There are many experiences and myths associated with the eruption of children's first teeth. Despite the fact that in the photo children with front milk teeth look touching, in fact this is a nightmare for most parents, who are accustomed to attributing all the whims and ailments of the child to “teeth”. However, modern dentists and pediatricians are not so categorical and recommend reconsidering your attitude towards such an important moment in life. “Forewarned is forearmed,” so first you should find out as much information as possible from the primary source, that is, from practicing pediatric dentists.
What is milk bite? Formula
The appearance of baby teeth is a signal that the baby is growing up. From the point of view of human development, their appearance indicates the following:
- The child is ready for the transition from sucking to chewing, that is, from mother’s milk (or formula) to complementary foods and a gradual transition to normal food.
- From the intuitive production of individual sounds, the baby moves on to understanding speech addressed to him and even tries to imitate it.
The rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the womb, so the woman’s condition during the first trimester of pregnancy is responsible for the predisposition to “bad teeth”.
How many baby teeth should children have? The temporary bite has 20 teeth, of which 8 are incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars.
In dentistry, there are several ways to designate a temporary occlusion. In ordinary life, this information is unlikely to be useful to the mother, but it can help to better understand the dentist’s explanations and actions during the appointment.
- The classical Zsigmond-Palmer system, which was adopted for a long time in the USSR. In it, the milk row was designated with Roman numerals.
- A modern system accepted throughout the world, including by the International Dental Association. It involves using two numbers to designate each tooth. The first number indicates the quadrant in which the tooth is located (upper left or lower right), and the second number indicates the serial number of the tooth itself.
- An alphanumeric system in which each type of baby tooth is designated by a capital letter, and the index number is a serial number. This method is very convenient to indicate a changeable bite. To do this, you just need to replace lowercase letters with capital ones. This change is immediately noticeable.
- In America, it is customary to designate baby teeth using the letters of the English alphabet, placing them from the upper right molar to the lower right.
- You can also find the group designation of milk occlusion. In it, the number indicates the number of teeth of a certain group, and its location, in fact, the type of tooth.
- Similarly, temporary occlusion can be recorded using an alphanumeric system.
How does the jaw of baby teeth differ from permanent teeth?
There is an opinion among parents that baby teeth grow without roots. This myth appeared because during a change in bite, teeth fall out with reduced (resolved) roots. In fact, baby teeth have roots, and their number completely corresponds to that of permanent teeth. Despite the fact that the teeth of the temporary and permanent dentition are similar in appearance, there are several differences between them that help dentists accurately determine the group affiliation of the tooth.
| Milk bite | Permanent bite | |
| Number of teeth | 20 | 32 |
| Premolars | No | There is |
| Color | White-blue | Yellowish |
| Size | Small | Big |
| Crown sizes | The crown is wider than it is tall | High crown |
| Crown to root size ratio | The crown is more convex, making the roots appear smaller | Traditional ratio of crown to root sizes. |
| Presence of enamel roller | In the area of the neck of the tooth there is a thickening of the enamel, due to which the crown becomes larger. | No |
| Degree of mineralization | Low | High |
| Cavity dimensions | Extensive | Standard sizes |
| Channels | Wide canals and apical foramina | Narrow, sometimes difficult to pass with irregularly shaped branches |
| Root shape | Rounded | Long and elongated |
| Direction of root growth | Moved to the side to make room for the permanent tooth germ | Perpendicular to the jaw bone |
| Root reduction | Eat before changing bite | No |
| Tremas and diastemas (distance between teeth) | Normal physiological state as the jaw grows (from 4 to 6 years) | It shouldn't be normal. |
| Lumps and cutting edges | By the time the bite changes, they are erased (by 6 years) | Well expressed throughout life |
Possible abnormalities in the child
Parents should know when to expect changes in their child's bite . Late change of baby teeth, like premature change, is undesirable. They speak of lateness when an eight-year-old child has not yet lost any of his incisors; they speak of early eruption if a five-year-old child has already lost many of his incisors and fallen out. It is important to find out the cause of the changes occurring and, if possible, eliminate it.
Factors due to which the bite changes earlier than standard periods:
- severe jaw injuries;
- congenital diseases leading to anomalies in the eruption of temporary and permanent units;
- advanced caries, due to which crowns and roots are destroyed faster than necessary.
As for a late shift, it is possible due to:
- rickets, calcium and vitamin D deficiency in the child’s body;
- hereditary characteristics of the dentofacial apparatus;
- some infectious pathologies.
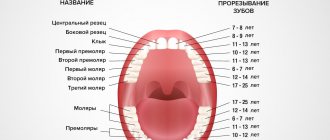
Which baby teeth do children cut first?
