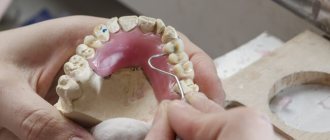
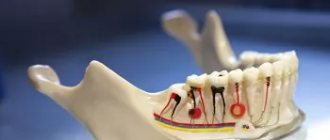
More and more patients are turning to the dentist to restore all their teeth, or one jaw completely. Conventional removable dentures, partial dentures and extended metal-ceramic bridges do not meet the high requirements for comfort, aesthetics and durability. All of these goals can be achieved with dental implants.
The technique of jaw implantation in the absence of teeth is significantly different from implantation in the absence of only a few teeth. For example, it is an obvious fact that you do not need to install 32 implants to restore all your teeth. All the details of full dental implantation are outlined in this article.
Methods of prosthetics on implants in the absence of teeth
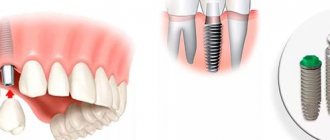
Prosthetics on implants in the absence of teeth can be divided into 3 types: removable, fixed and conditionally removable.
Removable prosthetics on implants is suitable for those patients who have already used a removable denture, but could not get used to it. Any option of removable prosthetics on implants will greatly improve the quality of life of such patients.
However, if you have never used a removable denture, then psychologically it will not be easy to get used to such a design. In this case, the best option would be fixed or conditionally removable prosthetics on implants. Conditionally removable means that the prosthesis is fixed with screws. It can only be removed by a dentist; the patient uses it as if he were his own teeth.
Implantation of both jaws with simultaneous loading with plastic crowns
More details about each treatment method are described later in this article.
Stages of the procedure
- Diagnostic
Assessment of the volume and general condition of the maxillary bone structures using x-ray diagnostics - orthopantomography and CT with 3D modeling.
- Preparatory
Hygienic cleaning is carried out - all dental deposits are removed, caries and other dental diseases are treated.
- Surgical
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The operation lasts on average 30-50 minutes; the use of laser equipment significantly reduces the intervention time.
- Orthopedic
After implantation of the implant, an abutment is installed, onto which the adaptive prosthesis is fixed. Permanent dentures are carried out after complete engraftment of the artificial root.
Lower jaw implantation
The lower jaw is denser in structure than the upper jaw, so in most cases, 2 to 6 implants are enough to restore all teeth. The integration period for implants in the lower jaw is 3 months.
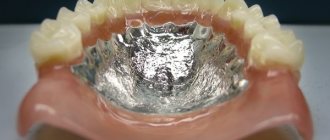
Removable prosthetics on implants in the lower jaw are carried out on 2-4 implants. The most common option is to install 4 implants with spherical attachments (or locators). The advantages of this method are good fixation of the prosthesis, easy oral hygiene, simplicity of design, and, as a result, its low cost. A removable prosthesis on 2 implants with attachments is used in cases where there is not enough bone tissue to install 4; the fixation of the prosthesis in this case is worse. The disadvantages of this treatment method are that the prosthesis distributes the load not only on the implants, but also on the gums. Under the pressure of the prosthesis, the gums atrophy, so it is necessary to reline the prosthesis on average once a year. The fastening on the attachments also weakens; it is necessary to periodically replace the retention matrices. The service life of the prosthesis itself is about 5 years.
Removable denture on 4 implants with spherical attachments on the lower jaw
The second option for a removable prosthesis on the lower jaw is prosthetics of the lower jaw on a beam on 4 implants. In this case, the load is distributed mainly on the implants and much less on the gums. The fixation of the prosthesis is very tight, the prosthesis feels almost like your own teeth. The prosthesis itself is made of plastic. It completely restores aesthetics and chewing function. The fact that the denture is removable simplifies oral hygiene. A plastic prosthesis is not as rigid as a metal-ceramic or zirconium one, so it is easier for people who have problems with the temporomandibular joint to get used to it. The disadvantage of this treatment method is that a properly manufactured beam prosthesis is comparable in cost to a fixed structure.
