There are many reasons for malocclusion, one of them is tongue dysfunction, or its constant incorrect position. Let us tell you in more detail why habits of sticking out the tip of the tongue, bending it, and the like are likely to lead to orthodontic problems.
Is your child sticking out his tongue? This is not a harmless habit, but a problem!
Tongue, nose, throat: everything is interconnected
The inside of a child’s nasopharynx is covered with mucous membrane, which should normally perform a protective function: trap viruses, bacteria, dust particles and other allergens. But if the mucous membrane dries out, it becomes too thin and vulnerable.
Therefore, by the way, the child’s room should be cool and fairly humid.
If the house is hot, the air is dry, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx dries out, and any virus can easily penetrate through the thinned protective barrier. This causes frequent acute respiratory viral infections associated with a runny nose and swelling of the nose.
Due to these diseases, the child’s nasal breathing is impaired, his mouth is constantly open and his tongue is visible. Gradually, the habit of breathing through your mouth in your sleep arises.
Breathing through your mouth during sleep is a very alarming sign
The mouth opens slightly, expanding space for the tongue. And, of course, the child's tongue begins to take up this additional space in and outside the mouth.
This is how tongue dysfunction arises, then it becomes fixed in the child’s habits.
A vicious circle arises: frequent ARVI - stuffy nose - habit of breathing through the mouth - dry mucous membrane - frequent ARVI, and in addition, tongue dysfunction occurs.
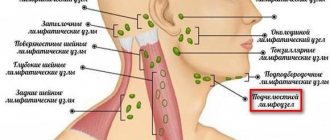
All this can lead to the proliferation of lymphoid tissue, and therefore to adenoiditis and tonsillitis, since it is the nose that filters the air, and when breathing through the mouth, allergens and viruses enter directly into the oropharynx. In this case, the blood is not fully saturated with oxygen and sleep at night is disturbed - in the morning the child gets up sleep-deprived, feels drowsy during the day and cannot concentrate on studies.
Please note: when a child sleeps with his mouth open, this is a very alarming symptom. This habit easily passes into adulthood: snoring, apnea and numerous negative consequences from this occur.
Harmless reasons
In the vast majority of cases, if a child sticks out his tongue at 3 months, then this is not a cause for concern. After all, this can only be a game and innocent pampering, the so-called “antics.” It is possible that the baby is simply trying to make a certain sound in this way, trying to repeat after the adult. Healthy children are quite capable of sticking out their tongues from time to time.
Often, if a baby sticks out his tongue at 3 months, it may be a sign that he is teething, despite his age. The sensations are unpleasant. After all, a child wants to scratch his gums in any way, touch them and explore his mouth.
Sometimes a 3 month old baby sticks out his tongue due to breastfeeding. Thus, he can ask to be attached to the breast, to be calmed, or simply to be fed.
Tongue dysfunction: how it affects teeth
The habit of breathing through the mouth, including during sleep, leads to increased tongue dysfunction. The child begins to stick out his tongue more often (and the tongue is the strongest oral muscle), make additional efforts and press his tongue on the teeth.
What will happen to the teeth if such a habit develops?
- A diastema may form - a gap between the front teeth.
- The contacts of the teeth in the frontal region may be disrupted, then an open bite will appear - a pathology that is quite difficult to correct: it causes noticeable harm to the condition of the teeth, since the entire load falls on the chewing teeth in the lateral regions.
Open bite in a child
- The front teeth can rotate (turn around their axis) or form a protrusion - a forward tilt.
Children's teeth are quite pliable, as the child grows, the size of his jaws and the space in the row of teeth constantly increase. Therefore, the effort exerted by the tongue is quite enough to move the teeth, but they will no longer be able to return back to the correct position on their own.
One more problem
In addition to orthodontic disorders, difficulties with pronouncing sounds will increase. Speech therapy correction is designed for the correct structure of the teeth and the functioning of the tongue, so classes with a speech therapist will be very long and ineffective if the main cause of poor diction is not eliminated.
What is the problem behind?
The baby cannot speak. He expresses all his desires and needs with the help of gestures and facial expressions. The tongue is one of the tools of communication. If a baby sticks out his tongue, it means he wants to eat or is simply seeking attention. Or he reports that he is sick and does not feel well.
