Causes of yellowness around the mouth
If problems occur that are characterized by a change in blood circulation, this will entail a change in the color of the facial skin.
Yellowness around the mouth may indicate diseases of the digestive system: liver, stomach, spleen, pancreas .
Green skin around the mouth occurs when there is stagnation in the organs, with serious problems with the liver.
The appearance of an unnatural color around the mouth is often accompanied by anemia, increased fatigue, loss of energy and general malaise.
Important! When red blood cells break down, a substance called bilirubin is formed, and when there is an excess of it, the skin becomes yellow; this condition occurs when too many red blood cells accumulate and the bile ducts become blocked.
Other reasons for the appearance of a yellow or greenish color around the mouth may be:
- disruptions in the cardiovascular system;
- problems with the thyroid gland and endocrine system;
- oncological diseases;
- diseases of the genitourinary system.
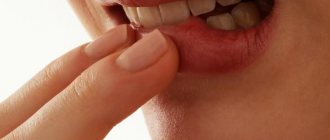
Photo 1: Yellowish color of the skin around the mouth often appears due to bad habits and poor nutrition. Source: flickr (bestacnemedicine02).
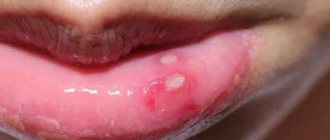
Cheilitis
Clinical manifestations of cheilitis
Exfoliative cheilitis
This type of cheilitis is classified as a group of psychosomatic diseases. It is often diagnosed in children or young adults. Patients usually exhibit two types of psycho-emotional disorders: in the dry form - depressive reactions, in the exudative form - anxious reactions. The disease is always clearly localized - the lesion appears on the red border of the lips and never moves to the oral mucosa and skin around the lips.
Dry form
Patients with the dry form of the disease usually experience congestive hyperemia of the lip border, the formation of dry gray scales, and constant peeling of the lips. The scales are easily removed, but appear again within a week. Patients often complain of severe burning and excessive dryness of the lips. The dry form of the pathology can eventually turn into exudative, which is characterized by greater severity of symptoms.
Exudative form
The exudative form of the disease is usually accompanied by swelling of the lips, pain, and the formation of a large number of scales, which sometimes reach quite large sizes and even hang from the lips. After the scales fall off, a hyperemic surface appears in their place. Patients also complain of sore lips, which makes eating difficult. When diagnosing the disease, the dry form should be distinguished from atopic, allergic and meteorological forms, and the exudative form from exametous cheilitis and lupus erythematosus.
Glandular cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis is an inflammation of the accessory salivary glands, which mainly affects the lower lip. The pathology is often diagnosed in patients over 40 years of age. The primary form of the disease can be triggered by an abnormality of the salivary glands, the secondary form can occur against the background of leukoplakia or lupus erythematosus. Simple glandular cheilitis is characterized by enlargement of the salivary glands, the appearance of red dots on the mucous membrane of the lips, and the active production of serous secretion, which accumulates in the form of dew on the inside of the lips.
In rare cases, patients are found to have a purulent form, which is accompanied by pronounced symptoms and a severe course. The clinical picture of the superficial form of purulent disease is almost the same as with simple glandular cheilitis, only the enlarged salivary glands produce purulent secretion. The deep purulent form of the disease is very difficult. The patient experiences swelling of the lips, the formation of purulent crusts and erosions on the red border. On palpation, severe pain appears.
Contact allergic cheilitis
This type of cheilitis is considered a delayed allergic reaction to chemicals that enter the body through cracks in the lips, then enter the bloodstream and ultimately lead to sensitization of the body. At the same time, the period of sensitization is very individual, since it can range from a couple of days to several years. The duration of sensitization depends on sensitivity to allergens, as well as the state of the endocrine, nervous and digestive systems.
Usually the inflammation is located on the red border of the lips, and also spreads slightly to the skin around them. Erythema appears at the site of contact between the allergen and the skin. Due to inflammation, the patient also develops small blisters, cracks and erosions, which is why he complains of itching, swelling and burning of the lips. The disease sometimes occurs without symptoms; the patient is only bothered by peeling of the lips.
If allergic cheilitis continues for a long time, then usually the red border of the patient’s lips becomes excessively dry, cracks and small furrows form on it. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of atopic and exfoliative cheilitis, which the doctor must take into account during diagnosis.
Meteorological or actinic cheilitis
Meteorological cheilitis is an inflammation of the surface of the lips, which occurs due to various climatic irritants, including high and low air humidity, wind, and temperature changes. Often this pathology is diagnosed in men because they do not use protective lipsticks. Patients are concerned about the feeling of tightness and dryness of the lips. Damage to the lower lip is also observed - its inflammation and swelling, slight infiltration. Peeling and small scales appear on the red border. It is noteworthy that the lesion does not extend to the oral mucosa and skin around the lips.
As a rule, this chronic disease worsens after exposure to any aggressive climatic factor. It is extremely rare for doctors to diagnose malignancy of the affected area, but precancerous processes are still detected. When diagnosing the disease, it is worth considering that its symptoms are similar to the symptoms of diseases such as atopic and allergic cheilitis.
Atopic cheilitis
Atopic cheilitis refers to inflammation of the red border of the lips, which is considered one of the manifestations of neurodermatitis. The disease occurs due to a genetic predisposition. Allergens can be medications, foods, dust, decorative cosmetics, and pollen.
