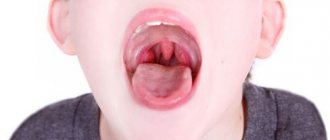
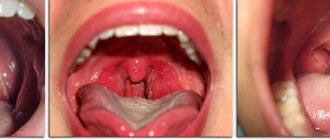
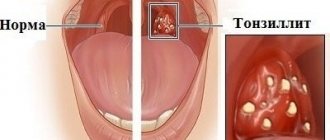
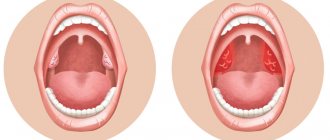
In some cases, tonsils may become enlarged without fever. Enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Author:
- Chuprikov Roman Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
3.45 (Votes: 33)
Tonsils (tonsils) are an important organ of the human immune system, involved in protecting the body from harmful carriers and preventing their spread. Their main task is to identify pathogenic microorganisms and produce antibodies to fight them.
Enlarged tonsils themselves are not a disease, but a symptom. They can increase:
- with infection;
- with genetically determined hypertrophy;
- for blood diseases (lymphoproliferative diseases);
- for autoimmune diseases;
- for allergic inflammation and swelling.
Usually these processes are accompanied by an increase in temperature, but in some cases the tonsils can enlarge without an increase in temperature. This often forces one to delay a visit to the doctor, since temperature is considered a marker of the disease. But enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Anatomy of the throat
In the pharynx, on the sides and along the back wall, as well as on the border of the oral and nasal cavities, there are accumulations of lymphoid tissue - the so-called lymphoid-pharyngeal ring. It performs a protective function, and each of the tonsils of this ring is an important organ of our immunity.
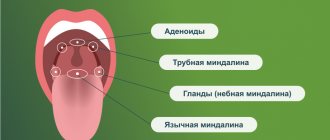
The largest accumulations of lymphoid tissue are called tonsils (they are also called tonsils ) and there are several of them: two palatine, two tubal, one pharyngeal (aka adenoid) and one lingual.
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils (in everyday life they are called tonsils) is called acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis .
1.General information
Hypertrophy means an abnormal or pathological increase in the size of an organ, structure, or tissue. This concept should be clearly distinguished from terms (and the phenomena they denote) such as hyperplasia, tumor or edema.
Hyperplasia, for example, is the rapid growth of tissue due to a hormone-mediated increase in the number of healthy cells typical of a given tissue; the tumor process is characterized by a local increase in the number of cells with certain abnormalities and, finally, edema is an excessive accumulation of fluid in the cells or intercellular space.
In contrast to the above, hypertrophy is an increase not in the number of cells, but in their size - with a relatively normal quantity for a given organ - and is considered as a response to certain factors, conditions, influences.
Further, the tonsils (medical lat. “tonsilla”, incorrectly “tonsils”) are a group of glandular formations from lymphoid tissue, collectively making up the so-called. lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring and perform mainly the role of an immune barrier at the entrance to the respiratory and digestive tracts, in close proximity to the brain and sensory organs - in an area where many blood vessels, nerve tracts, lymph nodes and ducts are concentrated. In other words, the presence of the pharyngeal ring here as an outpost of the immune system is completely understandable; however, the tonsils also perform other functions that have not yet been studied enough or are completely unknown.
The most significant is a pair of relatively large palatine tonsils located on either side of the entrance to the laryngopharynx.
Tonsil hypertrophy is common in the general population with an estimated incidence of 5-10 to 40 percent. The vast majority of primary patients with this diagnosis are children and, less often, adolescents. Hypertrophic enlargement of the tonsils, which develops in adulthood, is sporadically rare.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of tonsillitis
The most common pathogens should be highlighted:
| PATIENT | A COMMENT | ||
| pathogen: | Bacteria: beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group A and other groups, pneumococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Neisseria, enterobacteria | a comment: | Particularly worth highlighting is streptococcal tonsillitis, in which infection occurs with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which occurs in almost 30% of cases and is responsible for the further development of acute tonsillitis and exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.3 |
| pathogen: | Viruses: adenoviruses, enterovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza viruses, herpes virus | ||
| pathogen: | Mushrooms: yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida |
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets through direct contact, penetrating the mucous membrane of the tonsils. But it can also be in the body without manifesting itself in any way. Periods of outbreaks of seasonal ARVI, hypothermia, the presence of chronic diseases of the pharynx, poor diet, bad habits, injuries - all these factors can lead to a decrease in immunity, which in turn provokes the growth of bacterial, less often fungal flora, and activates some viruses.
