From this article you will learn:
- causes of gum inflammation,
- how gums are strengthened at the dentist,
- treatment regimens.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Complaints about weak, loose gums are typical for people with low-grade chronic inflammation of the gums (for example, chronic gingivitis or periodontitis). With a low severity of inflammation, such patients also experience bleeding gums and pain when brushing teeth, as well as swelling, redness or cyanosis of the gum margin.
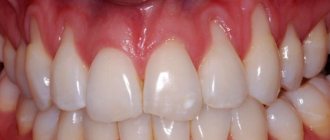
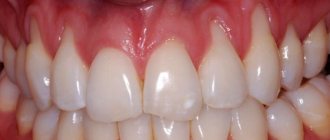
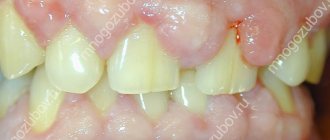
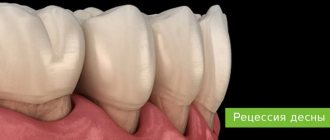
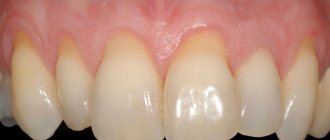
In moderate to severe forms of inflammation, the above symptoms are gradually joined - periodic discharge of pus from under the gums, increasing mobility of the teeth, exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth. Patients notice that the gums seem to move away from the teeth (Fig. 4), which indicates the destruction of the dentogingival attachment and the formation of periodontal pockets.
What weak, inflamed gums look like: photo
Most often, loose, weak gums are characteristic of patients who have been trying to treat inflammation at home for a long time, using various rinses, gum gels or anti-inflammatory toothpastes. Their independent incorrect use always leads to only a temporary improvement, while the inflammation does not completely disappear, and the condition of the gums continues to slowly deteriorate. In this article we will tell you why this happens and what to do about it.
Weak and loose gums: causes
To understand how to strengthen your gums at home, it is important to understand the causes of gum inflammation. If you look carefully at the photos of patients with gingivitis and periodontitis (Fig. 1-6), you will see that in absolutely all photographs in the area of the necks of the teeth or in the interdental spaces you can see accumulations of soft microbial plaque and/or deposits of hard tartar . And this is no coincidence. Inflammation in the gums does not occur on its own - it occurs solely due to the impact of pathogenic bacteria on the gums by microbial plaque and tartar.
Bacteria release various toxins and pathogens, which trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. And when you start using various mouth rinses, gum ointments or pastes for bleeding without removing plaque, all this does not in any way affect the cause of inflammation (plaque and tartar), but only allows you to muffle its symptoms. Due to strong active components, swelling and redness of the gums and bleeding are temporarily reduced. At the same time, pathogenic bacteria remaining on the teeth will continue to produce toxins, slowly and less noticeably continuing to destroy the gums.
Important: any antiseptic or anti-inflammatory agents for gums, used without first removing dental plaque, lead only to a temporary reduction in the symptoms of inflammation, but most importantly, to the transition of inflammation into a chronic form and unnoticed progression of the disease.
It is logical that the appearance of dental plaque is associated with insufficient/irregular oral hygiene. But when you start talking about this with patients, almost no one wants not only to admit this fact, but also to change their behavior pattern (dental care). Good oral hygiene includes more than just brushing your teeth after every meal, i.e. 3 times a day, but also be sure to use dental floss to clean the interdental spaces. Therefore, it is very important, among other things, to avoid snacking between meals.
Over the many years of working as a periodontist, I have seen thousands of patients who were willing to spend a lot of time preparing various tinctures, gum massage, all kinds of rinses and applications. But when it came to brushing their teeth, they were not able to spend 5 minutes 3 times a day to properly brush their teeth, first with floss, and then with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Although, it is this, and not various medications, that is the key to healthy teeth and gums.
Yes, and one more important point - looking in the mirror at their inflamed gums, some patients may not see the accumulation of plaque and tartar. How so? - you ask. Not only did they tell me that stones on the teeth are formed not from hard water, but from poor hygiene... there are also no stones on the teeth, but there is inflammation in the gums. What's the matter, doctor? I believed you so much... and then comes a crying emoticon. But the whole point is that hard dental deposits can be not only supragingival, but also subgingival.
