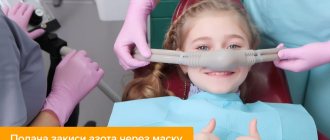
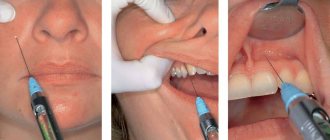
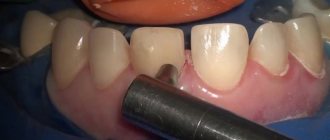
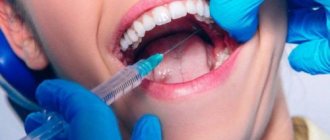
A new advanced system of dental treatment for children - sedation - has become available at the Marina Kurchaninova Smile Dentistry Center. A system that has long been used by specialists from Europe and the USA.
The discoverer of nitrous oxide was the English scientist Joseph Priestley, who first synthesized this substance in 1772. However, the pain-relieving properties of nitrous oxide were discovered by another researcher, Humphry Davy. He also gave the name to the new substance – “laughing gas”. This name is completely true - when inhaling this gas, a person falls into a slight euphoria, a very pleasant state. In addition, his pain sensations (if any) disappear, as well as the ability to experience them for some time.
ZAKS began to be used in dental practice in 1948, and to date, about 80% of cases of treatment of children cannot be done without the use of this drug.
Basically, all pediatric dentistry technologies that are now widespread in Russia are aimed not at treatment, but at healing teeth. The current situation is quite understandable - this is all that can be done during the time until the child agrees to open his mouth.
Now dentists have a tool that helps them provide full treatment to young patients - sedation.
What is sedation, in short?
Sedation is a superficial sleep in which the patient can be awakened at any time. This method is aimed at calming the patient so that the specialist can carry out all the necessary dental procedures. Sedation is an excellent addition to traditional anesthesia and is carried out using special sedatives.
Each physician may have individual sedative preferences. However, throughout the world, the greatest respect has been earned by such a drug as nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation (NAS). It is a mixture of inert gas and oxygen, which has an indistinct sweetish odor. The use of the mixture ensures the most harmless and safe sedation.
The sedation procedure is simple: the patient puts on a mask and inhales ZAC. After which he has a feeling of calm and relaxation. Nitrous oxide is supplied using special equipment. Exhaled gases are immediately collected by high-speed suction.
The resulting state is reminiscent of the sensations that we experience on a summer day after rain, when an increased nitrogen content appears in the air. We experience a feeling of joy, pleasure and pleasant relaxation.
The effect of laughing gas is short-lived. Within just a few minutes it is completely cleared from the lungs. Laughing gas is completely safe - when taken, heart rate and blood pressure remain normal, and there is no addiction to it.
Treatment of children after sedation is quick, effective and, importantly, leaves pleasant memories for the children. The child is in a state of light anesthesia, but at the same time he is conscious and able to communicate normally with the doctor. The use of nitrous oxide greatly facilitates the process of dental treatment for both participants in the process - both the doctor and his little patient. In addition, children develop a positive attitude towards visiting the dentist, and this also makes life easier for their parents.
Children willingly put on bright masks and inhale the sweet aroma. Their use makes the procedure even more enjoyable for the child.
Which anesthesia option is better?
So, we went over the main properties of drugs for general anesthesia.
Now let's look at which options are better in each specific case. There are no identical children, they are all different. Some children will calmly accept the placement of a catheter at a very young age, while others will refuse a painless mask at the age of eight or nine. Therefore, we always carefully communicate with both the baby himself and his parents. This is necessary to establish trusting contact between the doctor and the little patient. Without this, it simply won’t be possible to work normally. At the same time, the most detailed information on the child’s health characteristics is collected so that the anesthesiologist can choose the most comfortable and safe option for general anesthesia. Interestingly, children very quickly begin to trust doctors if they see that everything was painless and the tooth no longer bothers them. As a rule, further treatment is much easier. We had a case when a girl fell from a swing in kindergarten, hit herself and lost an artificial crown, which almost three of her had to install. As a result, she returned to the clinic with her parents, brought the crown in her palm and asked to return it to its place.
