Author:
- Elena Vitalievna Naumova, otolaryngologist, leading doctor of the clinic
2.82 (Votes: 11)
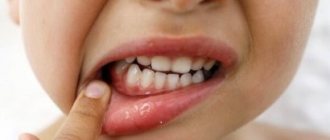
Acute tonsillitis with purulent exudate is considered the most common infection.
The disease occurs in both adults and children due to the entry of pathogenic microbes and bacteria into the oral cavity. It is not difficult to get a purulent sore throat even in the absence of direct contact with a sick person. Bacteria are spread through contact and airborne transmission, such as by sneezing or coughing in a public place or sharing household items.
How to squeeze out pus from the tonsils yourself
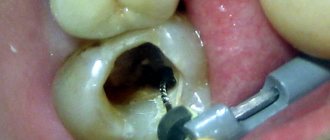
It is possible to remove purulent plugs from the tonsils at home if they are shallow and there is no swelling with hyperemia of the surrounding tissues.
Facilitates the process of assistance from an adult - a relative, a spouse, if it is impossible to seek professional cleaning from a doctor. Algorithm for step-by-step home elimination of bacterial plaque from the tonsils:
- Wash your hands with soap and water, treat with an antiseptic solution, and if necessary, use sterile gloves.
- Prepare a mirror, targeted home lighting from a lamp, a spoon, a plastic or metal flat stick, and a bandage. It is permissible to use a special sterile spatula, which is convenient and safe to remove pus, without the risk of infection from the outside.
- All objects and instruments for manipulation should be pre-treated with antiseptics and a mirror should be installed so as to see the deposits on the tonsils as much as possible. For disinfection, medications are used: Lugol's solution, Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin solution, potassium permanganate.
- You should take a clean household spoon in one hand and press your tongue, which can reflexively prevent you from clearing your tonsils. In the other hand is a spatula, at the end of which a bandage with an antiseptic is tightly wound.
- Carefully, without strong pressure, try to squeeze out plugs or remove films from the surface with a bandage, scraping without damaging the mucous membrane.
- You should not leave particles of pus or not completely remove bacterial deposits - this can cause new plugs to appear and the development of a sore throat with full-blown clinical symptoms.
- At the end of the home procedure for cleansing the tonsils, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic or chamomile decoction with calendula to disinfect, accelerate healing after manipulation, and prevent relapse.
You can squeeze pus out of your tonsils at home and avoid complications afterwards by following all the above rules. During the day after cleansing, you may experience a feeling of discomfort, soreness, hypersensitivity to cold or hot food, which is a normal reaction. You can relieve discomfort with throat tablets.
How to treat plaque on the tonsils?
To quickly restore health, as well as to prevent the development of complications and the disease becoming chronic, it is necessary as soon as you notice white on the tonsils
Depending on what microorganism provoked the inflammation, he may recommend the use of:
1
Antiviral medications. Drugs of this type are the first means that can be used when the first signs of a cold occur.
They help increase the body’s defenses, so pathogens die much faster and do not have time to cause serious disorders.
The most effective antiviral agents include:
Interferon, Nazoferon, Oscilococcinum, Isoprinosine, Aflubin, Anaferon, Viburkol, Proteflazid, etc.
2
Antiseptic solutions. If you start gargling with antiseptics in a timely manner, it is possible to suppress the development of infection in the early stages.
However, they are also used in later stages of disease progression, as they help eliminate the purulent film.
As a rule, for this purpose it is used
: Rotocan, solution of Furacilin, Streptocide, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin. If you don’t have them on hand, you can simply rinse your mouth with a weak solution of baking soda. More details about the methods:
3
Antibiotics. Since the main reason that the tonsils are covered with a white coating is bacterial flora, the main method of combating it is considered to be taking antibacterial drugs.
They destroy the cells of microorganisms and thereby lead to their death. Initially, they try to cope with the problem using local agents, for example, with the help of Polydexa or Isofra.
However, in severe cases it is impossible to do without the use of systemic drugs.
For respiratory infections, antibiotics of the penicillin group (Augmentin, Ampicillin), macrolides or cephalosporins are most often prescribed.
4
Fungicides. Antifungal drugs are prescribed exclusively for oral candidiasis. Initially, it is recommended to treat the affected areas with special local agents, for example, Candide.
But in the absence of the desired effect, they are replaced with systemic drugs:
Fluconazole, Itrungal, Nizoral, Orungal, Mikosist, Diflucan and others.
5
Tablets, lozenges and sprays. Such medications help eliminate pain and have a local anti-inflammatory effect.
They are present in a huge variety on the modern pharmaceutical market: Strepsils, Lisobakt, Faringosept, Septolete, Trachisan, Tos-Mai, Isla-Moos, Septefril, Lizak and others.
6
Antihistamines, usually used in conjunction with antibiotic therapy. These are: Loratadine, Eden, Erius, Diazolin, Suprastin, Fenistil.
Patients are also often prescribed professional film removal, carried out in the ENT doctor’s office.
It involves mechanical rinsing with a special solution supplied into the oral cavity from a syringe with a special type of tip. The procedure is quite unpleasant, but effective.
Causes of sore throat (acute tonsillitis)
The accumulation of purulent “sacs” in the tonsils occurs for various reasons. The main causative agents of tonsillitis are streptococci, but viral and fungal pathogens, staphylococci and pneumococci are also found. If the body is healthy, then the infection will not develop, but the following factors can aggravate the condition:
- Injuries to the tonsils and nasopharynx.
- Weak immunity.
- Chronic diseases of the ear, nose and throat, for example, stomatitis, caries, rhinitis, etc. foci of infection increase the proliferation of pathogens.
- Local and general hypothermia, for example, eating ice cream or drinking cold water.
- Autumn-spring vitamin deficiency.
The pathogenic factor penetrates deep into the tissues of the tonsils, forming a focus of infection.
