Allergy to kiwi in a child
According to statistics, kiwi allergy in children is more common than in adults. In terms of symptoms, it resembles a reaction to pineapples and other fruits that contain large amounts of vitamin C. Moreover, in recent years, the number of people with allergies to kiwi has been increasing.
In this regard, parents of small children may be advised to delay introducing this product into the child’s diet. If you do decide to experiment, feed fruits that contain high amounts of vitamin C very carefully. If your baby has previously had an allergy to citrus fruits, it is better to postpone tasting exotic fruits.
When a child tries kiwi for the first time, you should start with a very small portion and monitor the condition. You should not eat this fruit every day. As a rule, an allergy to kiwi in children manifests itself almost instantly: you will immediately notice that a rash has appeared on the skin.
In some cases, allergens contained in the fruit cause an asthmatic reaction. The child may experience difficulty breathing. It contains a protein that is a powerful allergen. This leads to breathing problems.
Kiwi - description and properties
Thanks to its tangible range of beneficial properties, this exotic fruit is successfully used in cooking as sauces for meat dishes, for filling delicious baked goods, and is added to creams, ice cream, cocktails, puddings, etc. The fruit is included in the diet for weight loss, it is given to children, and is eaten with pleasure by those who like its interesting taste, reminiscent of lemon, strawberries and banana combined. You often hear that after eating kiwi, your tongue, lips and gums burn and tingle. Why is this happening?
Allergy to kiwi in adults
The main diagnostic challenge is that symptoms of a kiwi allergy may not appear until two to three days after you eat the fruit or inhale its aroma. Because of this, people often do not understand what caused the allergy. Moreover, skin rashes and breathing problems can also begin as a result of the fact that a person simply held the fruit in his hands or smelled a cosmetic product with its extract.
You need to know that this food product can also cause serious consequences in case of intolerance to its components. In rare cases, it provokes anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. With such allergic reactions, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, because they are life-threatening.
What to do to get rid of unpleasant sensations?
Why is everything forbidden so attractive? It would seem that the tongue is stinging, an unpleasant sensation appears in the mouth from kiwi - why eat it then (we recommend reading: tongue stinging in the mouth: causes and treatment)? No, I still want to. Again the hand reaches out for this small furry fruit, and again it all starts again - it plucks. How can you get rid of these feelings? Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Before eating fruit
What can you do to prevent eating an exotic fruit from causing a tingling sensation in your mouth? Before use, peel the fruit and rinse thoroughly under running water. This technique allows you to calmly enjoy the taste of your favorite fruit, and there will be no talk of any pinching in your mouth.
You can also prepare ahead of time for your favorite meal. It is enough to peel the fruit and put it in this form in the refrigerator overnight. The acid will disappear overnight, and during breakfast you won’t have to remember that it stings.
After meal
To alleviate your condition as a result of eating another piece of fruit, some recommend rinsing your mouth with warm water until it goes away. A mug of black tea at room temperature or a glass of milk shows a good effect. The human body is individual. While milk helps some, simply rinsing your mouth with water may help others.
Allergy to kiwi: Causes
The fruit contains at least 12 powerful allergens. They are even transmitted from mother to child through breast milk. Therefore, nursing mothers (if the child has allergies) are not recommended to use this product.
Some allergens lose their properties when cooked, but others are resistant to elevated temperatures. Therefore, even after heat treatment, they can cause undesirable reactions.
Also, the exotic fruit is rich in various enzymes that cause allergies.
Recommendations from experts
This healthy fruit of exotic origin perfectly strengthens the immune system, helps against colds, stimulates digestion, normalizes protein metabolism, etc. But it should be remembered that, first of all, it is considered an allergic fruit. Therefore, it is not recommended to eat it:
- for allergy sufferers;
- people with low blood pressure;
- with gastritis and other gastrointestinal problems;
- sharply limit product consumption for people with inflammatory kidney disease;
- It is strictly forbidden to introduce it into the diet of children under 3 years of age.
If your mouth burns, hurts, or your tongue tingles as a reaction to the fruit, you should not eat more than one fruit, and before eating, be sure to peel and rinse under running water (we recommend reading: why does the side of your tongue hurt and what to do?). Carefully monitor your body’s reaction and be happy to include exotic fruits in your diet if no side effects are observed.
Source
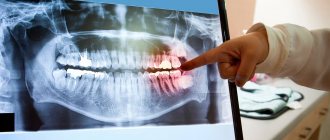
Kiwi allergy: Symptoms
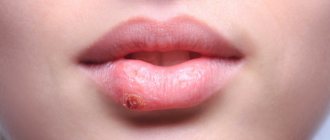
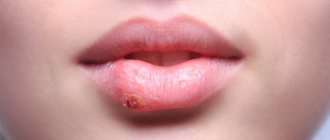
Symptoms of an allergy to kiwi in a child are immediately noticeable. In children, allergies immediately make themselves known in the form of a rash and red spots on the skin.
