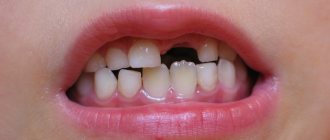
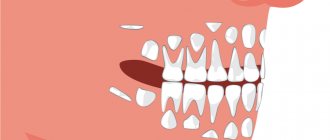
Children's teeth appear in a certain sequence and in pairs (for example, two central incisors or two canines). But often the timing of teething in children shifts upward: many parents begin to worry and get nervous, but this is not worth doing, since the deviation from the norm is explained by the individual characteristics of the body, the uncharacteristic course of pregnancy, or various injuries received during childbirth.
Why do we need baby teeth?
It's no secret that baby teeth perform their function for an average of 10 years, after which they are replaced by molars. If we compare this figure with the average human life expectancy, it turns out that we spend almost all our time with molars. What then is the function of baby teeth? Generally speaking, baby teeth are one of the main components of the proper development of the facial skeleton. As for the details, they are presented below.
- Milk teeth provide chewing load.
The bone tissue of the jaw is formed only under the influence of mechanical pressure. Milk teeth provide the necessary load, thanks to which the harmonious development of bone tissue and jaw bones occurs. - They form a bite.
If a child’s primary bite has any abnormalities, this will inevitably affect the permanent teeth in the future. That is why it is recommended to regularly show the child to the orthodontist until the complete change of the dentition. - They are the “progenitors” of molars.
The rudiments of molars are formed under the temporary teeth, and the milk teeth are a kind of navigators that determine the place of the permanent ones. A correctly formed row of baby teeth means that molars are likely to appear in their place. - Participate in the formation of diction.
Milk teeth are part of the speech apparatus and are directly related to the reproduction of sounds.
Milk and molar teeth: what are their differences?
Externally, baby teeth and molars are very similar, but if you look closely, you will notice some visual differences: baby teeth are smaller in size, and the incisors and canines have a more rounded shape. The main differences are related to anatomy and structure.
- Primary teeth have thinner enamel with less mineralization.
- The root canals of baby teeth are much wider and, accordingly, more susceptible to the entry of pathogenic bacteria.
- The dentin layer of baby teeth is thinner, and the pulp is thicker.
- Milk teeth have roots, but they are less pronounced and dissolve during the process of changing the dentition.
When do baby teeth appear?
The formation of a child’s teeth begins in the womb: this is partly why doctors recommend that pregnant women eat foods rich in calcium and other beneficial minerals. After birth, the first baby tooth (in the vast majority of cases, this is the lower incisor) appears when the baby is six months old. There are cases when the first teeth erupt already in the third month, and sometimes a child is already born with one or more teeth (among many peoples this is considered a lucky sign). Conversely, some children acquire their first teeth after reaching one year of age. Below you can see a table that shows the current timing of the appearance of baby teeth.
Milk teeth on the lower jaw
| Name of teeth | Age of appearance |
| Central incisors | 6 – 9 months |
| Lateral incisors | 10 – 14 months |
| Fangs | 17 – 21 months |
| Premolars | 13 – 16 months |
| Molars | 23 – 30 months |
Milk teeth on the upper jaw
| Name of teeth | Age of appearance |
| Central incisors | 8 – 11 months |
| Lateral incisors | 9 – 12 months |
| Fangs | 16 - 19 months |
| Premolars | 13 – 16 months |
| Molars | 25 – 32 months |
Read also
What to do if your tooth aches
Sometimes aching pain in a tooth can appear for no apparent reason at first glance.
Why do teeth crumble?
Tooth decay in general, and crumbling in particular, is not an aesthetic problem.
Disorders during the eruption of primary teeth
The most common timing for the eruption of baby teeth is listed above. It is optimal when, upon reaching the age of three, the child has a full set of primary teeth. If baby teeth erupt late, experts advise parents not to worry unnecessarily: a delay of 2 to 3 months is considered normal. If after this period the teeth do not appear, then you should consult a doctor who will examine the child’s oral cavity, take tests and take panoramic photographs of the jaw, after which it will be possible to draw certain conclusions about the reasons for this delay. This usually occurs due to a lack of minerals and vitamins, which is easily solved with the help of restorative therapy. It is much worse when the rudiments of baby teeth are simply absent. This occurs extremely rarely and is usually caused by genetic abnormalities, periodontal inflammation and mechanical damage. In this case, to properly distribute the chewing load and develop the jaw bones, it is necessary to wear a removable denture.