All these factors lead to inflammation of the tonsils and surrounding structures.
Depending on the pathogen, there are:
- Purulent tonsillitis (caused by bacteria)
- Viral tonsillitis
- Fungal tonsillitis
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
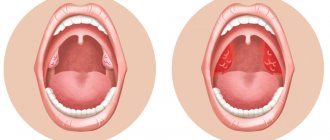
It should be especially emphasized that hypertrophy itself is not an inflammatory process and should not be perceived as equivalent to tonsillitis (acute or chronic inflammation of the tonsils). Until the tonsils reach a certain size, a person may not experience any discomfort at all.
However, over time, the anomaly begins to affect itself and takes on an increasingly distinct pathological character, simultaneously causing a cascade of progressive disorders and changes in the ENT organs.
Diction is impaired, speech becomes nasal, nasal breathing becomes difficult, which may become impossible in the future. As a result, the patient is forced to constantly breathe through his mouth, which in a few years, and even faster during periods of rapid growth, can significantly change the maxillofacial proportions (“adenoid face”). With further growth of the tonsils, the pharyngeal outlet of the auditory tube is blocked and hearing loss gradually increases, swallowing becomes difficult, bad breath appears, and the patient loses body weight.
Inadequate breathing leads to chronic hypoxia; the result is fatigue, emotional instability, and decreased intellectual and mental productivity. Sleep becomes disturbed, restless and often interrupted, a tendency to snore appears and intensifies, episodes of night cough and apnea (complete cessation of breathing, sometimes for tens of seconds) may occur. The patient does not get enough sleep, and the above disorders progress in a vicious circle.
As can be seen from the above, hypertrophy of the tonsils is by no means an asymptomatic and harmless process; on the contrary, it creates combined and quite serious threats to health, and not only in the otorhinolaryngological field.
Diagnosing this situation is quite simple: a history and complaints are collected, a standard examination of the ENT organs is carried out using spatulas, dilators and mirrors. A clinical blood test is prescribed, which in this case has its own correlates of hypertrophy, in contrast to the biochemical picture of other diseases. X-ray or tomographic imaging is used as needed.
A differential diagnosis must be carried out between “pure” hypertrophy and the hypertrophic variant of chronic tonsillitis, tumor processes, etc.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Forms of tonsillitis
There is a large classification of forms of acute tonsillitis :
Catarrhal
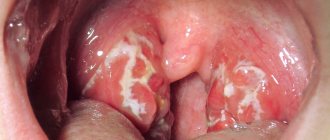
The mildest form, in which the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected. The palatine tonsils are not very enlarged, the mucous membrane of the throat is red, there is no plaque or pus.
Follicular
In this form, the follicles of the tonsils, that is, the deeper structures of the tonsils, are affected. They are visible through the tissue of the tonsils in the form of whitish-yellow round formations.
Lacunarnaya
It leaks more severely. When examined, yellowish-white and purulent plaques can be seen on the tonsils.
Fibrinous
A dense film of grayish fibrin forms on the tonsil, which is difficult to remove with a spatula.
Herpetic
Characterized by the appearance of blisters on the tonsils. When they rupture, painful, difficult-to-heal ulcers form.
Phlegmonous
With this form, after 1-2 days of acute tonsillitis, an abscess (cavity with pus) develops.
Ulcerative-necrotic
Angina of Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent.
As a rule, one tonsil is involved in the process, on which a grayish-yellowish coating forms with the development of ulcers underneath it.
Mixed forms
In this variant of the disease, infection occurs with several pathogens at once, as a result of the addition of a secondary infection or with a severe decrease in immunity.
Chronic form of tonsillitis
Relevant in the same way as acute.
Understanding the significance and prevalence of bacterial tonsillitis pathogens, especially group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, has a huge role in preventing the development of chronic tonsillitis. Allergic syndrome is caused by the allergenic effect of streptococcal lipopolysaccharides, which, when absorbed throughout the disease, cause an allergic mood and create the preconditions for the development of local and general complications.