You can identify a whole group of symptoms by which you can identify such a food allergy:
- the skin of the face is red;
- noticeable rashes appeared on the body;
- stuffy nose;
- started coughing, sore throat;
- lips and face are swollen;
- in serious cases, the tongue and larynx swell;
- the mucous membranes are red;
- the skin began to itch;
- an allergy to kiwi is accompanied by vomiting and problems with stool (constipation, diarrhea);
- shortness of breath and frequent sneezing appeared;
- head is spinning;
- abdominal pain appeared;
- blood pressure dropped sharply.
What to do if you are allergic to kiwi
As soon as you notice signs of an allergy, go to the doctor as soon as possible to consult and conduct the necessary examination. If symptoms are very severe, call an ambulance.
If you notice any of these allergy symptoms, do not eat this fruit. Also limit the consumption of all products (including cosmetics) that contain this fruit. Study the ingredients of sweets, ice cream, yoghurts and cosmetics in the store.
If you are being treated for a kiwi allergy, temporarily eliminate citrus fruits, papaya and pineapples. They may cause symptoms to worsen. In many cases, this practice is observed: if a patient is allergic to a fruit with a high content of vitamin C, then other fruits with vitamin C can cause a similar reaction. The difference lies only in the severity of the symptoms.
Black tongue
Fungus
Gastritis
Colitis
22903 September 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Black tongue: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Black tongue is a condition in which a person's tongue is completely or partially dark or black in color. This symptom is more common among older people, although it occurs in all age groups, and is more common in men than women.
Varieties of black tongue
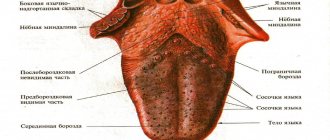
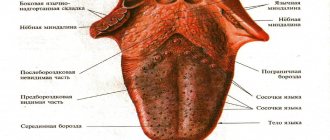
Normally, the tongue has a pale pink color, it is moist, with a smooth surface and clearly visible papillae.
Plaque on the tongue is formed by food debris and exfoliated dead cells of the mucous membrane of the tongue, which can become saturated with food dyes. The appearance of a thin, white, easily cleaned plaque that does not have an unpleasant odor is considered acceptable, and the formation of a dense plaque with a non-physiological color is regarded as a pathology.
On the surface of the tongue there may be individual black dots, one large spot, the tongue may be colored on the sides or completely.
Most often, a black tongue is caused by staining from plaque, such as food or medications, but it can also result from excess melanin deposits or lead poisoning.
In addition, there is such a thing as “black hairy tongue” - a benign and temporary phenomenon in which the filiform papillae of the tongue lengthen, and the keratinized cells of the epithelium of the tongue do not exfoliate and become black or brown due to the activity of certain bacteria and fungi. The length of the papillae can reach 1-3 cm, and the diameter is 2-3 mm. Hyperplastic filiform papillae are located mainly on the posterior and middle third of the dorsum of the tongue. The tongue takes on a “hairy” or “furry” appearance. The disease occurs in both children and adults, but is much more common in older people. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation on the tongue, itching of the palate, burning of the tongue, dry mouth, impaired taste sensitivity, and bad breath. If enlarged taste buds touch the palate, a gag reflex occurs, especially during conversation.
Possible reasons for the appearance of a black tongue
A black tongue is often associated with poor oral hygiene. In addition, people who abuse tea and coffee, smoke, suffer from alcoholism, and use intravenous drugs are at risk. Dry mouth contributes to the tongue turning black when, due to insufficient salivation, more bacteria accumulate on the tongue, the activity of which leads to the plaque becoming pathologically colored. Severe dehydration of the body is accompanied by the formation of a dark, sometimes almost black coating, which is difficult to remove from the tongue.
Some medications give the tongue a black color, for example, activated carbon, iron, bismuth, or antibiotics that disrupt the balance of microflora in the mouth.
A black tongue can also be observed in harmless situations, for example, after eating blueberries, red wine, and foods that contain dyes (sweets, chewing gum, lollipops).
Diseases that can cause the tongue to turn black
A black tongue is often observed with severe advanced candidiasis of the oral cavity, with sore throat, with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (diseases of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal insufficiency, acid-base imbalance and with the development of increased acidity (acidosis). If a chromogenic fungus has settled in the mouth, then the gums, teeth and tongue become covered with a black coating with a greenish tint. In adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), one of the signs of the disease is hyperpigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes due to increased levels of melanin. Pigmentation of the oral mucosa occurs, spots and stripes of brown or grayish-black color appear on the red border of the lips, in the corners of the mouth, on the gums and on the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
Predisposing factors to hypertrophy (enlargement) of the papillae with a black hairy tongue can be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (anacidic gastritis, hypoacid gastritis, colitis, infectious diseases). In some cases, the formation of a black hairy tongue occurs against the background of a deficiency in the body of riboflavin (vitamin B2). In addition, black hairy tongue occurs with pulmonary tuberculosis, papillary pigmentary dystrophy, and after the use of certain medications (for example, antibiotics).
Which doctors should I contact if a black tongue appears?
If you have an oral disease that has caused the formation of a black coating on the tongue, you should consult a dentist.
