Dentistry includes 4 specializations: therapy, surgery, orthodontics, orthopedics. Most dental patients do not understand why they are referred to a podiatrist's office if that doctor specializes in treating and correcting the musculoskeletal system. The article will discuss the question of what an orthopedic dentist does and what issues they turn to him for. We will also consider the types of orthopedic systems called prostheses, bridges and implants.
Table: how to figure out who to contact
| What's troubling? | Which dentist should I contact? |
| Bleeding gums/Teeth sensitivity | Hygienist or periodontist |
| Missing teeth | Orthopedist |
| Have crooked teeth/bad bite | Orthodontist |
| Tooth hurts / The wall has broken off / There is caries | Therapist |
| The wisdom tooth is painfully erupting / Swelling has appeared on the side of the cheek | Surgeon |
All dentists conduct an examination, consultation, draw up a treatment plan and perform a thorough diagnosis of the entire oral cavity. In modern dentistry, an integrated approach to each clinical situation is valued, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
What is orthodontics?
Orthodontics is a field of dentistry dedicated to the study, correction and prevention of developmental disorders of the dentition and abnormal bite formation.
Studies have shown that more than 90% of people have deviations in the development of the dental system. More than half of them require mandatory treatment . And this is where orthodontics can help.
Modern methods make it possible not only to successfully solve problems of smile aesthetics, but also of the profile as a whole. Orthodontic treatment can be carried out equally successfully in both childhood and adulthood.
Dentist-therapist
The main field of activity of this doctor: treatment and prevention of caries and its complications. What manipulations does:
- treatment of caries;
- endodontics (work in root canals) for pulpitis, periodontitis;
- root canal retreatment;
- chipped fillings, tooth walls;
- carrying out treatment using a microscope (treatment of caries, work in canals);
- providing assistance for acute toothache.
The therapist also conducts a thorough examination and can refer the patient to related specialists if he notices any pathology.
Features of treatment for children
Many people believe that going to the dentist during the period of baby teeth is not necessary for anyone. The prevailing opinion that temporary crowns will fall out and problems will be solved on their own is fundamentally wrong. It is at the stage of formation of a temporary bite that the foundations of a permanent one are laid.
If a child has problems with the formation of dentition, then this period is the best suited to obtain a positive result in a short period of time. It is worth remembering that the older the child, the longer the treatment will take.
One of the main problems during the period of temporary occlusion or its change may be premature tooth loss. This often leads to displacement of adjacent crowns, malocclusion and difficulty in the eruption of permanent teeth.
To prevent this from happening, the orthodontist installs a temporary crown or spacer that fixes the required distance for the formation of the dentition.
Orthodontic correction in children allows for the normal development of the entire maxillofacial system , the abnormal development of which often leads to the occurrence of common diseases.
For this, braces, special removable plates, mouth guards and other means that do not harm the child are used.
In order to conduct a detailed diagnosis, the orthodontist relies on the following factors:
- type of feeding;
- genetic predisposition;
- timing of eruption;
- the presence of common diseases that provoke dental abnormalities;
- the presence of solid foods in the child’s diet;
- baby's habits;
- sleeping position.
The most appropriate age to begin treatment with an orthodontist is 3 years , until the temporary occlusion begins to affect the formation of the jaw muscles and tooth growth.
Dental hygienist
A dental hygienist has a secondary professional medical education. A prerequisite for working as a hygienist is to successfully complete the course “Preventive Dentistry”. What does a dental hygienist do:
- professional oral hygiene;
- treatment of gums with the Vector device;
- whitening;
- provides training in proper oral hygiene;
- selection of personal hygiene products;
- deals with the prevention of gum disease in adults and children.
In short, the main area of work of a dental hygienist is the removal of dental plaque (tartar, plaque). It is important to see a hygienist every six months to maintain oral health.
Is it difficult to become one?
The work of an orthodontist is very painstaking and hard work, which most often pays quite well. To obtain this qualification, you also need to work hard.
To do this, you need to go through several steps:
- Studying at a medical university at the Faculty of Dentistry.
- Completion of residency or internship in the specialty “orthodontics”.
- Receiving additional training in dental courses.
On average, the main period of study lasts about 8 years.