Local anesthesia only
Suitable for
: brave children of all ages who trust the doctor.
This option is a little beyond the main topic of our post, but I also want to mention it. If a child initially comes with a bunch of damaged teeth, and for some reason intimidated by relatives, then such a scenario may be impossible. But it is necessary to treat. This is where the entire arsenal of general anesthesia tools will help us.
Local anesthesia and nitrous oxide
The child should have free nasal breathing. Nitrous oxide has a bunch of effects that we need. It relaxes, eliminates anxiety, and slightly improves your mood. The patient will be conscious during treatment. At the same time, in its pure form it will not be possible to numb the pain; preparing teeth will still be painful. Therefore, we usually let the child breathe through a special mask that covers only the nose. Many people really like this, plus we often tell stories about test pilots who also have special masks with a breathing mixture.
When the child relaxes, you can apply topical anesthesia with gel and then inject the main anesthetic. Unfortunately, under nitrous oxide it will not be possible to do a large amount of intervention at once. Children get tired of lying with their mouths open, and the mask begins to irritate them. Therefore, this method is better suited for small one-step interventions - one or two teeth. At the same time, we cannot increase the concentration above 50% for a child; we need to look for other, stronger, but safe drugs.
Local anesthesia and sevoflurane
Sevoflurane can be given to school-age children without any problems, but there are several nuances.
With older children, it is easier to agree on local anesthesia while awake or the use of propofol with intravenous administration. There are several advantages to completely turning off consciousness, which does not happen with nitrous oxide. Firstly, the child does not experience extreme stress and does not develop dental phobia for the rest of his life. There is nothing worse than a stern nurse who kneels on you and holds a mouth opener while the doctor frantically tries to do something in the oral cavity.
Secondly, this allows for high-quality treatment when the doctor is confident that the patient will not twitch, start waving his tongue, or try to run away in the middle of an important stage.
The anesthesiologist can vary the depth of anesthesia by changing the composition of the gas mixture. This makes it possible to accurately monitor the patient’s vital signs and ensure the desired level of relaxation and immobility. If you need to treat caries, then there is no point in injecting an additional anesthetic. The degree of CNS suppression is sufficient to make the patient comfortable. If you plan to treat pulpitis or periodontitis, or remove teeth, we additionally administer a local anesthetic. Otherwise, pain impulses will still reach the “sleeping” brain and cause a surge of adrenaline and involuntary movements. When consciousness is completely turned off, we can carry out any amount of intervention. Moreover, we are talking not only about some painful things like treating six carious teeth in one go, but also, for example, about taking accurate impressions for the subsequent production of orthopedic and orthodontic structures. Try convincing a sobbing four-year-old that he needs to sit still while the silicone in the impression tray hardens in his mouth.
Local anesthesia and propofol
This is prohibited for a child under three years of age to use. We have already discussed the features of propofol above. It does not have an analgesic effect, but only suppresses consciousness. This is why it must be supplemented with local anesthesia, as if the patient were awake. But its main advantage when working with teenagers is that they can follow simple commands. This makes the doctor's work easier. You can reduce the depth of anesthesia and ask to bite down on a template, model the structure based on the bite, or something similar. It is important for the dentist not just to depict fillings at the site of carious defects, but to carefully model the occlusal relationships of the jaws so that after treatment the biomechanics of chewing are ideal.
