11.12.2011
Author: Dentist-periodontist Tamara Valerievna Kudzieva
- Periodontium
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Periodontal disease
- Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the lips and tongue
- Plastic surgery of the oral vestibule (vestibuloplasty)
Most patients believe that tooth loss is associated with the occurrence of caries and its complications. But this is by no means true! In recent years, the most common disease in dentistry is periodontal disease.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, caused by the adverse effects of local and general factors and occurring without disruption of the periodontal junction.
Forms of gingivitis:
- a) catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gingival margin. There are chronic and acute forms of catarrhal gingivitis. The acute form of catarrhal gingivitis often develops against the background of some general infection or intoxication. Often catarrhal gingivitis occurs during the period of spring hypovitaminosis, after suffering from influenza and acute respiratory infections.
- b) ulcerative gingivitis is an inflammatory process characterized by the appearance of ulcers and necrotic plaque on the surface of the gingival margin. The development of ulcerative gingivitis is facilitated by the presence of multiple untreated caries and damaged tooth roots. More common during puberty.
- c) hypertrophic gingivitis - leads directly to gum hypertrophy. There is swelling and inflammation. Patients complain of an increase in the volume of the gums, the color of the gums is slightly changed, there is no pain or bleeding of the gums when irritated. The gum has the appearance of a thickened cushion at the base, the gingival papillae are compacted, and the surface is lumpy.
- d) gingivitis of pregnant women and teenage gingivitis, these are those types of gum inflammation that do not occur against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
Severity of gingivitis:
- light,
- average
- and heavy.
Course of gingivitis:
- spicy,
- aggravated,
- chronic.
Frenulotomy at Art Dental Clinic
Over the years of work, the specialists of Art Dental Clinic have proven themselves to be attentive to any problem of our patients. In each case, we advocate a responsible, personal approach. The appropriate technique and surgical strategy are selected taking into account the condition of the frenulum and the characteristics of the pathology. After anesthesia, the frenulum is excised, cutting the mucous membrane along the edges. After its mobilization it will be sutured. When performing surgery on young children, it is better to work with absorbable suture material, preventing the occurrence of injury during suture removal. We work in the interests of the health and beauty of each patient, taking a responsible approach to determining the condition of the oral cavity, identifying and eliminating pathologies.
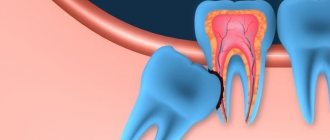
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, characterized by progressive destruction of the periodontium and bone of the alveolar process of the jaws.
There are 3 degrees of severity.
- 1st degree – bone destruction up to 1/3
- 2nd degree – bone destruction up to 1/2
- 3rd degree – bone destruction more than 1/2
If the inflammatory process has reached degree 3, then the teeth cannot be saved!!!
Course of periodontitis:
- spicy,
- chronic,
- exacerbation of chronic
- abscess
- and remission.
The prevalence of periodontitis can be:
- localized (the cause may be incorrect position of the teeth, poorly made orthopedic construction or filling)
- and generalized (untimely removal of supra- and subgingival dental plaque, hereditary predisposition, general diseases).
Signs of periodontal disease:
- Bleeding gums.
- Pain when brushing teeth and eating.
- Bad breath.
- Exposing the necks of the teeth.
- The appearance of tooth mobility.
If you have at least one of these points, contact your dentist URGENTLY!
Rehabilitation period
To eliminate the risk of wound infection, dentists usually prescribe antibacterial drugs. In addition, it is necessary to treat the seams with prescribed solutions or ointments. Doctors also recommend:
- temporarily give up too cold and hot food, carbonated drinks, spicy and sour foods;
- do not visit the sauna or bathhouse for a week after surgery;
- limit physical activity and do not overload your jaw muscles.
Full recovery takes on average 14 days.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a degenerative process that affects all periodontal structures. Its distinctive feature is the absence of inflammation on the gingival margin and periodontal pockets. The course of periodontal disease is always chronic.
According to severity they are distinguished:
- a) mild – exposure of tooth roots up to 4 mm;
- b) average – 4-6 mm;
- c) heavy – more than 6 mm.
The prevalence of periodontal disease is generalized.
Flap surgery is a periodontal operation that involves cutting out and folding a mucoperiosteal flap, followed by careful treatment of the surfaces of the roots of the teeth, bone pockets and the inside of the flap.
The advantages of this operation are the complete removal of pathologically altered tissues under full visual control.
Operation stages:
- the mucoperiosteal flap is cut out and folded back,
- subgingival dental plaque and granulation tissue are removed using an ultrasonic tip and curette,
- antiseptic and antibacterial treatment of periodontal tissues,
- if necessary, implantation of bone tissue,
- the flap is then placed in place and secured with sutures.