Prevention
In order not to fight white plaque during the period of sore throat, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system in a timely manner. The body's defenses do not prevent the entry of harmful pathogenic microorganisms, so treatment of a disease with weak immunity may be delayed. For prevention purposes it is appropriate:
- Do not overcool;
- Eat properly;
- Temper yourself;
- Carry out immunotherapy during epidemics;
- Undergo preventive examinations with doctors;
- Take vitamin complexes;
- Completely cure dental caries;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- Walk in the fresh air at least 1 hour a day;
- Engage in moderate physical activity.
Do not forget to visit a doctor at the first manifestations of the disease. If you self-medicate, there is every chance of developing the disease.
White plaque on the tonsils is only a symptom that needs to be dealt with. A competent and professional approach to treatment will help you forget about a sore throat within a week. If you ignore the advice of doctors, a sore throat will lead to a number of complications.
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis
Drug therapy is prescribed only after examination by an otolaryngologist, laryngoscopy, and blood and smear tests. The examination will show the nature of the plaque - lacunar tonsillitis is characterized by a fluffy filmy coating.
Basically, the treatment regimen does not differ from ordinary tonsillitis. It includes:
- Taking medications. This necessarily includes antibiotics of the penicillin group and macrolides. They are the ones who fight the main cause of the disease – streptococcus. Antipyretics, antihistamines to relieve swelling of the tonsils, and eubiotics to restore intestinal flora after taking antibiotics are also prescribed.
- Gargling.
- Irrigation of tonsils with antiseptics.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Inhalations. Cleansing the upper respiratory tract with steam reduces swelling, inflammation and bacterial growth. Inhalation of alkaline water, saline, antiseptic, and homeopathic medicines has a beneficial effect. It is convenient to use a nebulizer as a nebulizer.
The duration of treatment is at least 7 days and no more than 14 days.
After the inflammation has decreased and pus has ceased to be produced, physiotherapy is prescribed. Infrared irradiation, magnetic therapy, and phonophoresis are effective. These procedures increase local immunity, accelerate tissue regeneration, and shorten the recovery period.
In case of inflammation of lacunae, nutrition is an important factor. Since swallowing is difficult, you need to eat liquid food. You should exclude all foods that scratch and irritate a sore throat. It is recommended to drink up to three liters of fluid per day to reduce signs of intoxication.
Treatment of white plaque on tonsils and tonsils
When plaque appears on the tonsils, both with and without pain, it should be taken into account that this is only a symptom. It will not be possible to get rid of it with solely symptomatic therapy; complete treatment of the disease is necessary, which includes:
- Antibacterial therapy for diphtheria, bacterial sore throat, stomatitis of bacterial origin.
- Antiviral therapy for acute respiratory infections, sore throats and stomatitis of viral origin.
- Antifungal therapy for pharyngomycosis or thrush.
- Rinsing with disinfecting solutions to remove film from the tonsils and oral cavity.
- Washing off the purulent film from the tonsils using a special syringe with a solution (this is how plaque is removed only in a hospital).
- Antipyretics for fever.
- Painkillers for severe pain in the tonsils.
- Immunomodulators.
- Maintain a gentle regimen for the throat: avoid spicy foods, loud and long conversations.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Taking multivitamins if you have a weak immune system.
It is prohibited to independently select medications to remove the accumulation of pus from the tonsils. At home, without diagnosis and consultation with a specialist, it is impossible to determine the type of pathogen, and therefore the direction of treatment.
Washing and rinsing
Washing of the tonsils is performed by specialists only on an outpatient basis.
The procedure requires special care to avoid injury to the tonsils. It is unpleasant and a little painful, so it is especially difficult to wash off the white coating from the child’s throat. There are also contraindications for this procedure: it cannot be done during pregnancy, cancer, severe hypertension, open tuberculosis, disorders of the autonomic nervous system
But proper rinsing effectively clears a white throat for various causes of plaque.
There are also contraindications for this procedure: it cannot be done during pregnancy, cancer, severe hypertension, open tuberculosis, or disorders of the autonomic nervous system. But proper rinsing effectively clears a white throat for various causes of plaque.
Washing tonsils in the clinic
Rinses can be varied: from cheap home remedies (soda-salt solution, chamomile decoction, furatsilin solution) to expensive pharmaceutical ones. The main condition is the frequency of manipulations. If you wash the tonsils rarely, the effect will not be achieved, since within a few hours the pus accumulates again.
Regular, frequent rinsing (once an hour or as prescribed by a doctor) allows you to remove germs, food debris, and immune cells, which eliminates the formation of a favorable environment for the life of microorganisms. Your tonsils will become less red and painful.
Complications
Lacunar tonsillitis can cause a number of negative consequences if you attempt self-treatment:
- Lack of oxygen.
- Swelling of the larynx.
- Abscess and phlegmon of affected tissues.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes, etc.
It is for this reason that it is important to immediately seek help from an otolaryngologist.
Experienced ENT doctors provide consultations at the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo. They will find an approach to both adults and children. Without fail, they will first conduct an examination to distinguish lacunar tonsillitis from another type, and then prescribe therapeutic therapy. Positive dynamics will be noticeable the next day. During the recovery period, to prevent relapses, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out - washing the palatine tonsils using the CAVITAR device (USOL therapy), exposing the tonsil tissue to low-intensity red laser radiation, introducing drugs into the tissue of the palatine tonsils using ultrasound.
How to remove white plaque from tonsils with sore throat
The appearance of white plaque on the surface of the tonsils is often observed with angina, in particular with its lacunar and follicular forms. The differences between these forms of the disease are that with follicular angina the plaque has the form of dots, and with lacunar angina - extensive spots or a continuous film.
In any case, the formation of plaque indicates a bacterial infection of the tonsils. It is necessary to treat bacterial tonsillitis on time, as it often leads to complications - paratonsillitis, otitis media and even rheumatism.
The question that worries everyone who is worried about sore throat and white plaque on the tonsils is how to remove and remove spots in the throat? Is it possible to do this at home, and how? This article will talk about how to remove plaque from tonsils with a sore throat in a safe way, and how not to do it.
Symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis
Signs of lacunar angina include general symptoms of intoxication and local inflammation of lymph tissue.