One of the main conditions for the long-term functioning of such a prosthesis is that the beam connecting the implants must be very accurately connected to them. For this, multi-unit abutments are used, which ensure precise connection of the implant with the beam; the beam itself must be made on a milling machine. Unfortunately, patients are often offered a bar prosthesis made without multi-unit abutments, or made by casting rather than milling. In this case, the beam will be fixed to the implants with tension, which will lead to a negative result, possibly even to the loss of the implants due to their overload.
Removable denture on a beam fixation on the lower jaw
Fixed prosthetics of the lower jaw are performed on 6 implants with classical implantation. It is also possible to restore teeth on 4 implants using the all-on-4 method, in which case 2 of the 4 implants are placed at an angle of up to 45 degrees. The technique has its pros and cons. All-on-4 will be written about later in this article.
Fixed prosthetics completely imitate your own teeth and are the easiest to tolerate psychologically. During the period of implant integration, the patient uses a temporary removable prosthesis, or dental implantation is carried out with a simultaneous load using a fixed plastic prosthesis. The service life of a plastic prosthesis is 1 year. It can be replaced with metal-ceramic or zirconium after the implants have completely healed. On the lower jaw after 3 months. The implants themselves are not affected.
In the case when a permanent prosthesis is made with screw fixation, we are talking about conditionally removable prosthetics on implants. Conditionally removable means that the prosthesis can only be removed by a dentist. The patient cannot remove it on his own; it feels and functions like his own teeth.
The advantages of screw fixation are that the prosthesis can be removed if necessary. Unlike cemented dentures, which cannot be removed without sawing them. However, the complexity of the design, and as a consequence the cost, is increasing.
Fixed denture on the upper jaw on 6 implants, on the lower jaw on 6 implants
How many implants are needed for a prosthesis for the entire row?
Previously, it was believed that only two implants were enough. However, this approach is sometimes used today. Two implants are placed in the frontal zone and a complete prosthetic structure for an edentulous jaw, designed for approximately 10-12 crowns, is attached to them. Sometimes they are connected by a beam. But in fact, such a system is doomed to failure from the very beginning of use: the implants will be overloaded, because it is on them and the distance between them (more precisely, on the beam) that all the pressure that occurs during chewing will fall. This means they will become mobile very quickly and will have to be removed. Practice shows that the service life of such a system is only a couple of years.
Today, THREE pieces per jaw is the absolute minimum. We are talking about the Trefoil protocol, for which Nobel has developed not only special implants, but also an attachment system and a special connecting beam that extends beyond the boundaries of the outermost implants. The company worked on this protocol for a very long time - almost 15 years, until they brought it to the market in impeccable form.
It is impossible to repeat the Trefoil system on implants of another brand - there are no components. Therefore, the minimum number in other situations is four. But again, you need to pay attention not only to the condition of the bone tissue, but also to the model and brand of the implant used, since they must be designed for installation at an angle, fixation in the deep parts of the jaw bone and have a high degree of primary stabilization in order to withstand the load from the prosthesis with crowns. Both immediate and delayed.
Upper jaw implantation
The bone tissue of the upper jaw is less dense than that of the lower jaw, therefore, for complete prosthetics on implants in the upper jaw, more implants are needed - from 4 to 8. Healing of implants in the upper jaw occurs within 6 months.
Removable prosthetics of the upper jaw are performed on 4-6 implants. On 4 implants it is possible to install an overdenture with spherical attachments. The overdenture has the same boundaries as a regular removable one; it completely covers the palate. To make a prosthesis on the upper jaw without a palate, you need to install 6 implants. Ball-shaped attachments, locators or a beam can be used as connecting elements. The best fixation of the prosthesis is achieved on a beam. However, the cost of such a prosthesis is comparable to a fixed structure.
