- Service life of different types of crowns
- Late crown replacement
- When to change a crown
- How to change crowns
- How often are crowns replaced?
- Additional videos
Sooner or later, most people have to deal with dental prosthetics.
Perhaps the most common type of prosthetics is the so-called “dental crown” (more information about different crowns here). Many patients are their owners, but only a few patients ask questions: do dental crowns need to be replaced, how often should dental crowns be changed, etc.
Let's try to figure it out.
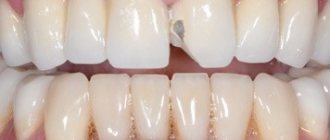
What is the service life of different types of crowns?
As you know, any structure has a certain service life. Unnecessarily long use can lead to dire consequences.
So: how often should crowns be replaced?
It is believed that the average service life of a crown is 5-7 years. At one time, scientists proved that it is after such a period of time that the cement on which the crown is fixed begins to undergo changes. But this does not mean that the crown must be changed every 5 or 7 years. During this period, a doctor should evaluate it to understand whether it can still serve or whether the crown needs to be replaced.
In addition to the duration of use, during a preventive examination, the doctor evaluates the following parameters: the quality of the marginal fit of the crown to the tooth, the condition of the gums and bone tissue next to the crown, X-ray data of the tooth, patient complaints, etc.
Materials for dentures:
- Zirconium dioxide is the most durable of materials. Withstands up to 20 years of use without changing its characteristics. Does not respond to sudden temperature changes. It also does not cause intolerance and is absolutely safe.
- Aluminum oxide is almost as good in appearance as zirconium and other ceramic structures and has a natural white color. At the same time, it is less durable and less resistant to abrasion or impact, so it is rarely used to restore chewing teeth. In some cases, an allergic reaction to aluminum may occur.
- Porcelain - in terms of aesthetics, this is the most preferred type of material. It is also absolutely harmless in terms of allergic reactions. However, despite its strength, it is also the most fragile. Porcelain can withstand pressure, but impacts can damage it. Therefore, it is also almost never used on chewing teeth.
- Usually it is used for prosthetics of incisors or canines.
Such prostheses require careful handling, but if precautions are taken, they last up to 15 years.
The main disadvantages are:
- Increased risk of chipping
- High price for all varieties.
What determines the service life of a crown?
- The service life and the need to replace the structure greatly depend on the accuracy of manufacturing at all stages. Precision work means that the crown fits to the tooth without gaps, without steps, without voids, oral fluid and food do not get under it, the gums around it do not become inflamed, it is no different from the “native” tooth. It is the precision of manufacturing that determines the quality of work, and therefore is the key to a long service life of the crown. For example, I had to deal with a situation where the crown was made only a year ago, and upon examination, strict indications for its urgent replacement were revealed (due to poor quality, namely inaccurate manufacturing). And vice versa, when examined, the crown meets all the requirements, all parameters are normal, there is no need to replace it, and it has been standing for 10 years (which means it was manufactured very accurately and in a timely manner).
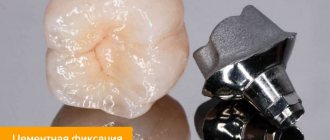
- We have repeatedly mentioned that accuracy, and therefore quality, is at the forefront. If we take quality as a given, then the material and method of fixation come to the fore. So, the service life also depends on the material from which the crown is made and, accordingly, on the method of fixing it to the tooth . Classic metal-ceramics and zirconium dioxide-based crowns are attached to a special “cement,” that is, an intermediary between the crown and the tooth, and do not enter into a “chemical” bond with either this cement or the ground tooth. Namely, this cement is “destroyed” and “washed out” over time, leading to a violation of the seal of the entire structure. Crowns based on lithium disilicate (also called “E-max”) are fixed without an intermediary: using the adhesive (“glue”) method, that is, they are glued to the tooth tissue, which leads to a very strong connection between the crown and the tooth. Accordingly, the service life of such structures is longer than the 5-7 years described above, which means that a crown change will not be required soon.
- In addition, the service life is greatly influenced by the condition of the tooth for which the crown was made. If a patient hesitates for a long time to adequately restore a damaged tooth, he comes for prosthetics at an untimely rate, in particular when the tooth is destroyed by a carious process to the level or below the level of the gum, becoming “soft” and unreliable. In such conditions, the doctor is no longer able to make an accurate marginal fit; such a structure will never be completely sealed, which means the tooth under such a crown will be destroyed. In such conditions, neither good materials nor the method of fixing the crown will help. And if the doctor nevertheless undertakes the restoration of such a tooth, this will be the last crown on it, since it will be impossible to repeat the restoration.
Important! Dear patients, do not delay the restoration of damaged teeth, do not deprive yourself of the opportunity to save your own tooth faster, more reliably and cheaper!
By clicking on the “Make an appointment” button, I consent to the processing of my personal data.
I have read and agree with the conditions for processing personal data set out on the website ds-chocolate.ru.