Caring for children's teeth
The pattern of teething in children determines the approximate time of their appearance, but it is necessary to start observing oral hygiene as early as possible, without waiting for the teeth to erupt.
Breasts cannot take care of themselves, so they need help cleaning their gums. This is done either with the help of a fingertip, or, if there is none, with the help of an ordinary bandage dipped in warm boiled water and wound around the finger.
If teeth begin to erupt, you cannot do without the use of special products (baby pastes, brushes, etc.).
When do baby teeth fall out?
“Childhood is over,” some parents say to their children whose baby teeth have been replaced by molars. Of course, this statement is mostly in a humorous form, since the average age when a child’s dentition ends is 12 years. At this time, the time of adolescence begins - one of the most interesting and eventful periods of our lives. As is the case with the eruption of baby teeth, their loss does not have a clear age limit. For example, today dentists are increasingly noting the early appearance of a full set of molars (as early as 10–11 years), whereas 20–30 years ago this could occur in adolescence (at 14–15 years). The service life of each baby tooth is on average 3-4 years: before the process of changing the dentition begins, the roots of the baby teeth are absorbed, so their loss does not bring severe pain and discomfort to children. Below is a table with the approximate timing of the loss of different groups of baby teeth.
Milk teeth on the lower jaw
| Name of teeth | Drop time |
| Central incisors | 5 - 6 years |
| Lateral incisors | 7 - 8 years |
| Fangs | 9 - 10 years |
| Premolars | 10 - 11 years |
| Molars | 11 - 12 years |
Milk teeth on the upper jaw
| Name of teeth | Drop time |
| Central incisors | 7 - 8 years |
| Lateral incisors | 8 - 9 years |
| Fangs | 10 - 11 years |
| Premolars | 11 - 12 years |
| Molars | 12 - 13 years old |
**Note: The first molar becomes the sixth molar, which does not have a primary tooth and erupts on its own at the back of the jaw.
Possible problems
At the moment the molars appear, certain dental problems are possible. In order to take timely measures to eliminate them, parents must have an idea about them.
Molars do not erupt
A situation is possible in which baby teeth do not fall out in a timely manner, or they have fallen out, but molars have begun to appear in their place. The reason for this must be determined by the dentist, who must be visited without delay. A general x-ray is usually taken to show the degree of development of the molars.
Among the options for the lack of eruption of molars in due time can be indicated:
- Hereditary predisposition, which is the cause of a possible delay in the appearance of molars. If the x-ray shows that the process of forming the rudiments of teeth is underway, then you will just have to wait a little for their appearance.
- Adentia. Disturbances in the processes of formation of tooth germs during the intrauterine development of a child, inflammatory processes can lead to a similar pathology - the absence or death of tooth germs. The solution is prosthetics.
Pain
The first time after teething, the tooth is poorly protected from caries and the effects of various bacteria. This is explained by the low degree of enamel mineralization at the initial stage. Almost nothing interferes with the development of caries; tooth tissue is destroyed, pulpitis occurs, with the subsequent risk of its transition to periodontitis. Severe pain, changes in body temperature and deterioration in well-being may occur.
It is highly advisable not to let the situation get worse, not to cause severe pain, but to visit a dentist as soon as painful sensations appear. If a child is predisposed to caries, it is better to carry out preventive procedures, for example, fissure sealing. The folds on the chewing surface are covered with a composite material that protects such natural cavities from the accumulation of food debris in them, the development of bacteria, and inflammatory processes.
In the worst case, you can lose a tooth.
Teeth grow crooked
A common situation is when the molar has already begun to erupt, but the baby tooth does not want to fall out. The result is that the new tooth seeks alternative growth paths, which leads to its displacement and change in the direction of growth. Hence the malocclusion and the alignment of the dentition. Treatment by an orthodontist will be required.
If this situation occurs, you should not remove or loosen a baby tooth yourself; you should visit a doctor.
Loss of molars
An alarming symptom of the presence of diseases (caries, etc.) in the oral cavity, or there are problems with the entire body (connective tissue diseases, diabetes, etc.). A visit to the doctor is mandatory.