Chronic pharyngitis
According to the depth of damage to the pharyngeal mucosa, chronic pharyngitis is divided into: catarrhal, hypertrophic and atrophic forms.
- Chronic catarrhal pharyngitis - there is slight swelling of the tissue layers of the pharyngeal mucosa. Individual areas are sometimes covered with clear or slightly cloudy mucus. It develops as a result of acidic gastric contents entering the throat, for example, in the case of a hiatal hernia. Therefore, catarrhal chronic pharyngitis is a consequence of the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis is a significant severity of swelling of the mucous membrane. Additionally, thickening of the uvula and swelling of the soft palate are observed.
- Chronic atrophic pharyngitis is characterized by some thinning of the lining of the pharynx. They are usually pale pink, sometimes shiny varnished. Some of their areas become covered with crusts, viscous mucus and pus.
Any type of chronic pharyngitis develops due to the fact that the acute form of the disease was not cured in time and developed into a more serious form. Chronic pharyngitis also appears as a consequence of rhinitis, sinusitis, deviated nasal septum, nasal polyps - that is, when nasal breathing is difficult for a long time. In addition, long-term use of vasoconstrictor drops also leads to the appearance of chronic pharyngitis.
Symptoms of acute tonsillitis
The onset of the disease is characterized by an acute and abrupt onset.
- Pain in the throat and when swallowing is the main symptom of a sore throat. The pain can be very intense, intensifies when swallowing, radiates into the ear, and this greatly reduces the patient’s quality of life
- The development of a sore throat is explained by irritation of a large number of nerve endings in the throat due to swelling and inflammation.4
- Depending on the form of acute tonsillitis, there is an increase in temperature from 37 to 39, and sometimes up to 40 degrees
- Against the background of increased temperature and intoxication, headache, weakness, weakness, and loss of appetite may occur.
- The submandibular and cervical nodes increase in size and may be painful when pressed
Under what conditions can tonsils be enlarged without fever?
Without an increase in temperature, the tonsils can become inflamed due to:
- Allergies. Enlarged tonsils often occur in people prone to allergies. Allergens include various substances - animal hair, dust, pollen, food, insects, household chemicals.
- Fungal infection. The following symptoms are observed: sore throat, dry mouth, visible cheesy coating on the mucous membrane.
- Dry air. Due to constant inhalation of dry air, the mucous membrane of the larynx dries out, causing the tonsils to swell. Working in polluted conditions also leads to this.
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke burns the mucous membrane, which can result in swelling of the tonsils.
- Some forms of sore throat (tonsillitis). The biological meaning of an increase in temperature during infectious diseases is to accelerate the death of pathogenic carriers in an environment with high temperatures. Consequently, if the body temperature has not increased, it means that the number of infectious carriers that have entered the body is small. Usually, if the infection was minor, then the person easily and quickly suffers from this illness. But with enlarged tonsils and no temperature, we can talk about an untreated acute inflammatory process in the tissues of the tonsils and its transition to chronic. In this case, the recovery process will take longer, and in addition, there is a possibility of complications developing. Both variants of pathologies require examination and prescription of correct treatment by an otolaryngologist.
What tests need to be taken for tonsillitis?
In order to determine the pathogen and determine further treatment, the doctor may prescribe a number of laboratory tests to the patient, for example:
- a smear from the tonsils, arches and back of the throat to identify bacteria and their resistance to various groups of antibiotics, but such a study may take several days
- rapid test for the detection of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus to determine streptococcal tonsillitis5
- a general blood test with a leukocyte formula, which pays attention to elements that reflect inflammation and the immune response to the disease. Increased band neutrophils, leukocytes, increased ESR, decreased lymphocytes
- CRP (C-reactive protein - a marker of inflammation) is the most sensitive protein responsible for inflammation in the body
When should you have your tonsils removed?
And yet, under certain circumstances, surgery cannot be avoided.
1. Extreme difficulty breathing
. If none of the usual treatments have sufficiently relieved the inflammation, swollen tonsils will continue to compress the throat and block the passage of air. The result is problems with the heart and blood vessels and a lack of sufficient oxygen in the brain. The consequences of this condition can be dire and irreversible.