In patients with chronic periodontitis, hard dental deposits (tartar) most often form in periodontal pockets, and look like microbial plaques of different sizes, firmly attached to the surface of the tooth root. Such subgingival dental plaque causes even more damage to the gums than supragingival plaque. At the same time, finding and removing them, due to the lack of visual control, is much more difficult and requires a certain skill and perseverance.
In the photo below you can see how teeth with periodontitis that appear to have completely normal gums can actually have a deep periodontal pocket with a large amount of destroyed bone tissue (the second photo was taken after gum detachment). And this destruction was caused by the very subgingival tartar that we indicated with the arrow.
This bone destruction caused by subgingival dental plaque proceeds unnoticed until a certain point - until the amount of bone destruction becomes so large that tooth mobility occurs. In general, after this, all treatment comes down to the fight for survival and an attempt to delay tooth extraction. Therefore, you need to go to the dentist and remove deposits - not when it gets really bad, but much earlier.
Strengthening gums: the right approach
Strengthening gums and teeth during gingivitis and periodontitis is possible in 2 options. Firstly, it is undergoing a professional course of treatment at the dentist, which primarily includes ultrasonic cleaning of teeth from stone and plaque. Plus a course of anti-inflammatory therapy, consisting of antiseptic rinses and special gels for the gums, which (with the exception of severe cases of periodontitis) can be easily carried out at home.
The second option concerns strengthening the gums in between courses of professional gum treatment at the dentist. If during the period of professional treatment (after removing dental plaque) products containing antiseptics and antibiotics are used, then for long-term maintenance therapy anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which will not cause harm with constant long-term use. We hope that it has become clear to you: the correct approach to gum treatment includes both professional treatment at the dentist and supportive treatment at home.
1) Removal of tartar and plaque –
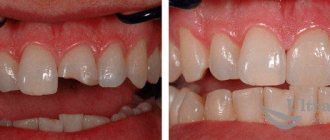
How important it is to professionally clean your teeth to remove plaque and tartar, and how the condition of your gums changes just a few days after high-quality removal of dental plaque – you can see in Figure 9-10. But we once again draw your attention to the fact that in case of periodontitis, it is best to remove dental plaque not from a dentist or hygienist, but from a periodontist.
→ Video of ultrasonic teeth cleaning procedure
2) Anti-inflammatory therapy –
After removing dental plaque, the doctor will prescribe you anti-inflammatory therapy, which you can do at home. Only in cases of severe periodontitis and deep periodontal pockets (in parallel with home therapy), the doctor usually schedules an appointment once a day (for 10 days) to rinse the periodontal pockets with antiseptics. The course of treatment usually lasts 6-7 days for gingivitis, and 10 days for periodontitis.
Home therapy consists of antiseptic rinses and applications of anti-inflammatory gel to the gums. Gum treatment is carried out 2 times a day. The following drugs are usually used in the complex: Chlorhexidine solution for rinsing (its concentration can be from 0.05 to 0.25%, which will depend on the severity of inflammation), and CholisalGel for applications. How to properly treat gums with these drugs is described in detail by us in the article at the link below:
→ Treatment of gum diseases
Important : if you decide to start drug treatment, ignoring the need to remove dental plaque, then remember that behind the visible temporary decrease in the symptoms of inflammation from such treatment, you will receive a subtle, increasing destruction of the attachment of the tooth to the gum and bone tissue. Over time, it will lead to tooth mobility, their removal, and the need for expensive treatment methods (for example, splinting teeth with fiberglass or curettage of gum pockets).
What to do to prevent the disease?
Preventive measures do not provide a 100% guarantee that you will never experience gum recession, but following them will help minimize the risks:
- regular and high-quality hygiene;
- professional cleaning of dental plaque;
- using a medium-hard toothbrush and proper brushing technique;
- timely diagnosis of caries and inflammatory processes;
- taking vitamins and amelogenin if there are risks of recession;
- giving up bad habits, especially smoking;
- correction of malocclusions, if you have them.