This is necessary to develop a strategy for restoring a lost tooth. This is necessary for the proper growth of the remaining teeth and the formation of the maxillofacial system. Considering that the jaw tissue is still in the process of growth, prosthetics are only possible temporary, which must be adjusted as the jaws develop. Permanent prosthetics will be available only after their formation is completed.
Injuries
The first few years after teething, teeth are at increased risk of injury from impact. Sports injuries, falls, and blows can lead to chipping of parts of the tooth and cracks. Be sure to contact a dentist who will restore the lost part with modern materials.
Problems with changing teeth
As with the eruption of baby teeth, molars can also be difficult to erupt. Sometimes the crown part of the tooth does not appear completely or is completely hidden in the soft tissues. This situation is usually called retention: it can be caused by improper or too deep seating of the germ, as well as late loss of a baby tooth in its place. Just as in the case of baby teeth, a child may have no molar rudiments at all: this happens due to metabolic disorders, insufficient mineralization or damage to the rudiments at the intrauterine stage of development. This can also occur when infections and inflammations are transferred from baby teeth and in some other individual situations. This problem can only be corrected by prosthetics or implantation after reaching adulthood.
How does teeth change?
The rudiments of future permanent units are located under the root of the baby tooth and are separated from it by a thin bone septum. At 6–7 years of age, osteoclasts of the connective tissue surrounding the baby tooth dissolve the mineral component of the septum and destroy it. At the same time, the pulp of the temporary unit is gradually transformed into granulation connective tissue rich in osteoclasts, which gradually destroy the dentin of the primary tooth. At the same time, the roots of the temporary units dissolve and, in fact, only the crown of the baby tooth remains. It can be easily removed on its own, with the help of the dentist’s manipulations, or it can be pushed out by an actively growing molar (permanent) tooth.
Anatomy of permanent teeth The permanent units of a child (and an adult) have a complex anatomy.
Visually, the tooth consists of three parts - crown, neck, roots.
- The crown is the visible part of the tooth that rises above the gum.
- The neck is the part of the tooth at the gum level, in the place where the crown meets the root, and the enamel of the unit turns into cement.
- The root is the part of the unit invisible to the eye, located in the alveolar socket. The base of each unit is made of dentin, a hard tissue. In the coronal part, dentin is covered with enamel, and in the root part there is cement. Inside the dentin is the dental pulp - loose fibrous soft connective tissue, penetrated by a large number of blood and lymphatic vessels and nerve endings. Passing along the root canal, through the apical foramen located on the upper part of the root, they communicate with the main neurovascular bundle, providing nutrition to the tooth, drainage of excess fluid and its innervation.
Normally, by the age of 13, when a permanent bite is formed, a child has 28 permanent teeth. At the age of 17 - 25 years, third molars (wisdom teeth) erupt and the number of units may increase - 32 teeth.
Milk teeth in adults: when childhood drags on
Yes, this happens, but very rarely. In dentistry, there are cases where baby teeth were found in thirty-year-old and even fifty-year-old people: doctors call such teeth persistent. What is the reason for such dental infantilism? This happens precisely for the reason that we talked about above. When a person lacks the rudiments of permanent teeth, the replacement mechanism does not start. Simply put, nothing puts pressure on the roots of baby teeth, which is why they do not dissolve, but remain in the oral cavity of an adult. It also happens that the rudiments of the molars are located too deep and also do not come into contact with the roots of the milk teeth. Treatment here is purely individual. If a person has a healthy baby tooth with intact roots, under which there is no molar rudiment, it makes sense to have it replaced with a veneer or crown in order to protect it from the external environment and give it the desired shape. If the baby tooth is unstable and its roots are resorbed, extraction is recommended. If there is a permanent tooth germ underneath, then it is “pulled” out; if not, a prosthesis is installed.
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
If you have carefully read the article up to this point, then you should have no doubts. Baby teeth must be treated, since they are directly involved in the formation of the bite and the appearance of permanent teeth. If baby teeth are not treated and cared for properly, there is a high risk of early loss. The enamel of baby teeth is thin; it quickly succumbs to the pressure of carious bacteria and the destructive effects of the external environment. Moreover, the inflammatory process, having penetrated into the depths of a baby tooth, can damage the rudiments of a molar, and then you will lose not one, but two teeth at once. Monitoring the child’s hygiene and regularly taking him for preventive examinations is the task of every parent.