- Next comes the application of a healing bandage.
- After a week, the sutures are removed.
Curettage is the removal of pathological tissues around the tooth (supragingival and subgingival calculus and granulations). There are closed and open curettage. The essence of these manipulations is to clean periodontal pockets using special instruments - curettes.
In this case, pathological tissues are removed mechanically (with constant irrigation of the surgical field with antiseptic liquids), which are irritants that support inflammation.
It is important to realize that if pathological tissue is not removed, the process will worsen due to the presence of that same irritant. Ultimately, this will lead to the loss of a tooth, which, by the way, may be completely healthy.
Splinting of teeth is a manipulation aimed at combining mobile teeth into a single block, the so-called “splint”. Splinting is most often carried out in the area of the lower incisors, because It is they who suffer more during the generalized process of periodontitis or periodontal disease. To do this, a special wire or an orthodontic retainer is glued to the composite material on the inner surface of the teeth undergoing splinting.
Before installing a splint, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene - remove stones, plaque and thoroughly polish the surfaces of the teeth.
Gumplasty is an operation to correct changes in the appearance of the gingival margin, in the form of excessive growth, or vice versa - recession (reduction in the volume of the gum, accompanied by exposure of the tooth root). Gum plastic surgery is often performed to achieve maximum aesthetic effect. For example, in orthopedic dentistry to increase the clinical height of the crown, when forming an ideal smile. Also after patch surgery, implantation, surgical treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis, etc.
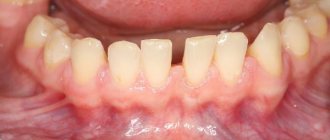
Recession is a decrease in gum volume, accompanied by exposure of part of the root. Recessions can be localized or generalized.
Recessions arising from:
- structural features of the jawbone - when the teeth have a massive root, and the bone in this area is thinned.
- negative microbial flora – the presence of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year.
- chronic trauma to the gingival margin. This occurs more often due to improper brushing of teeth (incorrect brush movements, use of brushes with hard bristles, often the use of electric brushes).
- bad habits - using toothpicks, matches to clean the contact surfaces of teeth, biting pencils and other objects.
- external trauma of teeth in the form of dislocations accompanied by chipping of the edge of the socket.
- orthodontic pathology.
During recessions, patients mainly complain about an aesthetic defect and also about increased sensitivity of the teeth. The problem of recession can be solved either orthodontically (if the cause of recession is orthodontic pathology) or surgically.
Surgical methods for treating recession include various types of plastic surgery:
- Moving the pedicle flap
- Relocation of the free flap, with the autograft most often taken from the palate.
- Moving the gingival trapezoidal flap coronally to the defect area.
After surgery, a healing period begins and in less than a month, the patient sees the result.
Methods of vestibuloplasty
The vestibuloplasty operation is performed under local anesthesia using a scalpel or laser. Depending on the specific case, various surgical techniques can be used:
Open methods
. The vestibule of the oral cavity is deepened by dissecting the soft tissues and exfoliating part of the mucous membrane. After surgery, wound surfaces remain on the alveolar process and the inside of the lip, healing of which occurs by secondary intention.
Closed methods
. At the end of the operation, the wound surface is covered with soft tissue and sutures are applied using catgut.
Methods involving the use of mucous and skin flaps, autografts to restore the wound surface.
Methods that involve the use of special plates of soft material to form the vestibule. The patient wears such plates for two to three months after surgery.
Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the lips and tongue
The frenulum is a connective tissue cord present on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. There are frenulums of the upper and lower lip and tongue.
If the frenulum develops incorrectly, various functional disorders develop.
- with a short frenulum of the tongue in children, there is a violation of the pronunciation of individual sounds; by the age of 15-18, this can lead to exposure of the necks of the teeth on the oral side.
“How to determine that a child has a short frenulum?” There are the following signs of a short frenulum of the tongue:
- child's speech delay
- The frenulum does not start from the middle of the tongue, as is normal, but is woven into its tip
- if you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, the tip of the tongue bends downwards
- If you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, it splits
- if you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, then ischemia (blanching) of the frenulum is visible
- with a short frenulum of the lip (most often observed on the upper lip), there is a gap between the central teeth (diastema)
Signs of a short frenulum of the lip:
- blanching of the frenulum when the lip is pulled back
- presence of diastema
- low weaving of the frenulum (directly into the gingival margin).
With age, a short frenulum of the lip can lead to exposure of the necks of the teeth.
The short frenulum of the tongue can be stretched with the help of speech therapy exercises, but with severe pathology, surgery is necessary - frenulotomy (dissection of the frenulum).