Upon examination, inflammation is visualized on both sides; one tonsil on one side is rarely inflamed. The clinical picture of lacunar tonsillitis is as follows:
- Sore throat.
- Pain when swallowing, talking and eating. At rest, pain does not bother the patient.
- Decreased appetite.
- Fatigue, lethargy, general malaise.
- Chills and fever due to elevated temperature. The temperature reaches 40° and lasts up to six days.
Specific symptoms include:
- Accumulation of purulent plugs of yellowish color. First, a yellowish-white coating appears around the tonsils, which is easily removed. Gradually it develops into a dense film, and it turns into purulent deposits if treatment is not started on time. Pus fills all the space in the recesses of the tonsils and surrounds them.
- Lumps under the lower jaw in the neck area.
- Bad breath.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
- Difficulty swallowing food. Swallowing disorder is associated with a strong increase in the size of the tonsils, which causes the digestive tube to narrow.
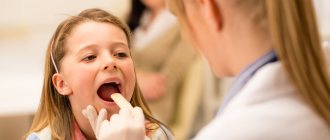
Diagnostics
Not many pathological conditions can cause the appearance of a layer on the tonsils, which is why an experienced specialist will not have difficulty establishing the correct diagnosis. The exception is plaque on the tonsils without fever.
In any case, diagnosis requires an integrated approach and includes:
Palpation of cervical lymph nodes
- conducting a detailed survey of the patient or his parents - to obtain a complete clinical picture for the clinician. It is necessary to inform the doctor about the first time of onset and intensity of symptoms;
- the doctor's examination of the patient's medical history and life history - this is necessary to search for predisposing factors;
- palpation of the neck - to identify enlarged lymph nodes;
- examination of the throat using special ENT instruments;
- laboratory blood tests will indicate the occurrence of a pathological process in the body;
- taking a smear from the tonsils for subsequent bacterial culture;
- PCR - to detect the pathogen that could cause the appearance of a pathological layer on the tonsils.
Only after the otolaryngologist has familiarized himself with the results of all examinations, can he prescribe an individual tactic on how to remove plaque from the tonsils.
To eliminate plaque from the tonsils in adults and children, conservative therapy is indicated, which is aimed at taking medications and using alternative medicine techniques.
Drug treatment includes:
- taking antibacterial and antifungal agents;
- treating the throat walls with antiseptic solutions;
- prescription of a vitamin complex;
- local use of dental anti-candidal ointments, which provide not only treatment, but also pain relief;
- taking agents that absorb and remove toxins;
- rinsing the mouth and throat with soda, saline and furatsilin solution;
- taking painkillers.
Folk methods for removing plaque from tonsils include rinsing the mouth or sucking using the following components:
- chamomile and calendula;
- sage and garlic;
- beet juice;
- lemon and honey;
- Luke.
Before starting such treatment, you should consult your doctor.
Surgical intervention for plaque on the tonsils and throat is used extremely rarely.
What is a sore throat
Classification
The disease can be classified according to the course of the process: acute (tonsillitis) and chronic (chronic tonsillitis). By localization - one-sided and two-sided. By form - typical or banal and atypical or isolated, rare.
Typical forms:
- catarrhal – the most common and relatively easily tolerated;
- lacunar – the second most common form;
- fibrinous - not only the tonsils are affected, but also the mucous membrane of the throat;
- follicular - characterized by purulent inflammation of the palatine, tubal, pharyngeal and lingual tonsils, locally manifested by separate purulent foci on the tonsils;
- phlegmonous (intratonsillar abscess) - characterized by purulent inflammation of the palatine tonsils and other lymphoid formations of the peripharyngeal ring. Most often it occurs as a complication of other types of acute tonsillitis.
Atypical forms:
- the ulcerative-necrotic or ulcerative-membranous form develops in people with severely weakened immunity and vitamin deficiency;
- laryngeal (submucosal laryngitis) can occur not only from exposure to pathogenic microflora, but also against the background of injury or burn of the throat;
- fungal form;
- herpetic – caused by the herpes virus (Kosaki virus) and, unlike other forms, spreads in the summer;
- syphilitic – one of the forms of syphilis, characterized by a long, sluggish course;
- monocytic – one of the forms of mononucleosis;
- agranulocytic – a rare manifestation of agranulocytosis.
Clinical manifestations
The disease is also characterized by severe pain in the throat when swallowing and in the tonsils, severe swelling of the tonsils and lymph nodes, plaque on the tongue and on the mucous membrane of the throat, and purulent plugs in the tonsils.
Treatment
Depending on the pathogen and the form of the disease, treatment is prescribed. The basis of treatment for acute tonsillitis is bed rest, antibacterial therapy, vitamin therapy, diet, and drinking regimen. In case of a viral nature of the disease, antibiotics are not prescribed.
For differential diagnosis and selection of adequate therapy, it is necessary to contact a specialist at the first manifestations of the disease.
Gargling with antiseptics, herbal decoctions, inhalations, and treatment of the mucous membrane with antiseptic solutions are mandatory.
Local treatment for sore throat is no less important than general treatment. Medications are used to relieve symptoms: painkillers, antipyretics, antitussives, and runny nose medications. Sore throat is accompanied by a runny nose and cough in the case of a secondary bacterial infection.
Cough and rhinitis are not typical for this pathology. It is strictly not recommended to remove purulent plugs from the tonsils on your own, as this can lead to complications (for example, an abscess, bleeding from the tonsils)
A sore throat is accompanied by a runny nose and cough if a secondary bacterial infection is attached. Cough and rhinitis are not typical for this pathology. It is strictly not recommended to remove purulent plugs from the tonsils on your own, as this can lead to complications (for example, an abscess, bleeding from the tonsils).
Consequences of tonsil removal
One of the most unpleasant consequences is weakening of the immune system throughout the body. As mentioned above, the tonsils are a natural protective barrier that blocks the passage of many bacteria and viruses into the lungs. After their removal, infectious diseases, flu and colds may occur more often. The same new coronavirus will have easier access to your respiratory tract.
