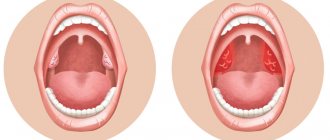
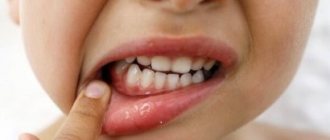
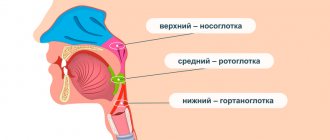
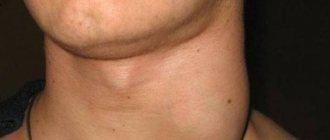
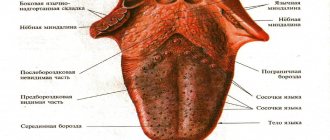
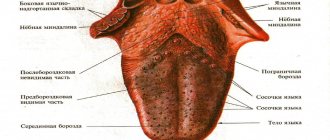
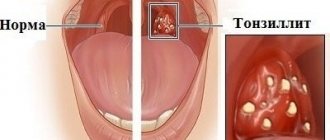
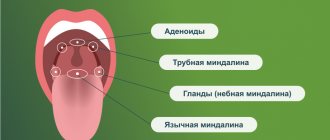
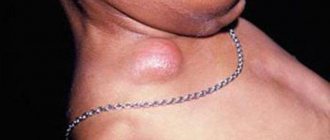
In some cases, tonsils may become enlarged without fever. Enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Author:
- Chuprikov Roman Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
3.45 (Votes: 33)
Tonsils (tonsils) are an important organ of the human immune system, involved in protecting the body from harmful carriers and preventing their spread. Their main task is to identify pathogenic microorganisms and produce antibodies to fight them.
Enlarged tonsils themselves are not a disease, but a symptom. They can increase:
- with infection;
- with genetically determined hypertrophy;
- for blood diseases (lymphoproliferative diseases);
- for autoimmune diseases;
- for allergic inflammation and swelling.
Usually these processes are accompanied by an increase in temperature, but in some cases the tonsils can enlarge without an increase in temperature. This often forces one to delay a visit to the doctor, since temperature is considered a marker of the disease. But enlarged tonsils without fever require the same attention and treatment approach to avoid the development of complications.
Under what conditions can tonsils be enlarged without fever?
Without an increase in temperature, the tonsils can become inflamed due to:
- Allergies. Enlarged tonsils often occur in people prone to allergies. Allergens include various substances - animal hair, dust, pollen, food, insects, household chemicals.
- Fungal infection. The following symptoms are observed: sore throat, dry mouth, visible cheesy coating on the mucous membrane.
- Dry air. Due to constant inhalation of dry air, the mucous membrane of the larynx dries out, causing the tonsils to swell. Working in polluted conditions also leads to this.
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke burns the mucous membrane, which can result in swelling of the tonsils.
- Some forms of sore throat (tonsillitis). The biological meaning of an increase in temperature during infectious diseases is to accelerate the death of pathogenic carriers in an environment with high temperatures. Consequently, if the body temperature has not increased, it means that the number of infectious carriers that have entered the body is small. Usually, if the infection was minor, then the person easily and quickly suffers from this illness. But with enlarged tonsils and no temperature, we can talk about an untreated acute inflammatory process in the tissues of the tonsils and its transition to chronic. In this case, the recovery process will take longer, and in addition, there is a possibility of complications developing. Both variants of pathologies require examination and prescription of correct treatment by an otolaryngologist.
Preoperative preparation
Directly for the operation, it is necessary to undergo a preoperative examination, the scope of which is determined by the doctor after the examination.
Preoperative preparation is standard:
- Laboratory tests - general blood test, blood biochemistry, blood for RW, HIV, hepatitis B and C, coagulogram, Rh factor, blood group.
- Instrumental data - ECG, fluorography or chest x-ray.
- Conclusion of specialists - therapist (pediatrician) and dentist about the absence of contraindications to surgical intervention.
