What is burnt alum
Burnt alum is a powdery substance that is obtained by heating a potassium-aluminum compound. After heat treatment, the substance is ground and sieved to isolate the hygroscopic powder. Burnt alum is white, odorless, and has a sour-astringent taste. Natural origin allows you to exclude perfume components, fragrances and artificially synthesized substances from the composition.
You can buy burnt alum in 50 g plastic jars. The instructions indicate that the product is intended for external use. It does not completely dissolve in water and tends to clump when left in the open air.
Manufacturers indicate only 100% crystalline powder of potassium alum in the composition.
Instructions for use
Alum is used as a mouth rinse for stomatitis.
To prepare the solution, add 0.5 tsp to a glass of boiled water. powder and stir it thoroughly.
In this case, the consistency of the solution becomes slightly viscous (like laundry starch), and the taste becomes sour. Should be used 5-7 rubles/day, duration of procedure is 1-2 minutes.
The use of the solution for the treatment of stomatitis in children is not prohibited, but the application pattern is modified: it is necessary to lubricate the oral cavity with a cotton swab 3-4 times a day and for 30-40 minutes. After the procedure, refrain from eating and drinking.
How burnt alum works
When applied topically, the powder acts in several ways:
- relieves inflammation and disinfects;
- dries;
- relieves itching;
- prevents and eliminates unpleasant odors.
The substance does not irritate the skin at the site of application. After application, it forms a colloidal film that envelops the nerve endings. It relieves pain, itching and burning sensations, and discomfort from insect bites.
Lotions, rinses
The rinse solution is prepared as follows:
- take the following ingredients: a glass of boiled water, 4-5 g of burnt alum;
- mixing until the crystals are completely dissolved;
- store the solution for no more than two days in the refrigerator;
- The liquid must be stirred before use.
To cure stomatitis in a child, you can use the method of spot treatment of ulcers with a concentrated solution.
To obtain the working fluid, you need to take 10 g of alum per glass of water. The solution is applied using cotton pads and rubbing.
The resulting solution should be used every 3 hours by rinsing. Afterwards it is recommended to treat the ulcers locally.
In what cases will burnt alum help?
According to the instructions for the drug, burnt alum is used in:
- combating excessive sweating. The ability to adsorb moisture and reduce the functioning of glands that secrete sweat and sebum is actively used by patients with hyperhidrosis. In addition, alum is able to disinfect areas with excessive sweating and get rid of bacteria and fungi that are sources of unpleasant odors; can be used as an antiperspirant;
- prevention of skin irritations, for treating minor scratches, including after using a razor;
- therapy of dermatological pathologies: dermatitis, diaper rash, eczema, neurodermatitis, fungal infections of the feet;
- gynecology and urology – for the treatment of vulvovaginitis, balanitis;
- dentistry - for the treatment of gingivitis, stomatitis;
- cosmetology - to narrow pores, increase elasticity, relieve inflammation. Added to powder or cream.
Burnt alum powder can be used to treat festering wounds and trophic ulcerations on the skin. As a result, the damaged surface of the skin will dry out and tighten, and bleeding will stop.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
There are several types:
- sharp;
- chronic.
This type of damage to the oral mucosa occurs when the herpes virus first enters the human body. Acute stomatitis is typical only for young children. Herpetic stomatitis that occurs repeatedly is called chronic. Herpes stomatitis in an infant appears due to infection of the child by the mother or other people who kiss the baby out of excess of feelings or taste food with the spoon with which he is then fed.
Acute herpes-type stomatitis
The herpes virus enters the baby's body after he reaches the age of six months. At this time, the antibodies the child received from the mother gradually cease to act. In the vast majority of cases (about 90%), the symptoms of stomatitis at such an early age are mild, and only in 10% of children the disease is acute.
Stomatitis in children under one year of age, the treatment of which takes about 2 weeks, is accompanied by weakness in the body, general malaise and muscle pain, which is explained by poisoning of the body. In some cases, the temperature during the first two days of the disease may rise to 40 degrees or higher. The lymph nodes become inflamed, and touching them causes pain to the baby.
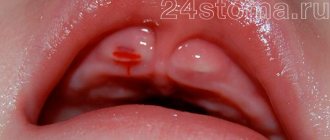
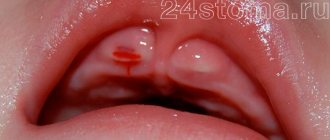
A distinctive sign of the disease are small bubbles that appear in groups on the lips, palate, and tongue. The oral mucosa takes on a bright red hue. The bubbles are filled with a clear liquid that gradually becomes cloudy. After about 3 days, the blisters burst, leaving behind erosions covered with a yellow or white fibrinous coating.
Sometimes the gums near the teeth may turn red, so the disease is often confused with gingivitis.
Chronic stomatitis
Once the herpes virus enters the human body, it remains there forever. Symptoms may occur when:
- cold;
- lack of vitamins;
- stressful situations;
- exacerbation of sinusitis, tonsillitis and other chronic diseases;
- injury to the mucous membrane;
- gingivitis or caries;
- habit of breathing through the mouth (lips become dry, causing the skin in the corners of the mouth to crack).
Chronic stomatitis develops in exactly the same way as acute stomatitis, with the exception that the disease does not affect the general condition of the body, because intoxication is minimal.
Herpetic stomatitis in children: how to treat
Types of treatment:
- Use of antiviral agents. Ointments and gels, which are often used to treat herpes on the lip, should not be applied to the oral mucosa. Treatment is possible with suppositories or tablets. The most effective drugs include two drugs. The first of them is “Viferon”, which contains interferons that have an immunostimulating effect. Available in the form of suppositories and gel. There are no age restrictions on the use of the product. The gel should be applied directly to the affected mucous membrane, after drying it with a swab. The treatment period does not exceed one week, provided that the product is regularly applied three times a day. The second is the antiviral drug Acyclovir, which acts on the herpes virus itself, and does not simply increase immunity. The dosage regimen is the same for children over 2 years of age and twice.
