swallowing and other functional movements, as well as to make phonetic correction of the edges of the prosthesis. In areas where the edges of the prosthesis are exposed, the latter are shortened, covered again with orthocor and reinserted into the oral cavity. Having completed the correction, the prosthesis is plastered into a ditch and the orthocor is replaced with plastic in the laboratory. The finished prosthesis is handed over to the patient and the dentition is corrected under the control of carbon paper, achieving smooth gliding of the dentition.
Anatomical articulator design and model fixation technique
If the complete upper denture is poorly fixed, then the cause of poor fixation is determined. If the posterior edge of the prosthesis is located 2-3 mm posterior to the blind foramina and overlaps them, it should be assumed that the soft palate was not pressed upward when taking a functional impression. In this case, a narrow strip of heated wax is placed on the back edge of the prosthesis, and the tissue of the soft palate is pressed out with it. As a result, the prosthesis begins to stick, which confirms the correctness of the assumption made.
In cases where the prosthesis does not cover the blind holes, its posterior edge is lengthened. For this purpose, the wax plate is heated and folded into 2 layers so that the upper one is a continuation of the prosthesis, and the lower one extends to its surface facing the oral cavity. The wax plate is fixed to the prosthesis using a heated spatula. The prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity and the wax part is pressed upward on the soft palate, cooled in water and reinserted into the oral cavity. If the prosthesis begins to stick, it should be assumed that its posterior edge has been shortened. If, when you press your fingers on the front teeth, the prosthesis is well fixed on the jaw, this means that its rear edge not only properly presses the soft palate upward, but also has a sufficient length.
A.I. Betelman and co-authors (1954) recommend marking the posterior border of the prosthesis on the soft palate with a blue pencil, getting a pencil imprint on the back of the prosthesis and cutting off excess wax outside the valve area. If using wax it was possible to eliminate the cause of poor fixation, the prosthesis is plastered in a ditch, the wax is replaced with plastic and the prosthesis is given to the patient.
If using the described manipulations it was not possible to improve the fixation of the prosthesis, the back side is covered with a heated strip of wax, it is strengthened and, after heating the wax strongly on an alcohol lamp, the prosthesis is inserted into the patient’s mouth. Holding the prosthesis on the jaw, the patient is asked to functionally design its edges. After clarifying the boundaries of the prosthetic field 2-3 times and cooling in water, the prosthesis should stick, as a valve will form under it. However, in some cases this does not happen, and the prosthesis, at the slightest tension of its soft tissues, begins to “slide” from the jaw. Consequently, the excessively elongated sides of the prosthesis are located much above the neutral zone on the moving soft tissues. In these cases, it can be difficult to correct the denture by shortening its sides using wax. Sometimes more serious deficiencies cannot be eliminated at all, and the prostheses must be remade.
Metal ceramics on the front teeth –
An aesthetic problem when replacing anterior teeth with metal-ceramics is associated with the presence of a metal frame under the surface layers of the ceramic mass. The first problem is that the ceramic layer must be made opaque - otherwise the metal frame will be visible through the ceramic layer. In turn, dental tissues have a certain light transmittance - enamel is capable of transmitting about 70% of light, and the dentin lying under the enamel is about 30%.
Such optical properties give natural teeth a certain degree of transparency, as well as color, which also changes from the cutting edge to the neck of the tooth. Therefore, when metal-ceramic crowns are installed on one or two front teeth, in most cases they are noticeable against the background of natural teeth. Therefore, if we are talking about budget metal-ceramics, this problem can be more or less solved only if you install metal-ceramics on all 6-8 front teeth at once, and in this case, all the front teeth under the crowns will look at least the same.
If you have a sufficient budget, the problem of color and transparency can be solved by using more expensive ceramic mass, the use of which, however, will significantly increase the cost of crowns. Among the best options (according to many of our colleagues) are the ceramic masses “Vita” (Germany) and “Noritake” (Japan), as well as “Ivoclar” (Liechtenstein). The use of a good ceramic mass allows us to minimize the difference between metal-ceramics and natural teeth, but again, only to a certain extent.