Strengthening gums at home: drugs, methods
As we said above, the best way to strengthen gums is proper and regular oral hygiene. However, there are a number of remedies that can further help you - improve the condition of your gums. Such products should not contain antiseptics and antibiotics, because the latter should be used only in short and infrequent courses (24stoma.ru).
High-quality oral hygiene –
In short... Teeth should be brushed after every meal, including lunch. To brush your teeth, you must first use dental floss, without which nothing will ever allow you to clean the interdental spaces from rotting food debris (toothpicks and mouth rinse are ineffective for this). At lunchtime, good hygiene involves a combination of dental floss + chewing gum. But if you no longer have gingivitis, but periodontitis, we advise you to have a second set of toothbrush and toothpaste at work.
You need to brush your teeth not 15 minutes after eating, but within the first 5 minutes. If you are visiting, at a restaurant, or outdoors, you should always have dental floss and a pack of chewing gum in your purse/pocket. It is very important to avoid snacks between main meals - no cookies, chocolate buns, etc. (apples that are not too soft are fine). If you eat candy, you need to brush your teeth. These are the simplest basic rules, the implementation of which is much simpler than the expensive and lifelong treatment of chronic periodontitis.
How to use dental floss and brush correctly -
Important: If you have crowns and bridges on your teeth, or if you have diagnosed periodontitis with deep periodontal pockets, be sure to use a home irrigator to rinse periodontal pockets and clean artificial crowns (in addition to basic hygiene methods). The cost of the irrigator will be 3-5 times cheaper than the cost of splinting mobile teeth, and also 10-20 times cheaper than the cost of open curettage of periodontal pockets.
Toothpastes for weak gums –
Such toothpastes can be divided into 2 groups. The first group of pastes contains potent antiseptics (usually chlorhexidine), and it is undesirable to use them for more than 2-3 weeks. It is optimal to use such pastes only as part of complex therapy during professional treatment of gingivitis/periodontitis at the dentist. Such pastes are good for relieving bleeding and swelling of the gums, and you can read more about them here .
But such pastes are not suitable for constant use, and their uncontrolled use can even cause harm (such pastes only suppress the symptoms of inflammation, making a person think that everything is fine). Therefore, to strengthen the gums, not antiseptics are used, but mild anti-inflammatory agents - extracts of medicinal plants, thymol, eugenol, clove oil, eucalyptol, bisabolol, allantoin, phenyl salicylate, as well as sodium fluoride.
a) Toothpaste “Parodontax-F” –
instructions for use- manufacturer - UK,
- active ingredients – extracts of echinacea, peppermint, sage, myrrh, chamomile, ratania, mineral salts, zinc citrate,
- fluoride content – 1400 ppm,
- price from 150 rubles (75 ml tube).
Comments: Parodontax toothpaste has a formulation that has remained unchanged since approximately 1890. This is a natural toothpaste that contains high concentrations of medicinal plant extracts and mineral salts, which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and astringent effect, due to which gum bleeding is reduced. Unlike many others, these pastes can be used on an ongoing basis to treat and prevent gum inflammation (due to the fact that they do not contain antiseptics).
b) Toothpaste “Parodontocide” –
instructions for use- manufacturer – Russia,
- active ingredients – mint and sage extracts, thymol, eugenol, allantoin, phenyl salicylate, sodium fluoride,
- fluoride content – 1000 ppm,
- price from 120 rubles (50 ml tube).
There are other good anti-inflammatory toothpastes besides the ones listed above. You can independently evaluate the compositions of pastes, taking into account our recommendations for active ingredients made above. However, an important point is not only the names of the active ingredients, but their concentration in the paste. And in the above pastes there is a fairly high concentration of medicinal plant extracts, as well as other medicinal components.
Treatment at home
Treatment of gum recession at home is impossible, since in advanced stages of the disease only surgical intervention can correct the situation. It is not possible to get rid of gum recession with ointments, gels and tinctures: at best, they will help cope with inflammation, but they cannot restore the edges of the gums. Anti-inflammatory therapy is used only as an addition to the main treatment. Folk remedies should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor or as a preventive measure. In the absence of pharmaceutical drugs, folk remedies may provide some benefit. A solution based on soda and salt, propolis extract, decoctions of oak bark, juniper and chamomile are just a small part of the folk recipes that can be used for gum diseases.