You should be alarmed when the tongue sticks out not only during play, but constantly, even in sleep. In this case, you should definitely visit a pediatrician. After examining the child, he can refer him for consultation to other specialists.
If a child shows his tongue, this may be the cause of neurological, endocrine or infectious diseases. There will definitely be other warning signs.
Disease of the endocrine system – hypothyroidism
The problems are related to the thyroid gland. The main reason is the lack of a trace element such as iodine in the body. To determine its level, blood is examined. Blood is collected from infants from the heel in the maternity hospital.
In addition to the fact that the child sticks out his tongue, other symptoms are present:
- skin color becomes yellow or pale;
- the surface of the skin is dry and flaky;
- there is a delay in mental and physical development;
- the tongue protrudes outward because it does not fit in the mouth due to large swelling;
- the area around the nose and lips becomes blue;
- no weight gain;
- persistent constipation develops.
In this case, treatment (the basis of therapy is hormones) and additional examination (ultrasound, blood tests) are prescribed by an endocrinologist.
Neurological disorders - atrophy of facial muscles
The trigeminal nerve is most often affected. This may occur due to malfunctioning of the thyroid gland. The problem becomes a consequence of previous respiratory diseases or various facial injuries.
Additional symptoms appear:
- the face becomes immobilized, facial expressions change (the child does not cry, does not smile, there are no facial folds);
- swelling of the lips is observed;
- facial asymmetry is observed;
- eyelids droop;
- the chin moves to the side.
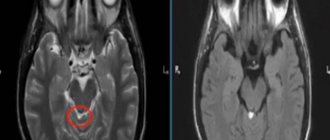
The treatment is carried out by a neurologist. The results of MRI and ultrasound examinations may be needed. Treatment is mainly medicinal. Additionally, vitamins, massage, and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Infectious disease - thrush
The mucous surface of the oral cavity is affected. The reasons for its occurrence may be a decrease in immunity, frequent regurgitation.
The child sticks out his tongue, and other symptoms appear:
- a white, cheesy coating appears in the mouth;
- gums, tongue, palate become inflamed and red;
- If treatment is not started, the plaque becomes gray or yellow.
Consultation with an infectious disease specialist and dermatologist is necessary. Ointments and solutions, vitamins, and drugs that help improve immunity are prescribed locally.
The main condition is compliance with a special diet for a nursing mother.
Stomatitis
The reason that the baby constantly shows his tongue may be stomatitis. This disease occurs when viruses and bacteria enter the body. The symptoms are easy to notice:
- the oral cavity is inflamed, swollen, red;
- ulcers are clearly visible, which can appear anywhere: on the tongue, on the palate, on the gums;
- body temperature rises;
- the child is capricious and refuses to eat;
- sleep becomes restless.
A dentist, immunologist, and infectious disease specialist can help. Vitamin complexes, immunomodulators, ointments and medicinal solutions, antiviral or antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Increased intracranial pressure
It is caused by serious disorders of the central nervous system. This can happen due to a birth injury or a serious infectious disease such as meningitis.
Symptoms that are a reason to consult a doctor:
- the diameter of the child’s head exceeds the age norm;
- constant throwing of the head back;
- swelling of the fontanelle;
- severe muscle tension;
- the child squints his eyes;
- trembling of hands and chin;
- poor sleep;
- rolling the eyeballs downwards.
Consultation with many doctors is necessary, including a neurologist and an ophthalmologist. A prerequisite is to undergo brain tomography, neurosonography, and the fundus of the eye is studied. Treatment is aimed at improving circulatory functions. Additionally, therapeutic exercises, massage and vitamins are prescribed.
Tongue hypotonia (muscle weakness)
This disease is caused by birth trauma, disruption of the endocrine system, and premature birth. Past infectious diseases also have an impact.
Signs that accompany tongue protrusion are:
- lethargy, low mobility of the child;
- he sleeps for a long time;
- lack of weight gain;
- poor appetite;
- retardation in physical development.
A neurologist will help solve the problem. Drug treatment, massage, and gymnastics are recommended.
If parents often notice their baby’s tongue sticking out, it is necessary to carefully examine his skin and mucous membranes. If warning signs are detected, you should immediately visit your pediatrician. Only he can give recommendations on further treatment tactics.