Typically, the lower primary teeth erupt first, followed by the upper pair of antagonists. The first teeth always grow in twos, with a slight time difference.
So which tooth comes in first? First, 2 central lower incisors appear, then 2 central upper ones. Following them, the lateral incisors are cut in a similar sequence - first the lower, then the upper.
Then the lower pair of first molars erupt through a short space from the lateral incisors. A similar picture is observed from above. After some time, a pair of fangs will grow in this gap. The formation of a temporary occlusion ends with the appearance of second molars, which also erupt first from below and then from above.
Dentists and pediatricians allow some deviations in the order of eruption, designating this as a variant of the individual norm.
Drop order
The dropout pattern looks like this:
- 5-7 years - central incisors;
- 7-8 - lateral incisors;
- 9-11 - first molars of the upper jaw and second molars of the lower jaw;
- 9-12 - fangs;
- 10-13 - second molars of the upper dentition and first lower ones.
The diagram shows that the timing of changing units is quite arbitrary and quite long. This is why some children already have a permanent bite at the age of ten, while others still walk around at the age of 12 with actively loose baby teeth.
When do babies get their first teeth?
Undoubtedly, the question at what age children begin to develop their first baby teeth is very important for all parents. It is a kind of measure of the “normality” of the baby and determining the degree of its development. The classic timing for the appearance of a milk bite is as follows:
| Age, month | |
| Lower central incisors | 6-8 |
| Upper central incisors | 7-9 |
| Lower lateral incisors | 7-9 |
| Upper lateral incisors | 8-10 |
| Lower first molars | 12-16 |
| Upper first molars | 13-17 |
| Lower canines | 15-20 |
| Upper canines | 16-20 |
| Lower second molars | 20-30 |
| Upper second molars | 21-30 |
Recently, cases have become more frequent when a baby’s first tooth is cut before the generally accepted period of an average of 4 months. Many cases of babies being born with an erupted tooth have been recorded. Modern pediatricians consider this normal and do not recommend that parents worry about this.
However, parents are much more worried about the late appearance of teeth. The first incisors can appear at 10 months, a year or even later. No one can say in advance how many months a child’s first tooth will erupt. If the baby is healthy, eats well and receives a preventive dose of vitamin D in the autumn-winter period, then late teeth are also an individual version of the norm. By the way, the time of teeth appearance does not affect the “painfulness” of the process. This is another myth that the later the teeth are, the harder it is for the child to bear it.
How long does it take for a baby to cut his first tooth?
From the very moment the baby’s gums swell, and with all his appearance he shows that his first teeth are about to appear, mothers begin to worry about the question, how long does it take for the very first tooth to appear? How long will the child be capricious, hungry and have difficulty sleeping?
Since the schedule for the appearance of baby teeth is individual, the time required for the appearance of one is also difficult to predict. The speed of teething can be affected by the child’s health status, lack of calcium and other factors.
Scheme of eruption of the first milk teeth in children
The timing of the eruption of baby teeth is indicated in the table above, and how they are located in the jaw is shown in the figure.
On average, by the age of one year, a child should have 4-6 milk teeth, ideally 8, however, modern pediatrics and dentistry do not consider it a pathology if a completely healthy child has deviations in one direction or another.
Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
The chewing apparatus is improving and developing. In infancy, it is adapted exclusively for the intake of liquid food - breast milk. But closer to six months, you can already see baby teeth in children’s mouths. They allow the baby to get acquainted with the variety of solid adult foods.
There are few temporary teeth - ten pieces in each jaw. This is quite enough for the baby to eat well and talk normally. Closer to primary school age, the jaw grows. She is ready to cope with more serious chewing loads. Then children's incisors, canines and molars begin to wobble. They are replaced by a constant shift.
What does a baby tooth look like?
Externally, baby teeth are very similar to molars. The differences that exist between them are described in detail in the table above and are practically invisible to anyone except the dentist.
The milk bite consists of:
- 8 single-rooted incisors;
- 4 single-rooted canines;
- 4 double-rooted lower molars;
- 4 three-rooted upper molars.
What is the name of the first tooth that appears in the jaw? Typically, bite formation begins with the lower central incisors.
Timing of baby teeth loss
The primary bite is formed during the period of active jaw growth. In this regard, already at the age of 3-4 years, three spaces should be formed - interdental spaces, which are necessary to ensure the physiological displacement of teeth during their replacement, the correct location of the erupting permanent teeth in the dentition.