For fixed prosthetics of the upper jaw, it is necessary to install from 6 to 8 implants. It is also possible to install a fixed denture on the upper jaw on 4 implants using the all-on-4 technique. It will be written about later in this article.
Installing 6-8 implants in the classical way is the most studied and reliable option for implanting the upper jaw. The number of implants is determined by the presence of bone tissue and the shape of the upper jaw. While the implants are healing, the patient uses a temporary removable prosthesis, or implantation is carried out with a simultaneous load using a fixed plastic prosthesis.
The service life of a plastic prosthesis is 1 year. It can be replaced with metal-ceramic or zirconium after the implants have completely healed. On the upper jaw after 6 months. The implants themselves are not affected.
Just like in the lower jaw, in the upper jaw it is possible to make a permanent screw-retained structure - conditionally removable prosthetics. Only a dentist can remove a screw-retained prosthesis. The patient uses it as if he were his own teeth.
The advantages of screw fixation are that the prosthesis can be removed if necessary. Unlike cemented dentures, which cannot be removed without sawing them. However, the complexity of the design, and as a consequence the cost, is increasing.
Different implantation options for complete absence of teeth. 8 implants on the lower jaw, 6 implants on each jaw, 8 implants on the upper jaw
Is it possible to secure a full denture with mini-implants?
Full mini-implantation was very popular five years ago - just a few thin implants, which were placed in a matter of minutes without massive incisions, made a real revolution among patients. And many doctors took up this idea - mainly to make money. But in reality, it was immediately clear: such implants are thinner and smaller. They cannot become a full-fledged support for the prosthesis and an alternative to standard-sized models - they simply will not withstand any chewing load. Therefore, the only option when their use can be considered is as temporary support for removable dentures. For example, at the stage of preparation for the main implantation or in a situation where implantation is impossible right now due to health reasons, you first need to undergo appropriate treatment.
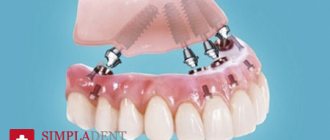
All-on-4
The All-on-4 technique (all-on-four) was developed by Nobel Biocare. It involves the installation of 4 implants on one jaw with simultaneous loading with a fixed prosthesis on a screw fixation. The 2 outermost implants are placed at an angle of up to 45 degrees, which allows you to bypass anatomically difficult places: the maxillary sinuses in the upper jaw and the nerve exit site in the lower jaw.
Initially, the All-on-4 technique was positioned as minimally invasive, without bone grafting. However, for successful functioning it is necessary to install sufficiently long implants, because 4 implants must bear the load of the entire dentition. Unfortunately, not all patients have the required alveolar ridge height. Installing shorter implants may result in one of the implants not taking root due to increased load. And then everything-on-four will turn into nothing-on-three. This is why patients are offered “all-on-4 modifications”, for example All-on-6 (all-on-six implants), because Installing an additional 2 implants significantly reduces the risks.
3-6 months after implantation using the All-on-4 method, gaps appear between the prosthesis and the gum, because This is why gum remodeling occurs after implantation. It is necessary to either reline the existing prosthesis or replace it with a permanent one - metal-ceramic or zirconium.
Recommendations
Recommendations after dental implantation of the upper jaw are as follows:
- try to avoid increased stress at first - do not blow your nose (both after bone grafting and for the first time after fixing the implant), do not chew hard foods, postpone flights;
- it is necessary to pay attention to hygiene - brush your teeth and use recommended rinses, visit a doctor according to the schedule;
- limit physical activity;
- avoid visiting the bathhouse, beach, pool;
- take medications prescribed by your doctor.
Following the doctor’s recommendations will reduce the risk of complications and ensure a long service life of the implants.
Bone grafting for jaw implantation
The more implants are installed, the greater the likelihood that the existing bone tissue will not be enough to install implants and it will be necessary to build it up. Bone deficiency can be in thickness (very thin bone) or in height (close to the maxillary sinuses in the upper jaw, nerve in the lower jaw).