How to help a child?
It is worth understanding that these habits do not arise on their own and not because of bad behavior. Comments and reminders that you should not stick your tongue out will not work - you need to work with the root cause of the disorder.
- Restore nasal breathing.
Orthodontists often prescribe consultations with an otolaryngologist, since the dental system and respiratory organs are closely connected. Removal of adenoids, treatment of chronic diseases, normalization of the microclimate at home to reduce the frequency of acute respiratory viral infections, hardening and other restorative procedures - all this can be prescribed by a doctor to achieve remission.
ENT can help restore health for proper tongue function
- Contact an orthodontist.
Only in this order, otherwise the treatment will not be effective. As soon as the child is able to breathe with his mouth closed, you can move on to correcting the position of the teeth and tongue.
For this purpose, children's orthodontic devices have been created:
- Plates.
- Trainers.
- Twin Block device.
- Children's aligners Kinder Smile.
All these devices are removable and act quite gently, guiding teeth during the period of their active growth. Wearing requires parental supervision, but with proper use, problems are solved quite quickly - within a few months.
Only after this can you begin classes with a speech therapist - when the malocclusion and the main manifestations of tongue dysfunction are eliminated, the correction of sound pronunciation will be much more successful.
Category: Master classes.
ABOUT THE PROJECT
As part of the project “Educational photo and video master classes on breastfeeding,” 17 instructions have been created to correct the most common difficulties during breastfeeding. Master classes will be released in photo and video format in Russian and Kazakh languages.
The materials were created for parents and professionals and are available free of charge. All master classes are protected by copyright law. The authors of the project give permission to those who wish to use materials on their resources, provided they maintain a link to the author’s website (original source) - milky-help.org.
If you wish to use these materials to create any printed materials, you must contact the authors of the project to obtain approval. Request permission
The implementation of this project was made possible thanks to the full support of the following organizations:
Publishing house "Resource" Representative office of Biolane children's cosmetics in Kazakhstan Pharmaceutical trading company Pharmacy Plus
We thank the project sponsors for their trust and support in us at all stages of implementation. The models for the master class “Help from a specialist: lying down breastfeeding” were:
- Voloshinenko Liana – breastfeeding consultant, perinatal psychologist, AKEV teacher, teacher and author of the course “Psychology of Motherhood. Natural feeding", coordinator of the branch of the MOO "Molochnaya Pomoshch" in St. Petersburg, head of the MOO "Molochnaya Pomoshch".
- Baby Asadchiy Efim (age – 40 days).
- Elena Asadchaya - breastfeeding consultant, educational psychologist, breastfeeding teacher, coordinator of the branch of the MOO "Dairy Pomoga" in Almaty, head of the MOO "Molochnaya Pomoshch".
The “tongue smoothing” technique may be useful if:
- the child has piston sucking, he does not lay his tongue on the lower gum;
- the child cannot attach to the breast after using a pacifier or breast pad;
— it is necessary to teach the child to suck after cutting the frenulum under the tongue.
You can also let your child suck his finger if you need to diagnose what kind of tongue movements the child is making. And also when a very small child wants to suck, but the mother for some reason cannot breastfeed (for example, she has been weaned), instead of a pacifier, it is more advisable to offer a cleanly washed finger of an adult for sucking (nails should be cut short).
Thumb sucking is used as one of the ways to supplement a baby's feeding without a bottle.
Diagnostics of sucking
The lactation consultant performs the technique while wearing gloves; the mother can limit herself to thorough hand washing. Nails should be cut short to avoid injuring the child.
- It is most convenient to perform the technique with your thumb (the child gets used to the feeling of greater fullness in the mouth, it is more similar to sucking at the breast).
- Position the child comfortably, the head should be slightly thrown back, the back should be straight, nothing should interfere with the free opening of the mouth.
- Bring your bent thumb to your baby's mouth.
- Place the knuckle of the thumb on the baby's lower lip, encouraging him to open his mouth. You can gently press on the sponge so that the child opens his mouth wide.
- When the child has opened his mouth wide enough, straighten your finger - it will fit into the child’s mouth.
- The finger should be deep enough in the mouth (a whole phalanx or a little more). The child should not choke on his finger. The pad of the finger barely touches the palate, the nail lies on the tongue.