Features of the condition with enlarged tonsils without fever
Even at normal body temperature, but in the presence of pathological processes in the body, a person may feel completely unwell. Inflammation of the tonsils without fever, regardless of the cause, can interfere with a normal lifestyle and be accompanied by:
- headache;
- sore throat;
- lack of appetite;
- difficulty swallowing;
- dryness and sore throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes and pain on palpation;
- fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, decreased performance, irritability.
Complications and how to avoid them
One of the very rare complications: velopharyngeal insufficiency. After surgery, velum closure may be impaired. This complication is manifested by the appearance of a nasal voice in the patient, the appearance of snoring during sleep, and disturbances in the processes of speech and swallowing food. More often, this complication appears in patients with a hidden cleft of the hard palate that was not diagnosed before surgery. To exclude such a condition, a thorough examination of patients is necessary. One of the signs of the presence of a submucosal cleft of the hard palate is the splitting of the uvula.
Treatment of enlarged tonsils without fever
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause of inflammation of the tonsils.
If the cause is an infectious or fungal infection, then the patient is prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy, treatment of the throat and mucous membranes with special preparations, infusions into the larynx, rinsing the tonsils, and taking vitamin complexes to support the immune system.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, a tonsillectomy may be prescribed - surgical removal of the tonsils. Most often, this is an indication for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis, which occurs with toxic-allergic manifestations and seriously interferes with a person’s comfortable life.
If swelling of the tonsils is associated with external factors - smoking, working in unsuitable conditions, attacks by allergens, the doctor will advise correction of lifestyle or environmental conditions, and taking supportive medications.
Comparative characteristics of the two methods
Laser tonsil removal
Carbon dioxide laser is used (CO2 laser)
- the operation is almost bloodless
- lower risk of bleeding after surgery
- faster wound healing compared to traditional removal
- less pain in the postoperative period
- Minuses:
- heating of surrounding tissues, there may be burns to the edges of the wound.
Radio wave tonsil removal
Surgitron radiosurgical device is used
- the operation is also almost bloodless
- radio wave produces an antibacterial effect, reducing the likelihood of inflammation after surgery
- postoperative swelling in the wound is less pronounced, the wound heals much faster
- there are no burns or damage to healthy tissues, because the effect of the cut is carried out without physical pressure, the removal of the tonsil is carried out carefully
- early complete tissue healing without the formation of a rough scar
In some cases, to achieve maximum effectiveness, doctors can use a combined method: both laser and radio wave.
Prevention
To prevent pathological enlargement of the tonsils, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Increase immunity: eat properly and well, exercise, exercise, give up bad habits, and maintain proper sleep patterns.
- Avoid provoking factors: do not overcool, humidify the air in the room, remove allergens from the environment.
- Treat infectious diseases promptly at the very beginning and prevent them from becoming chronic.
- Carry out preventive gargling and rinsing of tonsil lacunae. These procedures are carried out in our clinic, and our doctors will be happy to advise you about them.
If you are concerned about enlarged tonsils without fever, make an appointment with otolaryngologists at the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic - you will receive comprehensive consultations and quality treatment.
Anesthesia
Tonsillectomy surgery is performed under both local anesthesia and general anesthesia (anesthesia). Both methods of pain relief have pros and cons, so the decision is made by the attending doctor, taking into account the health condition and wishes of the patient.
Local anesthesia
The classic surgical technique (under local anesthesia) has been performed for many decades and still exists today. An anesthetic solution in an amount of about 20 ml is injected into several points around the tonsil - usually 1% lidocaine with the addition of adrenaline (to reduce bleeding). The effect is that the tissues are deeply impregnated with the drug, so the pain is almost not felt, and the tonsil appears to be raised above the palatine arches and is easy to isolate. This technique is called infiltration anesthesia.
If the patient has had allergic reactions to these drugs, they are replaced with ultracaine. Next, the operating doctor proceeds directly to removing the tonsils. The patient is only required to strictly follow his instructions. A tonsillectomy lasts about half an hour; before sending the patient into the room, the surgeon carefully checks whether the bleeding has stopped. This is an important point in the operation.