If there is a slight lack of bone tissue in thickness, one-step bone grafting with the installation of implants is possible. It is also possible to carry out a sinus lift (a type of bone tissue augmentation when the distance to the maxillary sinus is insufficient) with the one-step installation of implants.
If there is a large deficiency of bone tissue, operations are first performed to build it up (open sinus lift, harvesting and replanting of a bone block), and after 3-6 months, implantation is performed. In this case, the total duration of treatment can be from one to one and a half years.
Restoration of chewing teeth
The doctor pays special attention to uniform distribution of the load. If it is necessary to restore 1-2 units, the classic protocol is used. If there is a lack of bone tissue, a sinus lift is performed. Implantation is possible without sinus lift using zygomatic implants, on which prostheses can be immediately fixed. But the method is used for long-term defects - from 3 teeth.
How to avoid bone grafting?
There are proven methods that allow you to reliably restore teeth on one or both jaws without additional operations to build bone tissue.
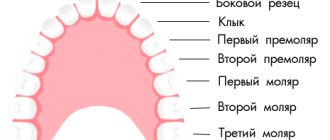
First of all, it’s worth talking about the positions in which implants are installed. Humans have a total of 32 teeth, 16 teeth on each jaw. The 2 outer teeth are wisdom teeth; they do not bear a functional load, therefore they are not restored during prosthetics. Of the remaining 14 teeth (7 on each side), the most problematic in terms of restoration are the sixth and seventh teeth (counting from the center). They are located close to the maxillary sinus in the upper jaw and to the nerve in the lower jaw. It is precisely to restore the sixth and seventh teeth that lengthy osteoplastic operations are necessary.
According to the recommendations of the international association of implantologists ITI - International Team for Implantology , in the case of complete absence of teeth, it is necessary to restore the dentition up to the sixth tooth inclusive (12 teeth on each jaw). This method completely restores both the function of the jaw and the aesthetics of the smile. At the same time, additional risks associated with the close location of anatomically important formations (maxillary sinuses and nerve) are avoided.
In this case, the implants are installed in the anterior part of the jaw, and the outer ones in the area of the fifth teeth (the so-called Frankfurt University protocol ). Subsequently, a one-piece fixed prosthesis is installed on them. Combining all implants into a single structure compensates for lateral chewing loads and ensures full functioning of the entire jaw with only 6 implants in the lower jaw and 6-8 in the upper jaw.
Another problem is a deficiency of bone tissue thickness ( thin bone ). To avoid bone grafting in this case, it is possible to use thin implants. However, not all systems guarantee that their thin implants can withstand the load of full jaw prosthetics. Such guarantees are provided by German implants Ankylos , and the Straumann has developed a special alloy of titanium and zirconium, which allows thin implants to function without building up bone tissue, it is called Straumann Roxolid .
And lastly, if there is a deficiency of bone tissue both in height and width, a possible solution is to install short and thin implants, but in larger quantities. Instead of 6 standard ones - 8 short ones. The total length of the implants in this case will be equal.
Choosing an implant for the smile area
The front teeth do not take part in chewing food, so special implants are installed in this area, characterized by maximum aesthetics while preserving the volume of bone tissue, minimal trauma to the gums and a shortened healing period.
Such implants are distinguished by their small diameter, as well as a special thread design and coating that stimulates the process of osteogenesis and osseointegration. To avoid the titanium structure showing through the crown or gum, zirconium structures can be used. A ceramic or zirconium prosthesis for tooth restoration replicates the properties of natural enamel, which ensures complete identity with the rest of the dentition.
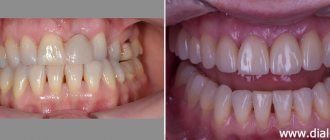
Work examples
How often do you visit the dentist?
Which implants to choose?