- Rinse. It is necessary to use solutions whose action is aimed specifically at suppressing the herpes virus (such popular and cheap remedies as chlorhexidine and various herbal infusions are not suitable). The most effective drug is Miramistin, which should be rinsed three times a day. For greater results, you can apply Viferon a short period of time after rinsing.
- Use of symptomatic remedies. Antipyretic drugs are used when body temperature exceeds 38 degrees. At lower temperatures, such tablets will do more harm, since they will interfere with the formation of natural immunity and the production of interferons.
- Use of immunomodulators. If stomatitis in children, which was treated according to all the rules, makes itself felt again, you can resort to the use of immunomodulators, the most effective of which are:
- “Immunal” is a basic drug that increases immunity.
- “Imudon” stimulates the immunity of the oral mucosa. One course lasts 20 days (you need to take 6 tablets every day). 2 courses per year are recommended.
- Toothpastes with lactoferrin and lysozyme (these substances are contained in special Splat children's toothpastes).
How to use burnt alum powder
The manufacturer prescribes the use of the drug, if indicated, externally as a powder; the frequency of administration is not limited.
Wounds and ulcers are treated with a solution of powder. To prepare, take ½ teaspoon of the substance and add to 200 ml of hot water. The composition is applied to the wound surfaces the required number of times; a gauze bandage may be applied.
When used simultaneously with other drugs, the powder does not react with them.
Preventive measures to prevent stomatitis in children
To minimize the risk of developing stomatitis you need to:
- wash the child’s toys, bottles and other things regularly, and do not forget to thoroughly wash the baby’s hands;
- strengthen the child’s immunity;
- do not let your child bite his nails;
- create a balanced menu containing all the necessary minerals and vitamins. The diet should be followed;
- promptly treat diseases such as tonsillitis, gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. If you extinguish the outbreak in time, this will prevent stomatitis from developing;
- At least once a year, and preferably twice, visit the dentist for a detailed examination of the oral cavity.
All these simple recommendations will help avoid the occurrence of stomatitis, because any disease is much easier and cheaper to prevent than to treat it later. If it was not possible to avoid the disease, at the first signs of it, you must consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment. If stomatitis appears again and again, a thorough immunological examination is required. The child should be examined by a pediatrician and an immunologist; it is also advisable to contact an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist (perhaps they will identify a chronic disease leading to relapse of the disease).
It is equally important to teach your child proper oral hygiene. If the teeth are affected by caries and covered with plaque, and there are fistulas on the gums, the fight against stomatitis will not be successful. A child must be taught how to properly brush his teeth and gums by buying him a brush and toothpaste appropriate for his age.
Recipes
A remedy to combat armpit sweating. To prevent the white powder from crumbling during application and to ensure that the composition gets directly onto the skin, it is better to prepare the composition:
- dissolve two teaspoons of burnt alum in 500 ml;
- add a few drops of essential oil with your favorite scent;
- pour the solution into a bottle equipped with a sprayer.
At first, the product must be used twice a day, then the composition can be applied to the armpit area once a day.
- For sweaty feet. In this case, dry alum is used. First you need to clean your feet with a pumice stone or a scraper. Then the surface is treated with alum. To enhance the effect, you can treat socks and shoes that are worn every day with alum. Already on the third day, sweat production decreases, cracks in the legs heal, and small wounds heal. To prevent the skin from drying out, the skin of the feet can be treated with cream.
- Face mask for enlarged pores. Ingredients you will need: one egg white, 5 grams of burnt alum powder, one teaspoon of almond or apricot oil. The protein must first be whipped into a foam, add other ingredients and mix. Apply to clean skin for half an hour. Then wash off with warm water.
Causes of stomatitis in a child
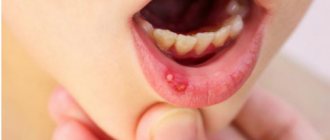
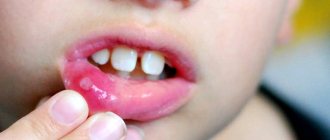
In childhood stomatitis, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected: small pimples of white or yellowish color, filled with liquid, appear on its surface. In some cases, ulcers form.
Stomatitis is predominantly a childhood disease, although it can also occur in adults. The rash affects the inner surface of the cheeks, tongue and gums. The disease causes a lot of inconvenience: pimples hurt and itch, their appearance is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mouth.
Among the main reasons for the development of stomatitis are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- injury to the mucous membrane;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- oral burn;
- pathogenic bacteria that enter the oral cavity from dirty hands, toys, etc.
Reviews
According to customer reviews, burnt alum works well in treating skin problems, including complex wounds with suppuration and trophic ulcers.
However, the powder is mainly used in the fight against sweating and its consequences; it is applied instead of deodorant to the armpits, on the feet and palms, and in shoes to prevent unpleasant odors. The downside is that it stains clothes when applied.
Some buyers note that alum does not help overcome excessive sweating, but an unpleasant odor does not appear after application.
Diagnostic features
A dentist can detect stomatitis during the first visual examination. But in controversial cases, laboratory tests may be required. Thus, bacterial inflammation may require identification of the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics. A scraping and/or virological study will help determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If a combination of several ailments with a similar picture is suspected, as well as if the child’s general well-being deteriorates, laboratory tests of blood and urine and consultations with other specialists may be prescribed.
Sometimes stomatitis can be the first manifestation of systemic diseases, general somatic pathology, for example, diabetes mellitus or malignant neoplasms. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor is extremely important.