Orthopedic dentist
Dental services include dental prosthetics. It is the orthopedic dentist who deals with all types of dental restoration using orthopedic structures. These include:
- crowns;
- bridges;
- veneers, lumineers;
- inlays, overlays;
- mouthguards, splints;
- temporary structures for long-term orthopedic treatment;
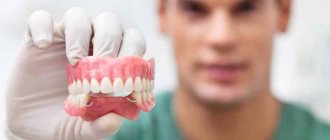
- removable and fixed dentures;
- prosthetics on implants.
Prosthetic methods
Let's consider all the methods of installing prostheses and implants known to modern orthopedics.
Microprosthetics
The method is indicated when it is inappropriate to install a filling on a crumbled molar: if the tooth walls are severely damaged, but the root is intact. To save the unit from further deterioration, lumineers or veneers are installed. These are dental onlays made of ceramic or other dental material.
In orthopedics, dental inlays and dental onlays are used. An onlay is a plate that is fixed to the tooth enamel of the front part of the crown. Inlays cover the dental canals. They are used to restore chewing lateral molars.
Microprosthetics has no analogues; it is the fastest and most gentle way to restore the integrity of teeth.
How are veneers different from lumineers? To install veneers, grinding is required; lumineers are fixed to the front part of the teeth walls without preliminary grinding of the enamel coating. They are much thinner than veneers. The disadvantages of veneers include the impossibility of installing another type of prosthesis after removal: only the same ones. This is due to the grinding of the enamel layer during installation. Turning is necessary due to the thick layer of veneer plates.
To fix lumineers, turning is not necessary, because the thickness of the plates does not exceed 0.03 mm. But lumineers do not hide all aesthetic imperfections. For example, they do not mask chips in the enamel, unlike veneers.
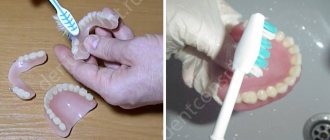
Removable dentures
Removable dentures are available to everyone due to low prices, and discounts are provided for pensioners. The disadvantage is that turning healthy units is a painful and tedious procedure. Next, the doctor makes a plaster cast and sends it to the laboratory, where a technician models the removable structure.
Removable dentures differ in design features, price, fastening method, and material. These structures provide a solid base to which artificial dental crowns are fixed. In edentulous cases, removable dentures are secured with dental glue. If molars are partially lost, they are fixed to the remaining units in the jaw.
Methods of attaching prostheses:
- staples-clasps;
- locks (attachments);
- pilots;
- telescopic devices.
Clasps are iron brackets that cover the supporting units and securely fix the structure in the oral cavity. They are made in the shape of a semi-arc. The butterfly prosthesis is secured using clasps. This is an orthopedic design whose shape resembles the wings of a butterfly.
Plate dentures are a plate-shaped base to which artificial crowns are attached. This design is easy to put on and take off, and is easy to care for—no need to stick it to the gum.
Removable plates are installed for children who have lost their baby teeth. They help keep your teeth straight.
Clasp prosthetics are used when the patient cannot pay for implantation, and fixed structures cannot be installed. Clasp dentures are an arch on supports on which artificial crowns and acrylic gums are installed. The advantage of this design is the absence of surgical intervention to increase bone mass or the use of a flap technique for restoring the gum edge, as well as an open palate.
However, there are also quite a few disadvantages:
- it takes time for the jaw to adapt to a foreign object;
- daily care of the prosthesis is required;
- the patient cannot remove the prosthesis on his own;
- bone mass continues to decrease due to inadequate chewing load.
Due to subsidence of the bone mass, it is often necessary to replace the old prosthesis with a new one with different parameters.
The best option for the loss of several molars is implantation. Thanks to it, not only the integrity of the dentition is restored, but the patient’s health is also maintained. A full chewing load ensures blood flow to the tissues, and the loss of bone mass stops.
Fixed
Fixed orthopedic structures include bridges and crowns. They are securely fixed in the jaw and can only be removed by a doctor. Single implants are attached to titanium pins implanted into the gums, which replace the tooth root. On top of them are placed artificial imitations of teeth - crowns. If the molar is only partially destroyed, then it is covered with an artificial crown for strengthening and aesthetics.
Metal-ceramic crowns
Crowns are made from various materials - from medical plastic to gold plating. Recently, hypoallergenic crowns made of metal ceramics, which imitate a natural molar, have become widespread. Ceramics reliably protects the mucous membrane from contact with metal alloys, is easy to clean, and does not stain the color of food. Disadvantage: Some metal alloys can cause inflammation in the gum tissue.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
Unlike analogues, zirconium dioxide is not oxidized by saliva. Accordingly, in the absence of oxidative reactions, inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the gums do not begin. When modeling crowns, computer technology is used, which allows you to create sizes and shapes that are as close to natural as possible. Also, models made of zirconium dioxide have a greater choice of colors: this allows you to choose a tone that will not stand out among the dentition.