2. Recurrent tonsillitis
. Inflammation that appears every week and constant treatment with antibiotics can provoke a decrease in immunity and cause serious harm to many organs. Sometimes it is better to remove the tonsils, lowering local immunity, but thereby saving the rest of the body.
3. Severe forms of tonsillitis
. The patient's condition may be so severe and dangerous that there is no time left for treatment with other methods. There is a danger of airway obstruction, and this is a matter of life and death.
In all other situations, surgery is not only not necessary, but can also be the beginning of more serious diseases.
How to treat acute tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis depends on the pathogen and the severity of the disease.
1. If we are talking about bacterial infection, then it is necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs of different groups.
Only a doctor can prescribe an effective antibiotic!
Antibiotics are not effective against viral tonsillitis.
2. Symptomatic treatment:
Includes taking antipyretics, painkillers, as well as the use of local anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs in the form of solutions, lozenges, tablets.
3. A gentle diet. Namely, the exclusion of spicy, fried, and sour foods will help reduce irritation to the inflamed tissues of the throat.
4. If treatment is ineffective or complications occur, hospitalization is indicated. In the hospital, the patient will be under the close attention of doctors, blood tests will be monitored, and hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs may be administered. It is possible to use systemic antibiotics in the form of tablets or intravenously or intramuscularly.
If necessary, surgical intervention is performed.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, pathogen and form, treatment must be comprehensive, that is, have an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Uncontrolled treatment with folk remedies can only do harm.
Treatment without surgery
Conservative treatment includes general and local drug therapy, physiotherapy, lavage of lacunae and other methods of cleansing the tonsils. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, and immunomodulatory agents are prescribed.
Conservative therapy is widely used in modern otorhinolaryngology. But it does not always completely cure tonsillitis. The tonsils may remain enlarged even after drug suppression of the infection and deep cleansing; the risk of relapses and complications remains. In approximately 1/3 of patients, it becomes necessary to treat the disease surgically.
Acute tonsillitis in pregnant women
The pregnancy period is always accompanied by a physiological decrease in immunity due to complex hormonal changes, therefore, during the period of colds, the body's susceptibility to bacteria and viruses increases or activation of any chronic foci of infection, including chronic tonsillitis, is possible.
throat or acute tonsillitis are extremely undesirable diseases during pregnancy, since treatment of this group of patients can be difficult due to restrictions on the use of most medications, especially antibiotics. Therefore, the prevention of colds during the period of influenza and ARVI is of great importance: avoid crowded places, avoid contact with people with sore throat, thoroughly wash your hands, ventilate rooms, walk in the fresh air.
Pregnant women suffering from chronic tonsillitis without exacerbation are recommended for local treatment in the form of gargling with herbal solutions at home.12
The use of ANY medications, including dietary supplements, is permissible only after consulting your obstetrician-gynecologist!
Complications of tonsillitis
With proper treatment, recovery occurs in 7-10 days. If medications are ineffective, life-threatening complications may develop:
- paratonsillitis - acute inflammation of the tissues near the tonsils;
- peritonsillar abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus inside the same area;
When the process spreads into deeper tissues, phlegmon may develop. All types of complications are observed and treated exclusively in the hospital, with further use of surgical treatment methods .
Advantages of visiting the Miracle Doctor clinic
When prescribing surgical intervention, along with traditional surgical methods for removing tonsils in children, the Miracle Doctor clinic performs tonsil removal under anesthesia using the cold plasma coblation method, in which a special device with an electrode is used instead of a scalpel. Removing tonsils with a coblator avoids damage to surrounding tissues; the operation is quick and almost bloodless.
Regardless of whether general or local anesthesia is used, highly effective and safe drugs of the latest generation are used. To ensure comfort during the postoperative period, the patient is provided with a separate room in a 24-hour hospital. Pediatric otolaryngologist surgeons at the Miracle Doctor clinic can not only slow down inflammation of the palatine tonsils, but also, in advanced cases, perform surgery using progressive minimally invasive methods.
Prevention of tonsillitis
There are individual preventive measures aimed primarily at strengthening the immune system.
A healthy lifestyle and the absence of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol play a key role. Don’t forget about hardening the body, doing physical exercise, regularly spending time in the fresh air, and consuming enough vitamins with food.