Clinical case No. 1 (before and after photos) –
In Fig. 3-4 you can see how one terrible metal-ceramic installed on all the upper teeth was replaced with almost the same terrible one (the crowns look gray, there is no gradient of color and transparency; as if they were made of plastic). More or less, the only thing that saves the situation is that all the upper teeth look the same, because... They all have the same crowns. In fact, in this case, metal-ceramics are more like cheap plastic crowns.
Clinical case No. 2 (before and after photos) –
In Fig. 5-6 you can see that all 6 lower metal-ceramic crowns - 1) have an unnatural gray-milky color, which is especially visible on the fangs, 2) there is no transparency along the cutting edge, 3) there is no color transition from the neck of the tooth to the cutting edge . The situation is saved again only by the fact that all 6 front teeth are taken under crowns - which makes them at least identical. On the other hand, we must admit that many patients are quite satisfied with this level of aesthetics.
Important: it should also be noted that the transparency of tooth enamel can vary greatly from person to person. Therefore, if the enamel is highly transparent, metal ceramics will not suit you at all. But if your teeth have low enamel transparency, then high-quality metal-ceramics may be a good option. But in any case, keep in mind that in bright natural light, the difference in color and transparency between metal-ceramic crowns and “your teeth” will be most noticeable. It is also worth considering that metal ceramics will have a stronger effect in patients with a gummy type of smile, i.e. when the crowns of the teeth are completely exposed when smiling.
Another disadvantage of metal ceramics on the front teeth –
However, the lack of a gradient of color and transparency (which can be found in most cases of manufacturing budget metal ceramics) is not its only aesthetic problem. Many patients almost immediately after prosthetics note that the gums around the crown have become bluish (Fig. 7). Also, after several years, many patients notice that the gums have receded, exposing the subgingival edge of the crown at the neck of the tooth - which looks like the “dark line” in Fig. 8.
Disadvantages of economy class metal ceramics:
Patients react calmly to such things if they occur in the area of the chewing teeth. But on the front teeth, especially if the patient has a gummy type of smile (that is, the gums are exposed while smiling) - this is a serious aesthetic problem. All this arises due to the fact that the lower edge of the metal frame of a metal-ceramic crown is usually not insulated with ceramic mass. It is the contact of the metal with the gum that leads to a change in its color, and also contributes to gum recession and exposure of the edge of the crown.
However, such problems with gum aesthetics are typical only for standard economy-class metal-ceramic crowns. There are metal-ceramic crowns with a much higher level of aesthetics - the so-called metal-ceramics of increased aesthetics.
Metal ceramics of increased aesthetics –
To create high-quality, highly aesthetic metal-ceramics, you certainly need an expensive, high-quality ceramic mass, which will significantly increase the cost of such crowns.
However, this is not enough, because in order to also exclude the appearance of cyanosis of the gums or a dark line, it is necessary to manufacture metal-ceramics with “shoulder mass” (Fig. 9). For crowns with shoulder mass, the metal frame will be insulated with ceramics, including in the area of the ledge (where the crown wraps around the neck of the tooth), i.e. slightly below the edge of the gum. Moreover, isolation can be carried out either along the entire perimeter of the cervical part of the crown, or only on its front side, which is already good. Isolating the edge of the metal frame with ceramics helps to avoid the development of cyanosis of the gums and the appearance of a dark line in the future.
Clinical case No. 3 – before and after photos
In Fig. 10-11 we see a decent option for metal-ceramic prosthetics, which was installed on the 4 upper incisors (there is even transparency along the cutting edge). Additionally, the patient had teeth whitening. As we can see, there are practically no differences in the color and transparency of metal-ceramic crowns from your own teeth (although minor flaws will still be noticeable to professionals).
It should be noted that modern metal-ceramic crowns (thanks to the latest generation of ceramic compounds) can be almost as aesthetically pleasing as ceramic ones. But this requires expensive materials, and most importantly, a highly professional dental technician who must have artistic talent. And there are only a few such technicians even in Moscow and St. Petersburg. And in any case, the cost of 1 unit of highly aesthetic metal ceramics (in clinics where the best specialists work) will be no less than 25,000 rubles.