Solid ceramic
They are installed on the front part of the dentition; they are completely free of metal components. They cannot be installed on chewing molars: they will not withstand the load.
Implants
Unlike crowns and bridges, they are implanted into bone tissue with subsequent fusion. They look like metal screws and are made from special metal alloys. Implants completely replace lost roots; artificial crowns are attached to them.
Bridges
Installed in case of loss of several adjacent molars. The structure with artificial crowns is attached at the edges to supporting units or implants replacing them. Some designs may consist of five artificial teeth.
Types of bridges:
- metal;
- metal-ceramic;
- plastic;
- metal-plastic.
Metal
They are not used in modern orthopedics, although they used to be widespread. Metal bridges are reliable, durable, and inexpensive. But there is a significant drawback: they are heavy, bulky, and can cause an allergy to metal.
Metal-ceramic
Metal-ceramic bridges are also reliable and durable; they have an advantage over metal ones - ceramic lining. But often the metal base is visible through the ceramics, so such bridges are not installed on the front part.
Plastic bridges
Used as a temporary structure to replace the main installation. For example, they are used while waiting for the manufacture of a metal-ceramic bridge.
Plastic quickly absorbs dyes, so plastic bridges and crowns look unaesthetic.
Metal-plastic
More reliable than plastic ones. However, their service life is short - no more than two years. Then the structure needs to be replaced with a new one. With careful use, metal-plastic can last 5 years, but more often bridges fail much earlier.
According to the manufacturing method, bridges are divided into:
- stamped;
- adhesive;
- solid cast.
An adhesive bridge is used to fix one artificial molar. But it is not reliable because it cannot withstand the chewing load. Stamped products are a monolith of soldered crowns; such blanks are called soldered bridges. These models are already a thing of the past. Stamping has been replaced by more reliable casting methods.
The installation of bridges has a list of contraindications, including:
- bruxism (night teeth grinding);
- abnormal bite;
- periodontal diseases;
- pathological condition of bone tissue;
- lack of regular oral hygiene;
- lack of supporting elements or their poor condition.
Bridges are a good alternative to implants, but they have a significant drawback - preliminary grinding of healthy supporting units. They also do not solve the problem of bone tissue atrophy, which inevitably begins to decrease due to the lack of full chewing load.
Pediatric dentist
Treatment and extraction of teeth for patients under 18 years of age is carried out by a pediatric dentist. When working with young patients, the primary task is to find contact with the child and get him ready for treatment, because almost all children enter any medical office with fear. In addition, the children's doctor needs to tell the child's parents how to carry out home oral hygiene for the baby, what products to use, when the physiological change of teeth occurs, etc.
Maintaining dental health from a very early age is necessary for the normal formation of the dental system.
Bibliography
- Bogdan V. E. et al. Prevention of dental anomalies and orthodontic treatment at an early age // Chief Doctor of the South of Russia. - 2013. - No. 6 (37). — P. 4-6
- Kyzina S. L., Rebrova A. E. Orthodontics for everyone // Healthcare of Ugra: experience and innovations. — 2022. — No. 4. — P. 33-38
- Tokarevich I.V. General orthodontics // Educational method. allowance. — Minsk: BSMU. - 2015. - 80 p.
- Khotayt A. Kh., Butvilovsky A. V. Method of manufacturing a non-removable individual retainer // Orthodontics gnathology. — 2022. — November. — No. 2 (3). — P. 22-26
- Kipkaeva L. V., Belkevich V. V. Application of the aligner system in the treatment of dentofacial anomalies in the permanent dentition. Design features. Treatment effectiveness // Orthodontics gnathology. — 2021. — April. — No. 1 (4). — P. 50-55
- Bulgakova A.I. et al. Structure and equipment of dental organizations // Textbook. - Ufa: Publishing house of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education BSMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia. - 2016. - 84 p.
- Ganjali N. T. Braces or aligners? // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences. — 2014. — T. 4. — No. 4. — P. 370
- William R. Proffitt et al. Modern orthodontics // Textbook. — 686 p.