The rehabilitation itself, even with the most painless surgical methods, can become an unpleasant surprise: swelling in the bronchi, soreness, crusting and the sensation of a foreign body in the throat. No doctor can answer for sure how long this will last - everything is too individual.
Please do not resort to surgical intervention unless absolutely necessary and clearly prescribed by a doctor. The tonsils are an important organ in our body, and its presence protects us from many unpleasant diseases. Contact only trusted ENT specialists and start treatment as early as possible.
Take care of your health!
What leaves tonsillitis on the tongue and teeth?
What effect does tonsillitis have on the tongue and teeth, and what measures should be taken?
A healthy oral cavity is of great importance for the entire body. Bad teeth can cause the development of many diseases. Chronic tonsillitis sometimes causes negative changes in the oral cavity, since the body cannot cope with pathogenic microbes on the tonsils and their aggression.
Gray and white coating on the tongue with tonsillitis
Tonsillitis contributes to the development of various concomitant diseases. This disease is characterized by a particularly negative effect on the tongue. If tonsillitis develops on the tonsils, a coating may appear on the tongue. This area on the tongue will become painful and turn bright red. The tongue with chronic tonsillitis has a heterogeneous gray coating. The inflammatory process affects the pharyngeal ring and tonsils, and they are located between the palate and the tongue. Pain in the tongue indicates inflammation of the tonsils.
photo of white plaque on the tongue with tonsillitis
Inflammation of the tongue is not a rare occurrence in the acute form of the disease. When tonsillitis develops, the tongue may become slightly swollen and have a white coating. The presence of a white coating on the tongue during tonsillitis is caused by inflammation of the tongue and is felt as an unpleasant burning sensation, which intensifies when irritated by food. Any changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue should be immediately examined by a doctor to further prescribe the correct treatment.
The effect of tonsillitis on teeth
Inflammation of the tonsils has a direct effect on the teeth. An infection located on the tonsils is easily transferred to the teeth. As a result, caries occurs, the tooth begins to decay and inflammation develops. Chronic diseases of the mouth, including tonsillitis, very often cause caries. When a doctor diagnoses tonsillitis, teeth must be carefully protected.
Caries is directly related to chronic tonsillitis. First, the infection transfers to the teeth, and then the carious teeth affect the tonsils. That is why doctors prescribe complex treatment of the oral cavity and pharynx. When tonsillitis is completely cured and the teeth are checked by a dentist, only then is the oral cavity completely healthy.
To prevent the inflammatory process in the tonsils from affecting the tongue and teeth, it is necessary to take some preventive measures
If you have tonsil disease, it is important to rinse your mouth with various antibacterial compounds. It is better to use the healing solution 2-3 times a day. It will eliminate the infection developing in the oral cavity
It will eliminate the infection developing in the oral cavity.
Share “What does tonsillitis leave on the tongue and teeth?”
We have all encountered more than once the problem of treating a sore throat, especially in childhood. And each of us has memories left in our memory, like a fragment of a picture from a movie, a warm bed, tea with raspberries and an anxious mother who is watching you with pain in her heart, putting a cold towel to her forehead, trying to reduce the fever, because... Typically, such infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are accompanied by high fever. So what causes a sore throat and how can you cope with the consequences of this disease so as not to provoke complications.
According to medical statistics, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the mouth and throat account for an average of 30% of the total number of diseases of the ENT organs. The main causative agents of this kind of throat infection are bacteria, the so-called pathogenic microorganisms staphylococci and streptococci, which can easily get on the mucous membrane of the throat and provoke inflammation, especially in children, who are traditionally included in the “risk group”. But in addition to pathogens of a bacterial nature, yeast-like fungi of the Candida albicans group and mold fungi of the genus Aspirgillius can also complicate the course of throat diseases, which are difficult to treat and require, first of all, diagnostic measures to identify the causative agent of the infection, both bacterial and infectious in nature, that provoked inflammation, and selection of a treatment regimen that can suppress two pathogens at the same time. And diseases such as pharyngomycosis and laryngomycosis are among the socially significant diseases, because require an individual approach to therapy.
Usually, the presence of an acceptable amount of opportunistic microorganisms produced on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, larynx and throat serves as a natural barrier against external infection entering the body, but as a result of exposure to external and internal factors, their volume may increase, and due to additional infection by bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms , diseases of an infectious and bacterial nature can develop, including those aggravated by a fungal infection, such as mycosis of the throat or candidiasis.
It should be noted that fungi of the genus Candida are quite widespread and, as a result, the possibility of getting this infection in public places through shared objects, food, including by airborne droplets is quite high. In addition, the development of this type of infection can be caused by such reasons as uncontrolled and long-term use of antibiotics without special indications, less often, disruption of hormonal levels and the endocrine system, reduced immunity, frequent diseases of a viral nature, childhood, incl. and incorrectly selected therapy for ENT diseases.
Fungal infections of the throat differ from the symptoms of ordinary sore throat of a bacterial nature in the appearance of plaque, which resembles cottage cheese. It is easy to remove, but underneath there is an inflamed mucous membrane, with redness and ulcers. And if a fungal throat infection is caused by fungi of the genus Aspirgillius, then such plaque is quite difficult to remove and has a yellowish tint. It should be noted that the localization of a fungal infection in the mouth and throat is also characterized by the manifestation of symptoms of a common sore throat.
It is quite difficult to detect fungus in the mouth and throat at an early stage, because... at the beginning of infection it usually does not appear, only as the colonies increase. Characteristic symptoms begin to appear gradually, in the form of discomfort, soreness, burning and dryness in the throat, and pain during swallowing. In addition, there is a presence of white plaque in the larynx, tonsils, tonsils and tongue, as well as the appearance of erosive surfaces in the form of ulcers and cracks in the mucous membrane of the throat. Traditionally, the temperature rises, headaches appear, swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa occurs, as well as characteristic symptoms of general poisoning and intoxication.