General anesthesia (anesthesia)
Nowadays, tonsillectomy is performed more and more often under general anesthesia. This is due to the fact that anesthetic equipment and drugs for anesthesia have changed a lot recently. Modern anesthetics are considered to be of a high safety class; they are non-toxic and do not carry the same complications as before. Anesthesia is easily tolerated by the patient and feels similar to normal sleep.
The photo shows an anesthesia device from the German company Drager used in the clinic.
To carry out general anesthesia, the patient is carefully examined; before the operation, he is examined by an anesthesiologist, since, despite the safety of anesthesia, if there are deviations in the tests, the operation can be postponed. The operation is performed strictly on an empty stomach; the patient cannot even drink water. After the examination, the patient is escorted to the operating room, where he is placed on the operating table and put on a breathing mask. A mixture of oxygen and anesthesia medication is supplied to it, sleep occurs within a few minutes, and the operation ends for the patient - awakening occurs in the ward.
Doctors anesthesiologists
The clinic employs highly qualified anesthesiologists, including specialists from the Children's Clinical Hospital named after. N.F. Filatov, who have academic degrees of candidates and doctors of medical sciences, many years of unique work experience. Our specialists use an anesthetic apparatus from the German company Drager and the latest generation of medicines. All this allows operations to be performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia), which is safe for the patient’s health, with further rapid recovery in the postoperative period.
Drugs
In their work, anesthesiologists use the drugs sevoran, diprivan, esmeron, enfluron, isoflurane, dormicum and others. The choice of a specific drug is at the discretion of the anesthesiologist and depends on each specific case, test results and other factors.
The difference between tonsillotomy and tonsillectomy
Tonsillotomy is an operation in which enlarged tonsils are removed not entirely, but partially. This type of surgical intervention is indicated for patients with grade III hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils, when they occupy the entire space from the anterior palatine arch to the uvula. During a tonsillotomy, part of the enlarged tonsils is removed. Tonsillotomy, in contrast to the more radical method of complete removal of the tonsils, allows them to preserve their protective functions. This method is also recommended for treating children.
Recovery in the postoperative period
The operation requires the patient to remain in the hospital for several days. After the operation, the patient is transferred to a ward for further medical supervision.
The first day is the most unpleasant for the patient, since it is not recommended to swallow, eat or drink, and the patient may also experience severe pain. Bed rest is observed for 2-3 days. If the tissues heal well and there are no signs of bleeding, the patient can be discharged for further outpatient observation. On average, a patient is discharged from the hospital within a week. The tissues finally heal within three weeks. All this time, the patient may experience pain and discomfort in the throat, as well as periodic fever.
For 10-20 days after the operation, that is, throughout the recovery period, the patient is recommended to follow a diet: hot, cold, sour, spicy foods should be excluded, as well as the consumption of rough food in the form of cookies, gingerbread, crackers, since such food can irritate the injured area. It is recommended that the food be soft: in the form of baby food, cereals, and various soufflés.
In the postoperative period it is prohibited:
- play sports, lift weights, as exercise can lead to bleeding
- visit baths, saunas, take a hot bath
- consume hot foods and drinks
As noted above, pain is the most unpleasant ailment that accompanies the patient throughout the recovery period from the first day after surgery. The pain may bother the patient at rest, or may intensify when swallowing and talking. To improve the patient's well-being and reduce pain in the postoperative period after tonsillectomy, drugs for general and local anesthesia are used. The local drugs used must also have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Contraindications to tonsillectomy
Contraindications can be absolute, when surgery is completely excluded for the patient, and relative, when there are reasons that postpone surgery until these reasons are completely eliminated.
Absolute contraindications to tonsillectomy:
- blood diseases
- some heart diseases
- tuberculosis
- cirrhosis of the liver
Relative contraindications to tonsillectomy:
- ARVI and influenza
- exacerbation of chronic diseases
- menstruation
- pregnancy