Consent to the processing of personal data
Plastic crowns in Stavropol
Dental crowns made of acrylic plastic initially have an aesthetic appearance, but this advantage over stamped products is lost over time. Within a year or even less, the pleasant color of the plastic crowns, close to the natural shade of the teeth, changes: it darkens and becomes covered with stains. The hygienic qualities of plastic crowns are also not up to par, they are not particularly hard, and the structure of the plastic is porous.
Among the new products in the field of dental prosthetics are reinforced plastic crowns made of photopolymers; they are quite advertised. But theoretically, the strength of such structures has not been proven, and in practice, the tooth has to be heavily ground under a crown made of any type of plastic, otherwise it can quickly crack.
In addition, plastic does not have biological compatibility with the gums, which is fraught with inflammation and the appearance of a characteristic dark rim at the point of contact of the gums with the crown.
{steps}
What are the consequences of untimely crown replacement?
1. Destruction of the tooth under the crown with its subsequent loss.
The main function of a crown is to restore a badly damaged tooth and protect it. The first time after installation, the crown performs its function perfectly. But after a certain time, changes occur. The gingival margin rises, saliva and gingival fluid affect the cement that “secures” the crown. Over time, this cement can be partially washed out (dissolved), a microscopic gap is formed between the crown and the tooth, and the tooth begins to deteriorate under the influence of microbes and oral fluid. The most insidious thing is that these signs occur asymptomatically and unnoticed by the patient, since they are painless. Therefore, replacement of crowns often occurs untimely, when the tooth is destroyed too much and becomes simply unreliable.
Associated with this is the myth that teeth under crowns are destroyed. The truth is that crowns are simply replaced at the wrong time, but too late.
This can be prevented by timely replacement of the orthopedic structure.
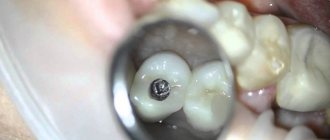
2. Inflammation of the tissues around the crown . This means the gums, tooth ligament and bone tissue. A poor-quality crown can lead to the formation of a chronic inflammatory process in the gums (gingivitis, periodontitis), which is manifested by redness, bleeding when brushing teeth, aching pain in the gums and an unpleasant odor. If such a crown is not replaced for a long time, the underlying tissues become involved in the inflammatory process, which may lead to the formation of bone pockets, disruption of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, and local periodontitis, which in severe cases leads to tooth loss.
Photo 2.1. Inflammation of the gums near teeth under crowns, associated with inaccurate marginal fit of the crown to the tooth and with a violation of the biological parameters of tooth restoration.
Important! Make it a rule to visit the dentist for a preventive examination at least once a year, if you have any dentures, in order to notice their failure in time and prevent or correct the problem.
Solid crowns in Stavropol
Cast crowns made of solid metal can be safely recommended to patients in need of prosthetics.
The advantages of such products are obvious:
- homogeneity of the metal, which means the absence of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- no soldering during manufacturing, therefore there will be no electrochemical corrosion and galvanism in the oral cavity;
- high strength of the one-piece crown that can withstand any chewing load;
- hygiene, if the crown is professionally made, it will fit tightly to the surface of the tooth, preventing the cement from collapsing and food from penetrating into the resulting cracks;
- the ability to model the ideal anatomical shape of the crown for effective grinding of food during chewing;
- product durability.
Among the disadvantages of cast structures are high thermal conductivity and low aesthetic qualities, therefore, they are preferred when prosthetizing “dead” teeth that bear a large chewing load.
The design is generally reliable, of high quality, subject to professional manufacture and installation, but from a cosmetic point of view it is far from ideal, although when viewed positively it looks like white gold.
How do you know if it’s time to change the crown or if it can still serve?
There are objective signs that reflect the condition of crowns/bridges, which are assessed by an orthopedic dentist during a routine examination:
- service life of the crown/prosthesis
- patient complaints (pain, food getting stuck near the crown, unpleasant odor near the crown, and others)
- fit of the crown to the tooth (marginal fit)
- the presence of areas of plaque accumulation
- condition of the gums next to the crown (color, bleeding, density, presence of other signs of inflammation, raising the edge of the gums (exposure of the root))
- presence of signs of inflammation of the bone tissue around the tooth with a crown
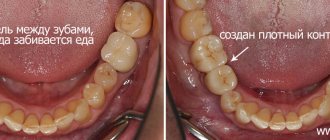
- density of interdental contact (crowns with adjacent teeth).
If one or a number of signs are present, the doctor decides whether the crown needs to be replaced.
Indications and contraindications for the use of stamped crowns
Stamped metal crowns are used:
- In case of incomplete tooth decay. In this case, the tooth is ground to the required size, all its defects and carious lesions are eliminated to prevent further destruction.
- If removable dentures, for example, clasp or bridges, will be installed. Crowns are installed to protect supporting teeth.
- To restore a damaged baby tooth
There are some contraindications to their use:
- Bruxism (teeth grinding, which destroys enamel).
- Complete tooth destruction, in which there is nothing left to save.
- Infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
Can the patient himself understand that it is time to replace the crown?
Certainly! There are a number of signs, the presence of which should give cause for concern.
- The most common is crown edge exposure , when the gingival margin rises and the tooth root becomes visible (“gingival recession”). In this case, root caries may develop, that is, the tooth may be destroyed.