- Let your child suck on your finger. If he doesn't start to suck, you can gently stimulate the roof of your mouth with your fingertip.
Correct sucking
When diagnosed, you will feel proper sucking like this:
- You feel the baby's tongue wrap around your finger;
- the tongue is extended so that it covers the lower gum; during sucking movements, the tongue continues to lie on the gum;
- You feel expressing wave-like movements with your tongue;
- The tongue does not slide along the finger “back and forth”.
Incorrect sucking
Improper sucking is most often associated with:
- using breast substitutes (bottle with pacifier, pacifier, breast pads);
- short frenulum under the tongue;
- improper attachment to the breast (how to correct attachment to the breast, you can see here).
Incorrect sucking can be piston-like or shallow peristaltic.
Signs of piston sucking:
- on the tongue, approximately in the center, there is a tubercle with which the child can press his finger against the palate, sometimes quite firmly;
- movements of the tongue along the finger “back and forth”, the amplitude is quite large (more than 5 millimeters);
- the lower gum is not covered with the tongue, the child can strongly squeeze the finger between the gums;
- The baby holds the vacuum while sucking by tensing his lips.
Signs of peristaltic sucking:
- the child’s tongue clasps the finger, the movements are generally correct (see CORRECT SUCKING), but the tongue does not cover the lower gum or periodically slides off it when making sucking movements;
- The child may squeeze the finger tightly with his gums while sucking.
After cutting the frenulum under the tongue, sometimes it is enough to simply attach the baby to the breast correctly. In some situations (for example, a child is accustomed to an incorrect sucking technique, or after surgery the tongue movements are discoordinated), this technique will help to cope.
Correction of improper sucking (tongue smoothing technique)
- After the child has sucked on the finger, slowly and carefully lower the tip of the finger lower (extending the finger) - gradually press the fingernail onto the tubercle of the tongue. Thereby forcing the child to straighten his tongue. You will be able to feel your tongue straighten and move forward.
- After this (almost simultaneously with step 1), slowly pull your finger out of the child’s mouth. He will push his tongue out even more because he doesn’t want to let go of the sucking object.
- This exercise can be repeated several times. After 2-3 repetitions, you can see that when giving a finger, the child will open his mouth wider and lay his tongue on the gum in the shape of a funnel.
- If you feel that the movements of your tongue have changed while sucking your finger, you can give breastfeeding.
- The breast does not help the baby as much as the finger, so the baby may not be able to start sucking correctly right away. Don’t worry, you just need to try your finger a few more times, then your chest again.
- Sometimes retraining can take 1-2 days. At this time, it is advisable that the child does not receive breast substitutes; the mother constantly monitors the correct attachment to the breast. It is advisable to give food without using a bottle with a pacifier. More information about methods of supplementary feeding without a bottle can be found in the master class “Supplementary feeding without a bottle.”
Correction of abnormal sucking in tongue dystonia
For various reasons (neurological disorders, deep cutting of the frenulum under the tongue, etc.), a child may experience tongue dystonia - incorrect distribution of tongue muscle tone. The most common condition is hypertonicity of the superior longitudinal muscle of the tongue. You can deal with this in the following way.
- The tongue smoothing technique is also performed, but with a little emphasis. Lower the tip of your thumb even lower. Slowly pulling your finger out of the child's mouth, use the tip of your finger to press quite intensely on the center of the tongue and move from the base to the tip. The result is a massage effect that allows you to relax your spasmed tongue.
- Repeat the exercise several times. Feeling that the tongue has become more relaxed while sucking a finger, has begun to wrap around the finger like a funnel and extends to the lower gum, you can offer the breast to the baby.
Authors of the master class:
- Voloshinenko Liana – breastfeeding consultant, perinatal psychologist, AKEV teacher, teacher and author of the course “Psychology of Motherhood. Natural feeding”, head of the local public organization “Dairy Help”.
- Asadchaya Elena - breastfeeding consultant, educational psychologist, AKEV teacher, coordinator of the branch of the MOO "Dairy Pomoga" in Almaty, head of the MOO "Molochnaya Pomoshch".
Photo: Marina Tsaplina – family photographer.