Benefits of using sedation in children
Therefore, we can say with confidence that the use of sedation has undeniable advantages. Among the advantages of the method are the following:
- The use of ZAX (nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation) makes dental treatment painless;
- The child does not experience psychological discomfort in the doctor’s office: in a state of sedative anesthesia, he does not smell unpleasant odors, does not hear the frightening sound of a drill, and does not distinguish between medical instruments;
- The use of ZAX removes tactile sensitivity, so the baby will not be frightened by vibrations, pressure, compression, etc., made by the doctor;
- The doctor is able to provide full treatment, because his access to the patient is no longer hampered. Now the dentist has enough time to apply the most effective modern treatment methods. He can also use any preparations, even those that harden for a long time;
- The risk of complications after dental treatment is reduced.
The use of sedation has ushered in a new era in pediatric dentistry. After all, doctors now have the opportunity to use modern composite materials for treatment. And they are more durable, hygienic and aesthetically pleasing compared to those previously used. Until recently, composite materials were not used for the reason that their placement requires careful drying of the tooth. The doctor must also wait a long time for the material and fixing glue to harden. Now he has the necessary time reserve.
Coming out of a sedative state
At the end of treatment, the anesthesiologist turns off the nitrous oxide supply and increases the oxygen supply through the mask, which ensures faster removal of nitrous oxide from the patient's lungs. 5 minutes after the end of the treatment procedures, not even a trace of the sedative remains in the child’s body. Local anesthesia wears off after 1.5-2 hours. The child does not experience any consequences (such as dizziness or nausea, familiar to many from the effects of surgical anesthesia) after sedation. In rare cases, after sedation, a child may remain in an unusually calm state until the end of the day.
How to prepare for the sedation procedure?
It is necessary to strictly adhere to the recommendations given by the doctor, namely:
Before performing drug sedation, it is necessary to do a general blood test, coagulogram, ECG, biochemical blood test, tests for HIV, HCV, HbsAg, Rw. These studies are required for the safety of the patient himself. General preparation for the procedure is usually carried out directly in the dental clinic itself. Patients are advised to refrain from eating and drinking 4 hours before the procedure.
The doctor should be aware of whether the child has respiratory problems, in particular whether he has difficulty breathing through his nose. In the case of such diseases, the sedation procedure loses its effectiveness to some extent. Be sure to tell the dentist what medications your child took on the day of the clinic visit.
Preparation and stages of the procedure
Children do not require any special preparation for treatment under sedation. If you are very worried and in doubt, you can take a general blood test, give your child a cardiogram, show the doctor a medical card that notes previous and chronic diseases, and tell about your doubts.
Otherwise, it is better to try to avoid strong emotions on the eve of the procedure and do not feed the child too much. If your child is quite sociable, then you don’t have to tell him about the procedure - the doctor himself will explain everything to him. If the baby does not trust anyone except his parents, then you can prepare him in advance by telling him in general terms what the doctor will do.
In the office, before the procedure begins, the doctor will explain to the little patient what sensations await him, and during the game he will help him climb into a chair and put a “space” mask on his nose. After just a few breaths, treatment can begin. The baby will watch cartoons or listen to what the doctor is saying, while the dentist performs the required therapeutic actions.
Sedation scheme
The patient puts on a mask, and 100% oxygen first enters his lungs. The oxygen mass is supplied at a speed of 4-6 liters per minute. Nitrogen is gradually mixed with oxygen. Its content is increased to 30%. When the proportions of nitrogen and oxygen are brought to a ratio of 30 to 70, respectively, the moment comes favorable for starting treatment. However, it should be noted that the concentration of nitrous oxide may vary depending on the individual patient. It is important to achieve the desired effect, and it, in turn, can occur with a different ratio of nitrogen and oxygen. Individual indicators are recorded in the patient's record.
The blood is saturated with gas in about 5-7 minutes. Nitrous oxide is completely dissolved in blood serum and is not biotransformed in any way. As soon as the supply of ZAX stops, the process of removing gas from the lungs begins. The gas is removed completely unchanged.
ZAX differs from other sedatives in that the sedative effect occurs very quickly, and the trace effect is completely absent. This is caused by nonspecific depression of the central nervous system.