Photo 2.2. The initial stage of exposure of the roots of the teeth under the crowns.
Photo 2.3. The advanced stage of exposure of the roots of the teeth under the crowns.
- Inflammation of the gums around the crown , which manifests itself in redness of the gums, swelling, and bleeding when brushing.
Photo 2.4. Inflammation of the gingival margin of teeth under crowns, associated with inaccurate marginal fit of the crown to the tooth and with a violation of the biological parameters of tooth restoration.
- The appearance of crown mobility . Patients often say that the crown or bridge is “fixed.” This happens especially often when several crowns are combined (some of the crowns of the bridge have become uncemented, while the rest are still holding together).
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor or taste in the crown area.
- Food getting stuck between crown/crown and tooth.
Important! All of the above signs are a mandatory reason to visit the dentist.
Materials used for making crowns
The production of stamped crowns is a high-tech process implemented through the technology of stamping metal material. Such material may have additional coating in the form of expensive, noble metals (for example, silver or gold). Products with gold plating are very popular. Prosthetics using stamped crowns is in demand by people with low incomes, since this process using ceramics/metal-ceramics will cost much more.
How are crowns replaced?
A separate article will be devoted to this. Let us briefly describe the main stages:
Stage 1 : examination by a doctor and diagnosis (X-rays). We evaluate the accuracy of the crown fit, the condition of the tooth and surrounding tissues. We understand that the crown needs to be replaced.
2nd stage : silicone key (necessary for the doctor to make you a temporary crown so that you do not go without a tooth after removing the old one)
Stage 3 : we evaluate the tooth under the crown, give it the correct shape, clean it, and remove possible caries. We fix the temporary crown. You can't go a day without a tooth!
Stage 4 : we take impressions for the new crown and send them to the dental laboratory.
Stage 5 : we get a new crown, fix it on the tooth and happily say goodbye to the doctor until the next professional examination.
Indications
Typically, stamped crowns are placed when the natural parts of the tooth can no longer be restored with fillings or inlays. This usually happens when more than 1/3 of the tissue is removed along with caries.
Except in cases of caries or impact trauma, stamped crowns can be placed as bridge abutments. This allows you to avoid grinding down excessively healthy teeth, or when it is impossible to install a cast structure.
Sometimes such crowns can even be placed on children’s baby teeth to correct their bite.
Bottom line: how long does it take to replace crowns?
According to the book rules : in 5-7 years.
It is better to replace poorly made crowns immediately after placement, so that the teeth underneath do not deteriorate.
Well-made crowns can last 10 years or more.
Conclusion: any crown has a certain service life, which depends on the characteristics of the clinical situation (tooth condition), quality of workmanship, material and method of fixation. The need for replacement is determined by the doctor based on a number of objective factors. Timely replacement allows you to reuse the same foundation (tooth, root) to repeat the structure. Accordingly, the tooth will last for many years. Untimely replacement of the crown (unreasonably long use) can lead to deep tooth destruction, which will be impossible to restore.
An attentive attitude to one’s health on the part of the patient, coupled with timely and qualified assistance from a doctor, leads to a long-term positive result.
By clicking on the “Make an appointment” button, I consent to the processing of my personal data.
I have read and agree with the conditions for processing personal data set out on the website ds-chocolate.ru.
Consent to the processing of personal data
Be healthy!
Kirill Andronov on how often you need to change crowns
Is a metal crown on a chewing tooth harmful?
There is no clear answer to this question. I think it is harmful, although each case is individual. There are patients for whom the placement of steel products is contraindicated due to a genetic characteristic of the body that causes allergic reactions to metal, including galvanism, when the potential difference of metals in the mouth begins to produce an electric current. And this is accompanied by quite unpleasant sensations.
Therefore, before prosthetics, it is recommended to undergo a test for allergic reactions. If the result is positive, the client is offered an alternative type of prosthesis - metal-free crowns on the teeth.
Installation of non-metal crowns
on teeth I offer patients in such cases:
- If you need to restore teeth with a high functional load.
- The bone tissue of the tooth is destroyed to the base.
- The closing surface of the chewing units is heavily worn.
- Installation of bridge structures is required.
The rigidity of the frame and the duration of wearing the crown depend on the method of manufacturing the prosthesis. Today, only cast elements are used in prosthetics. They fit tightly to the base, preventing the penetration of harmful bacteria. Therefore, the risk of developing caries on prosthetic teeth, after high-quality installation of metal crowns, is zero.
When is it time to get a single denture?
- partial destruction (more than 50% of the visible part): as a result of trauma, caries and other pathological processes. In this case, the tooth will have to be ground and a single prosthesis will be fixed on the stump,
- the coronal part is almost completely destroyed, but there is a root: before installation, a fiberglass pin - it is quite aesthetic for the smile area and will increase the strength of the connection between the prosthesis and the root system,
- there is no root: this clinical picture is a direct indication for implantation. A durable titanium rod will be a complete replacement for a living root. After its installation and prosthetics, the bone tissue in the area of the defect will literally “come to life” - the implant, instead of the root, will transfer to it the chewing load, which is so necessary to activate metabolic processes in the jawbone.