If plaque is associated with an infectious disease, for example, sore throat or candidiasis, then treatment is carried out.
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you should contact.
If the cause of the black tongue is Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency), then consultation is required.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of a black tongue
Some tests may be needed to determine the cause of tongue discoloration:
- general blood analysis;
Kiwi allergy treatment
It is advisable that your doctor prescribe allergy treatment after diagnosis. Most often, patients are prescribed antihistamines. They help reduce itching, redness, swelling and the intensity of the rash soon after administration. Also, such drugs relieve a person from digestive problems caused by allergies.
To relieve local reactions, ointments and creams are used.
If symptoms are severe, help is required immediately. Doctors often inject hormones to quickly relieve allergy symptoms and prevent complications.
It is important to know that it is advisable to use antihistamines only according to the regimen prescribed by a doctor, as well as in emergency cases. Long-term use of such medications can lead to liver problems.
Preventing kiwi allergy: how to prevent recurrence
If you ever have signs of an allergy to kiwi, it is best to exclude this fruit from your diet. Repeated exposure to the allergen will cause symptoms to recur, even after successful treatment.
Antihistamines can reduce the body's reaction to allergens, but do not eliminate its cause. Therefore, the main method of prevention is to avoid exotic fruit and all products that contain it. This primarily applies to cosmetics with fruit extracts: washing gels, oils, creams, shampoos, balms, etc. Such cosmetic preparations can cause skin rashes and other manifestations. It is best to use special neutral cosmetics if you are prone to allergies.
Hypoallergenic cosmetics La-Cri
The La Cree skin care series is ideal for allergy sufferers. This cosmetics is designed specifically for people with sensitive skin, although it is suitable for everyone without exception. Each product is created on the basis of natural ingredients that nourish and restore the skin. These are extracts of medicinal herbs, natural oils and panthenol.
All active substances are combined with each other in such a way as to achieve a therapeutic effect. The composition does not contain parabens, hormones and harmful chemicals. Therefore, La-Cri cosmetics can be used by pregnant women and children from the first days of life.
Try La Cree Sensitive Skin Cream. It is absolutely safe for the body, but at the same time effectively relieves allergic itching, irritation, rashes and redness. The cream is non-addictive due to its non-hormonal composition, and natural ingredients quickly reduce inflammation. This product also helps with insect bites, and can also be used for daily skin care.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
The properties of the products are confirmed by a clinical study conducted jointly with the St. Petersburg Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
It has been proven that the cream for sensitive skin reduces itching and irritation, relieves redness, moisturizes and gently cares for the skin.
Sources:
- B.A. Shamov, I.G. Safiullina, A.B. Beshimova, T.B. Shamov, Differential diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, Journal of Practical Medicine, 2011
- Fokina R.A., Atopic dermatitis: stages of development of classification forms, Siberian Medical Journal, 2007
- A.N. Pampura, A.A. Chuslyaeva, Modern approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children https:/cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-podhody-k-terapii-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey
Photos of allergies in children
Photo album on the diseasePain and burning of the tongue: how to treat?
Probably every gastroenterologist in his practice has encountered a patient with complaints of pain or burning of the tongue. Turning to this specialist in the first place is probably due to the following logical chain: the tongue is in the oral cavity, where the digestion process begins, which means that if a problem arises, you should visit a gastroenterologist. Old publications also come to the aid of patients and doctors of other specialties, in which chronic diseases of the digestive organs were considered as the causes of burning tongue.
But is it really that simple? Is pain and burning of the tongue a separate disease and who should treat it?
A little history and terminology.
Pain/burning in the tongue has many synonyms: glossalgia, glossodynia, stomatodynia, glossopyrosis, oral paresthesia, neurogenic glossitis, tongue neurosis, glossalgic syndrome. This condition is traditionally part of the so-called burning mouth syndrome or “burnt mouth syndrome,” in which pain/burning sensations are localized in various areas: tongue, upper palate, gums, lower lip, pharynx.
Burnt mouth syndrome (SMS) was first described back in 1880; in the 20th century, the term glossodynia, i.e., appeared. pain in the tongue, since unpleasant symptoms from the tongue were most common. This syndrome was first identified as a separate disease in 2004.
Almost all existing review articles and recommendations consider glossodynia within the framework of the SOP. General recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of ROP may be applicable to the special case of glossodynia.
Definition
The International Association for the Study of Pain has designated glossodynia and oral burning as chronic pain, specifically “burning pain of the tongue or other mucous membranes of the mouth.”
Later, a detailed definition was given for ORS: “a burning sensation or sensation of altered sensitivity in the oral cavity, repeated daily for more than 2 hours a day for more than 3 months, without obvious causative lesions on clinical examination and examination.”
Epidemiology
Data on the prevalence of ROP and tongue pain/burning separately still vary from study to study. The average incidence of all cases of oral burning (including but not limited to tongue burning) is 0.1-3.7% of the population. Women suffer from this syndrome 2.5-7 times more often than men, especially often over the age of 60 and after menopause.