In the modern world, special attention is paid to the use of various biologically active additives (BAS) to improve health, including for the prevention of colds and strengthening the immune system.
The composition of such supplements is very diverse and rich, including various vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and substances of plant origin.
They come in the form of tablets, lozenges, dragees, drops, etc. But you shouldn’t count on “magic”; such supplements will not cure all diseases, but they will really help direct the body to work in the right direction and improve the effect of the main treatment. It is also important to choose the right biological supplement, focusing on the body’s needs and its problem. For example, lozenges can help strengthen the immune system.
Tantum® Propolis 13
Propolis is a valuable substance that has been used for medicinal purposes since the times of Hippocrates, Discorides, Avicenna and others, and is used in modern medicine to this day.
Plants from which bees collect and carry resinous substances have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and antiviral properties.14 Find out more
Not being a medicine, Tantum® Propolis can support the patient’s immunity during seasonal ARVI and influenza, reduce pain, irritation and itching in the throat, and also replenish the lack of vitamins in the patient’s body.
In preventing complications, it is very important to consult a doctor on time, follow the prescribed treatment regimen and recommendations, and avoid self-medication.
Answers to popular questions about tonsillitis
What antibiotics are prescribed for tonsillitis?
In the treatment of acute tonsillitis, there are several groups of antibiotics:
- aminopenicillins;
- amoxicillin;
- amoxicillin with clavulanic acid;
- II-III generation cephalosporins;
- macrolides - azithromycin, clarithromycin;
Only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics. Uncontrolled self-use of antibiotics is prohibited, as this is associated with the development of bacterial resistance to the antibiotic, which leads to the ineffectiveness of a certain drug against the bacterium in the future. Antibiotic treatment is not indicated for viral tonsillitis !
Is it possible to get vaccinations for tonsillitis?
You should definitely consult your doctor. Vaccination can be done for chronic tonsillitis, but ONLY IN THE ABSENCE OF EXCERNSATION.
Which doctor treats tonsillitis?
In modern medicine, acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis can be treated by an otolaryngologist (ENT), an infectious disease specialist, and a therapist.
Is it possible to do inhalations for tonsillitis?
The use of inhalation for acute tonsillitis is permissible only after consulting a doctor! This procedure is not suitable for all forms of angina. Indications and contraindications depend on the form of acute tonsillitis and the causative agent, so differential diagnosis plays a key role. Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine for inhalation and its correct dosage. Your doctor will also help you choose the right type of nebulizer.
Is it possible to eat ice cream if you have tonsillitis?
Eating ice cream for a sore throat is not recommended. There are many private opinions that cold ice cream will reduce a sore throat, but this is not entirely true. Cold does have a local anesthetic effect by affecting nerve endings, but only for a short time, it does not have any benefit or positive effect. Outside of an exacerbation, you can eat melted ice cream.
What tests are prescribed for tonsillitis?
- pharyngeal smear - from the tonsils, arches, posterior pharyngeal wall to determine the pathogen and antibiotic resistance, including for diphtheria;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- ESR;
Can tonsillitis occur on only one side?
Basically, tonsillitis always occurs with bilateral damage to the tonsils, but there are exceptions. Tonsillitis can occur not only as an independent disease, but also be a manifestation of some other disease. For example, with tularemia or primary syphilis, tonsillitis appears on one side.
How long does it take to treat tonsillitis?
On average, treatment can take 7 days. For example, antibacterial therapy is prescribed for 5-10 days. It all depends on the antibiotic group and the presence of complications.
Treatment of enlarged tonsils without fever
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of inflammation of the tonsils.
If the cause is an infectious or fungal infection, then the patient is prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy, treatment of the throat and mucous membranes with special preparations, infusions into the larynx, rinsing the tonsils, and taking vitamin complexes to support the immune system.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, a tonsillectomy may be prescribed - surgical removal of the tonsils. Most often, this is an indication for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis, which occurs with toxic-allergic manifestations and seriously interferes with a person’s comfortable life.
If swelling of the tonsils is associated with external factors - smoking, working in unsuitable conditions, attacks by allergens, the doctor will advise correction of lifestyle or environmental conditions, and taking supportive medications.