Diastema can be corrected with the help of orthodontic structures, however, if the cause, in the form of a short frenulum, is not eliminated, over time the teeth will return to their original position.
The most effective treatment for short frenulum of the lips and tongue is surgical excision. Excision of a short frenulum is a fairly simple operation, it takes little time and healing also takes place in a short time.
Oral plastic surgery
The need for oral surgery may arise for various reasons, such as orthodontic or speech therapy. But most often this is due to the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases.
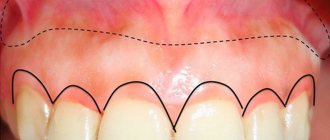
About 20 percent of people have a shallow oral vestibule. This is the space limited by the lips and cheeks on the outside, and the gums and rows of teeth on the inside. For the vestibule of the oral cavity, the normal depth is 5-10 millimeters. If the depth does not reach 5 millimeters, the dentist diagnoses a shallow vestibule of the oral cavity. Because of this, a number of dental problems arise (gum recession, periodontitis, and others). In an infant, this can lead to impaired sucking function. If a pathology is detected, the patient is recommended to undergo plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity, or, as it is also called, vestibuloplasty.
How much does vestibular plastic surgery cost?
Cost of plastic surgery (the exact cost of treatment is determined during consultation)
| Name | rub. |
| Plastic frenulum of the tongue | 3500 |
| Lip frenuloplasty | 2500 |
| Plastic surgery of the oral vestibule | 6000 |
| Gingivotomy | 500 |
| Gingivectomy | 750 |
| Flap surgery | 7000 |
| Gum recession plastic surgery | 10000 |
| Diathermocoagulation | 500 |
What are the stages of preparation for prosthetics?
Before starting the procedure to deepen the vestibule of the mouth, the Red Gate, the dentist carefully examines the oral cavity using x-rays, as well as special devices and instruments. This makes it possible to evaluate existing pathologies and choose the most suitable one among the available vestibuloplasty techniques. Further activities consist of performing the following steps:
- professional cleaning of mineralized plaque from the front side of the incisors;
- Before the procedure, the patient must stop using medications and painkillers not prescribed by the dentist;
- 6 hours before the procedure for deepening the vestibule of the mouth Red Gate, do not eat solid foods, so as not to damage the soft tissues;
- Before surgery, thoroughly brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush;
- It is advisable for the patient to tune in to a positive result.
How does the procedure work?
Surgical intervention to deepen the vestibule of the mouth Red Gate begins with anesthesia. Anesthesia can be general or local, it all depends on the method chosen. Basic techniques of vestibuloplasty:
- The open technique involves changing the depth of the threshold, while a wound appears on the surface of the alveolar part and lip, healing in about 2 weeks. It is performed by dissecting the mucous layer of the lower lip by cutting in the area of the anterior incisors. The resulting flap is peeled off; it is based on a transitional fold near the dental elements. The soft tissue is moved to the required depth, this helps increase the distance. The detached piece of tissue is placed next to the process of the alveolus of the lower jaw, then it is sutured. The wound that appears on the mucous surface is sutured, after which it heals by secondary intention.
- The closed method of deepening the vestibule of the mouth, the Red Gate, involves closing the wound formed after the procedure with soft adjacent layers. Here the gum is cut off through a barely noticeable vertical incision. In this case, the mucous membrane is almost not damaged, and therefore the healing process takes place quickly.
- The flap option consists of making several vertical and horizontal incisions, with the help of which the gum margin is excised to create a flap. Next, each flap is placed on a designated area of the dental line and secured with suture materials. This technique is indicated when exposing the necks and roots of the incisors.
What inconveniences can occur if vestibuloplasty is not performed?
If you do not perform an operation to deepen the vestibule of the mouth, the Red Gate, then this will lead to the following consequences:
- the appearance of a repulsive, pungent odor;
- recession;
- rapid development of periodontal diseases. The reason is destabilization of blood circulation in the gum tissues, or their damage due to eating hard foods;
- formation of pathological periodontal pockets;
- inhibition of the development of the jaw region;
- inflammation of the mucous surfaces in places of strong gum tension;
- speech therapy disorders;
- mobility of incisors;
- formation of a distorted bite;
- tooth roots are exposed;
- development of deformation of the jaws and teeth.
Causes and consequences
The defect can be congenital or acquired. In the latter case, the negative factors that act as the cause of the pathology include mechanical injuries received during surgical operations for non-union of the upper lip, elimination of burn areas or the consequences of mechanical injuries.
The disease significantly reduces the protective functions of the periodontium. Insufficiency of the vestibule leads to distortion of the bite, excessive mobility of the dentition and adentia, poor circulation, inflammation and muscular jaw atrophy, and can also cause the development of periodontitis.