In children, the course of fungal tonsillitis is much more severe than in adults, because In childhood, the phenomena of intoxication in the body and pain syndrome are especially pronounced. The child becomes weakened, more capricious, and refuses to eat. In addition, when removing plaque from the mucous membranes of children, the delicate skin may be injured, and sometimes minor bleeding may occur. Also, in children there is a high probability of dysbiosis and diarrhea, due to the fact that yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida can move into the intestinal tract and provoke intoxication and characteristic symptoms of poisoning.
The initial diagnosis for the presence of fungi in the throat can first be carried out independently by examining the mouth and throat for the presence of white plaque. But it is important to remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, because... Only with the help of laboratory diagnostics can one identify the pathogen that has caused infectious and inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and oral cavity and select the necessary treatment regimen for this disease.
Instrumental research or laboratory diagnostics includes the following studies:
1. Laboratory mycological research - analysis of biomaterial (smear from the throat), provides the most accurate determination of the pathogens that caused a fungal infection of the throat.
2. A skin test with fungal allergens is carried out by introducing a fungal allegory test under the skin. This research method is necessary to establish the most accurate diagnosis and also to identify the chronic stage of the disease.
3. An immunological test is carried out to detect antibodies to the fungus in the blood.
These studies are the most informative and will allow the specialist to choose the right tactics for treating emerging lesions of the throat mucosa with fungal colonies.
After the doctor has made the correct diagnosis and identified the causative agent of the infection, the next step towards recovery is treatment of the fungal infection. The main goal is to get rid of a large number of pathogens in the throat, restore microflora, the integrity of the mucous membranes and strengthen the immune system. Treatment of fungal tonsillitis is carried out comprehensively, combining traditional medicinal methods in conjunction with a balanced diet. First of all, antifungal agents are prescribed, and if this therapy does not give the desired effect, antibiotics are prescribed. The course of treatment can last up to 2 weeks, but in acute forms of the disease it is necessary to prescribe additional therapy in the form of vitamins, antiallergic agents and probiotics containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli to restore normal gastrointestinal microflora. In addition, local antiseptics are additionally prescribed.
One of these drugs, which has proven itself in the treatment of ENT diseases, including purulent-inflammatory infections of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and throat, is the modern anti-inflammatory drug of plant origin Abisil, created on the basis of natural terpenoids of Siberian fir. The drug has pronounced anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic, wound-healing, and anti-exudative effects. It should be especially noted that microbiological studies of the drug Abisil revealed a wide range of antibacterial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative strains and various types of pathogenic microbes, often causing purulent-inflammatory diseases. Abisil is especially sensitive to staphylococci and streptococci, which are the main pathogens for throat diseases, in particular purulent sore throat. In addition, the drug was found to have antifungal activity against yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and mold fungi Aspirgillus. But the most valuable thing about it is that microorganisms do not become resistant to the drug, and therefore it can also be used in complex cases when inflammation is caused by antibiotic-resistant microflora. Possessing a complex and multidirectional effect, Abisil helps to get rid of purulent sore throat in a short time, including sore throat aggravated by a fungal infection. And in most cases, when traditional therapy for the treatment of fungal tonsillitis, including the simultaneous use of antibiotics and antimycotics, does not give the desired effect, Abisil therapy acts as an alternative to antibiotic therapy and shows a positive effect in the treatment of these pathologies. In addition, Abisil helps restore the activation of the protective functions of the mucous membrane and restores the balance of the microflora of the nasopharynx, in contrast to local synthetic antiseptics, which suppress both pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and throat.
The drug does not accumulate in the body, does not have teratogenic or embryotoxic effects and therefore can be used in all age groups, incl. and in children, and is indicated for use in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory throat infections. But in any case, to provide effective assistance and prescribe therapy for fungal infections of the throat, it is necessary to consult a doctor and his observation during the treatment. It should be noted that treatment with Abisil is simple and accessible. For tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, it is recommended to irrigate the mucous membranes of the mouth with the drug 2-3 times a day after meals. This can be done using a pipette or a syringe through a special nozzle, distributing Abisil in an amount of 1-2 ml to the area of the palatine tonsils and adjacent palatine arches, larynx and pharynx. In this case, it is additionally necessary to drip 2-3 drops of the drug into the nose. The duration of treatment is 1-3 weeks. In case of chronic disease, the course of treatment can be repeated after 1-2 months. After the procedure, it is not recommended to eat, drink or rinse your mouth for 3-4 hours. For fungal infections of the oral cavity, it is recommended to treat the affected areas of the oral mucosa 3-4 times a day with a cotton swab moistened with the drug. In addition, rubbing the drug Abisil into the front of the neck, into the area of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes is also effective. In rare cases, a short-term burning sensation may occur at the site of application of the drug, but it quickly passes. Combining the drug with other external agents is not recommended.
Another component of a full fight against fungal infections of the mouth and throat is a balanced diet, which additionally helps to get rid of mycosis. The fact is that fungi can feed on the foods that we eat and therefore, when forming a diet for the treatment of fungal sore throat, we should exclude foods that can provoke the growth of fungi, thus depriving them of additional nutrition. First of all, you should exclude alcohol, sugar, baked goods, baked goods, sweets, condensed milk, jams and preserves, dairy products, as well as canned foods containing vinegar. And the following foods must be included in the diet: meat, fish, eggs, cereals, legumes, fresh vegetables and herbs, garlic, spices, mineral water and tea.
You should pay attention to the fact that with improper therapy or neglect of the prescribed treatment by a doctor, complications of the disease can be provoked, in which the mucous membrane of the throat is destroyed and open wounds and ulcers appear on it, into which infection can re-enter and provoke secondary infection in the form of bacterial inflammation . Repeated inflammation is characterized by the appearance of abscesses and abscesses of the larynx. In addition, the development of fungi in the body can also cause a reaction in the form of an allergy, and most often, mycotic eczema can occur, which manifests itself in the form of peeling and the occurrence of inflammation and wounds on the skin. Another complication may be the occurrence of recurrent tonsillitis, which can occur frequently, once every 1-1.5 months, up to 10-12 times a year, and this is associated with the life cycle of the fungus.