Sedation manifests itself as follows: a comfortable and relaxed state; good, elevated mood; movements are inhibited; deep breathing; motor activity of the eyes is reduced; sound perception is dull; resistance is reduced.
If you plan to undergo a particularly painful procedure, you can temporarily increase the concentration of nitrous oxide to 50% (acceptable limit is 70%). Nitrous oxide has an analgesic effect, and also enhances the effect of local anesthetics. If the child is suddenly frightened and painful sensations begin to “reach” him, manipulation with nitrous oxide will quickly calm the baby down and treatment can be continued.
Thus, the use of ZAX makes it possible to carry out treatment of any complexity in just one visit.
As for removing the patient from the state of sedation, it occurs smoothly and consists of supplying 100% oxygen for 5-10 minutes. At this time, the doctor communicates with the child, trying to reinforce his positive impressions of visiting the dental office.
In general, the successful use of ZAX is impossible without the competent use of behavior management techniques. Trying on a mask by a child should be done in a playful way so that the child has time to relax before the onset of sedation. The doctor calms the child by telling him about the condition he will soon find himself in. You cannot force a mask on, as this may cast doubt on the success of the procedure.
The use of nitrous oxide in pediatric dentistry
The relaxing and calming effect of nitrous oxide lasts only a few minutes, so the child must breathe the sedative mixture continuously throughout the treatment. For this, a special nasal (worn over the nose) mask is used, which does not interfere with the dentist’s work.
At the Natadent clinic, dental treatment for children under nitrous oxide usually includes the following steps:
- The doctor talks with the little patient, explaining to him what will happen next.
- The child lies down in a comfortable chair, above which there is a large screen with a cartoon.
- The doctor puts a nasal mask on him.
- When relaxation occurs, the doctor begins to work. If necessary, local anesthetics are used in the form of sprays and injections.
- During the entire procedure, the child remains conscious, so the doctor and parents can communicate with him.
- When the treatment is finished, the mask is removed and after a few minutes the child returns to his normal mood.
As you can see, nitrous oxide sedation
has nothing to do with anesthesia. Her main task is to create the most comfortable conditions for the child so that he tolerates the treatment well and is not afraid of the dental office in the future.
Is sedation with ZAX safe?
Yes, it's safe. ZAX is completely harmless for children. Moreover, today it can be called the safest sedative. It is easy to use, is eliminated from the body without a trace, does not have a heavy or overly strong effect, and is not addictive. The child remains conscious, his breathing is not difficult, all reflexes are preserved. The use of ZACS ensures maximum safety, complete controllability and early activation of the patient.
You may have doubts about how well this technology has been tested. Despite the fact that it represents an innovation for Russia, ZAX sedation has long been used throughout the world (more than 30 years). The vast majority of pediatric dental clinics in the USA, Israel and the UK use ZAX as the main sedative. Thus, this technology can only be called new conditionally - it has long been tested and approved by professionals.
FAQ
Is it possible to eat before anesthesia?
No you can not. And parents need to not only tell their child about this, but make sure that he doesn’t eat too many cookies from his secret reserves. The child is hungry, he will try to eat at least something. Anesthesia on a full stomach may result in vomiting during treatment or upon awakening. If it is “in the process of treatment,” then the substance can block the airways, which is not necessary for anyone.
How easy is the anesthesia to tolerate?
If all protocols are followed and the process is monitored by an experienced anesthesiologist, then everything goes without problems or any special side effects.
To do this, we comply with all protocols and everything that is necessary for complete safety. For example, here is a study that suggests that with proper anesthesia with propofol and isoflurane, all side effects after waking up last less than a day. But sometimes our hair just stands on end when a mother comes to our clinic after a not very proper anesthesia in another place. We usually catch these parents with a week's worth of food and the moral expectation of three days of continuous vomiting and dizziness after waking up. Here you immediately understand that in another place the general anesthesia did not go quite right.