Today there are more than 3,000 implant systems in the world. However, not all of them can boast a long history of observations and clinical trials around the world. There are also some implant systems that, despite their reliability, are not very common in Russia. This may lead to difficulties in terms of delivery of original components of implant systems.
It is worth choosing only generally recognized implant systems, which are used by different doctors independent of each other. Otherwise, the patient risks finding himself in a situation where no one can help him.
An important point when choosing an implant system is the type of implant-abutment connection. It determines how long the implant will last. The most reliable today is the conical implant-abutment connection with the effect of switching platforms. It is able to withstand greater loads compared to a flat connection, is leak-tight and does not cause resorption of bone tissue around the implant.
The healing of implants is affected by the purity of the titanium from which they are made. The most common is Grade 4 - commercially pure titanium. Grade 1,2,3 alloys are even purer. Grade 5 – less pure, contains impurities of vanadium and aluminum.
The surface of each implant is a unique patented technology, because... It is on the surface of the implant that osseointegration occurs—the fusion of the implant with the bone tissue. Serious implant manufacturing companies conduct a lot of research, proving that their implants are integrated not only in standard situations, but also, for example, in people suffering from diabetes or bleeding disorders. The following systems meet all these requirements: Straumann (Switzerland), Ankylos (Germany), Astra tech (Sweden), Nobel biocare (USA/Sweden). Among the inexpensive systems, we can highlight Osstem implants (South Korea). They have proven themselves throughout the world as a reliable and economical implant system.
How does the preparation work and how long does it take?
Implantation requires preliminary preparation of the patient, even if it is completed in a few days. At the first consultation, it is first decided whether implantation is the optimal solution to the problem. If yes, then the patient is given recommendations for careful preparation for the operation. This will significantly reduce rehabilitation time and avoid possible complications.
The preparatory stage includes:
1. Consultation with a therapist or dentist . Contraindications to surgery are identified, and the condition of the gums, teeth, and jawbone is assessed.
2. Taking general tests, diagnosing the oral cavity, determining:
- blood group, Rh factor;
- blood clotting indicators;
- presence of infectious diseases;
- state of hormonal levels, immune system.
3. Diagnostics . To assess the maxillofacial area, an orthopantomogram or computed tomography is used. This helps to identify hidden inflammatory processes (cysts, granulomas), assess the volume and density of the bone, and determine the location and angle of inclination for implantation.
4. Treatment . To achieve high-quality results, the following is carried out before surgery:
- Treatment of caries.
- Relieving inflammation of the gums, stopping the spread of infection.
- Removal of units that cannot be treated.
- A set of hygienic procedures (removal of stone, plaque using laser or ultrasound).
2-3 weeks before the procedure, you should strengthen your oral hygiene, give up alcohol, painkillers, and sedatives (except for medications prescribed by the dentist). It is recommended to eat 3 hours before the procedure.
How much does implantation cost if there are no teeth?
Despite the apparent high cost of implantation in the absence of teeth, it may turn out to be more profitable than restoring already hopeless teeth. In addition, the service life of implants is unlimited. Treatment is carried out in stages and is also paid for.
So, the price of jaw implantation in the absence of teeth depends on the type of structure (removable, fixed) and the implant system. For example, the cost of jaw implantation using the classical method with a one-time load with a non-removable plastic prosthesis ranges from 350,000 rubles. The price of a zirconium prosthesis on implants for one jaw starts from 200,000 rubles.
You can get acquainted with the prices for implantation in the absence of teeth by clicking on this link.
Author of the article: Akhtanin Alexander Alexandrovich. Dentist-implantologist, orthopedist. He trained for a long time in Berlin, Germany. Member of the international association of implantologists ITI - International Team for Implantology.
Options for setting teeth up
Implantation of the upper dental row is carried out in two ways - one-stage and two-stage. Recently, dentists are more often choosing the first technique due to the immediate aesthetic result, especially when restoring anterior units. However, the express method is more risky in terms of tissue infection and has a greater number of contraindications compared to the classical one.