What preventive measures must be taken so that the fungus in the throat does not develop further and does not develop into a chronic disease with frequent relapses. First of all, it is necessary to monitor hygiene and cleanliness of the oral cavity, and avoid contact with infected people. Take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, do not self-medicate and do not take antibiotics longer than the prescribed course. Make it a rule to visit the dentist for a preventative examination of the oral cavity and begin treating the disease immediately, without delaying it for later, and do not forget to strengthen your immune system. The most important rule in the treatment of fungal infections of the oral cavity and larynx is to identify the cause of the disease, eliminate the pathogen and adhere to the therapy prescribed by the doctor and a set of preventive measures so that possible relapses and complications do not arise in the future.
Causes of white spots on the tonsils in a child
The tonsils affected by white plaque are unable to perfectly perform their protective functions. This leads to the appearance of serious pathologies. To completely cure the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the formation of whitish spots.
If there is a temperature
If, in addition to white dots on the tonsils, the child’s body temperature is elevated, you should consult a pediatrician. Such symptoms may indicate a serious illness. Without treatment, the condition will only worsen; the pathology can lead to a number of complications and become chronic.
If a child has an elevated body temperature, then whitish spots on the tonsils can be caused by:
- Sore throat (acute tonsillitis). In addition to whitish spots, ulcers may be present. With a sore throat, the throat becomes red and sore, and the temperature rises to 39 degrees.
- Chronic tonsillitis. The disease develops as a result of prolonged inflammation of the tonsils after viral infections, which were accompanied by inflammation of the pharynx.
- Flu, ARVI or pharyngitis. The first symptoms of these pathologies appear in children on the tonsils in the form of white dots.
- Diphtheria. Whitish spots on the tonsils are combined with temperatures up to 40 degrees. Advanced cases can provoke the appearance of cardiovascular problems or disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Diphtheria is an infectious contagious disease. Therefore, a sick child must be hospitalized and isolated from contact with others.
Parents may also notice white dots in the baby’s mouth due to scarlet fever.
If there is no temperature
It happens that whitish spots on the tonsils are not accompanied by elevated temperature. This happens when food particles get into the loose tonsils. Thorough rinsing of the mouth quickly eliminates the problem. But it happens that plaque is a symptom of a serious illness.
Reasons for the appearance of white dots on the tonsils at normal body temperature:
- Stomatitis. In addition to plaque in the child, there is an increase in the submandibular lymph nodes and increased salivation. Erosion and ulcers form on the tonsils. Stomatitis is provoked by injuries, allergies, hypothermia, and low immunity. The disease is complicated by gangrene, loss of voice, and tooth loss.
- Candidiasis. Fungal infection can be a complication after therapy with antibacterial agents. Antibiotics not only inhibit pathogens, but also destroy beneficial microflora. This causes the proliferation of yeast-like fungus to become more active. Candidiasis is characterized by the formation of a white cheesy coating and ulcers on the tonsils.
- Leukoplakia. It manifests itself as keratinization and thickening of the oral mucosa. This process can take a malignant form. In addition to white spots on the tonsils, there are ulcers.
There is no point in trying to independently determine and eliminate the cause of the appearance of dots on a child’s tonsils. To avoid worsening the situation, it is better to take your baby to see a pediatrician.
Sore throat is dangerous because it can lead to serious complications from the gallbladder, heart, blood vessels and kidneys.
Questions
- Which doctor treats catarrhal tonsillitis in children?
ENT specialists are involved in identifying and treating catarrhal tonsillitis in children. - Is it possible to use traditional medicine methods for catarrhal tonsillitis?
Traditional medicine does not have official confirmation of effectiveness in the treatment of tonsillitis. However, one cannot deny the fact that in mild forms of the disease, local heat, hot tea and gargling with chamomile solution have a beneficial effect on the outcome of the disease. Therefore, such an unconventional approach to treatment is sometimes allowed. The main thing is to consult with a specialist to prevent the development of complications. . - Can a child eat ice cream after a sore throat?
Eating ice cream is not a direct cause of the development of catarrhal tonsillitis. Therefore, there is no need to strictly prohibit children from using this product. However, if the baby has just recovered, it is advisable to limit local hypothermia. Ice cream can be offered to him in a thinner and not so cold form. It will not cause harm, but, on the contrary, will cheer up the child. In addition, cold can act as a local anesthetic. - How dangerous is catarrhal tonsillitis?
The disease itself is relatively mild. In advanced cases, a secondary infection may occur, and the process becomes chronic. In the long term, this may cause damage to the cardiovascular system.
How to remove plaque from tonsils?
Having seen the film on the tonsils, many patients wonder - how to remove plaque from the tonsils with a sore throat? It is contraindicated to specifically remove plaque or remove ulcers. For this procedure, many patients lubricate the throat with various antiseptics using cotton swabs, but such manipulations should not be carried out. Such procedures only increase the likelihood of a bacterial infection connecting to an existing sore throat. The chances of introducing pathogenic microorganisms to the inflamed mucous membrane greatly increase, so it is not worth conducting such home “experiments”.
Plaque can only be removed with the help of a doctor, who will clear the throat with sterile instruments and in a sterile room. With proper treatment, the plaque will come off on its own.
Forms of purulent sore throat
There are two varieties:
- Purulent sore throat, affecting the lacunae of the tonsils. The infection is localized in the upper part of the throat and does not penetrate deeper. Purulent deposits are easily separated with a spatula.
- Purulent tonsillitis affecting the lymph nodes. The infection penetrates deeper and affects the lymphoid apparatus. Purulent exudate cannot be separated manually. The condition is extremely serious and threatens the formation of a peritonsillar abscess. Urgent medical attention and hospitalization are required.
Medicinal solution to the problem
Before prescribing the necessary medications, the cause of the disease should be determined. This will make it possible to choose the right remedy that will help you quickly get rid of not only the signs of the disease, but also its causes. If a sore throat is infectious, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Antibacterial and antiviral drugs are also selected. Sometimes the patient requires surgery.