Will he really wake up?
Yes. It's not a matter of probability, it's a matter of following protocol. You need to check the equipment, have a doctor with the required qualifications, and understand the characteristics of a particular patient. Then there will be no surprises. The process is closely monitored by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, who is ready to intervene at any time and adjust the anesthesia parameters. He knows how to smoothly introduce and recover from anesthesia, and knows all the nuances of resuscitation measures in children.
I was told about doctors who are against anesthesia
Yes, this happens.
But I think that they are not entirely right and they simply do not have a good anesthesiologist. The safety of general anesthesia for the health and mental abilities of the baby is confirmed by numerous studies. For example, they took 19,296 children and studied their development after many anesthesia experiences up to the age of 20. The results prove that everything is fine, and the children are no different from their peers. At the same time, many sources still come to the conclusion that repeated anesthesia before the age of two is undesirable. In general, sometimes misunderstanding and fear of general anesthesia take strange forms among some doctors. I remember one wild case when a doctor tried to protect children from terrible anesthesia by replacing it with temporary suffocation with a towel. Binds, holds and treats half-strangled. Such a kind doctor. Moreover, in fact, she uses a version of raush anesthesia. It’s just that it was relevant several hundred years ago, when even ether anesthesia was not invented, and the only option to carry out a conditional amputation was a precisely calculated blow to the crown of the head with a wooden mallet. But it was difficult to control the “depth” of such anesthesia and guarantee successful awakening.
What happens to the eyes during treatment?
The eyes dry only during deep anesthesia; in our case, they are sufficiently moistened with tears. The patient's eyelids are fixed with a special plaster. This way the eyes remain closed and the mucous membrane does not dry out. Well, there is no risk that something could get into them.
Will hair fall out after surgery?
I know it sounds strange, but parents ask this. The point is this: if you lose a lot of blood during surgery, hair loss may be a side effect. But when a mistake is made in surgery, it is most often attributed to uncontrollable factors in the spirit of: “This is a drug for anesthesia,” and not to the fact that someone was unable to perform the manipulation on time or did not make the right decision. And the anesthesiologist has nothing to do with it.
Will this affect the child’s memory or damage the brain?
It won't have any effect - neither good nor bad. The anesthesiologist carefully monitors the saturation level so that the young brain receives enough oxygen. The device does not supply pure gas, but mixed with oxygen. All sensors are built into the ventilator. If necessary, the doctor can, for example, adjust the composition of the gas mixture. All drugs have an excellent safety profile and a bunch of studies confirming their safety when used in pediatric patients. We also know how to work quickly. If on very voluminous interventions we used to work for six hours, then up to four, up to three, now the average duration is no more than 2.5 hours: this, in particular, is why technology and a professional team are needed.
Will he have bad dreams?
Will not. The child will not remember the process of anesthesia itself and, most likely, some short period before it. Just try not to frighten him again: children are very impressionable. Then we will try to make everything as comfortable as possible for him: he fell asleep, woke up, and then played.
Differences between sedation and general anesthesia
1) The occurrence of coughing, swallowing and other reflexes is excluded, which in turn allows for complete dental safety.
2) The dentist can fully control the patient’s condition, since he is conscious throughout the entire procedure. Another advantage of the action of sedatives is the fact that a person under its influence can be taken out of a state of superficial sleep at any time.
3) The patient is in a relaxed state and can communicate with the doctor.
Very often, due to anxiety, a person cannot clearly formulate his problem, and the patient’s internal tension can complicate treatment. Sedation makes it possible to relieve emotional stress without causing harm to the body. Also, when a person experiences psychological stress, hemodynamic changes occur. High blood pressure and rapid heartbeat force the attending physician to make certain changes to the given treatment regimen.
Depth of anesthesia
Let's generally understand what anesthesia is.