- Demina M.A. Positive and negative aspects of working with orthodontic structures, selection criteria // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences. - 2022. - T. 7. - No. 9. - P. 1440-1442
- Alimirzoev F.A. Modern ideas about complex treatment in orthodontics // Achievements of university science. — 2014
- Shkavro T.K., Pavlova I.A. Orthodontic devices // Textbook. – Irkutsk: IGMU. — 2022. — 32 p.
Gnathologist
Not everyone has heard of this doctor, and this is no accident. This profession is very rare.
This specialist deals with pathologies of the temporomandibular joint. If the patient is bothered by clicking in the joint, pain when opening the mouth, tooth wear, discomfort in the joint when chewing, then it is necessary to contact a gnathologist to eliminate the pathology.
- Pavel
October 7, 2022 at 08:17Thank you for your article, I learned a lot of new things. I had never had any problems with my teeth in my life, so there was no need to understand the areas of dentistry. And now the situation has changed, the first signs of dental ill health have appeared, we have to figure it out. First, I’ll go to my city free dentistry, then maybe I’ll go to a private clinic. Thank you for the clarification
Administrator
October 10, 2022 at 01:37 pm
Hello, Pavla! We are glad that you found the information useful. We invite you to see our specialists if you need dental care.
What diseases are most often treated by an orthodontist?
Most often, patients come to this doctor to correct their malocclusion. Moreover, patients notice such pathologies
Among the pathological bite are:
- Mesial (progenic): in the anterior region, the lower incisors overlap the upper ones or form a direct closure. With this pathology, the patient experiences protrusion of the lower jaw.
- Distal: The upper front teeth protrude above the lower teeth. The front teeth do not close together; upon examination, a gap is visible between them. The lower jaw is behind the upper jaw.
- Crossbite: there is a violation of the facial configuration, a displacement of the chin towards the lips.
Treatment of malocclusion must be started in a timely manner to avoid complications. We recommend that you consult with an orthodontist to determine if your situation has an overbite and how to treat it.
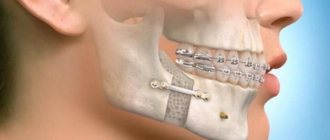
Maxillofacial surgeon
This specialist is needed for those whose bite pathology requires surgery. Usually this is a pronounced mesial bite or a combination of several disorders, especially with a pathological narrowing of the jaw. The operation itself is only one of the stages of treatment; in preparation for it and after it, you still need to wear braces to stabilize the occlusion (closing of the teeth) and improve the aesthetics of the smile.
Surgical correction of the bite: the jaws are given the correct shape, but the teeth still need alignment
Required qualities
We figured out what an orthodontist treats and how to become one, but in this profession, in addition to professional skills and knowledge, human qualities and certain character traits are also important. The course of orthodontic treatment usually takes from one to several years, during which the doctor will have to regularly meet with the patient, and this will require building a trusting relationship with the person.
Trusting relationships and professionalism are the key to successful treatment
Thus, a good orthodontist should not only be a first-class professional, but also a sociable, efficient and patient person. He must be able to win over the patient, calm him down and set him up for successful treatment, which for him can already result in serious stress, especially if we are talking about a child or teenager.
Share in the comments, have you ever had to communicate with an orthodontist? How do you evaluate him and what qualities do you value in this specialist? Your opinion will help many other patients decide on the choice of a first-class doctor.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 6 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
malocclusion
Diagnostics
On average, a diagnosis by an orthodontist takes 30 to 40 minutes, but can take several days. It all depends on the patient’s desire to take certain photographs. Standard procedures included in the diagnostic list:
- visual inspection;
- a panoramic photograph that allows you to see the full view of the jaws, including the roots of the teeth, wisdom teeth, and tooth buds;
- teleroentgenogram (TRG). It allows you to determine the cause of the anomaly, see the relationship of the jaws, and draw a conclusion about what treatment methods will be required;
- 3D scanning or taking impressions of the jaws, with the help of which the exact dimensions of the jaw are determined;
- photographing. It allows you to assess changes in the patient’s appearance and the dynamics of treatment;
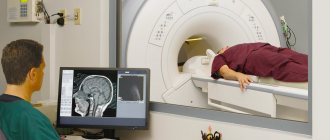
- 3D analysis or computed tomography (CT). Required if the doctor suspects a non-standard tooth tilt or other complex problems;
- video recording that allows you to record functional disorders in movement.