Medicines are prescribed in combination with rinsing, sprinkling, and cleansing the mouth. Suppuration is best removed by rinsing. The most popular rinse is furatsilin tablets. To carry out the procedure, you need 1 tablet of the product, dissolved in warm water. To eliminate the effects of microcrystals on the tonsils, it is worth straining the solution. The throat should be rinsed for 5 minutes, every 2 hours.
Chlohexidine is also prescribed. It removes germs and relieves pain, preventing the spread of infection. For rinsing you need 1 large spoon of product. Antiseptic stopangin is used undiluted, 1 tablespoon. Gargle with chlorophyllipt 3 times a day, dissolving 1 teaspoon in a glass of warm water.
To remove plaque, you can use disinfectant solutions, treating the tonsils and oral cavity with them. It is necessary to make tampons from cotton wool or a bandage, soak them in peroxide and thoroughly wipe the tonsils and oral cavity. The procedure is carried out until the plaque is removed. In this way, pus is removed using:
- oily chlorophyllipt;
- Lugol's solution;
- stomatidine.
How to remove plaque on tonsils?
After consulting with your doctor and determining the cause of the plaque, you can begin to treat it. You can remove plaque on the tonsil by rinsing the throat with antiseptic drugs dissolved in warm water, such as Furacilin, Nystatin or methyl blue.
The drug Hydrocortisone in tablet or cream form helps eliminate lichen planus, which can also cause a buildup on the glands. If the cause is candidiasis, then the layering is removed with universal antifungal agents.
Pain and sore throat accompanying inflammation of the tonsils can be relieved by lozenges with an analgesic effect - Decathylene, Septefril, Faringosept.
Washing the tonsils in a hospital is the most effective method to get rid of white plaque. An otolaryngologist will help eliminate the problem by manipulating the use of an antibacterial solution, which enters the lacunae with a strong stream, cleaning them. As a rule, it is necessary to do up to 10 similar procedures within a month to completely eliminate the problem. They also use vacuum washing - the plaque is quickly removed and plugs can be removed under pressure.
You can also remove the layer at home - a piece of bandage or a cotton swab moistened with an antiseptic, wrapped around a pencil and made in a circular motion to remove the pus. You can also use a large moistened cotton swab for this purpose. In this way, only the surface film can be removed; the lumps in the gaps remain untouched.
Oral candidiasis
Since Candida fungi are constantly present on the mucous membrane, but cause disease only under certain conditions (immunodeficiencies, taking antibacterial drugs, early cessation of breastfeeding, poor hygiene, etc.), oral candidiasis is an autoinfection. Plaque with this disease can be:
- dotted, islanded or solid;
- foamy, curdled, filmy;
- white, yellowish.
Sore throat with candidiasis is usually not intense. The exception is a severe form of the disease, in which plaque covers the entire surface of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, is tightly fused to it and is difficult to remove. The layers take the form of films, the surface of which is dirty gray, and the lower layers remaining after partial removal are white.
In mild to moderate forms, the pain is moderate and accompanied by dryness in the mouth and throat. In the first case, the plaque is localized only on the tongue and/or cheeks; it is easy to remove, after which the reddened, intact mucous membrane is exposed. In the second case, fungi affect not only the superficial, but also the deep layers of the epithelium. The layers are located on the tongue, cheeks, hard palate, lips, it is difficult to remove them; when trying to do this, the mucous membrane is damaged and sometimes bleeds.
The leading symptom of the classic course of oral candidiasis is a cheesy white or yellow coating in the oral cavity (including on the tongue).
For a more accurate description, there is a comparison of the layers with curdled milk. More common are mild forms of the disease, which are characterized by limited, sometimes focal, lesions.
The following treatment options are used to help the patient:
These are various types of antibacterial drugs (Amoxicillin, Cefuroxime) for bacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis, antitoxic anti-diphtheria serum for diphtheria, antifungal agents (Diflazol, Diflucan) for candidiasis. Local antiseptics, antibiotics and antimycotics in tablets, sprays, solutions (Anzibel, Bioparox, Ekalin) are also used.
- Pathogenetic and symptomatic.
This group includes anti-inflammatory drugs - usually topical (Tantum Verde, Isla-moos), antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol), painkillers (Strepsils Intensive) drugs. Gargling (chamomile decoction, tincture of calendula, sage, Chlorhexidine) is also recommended.
- Correction of regime, nutrition.
Bed rest is necessary for fever, eating only warm, comfortable temperature foods and drinks, humidifying the air in the room where the patient is, stopping smoking and alcohol.
In severe cases of any disease with damage to the oropharynx and tonsils, hospitalization and detoxification therapy (sodium chloride solution, glucose, Dextrose, Reopoliglucin) are necessary. The treatment of oral candidiasis includes probiotics (Bioflor, Bifinorm), while limiting the amount of carbohydrates in the diet.
Treatment of diphtheria is carried out only in an infectious diseases hospital.
There is no need to specifically clean or wash off plaque:
The presence of plaque on the tongue of a patient who is bothered by a sore throat cannot be considered a sufficient sign to make a diagnosis. It is necessary to evaluate all the symptoms that are identified during the survey and examination, as well as during laboratory and instrumental studies. It is worth understanding that in some cases you may encounter not a classic, but an atypical form of the disease, in which the main manifestations will look different from what was expected. Only a doctor should prescribe treatment, especially if the patient is a child.
2016—2017, OOO "Studi Group"
Any use of site materials is permitted only with the consent of the portal editors and by installing an active link to the source.
The information published on the site is intended for informational purposes only and in no way calls for independent diagnosis and treatment. To make informed decisions about treatment and medications, consultation with a qualified physician is required. The information posted on the site is obtained from open sources. The portal's editors are not responsible for its accuracy.
Higher medical education, anesthesiologist.
Doctor of the highest category, pediatrician.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Mild forms of the disease can be managed at home, under the supervision of a local doctor3. An exception is sore throats in children under one year of age: they need to be treated only in a hospital3.
Moderate and severe tonsillitis at any age is an indication for hospitalization, as are any forms of inflammation in children with immunodeficiencies, developmental defects and diseases of the nervous system3.