Our brain is a complex set of neurons that constantly exchange impulses with each other. Some substances can inhibit synaptic transmission between certain groups of neurons. Moreover, different substances have different mechanisms of action and their own characteristics. In fact, anesthesia is also a type of anesthesia. Only in contrast to the local shutdown of local pain neurons, with local anesthesia we partially “turn off the brain.” As a result, general anesthesia is not like completely “turning off” the brain. This is rather a kind of very deep sleep, from which you can wake up only when the anesthesiologist allows it. What is suppressed first? For starters, this is consciousness. The main purpose of general anesthesia is to reduce the patient's stress level. We want to make sure that the entire treatment goes unnoticed by him and does not leave any unpleasant memories. In addition, pain sensitivity is suppressed and motor activity is inhibited. That is, with proper anesthesia, the patient is not in pain, and he does not try to get up and leave, pretending to be a sleepwalker.
Of course, suppression of the functions of the central nervous system should turn off only consciousness and pain, without affecting the important autonomous centers for the regulation of heartbeat, respiration and vascular tone. Only experienced doctors can provide all this correctly. There are usually four degrees of anesthesia depth:
- Superficial anesthesia.
- Light anesthesia.
- Full anesthesia.
- Ultra-deep anesthesia.
If necessary, the anesthesiologist can vary the degree of CNS depression, for example, to ask the patient to move the jaw correctly.
This can be done when using propofol, for example. Or, conversely, increase the depth if the patient begins to worry. Why are such methods needed at all if there is a conditional local articaine, which can most often be done? The problem is primarily panic fear and dental phobia. A good patient is a calm patient, not one who tries to run away in horror and flinches at every move the doctor makes. This will not benefit the patient himself and will not help the doctor to properly treat him. Additional arguments in favor of anesthesia will be a very pronounced gag reflex and a large volume of intervention. We cannot simply inject anesthetic into a patient, especially a small one. The local anesthetic also has maximum dosages for simultaneous administration, and, for example, bilateral conduction anesthesia on the lower jaw can cause difficulty breathing due to the complete loss of tongue sensitivity. Well, and most importantly, even the most sensitive doctor will never agree with a child to treat 15–20 teeth at the same time. Yes, it also happens when children do not brush their teeth properly, eat buns and do not go to the dentist.
Therefore, oddly enough, general anesthesia can often be an easier and more comfortable choice for a young patient and the attending physician.
Recommendations for using sedation
In dentistry, this method is used if the patient wishes, when he wants to receive the most comfortable and safe treatment. Dental specialists recommend resorting to drug sedation in cases that require the patient to remain in the dental chair for a long time. This may include surgical manipulation of the maxillary sinuses and other long-term operations.
Sedation is very convenient during orthopedic procedures, which can last up to 12 hours and involve putting the patient into a sleep state. In case of diseases of the cardiovascular system, psychiatric and allergic reactions, the possibility of using sedatives is discussed individually in order to avoid undesirable manifestations.
Modern specialists are actively finding the use of drug sedation in the field of prosthetics, implantology and surgical dentistry. Sedatives are widely used because they are absolutely safe and do not have a narcotic effect on the body and are not addictive. The great advantage of using sedation in dentistry is the parallel use of the necessary equipment and a special cardiac monitor, with which it is possible to monitor the patient’s condition, which almost completely eliminates any complication.
At what age can teeth be treated with sedation?
Most often, teeth can be treated under sedation starting from the age of 3 - it is from this age that the child can already contact the doctor, understand what he wants, and fulfill his requests.
Up to 3 years, if long-term extensive treatment is necessary, anesthesia is used. The duration of treatment under sedation depends on the dental treatment, but can be up to 1 hour.
This is due to the effect of the anesthetic, which the doctor administers before starting treatment, and the fact that it is difficult for the child to sit in one uncomfortable position for more than 1 hour. During this time, you can treat 2-3 teeth in one area of the dentition. When using sedation, an individual approach is required - the doctor focuses on the patient, his condition, and the duration of dental procedures.