Often the course of atopic cheilitis is long, the disease either subsides or worsens again. The disease usually goes into an acute stage in the cold season, but in the summer it goes into remission. During periods of exacerbation, patients complain of peeling, redness and itching of the skin of the red border of the lips. Swelling and infiltration of this area also gradually appears.
Excessive dryness and infiltration often lead to cracks, due to which the patient experiences pain when opening the mouth. During remission of the disease, patients experience peeling and thickening of the skin near the red line of the lips. It is noteworthy that inflammation almost never spreads to the oral mucosa. The atopic form of cheilitis must be distinguished from pathologies such as streptococcal cheilitis, contact and allergic cheilitis.
Macrocheilitis
Macrocheilitis refers to swelling of the lips and paralysis of the facial nerve. The attack begins suddenly with swelling of one or both lips at once. At first, patients are bothered by itching of the lip, then they notice that it has begun to grow rapidly. With this type of cheilitis, a shapeless swelling of the lip may occur, it may acquire a bluish tint, and the edges may turn out. Over time, the swelling becomes so large that the lip increases in size three times.
There is uneven swelling of the lips, as one of them appears more swollen than the other. In patients, swelling is constantly observed, but it either increases or gradually subsides. During the day, the intensity of swelling usually changes. Another pronounced sign of the disease is paralysis of the facial nerve. The patient feels an unpleasant sensation in the mouth, the palpebral fissure widens and the corners of the mouth droop due to the loss of tone in the affected part of the face. Usually, incomplete paralysis is observed, since the patient retains autonomic, sensory and motor functions.
More than 60% of patients are diagnosed with a folded tongue, which is considered a developmental abnormality. In this case, there is pronounced swelling of the tongue, which leads to its enlargement. It is worth noting that not all patients are diagnosed with all the main symptoms of this type of cheilitis. Sometimes the disease can manifest itself with just one pronounced clinical sign.
The course of macrocheilitis is always chronic. At the very beginning of the disease, relapses occur, which alternate with long periods of remission. However, over time, the disease becomes chronic, and its exacerbations are extremely rare - usually after stressful situations and viral infections. During diagnosis, this pathology should be distinguished from angioedema, lymphangioma, erysipelas, and hemangioma. Typically, difficulties in making a diagnosis arise when the disease manifests itself with only one leading symptom.
Hypovitaminous cheilitis
Hypovitaminous cheilitis occurs due to a lack of B vitamins. Because of this, signs of the disease appear such as burning and dry tongue. In addition, there is redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance of cracks and peeling on the red border of the lips. Often the cracks are quite painful and often bleed. With this type of cheilitis, patients' tongue becomes enlarged and teeth marks appear on it.
Diseases associated with yellowing of the skin around the mouth
If increased breakdown of red blood cells occurs, the liver does not have time to process them and yellow pigment accumulates. If it becomes visible on the skin, then this indicates jaundice. The disease is characterized by yellowing of the tongue and whites of the eyes.
Inflammation of the pancreas and hepatitis will also give yellowness to the skin.
This is interesting! With false jaundice, the mucous membranes are not stained.
But yellowness can appear with constant consumption of vegetables and fruits containing a lot of carotene, as well as after the use of certain medications.
A green complexion or area around the mouth can occur with the following diseases:
- severe intoxication;
- liver cirrhosis, any form;
- oncology; kidney diseases.
A violation of the normal coloring of the skin of the face requires an immediate response ; some situations can be fatal to the body.
Reasons for color change
A yellow tint may appear due to smoking. Tar and tobacco smoke stain the mucous membrane, settling on the surface. A yellow coating appears. Due to vascular contraction and changes in blood composition, blood supply is disrupted. With a lack of oxygen, the mucous membrane turns pale and yellow.
The causes of yellowing of the palate are diseases of the oral cavity and body. This is also caused by age-related changes due to metabolic disorders and blood microcirculation.
What measures need to be taken
Bilirubin in excess is very dangerous for the human brain .
Important! If the skin suddenly changes its color to yellow, green, you should urgently call a doctor. While waiting, you can take some sorbent, for example, polysorb, activated carbon.
If the changes occurred gradually, the help of a doctor is also necessary. You need to take the following measures yourself :
- reconsider the diet, perhaps unreasonably high consumption of beets, carrots, pumpkins;
- find out about all the side effects of the medications you are taking;
- quit smoking;
- establish a normal daily routine;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, skin cells should be saturated with oxygen.
Photo 2: Along with this, consultation with a doctor is required, since the causes of changes in facial skin color can be very serious, requiring immediate intervention. Source: flickr (andranik).
Homeopathic treatment
| Purpose | Drugs |
| For the treatment of liver and gallbladder diseases, relieves pain in the epigastric region and other dyspeptic disorders. |
|
| For acute and chronic diseases of the liver and gall bladder, it can also help with skin diseases: dermatitis, neurodermatitis, etc. Restores the lymphatic system of the gland, acts as a detoxification agent. |
|
| To cleanse the liver. |
|
| With atrophic cirrhosis, which is accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium. |
|
| For any liver pathology. |
|
| For pain in the right side and flatulence. |
|
| With such a phenomenon as congestive liver, which is manifested by necrosis of hepatocytes, and is usually accompanied by heart failure. |
|