Mode
In the first 3-4 days of illness, bed rest is indicated2.
Diet
The diet is gentle, with a predominance of dairy and vegetable dishes, limiting salt, sugar, and excluding spices and herbs.
Drink plenty of fluids
It prevents dehydration due to fluid loss during fever and helps reduce symptoms of intoxication.
Antibacterial and antiviral therapy
Bacterial inflammation requires treatment with antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets, injections or intravenous infusions - it is prescribed by a doctor. Regardless of how long the temperature lasts, if a child has a sore throat, the duration of treatment with antibiotics is at least 10 days2,3.
It makes no sense to give your baby antiviral drugs, since respiratory viruses, which most often cause tonsillitis, are practically insensitive to them1. In addition, viral forms of the disease are mild1,2.
Antipyretic drugs
WHO recommends the use of antipyretic drugs in previously healthy children only if the temperature rises above 390 C, and if heat is poorly tolerated: headache, aching muscles and joints2. For babies under one year of age, as well as children prone to seizures, fever medicine should be given earlier - as soon as the temperature reaches 380 C.
In other cases, you need to use physical methods to combat the fever: light clothing, a fan, rubbing, cold compresses on the forehead, armpits and groin area2.
Local treatment
It includes gargling with special solutions, irrigating the tonsils, and sucking special tablets containing antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic components.
To gargle with a sore throat, children from the age of three can use HEXORAL® SOLUTION for gargling based on hexethidine5. Hexetidine is active against bacteria, including beta-hemolytic streptococcus, respiratory viruses and fungi, and has a mild analgesic effect, so it can be used as an adjunct to the main treatment of tonsillitis5.
HEXORAL® SOLUTION is not suitable for children who, due to age and lack of skill, simply do not know how to gargle. For such cases, there is HEXORAL® in the form of an AEROSOL, which is evenly sprayed over the entire surface of the pharyngeal mucosa and provides the necessary therapeutic effect6.
For a 4-year-old child, HEXORAL® TABS7 is suitable, and for sore throat in a child 6 years of age and older, HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC8. HEXORAL® TABS7 contains, in addition to the antiseptic component, the local anesthetic benzocaine, which helps fight sore throat and facilitate swallowing7,8. The composition of HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC8 includes two antiseptic components, amylmetacresol and dichlorobenzyl alcohol, which enhance the antiseptic effect of each other. The pleasant orange, lemon, honey-lemon, and blackcurrant taste of the tablets is usually liked by children and encourages them to undergo treatment8.
HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA is intended for children over 12 years of age9. It contains lidocaine, a powerful pain reliever that helps fight even the most severe sore throat9.
Please note that after using the drugs, the patient should not be allowed to eat or drink for half an hour.
Up to contents
“Plaque on the tonsils” is observed in diseases:
Lacunar tonsillitis is an acute illness of an infectious nature, characterized by local inflammation of one or several elements of the lymphadenoid ring of the pharynx. Usually the inflammation covers the tonsils, but damage to the larynx and pharynx is also possible. This disease can be provoked by pathogenic microorganisms, including meningococci, streptococci, hemophilus influenzae, etc. The disease has no restrictions regarding gender and age.
Streptococcal infection is a group of diseases that causes pathological processes in the respiratory tract and skin. Infections of this type are present in the body of a healthy person. The development of the disease is possible only if there is a favorable environment for this. Children and pregnant women are most susceptible to the disease.
Follicular tonsillitis is a disease characterized by purulent inflammation of the follicles of the tonsils. If such a disease progresses, pus is located on the surface of the lymphoid formations of the pharynx in the form of separate pinpoint foci. The pathological process can affect the pharyngeal, palatine, tubal and lingual tonsils. The progression of follicular tonsillitis is accompanied by regional lymphadenitis and severe hyperthermia.
Description of the disease
Catarrhal tonsillitis is clinically the mildest form of the inflammatory process that can occur in the palatine tonsils.
In pediatrics, it occurs in children aged 6 months to 18 years. The disease responds well to drug treatment if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The pathology belongs to the group of tonsillitis. The palatine tonsils are the first barrier to the penetration of infection deeper into the respiratory tract, and therefore are often affected by the inflammatory process. Depending on the nature of the disease, angina can be acute or chronic. The severity of the inflammatory process varies.
- Catarrhal sore throat. This is the mildest form, in which the child’s general well-being deteriorates slightly.
- Follicular. The pathological process is accompanied by a pronounced disturbance of well-being.
- Lacunarnaya. This is a severe variant of follicular tonsillitis with high fever and massive damage to the tonsils.
- Membranous-necrotic. A critical condition that can cause acute airway obstruction.
Catarrhal tonsillitis in children can occur without complications (94-95% of cases) or with the development of undesirable consequences - tonsillar abscesses, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and the addition of a secondary infection.
Frequent catarrhal tonsillitis at an early age indicates a reduced barrier function of the tonsils. This threatens the process becoming chronic with the formation of a persistent focus of infection in the pharynx. A possible result of this development of events is acute rheumatic fever with damage to the heart. In particular, the heart valves suffer, and intracardiac hemodynamic disturbances (stenosis, regurgitation) occur.
The best way to prevent complications from occurring is to promptly contact an ENT doctor if you have any suspicious symptoms.
Reasons for the raid
The reasons may be different, but the main one is the proliferation of viruses and bacteria in the nasopharynx. It can occur due to diseases such as:
- tonsillitis (purulent ones are common);
- ARVI;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis (both viral and bacterial);
- candidiasis in the oral cavity;
- diphtheria is a serious illness requiring hospitalization;
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- mononucleosis;
- lichen planus;
- leukoedema;
- chemical burns from medications;
- syphilis.
Harmful organisms can enter the nasopharynx either through airborne droplets or due to non-compliance with hygiene rules and consumption of unwashed foods.
As soon as you notice purulent inflammation of the tonsils, consult a doctor.
To establish a clear diagnosis, you need to immediately conduct a comprehensive examination of the body, taking into account the symptoms that appear.