GRATITUDE
The implementation of the project to create master classes for mothers and specialists was also made possible thanks to the contribution made by:
Proud Mom - clothes for expectant and nursing mothers. Breastfeeding clothing in the project is provided by the Proud Mom brand
Creative workshop Slingomama.kz
The project was also greatly assisted by the manufacturer of clothing for nursing mothers TM “Bambinomania” and the store for mothers “Ukhti-Tukhti”
Share
Comments
Why does an infant stick out his tongue: possible diseases
If this worries you, then go to an appointment with an endocrinologist and move on with your life in peace. My daughter kept her tongue sticking out between her lips since she was 2 months old. I want to note that the tongue was not in the mouth at all!
Then, having read passions on the Internet, I lost 12 kg in a month due to nerves. Then I flew home with the child. I went to all kinds of doctors and everyone gave up! When a child begins to stick out his tongue, many at first do not pay attention to it, regarding it as an accident or pampering. This often happens, but this reason is far from the most common. A child can stick out his tongue by adopting a new gesture from his parents.
When engrossed in a game, looking at objects, or trying to perform new actions, a child may stick out the tip of his tongue. This gesture is also typical for adults. Babies accustomed to the pacifier often replace it with their tongue. 1. Often a baby sticks out his tongue when he is bothered by unpleasant, painful sensations due to stomatitis or thrush.
Diagnosis of possible problems
To diagnose possible problems, you will need to visit a qualified specialist. An experienced pediatrician will be able to identify the characteristic symptoms of most of the pathologies described above based on an examination of the child and a survey of parents. Almost all pathological conditions that are accompanied by protruding tongue in an infant have specific symptoms.
If you suspect hypothyroidism, you will need additional consultation with an endocrinologist and a laboratory blood test (now this is often done in the maternity hospital). If the doctor suspects that the child is suffering from ICP, he will refer the child for examination to a neurologist. Based on the results of the consultation, neurosonography may be prescribed.
The child is over 6 months old
For infants under one year of age, the reasons why they stick out their tongue will be the same in most cases. At the age of 6 months and older, children tend to play and make faces more in order to entertain themselves and others and get some exercise.
If a 6-7-8 month old child sometimes sticks out his tongue and immediately hides it, we are talking about a completely natural action. Alarming accompanying symptoms are similar to those presented above.
A newborn's tongue falls out
A protruding tongue in newborns, especially in combination with tilting the head back during sleep, may indicate increased intracranial pressure. If you notice such symptoms, immediately consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations.
Sometimes the structure of a baby’s lower jaw simply does not allow the tongue to fit in the baby’s mouth. An enlarged tongue may also indicate the presence of some congenital disease. If your newborn's tongue does not just stick out, but rather falls out, seek medical help immediately. There can be many reasons: starting with problems with the thyroid gland, and ending with atrophy of the facial muscles, which cannot hold the tongue in the baby’s mouth.
As you can see, there are a huge number of reasons why a baby sticks out its tongue, and not all of them mean the presence of serious diseases. In any case, if you are not sure that a tongue that falls out or is simply shown by the baby does not indicate an illness. Having once heard the truth that a pediatrician is the main doctor for any family with small children, I realized that I had something to strive for. So I don’t understand how a protruding tongue is connected to the stool and indicates a problem with the thyroid gland!
The fact that a baby sticks out his tongue is perceived by many as pampering. Vera stuck out her tongue at 2.5 months, when her throat was red... 4. A child can also stick out his tongue when there is atrophy of the facial muscles, when he is not able to control their work. 6. The baby sticks out his tongue slightly with a short frenulum. Sometimes children stick out their tongues when thrush appears in their mouth. It’s just that a child’s tongue grows faster than his mouth, and at a certain age the child begins to stick it out a little, because it doesn't quite fit.
Further on this issue:
When is there nothing to worry about?
If the baby is cheerful and active, eats well and sleeps peacefully (without throwing his head back), then he is healthy, and his tongue sticks out for one of the natural reasons. You should also pay attention to the color and shape of the tongue - if there is no swelling or white coating, then most likely there is no cause for concern.
If parents are alarmed by the baby's tongue sticking out, but there are no visible alarming symptoms, it is better to visit a pediatrician. This way, pathology can be completely excluded, and if it is detected, it can be treated at an early stage. The characteristic symptoms can be found in the photo accompanying the article.