By the age of five, children begin to experience, and then steadily progress, loosening of their teeth. This process is due to the gradual resorption of the roots of baby teeth, the place of which in the jaw is taken by the rudiments of permanent teeth moving towards the edge of the gum. When the time comes, the loose tooth falls out, and a permanent one should begin to emerge in its place within 2-3 weeks.
The entire period of mixed dentition requires increased attention from parents and specialists to the condition of the child’s oral cavity. Any pathological changes can lead to impaired teething, the formation of occlusion anomalies, crowding of teeth and other changes. Ideally, at the age of 5-6 years, you should visit the dentist every 2-3 months.
Symptoms and signs of a baby's first teeth
How can you tell if your child is cutting a tooth? The symptoms are extremely varied in the range of organs involved, in duration, and in intensity. Usually the baby has:
- Runny nose - clear fluid discharges from the nose, similar to that of a viral disease.
- Redness and swelling of the gums is the most striking and main symptom indicating teething.
- Temperature – may rise to individually high levels, or may be completely absent.
- Diarrhea - judging by the reviews of mothers, the eruption of baby teeth is often accompanied by severe diarrhea. The feces are quite smelly and acidic, so they quickly cause irritation on the buttocks.
- Irritability, tearfulness, refusal to eat – all these are subjective signs that may indicate a deterioration in the baby’s condition. They indicate pain, discomfort and general malaise.
How to help your child when teething?
The most important thing is to identify the problem in a timely manner. It is necessary to exclude colds, gastrointestinal diseases and other pathologies. To do this, you should see a pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
In the case where teeth are definitely involved, the following must be done:
- Provide the baby with comfort and peace. Avoid attending noisy events and receiving guests. Walk more, ventilate the room, create a favorable psychological atmosphere at home.
- Limit food. Offer breast milk or formula more often, remove complementary foods. If the child is already eating nutritious food, then do not introduce new foods.
- Provide your baby with all kinds of teethers and chewers. Carefully ensure that they are appropriate for the child’s age.
- Special anesthetic gels can be applied to the gums. All of them are divided into three types - short-acting, long-acting and without anesthetic (based on plant extracts or homeopathy). It is better to consult your doctor about which one you should buy.
- If a child develops a fever when his baby teeth are cutting in, he can be given an antipyretic and pain reliever. The dose, form and composition of which should be discussed with your doctor. It is better not to abuse this measure, since such drugs can be used for no more than 5 days in a row.
What to do when the first tooth comes out?
From the moment your baby's first tooth erupts, you need to start brushing it every day. First, mom does this by wrapping her finger in clean gauze. It gently massages the gums and cleanses the enamel of the first incisors. You can also use a finger brush for this. You don't need toothpaste at this stage yet.
As the child grows up, it is necessary to introduce him to such an important item as a toothbrush. The optimal age for this is the first birthday. If parents regularly brush their teeth in front of their baby, then the process of involving him in this fun game will be quick and painless. At this point, you can already purchase a special children's toothpaste marked from birth.
Read the age restrictions on toothpaste carefully. Typically, those suitable for children under 3 years of age do not contain aggressive substances and can be swallowed. Toothpastes intended for ages above 3 years may contain fluoride and other necessary ingredients, which, however, are not recommended to be swallowed. Manufacturers are guided by the fact that at this age the child already knows how to spit out excess toothpaste and rinse his mouth.
What to do if the order and timing of the eruption of baby teeth in children is disrupted?
It is not uncommon for a child to cut his first milk teeth at the age of one year or even later, or, on the contrary, a four-month-old baby can already boast 1-2 incisors. Dentists and pediatricians recommend not to panic and not take any action. Under no circumstances should you start giving your child any medications or vitamins without a doctor’s prescription. The appearance and growth of primary teeth can occur according to an individual schedule, taking into account genetic predisposition.
If the baby is completely healthy, then parents should be patient and just wait. Primary (congenital) adentia is an extremely rare phenomenon. The complete absence of at least one tooth germ is found in less than 0.1% of newborns.
What to do if baby teeth are crooked?
No one can answer the question why children's baby teeth grow incorrectly. In the vast majority of cases, we are talking about hereditary predisposition or intrauterine malformations. In the photos and videos of babies you can see that the problem of crooked first baby teeth is quite common. So what to do in this case? Contact an orthodontist as soon as possible.
To correct malocclusion at a young age, the following are used:
- Vestibular plates of Dr. Hintz;
- Trainers and LM activators;
- Braces.
Often a permanent tooth appears under a baby tooth, breaking the orderly row. In this case, removal is often indicated, however, the final verdict remains only with an orthodontic specialist.