Classic technique with delayed loading
The two-stage implantation method includes:
- Implantation of an artificial root into the gum.
- Fixation of the crown after 2-5 months.
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes:
- sanitation of the oral cavity for inflammation;
- general examination to identify contraindications;
- consultation with an otorhinolaryngologist (for restoration of teeth in the upper jaw);
- X-ray examination of the maxillofacial apparatus and orthopantomogram.
Next comes the most important moment - the implantation of a titanium rod. The operation is performed under local anesthesia in the following sequence:
- An incision in the gum and detachment of the mucous membrane.
- Preparing a place in the bone for the implant by drilling.
- Threading (unless it is a model with self-tapping threads).
- Screwing in the titanium root.
- Stitching.
Once the healing process is complete, an abutment is attached to the implant and a crown is placed.
The duration of the process of osseointegration of the rod with tissues ranges from two to five months.
One-step installation with immediate loading
It is carried out quickly with an immediate load on the artificial root. Often used after tooth extraction. The specialist’s action plan is as follows:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Unit extraction.
- Preparing the bed for the implant.
- Installation of the rod.
- Installation of a temporary crown.
After the end of the osseointegration period, the temporary crown is removed and a permanent one is placed.
Alternatives
- Two-stage implantation with delayed loading. It is used if there is a sufficient amount of bone tissue. It involves the implantation of implants, waiting for their complete osseointegration (3-6 months), the formation of a gingival contour and the installation of a permanent bridge. In practice, the method is rarely used in cases of complete edentia, since the complete absence of teeth in almost 100% of cases is accompanied by bone atrophy. Preliminary tissue extension is required, which extends the treatment period by 6-12 months.
- Removable prosthetics on implants. The prosthesis is attached using a push-button (ball-shaped and locator) or beam type using a locking mechanism. The patient needs to periodically remove the prosthesis for maintenance. Fastening mechanisms require replacement over time (especially the push-button type).
- Classic complete removable dentures. Fixed on the gums due to the suction effect. The advantage of the method is its affordable price. Disadvantages - low level of comfort, risk of loss and breakage, dietary restrictions, mucosal injuries, worsening atrophic changes, need for relining and replacement of the prosthesis after 3-5 years.
What can replace implantation?
Implantation is the only method of restoring lost teeth that stops bone resorption. But there are cases when surgery is contraindicated or a person is not financially ready to undergo surgery. As an alternative from an aesthetic and functional point of view, the following are used:
- Removable dentures. They consist of a plastic base that serves as the gum and artificial teeth attached to it. Made from acrylic or nylon. Service life - 5-10 years. Due to improper load distribution, they put increased pressure on the gums, sag, and require constant relining. The jawbone under such prostheses is actively decreasing.
- Bridges. Several crowns welded together, the outermost of which are attached to the previously ground living teeth adjacent to the defect. Made from metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. The average service life is 7 years (depending on the condition of the supporting units). Due to uneven pressure, the bone in the defect area is resorbed.
We recommend not to delay the restoration of the dentition and consider implantation as an effective way to stop the process of bone tissue atrophy. Complete resorption over time makes any type of prosthetics almost impossible.
Why does bone loss occur?
When teeth are lost due to lack of natural load, the jaw bone atrophies. The process is activated 3 months after removal and reaches its climax within a year. Among the secondary reasons for the reduction of bone tissue in size:
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- age-related weakening of the tissues surrounding the tooth in older people;
- congenital pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus;
- jaw injuries;
- dentures supported by living teeth or gums.
Bone resorption leads to the following consequences:
- psychological discomfort due to a gap in the dentition, difficulty eating;
- change in the shape of the face: the appearance of wrinkles in the mouth, sagging cheeks, displacement of the chin, sunken lips;
- the need to reline a removable denture when using it.