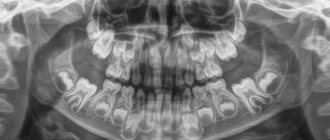
The structure of the human jaw: teeth and their formula
When citing one number for any tooth, the dentist means its anatomical and functional affiliation. If you conditionally divide the dentition into two halves and start counting from the first incisor, you will get 8 teeth in each direction (top and bottom). The first incisor is a one. The second, accordingly, is a deuce. And so on until the last molar, which is called the figure eight. If the doctor says - bottom seven on the left, then we are talking about the bottom left second molar. As you can see, everything is very simple!
This can be expressed schematically as follows (permanent teeth):
For baby teeth, everything is the same, only the teeth are designated by Roman numerals (there are no premolars in the primary dentition):
As for the two-digit designations, they were invented in order to simplify the written recording of medical history. The above is preserved, but a number appears before the number indicating which jaw and on which side the tooth is located. Conventionally, the oral cavity is divided into segments - upper right (number 1), upper left (number 2), lower left (number 3), lower right (number 4). As you noticed, the report is conducted starting from the top right and clockwise. The segment is written first, and then the tooth number. For example, the third canine from the top right would be designated tooth 13. The lower incisor on the left is 32 teeth. In children, the segments are designated by numbers 5 to 8, so as not to confuse the primary bite with the permanent one. Let's take the same third fang on the right. In a child, it will be designated as tooth 53. And so on by analogy. The main thing is to always start the report from the right side at the top, then you won’t get confused. These are not snails with 25 thousand teeth! Can you imagine their dental formulas?
Advantages of the method
- The ability to rotate, enlarge, and examine images in any projection and section, which is impossible with conventional 2-dimensional scanning.
- The examination lasts only a few seconds (8-20 seconds).
- Complete diagnostic information.
- Maximum security.
- Digital information format.
- Detection of any pathological processes at an early stage.
- No prior preparation required.
- 3D reconstruction without distortion or artifacts.
- A wide range of purposes - from endodontic dental treatment and implantation to maxillofacial operations.
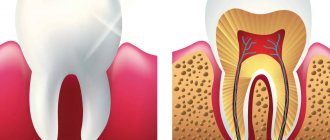
Anatomical structure of the tooth
We figured out the order of the teeth. Further - more interesting! After all, a tooth is a unique organ, designed by nature to perform very important functions, primarily chewing. To be firmly held in the jaw bone, you need a root. The longest root is at the canine. Teeth can be single-rooted or multi-rooted. The structure of the upper teeth (molars) is somewhat more complex than that of the lower ones, since they have 3 roots. There are especially many variations in the number and type of roots in “wisdom teeth.” But the visible part of the tooth protruding above the gum is called the crown. It has different shapes in the incisors, canines and molars to perform the functions of biting, crushing or chewing food. The boundary between the crown and the root is the neck of the tooth. It is usually not visible, but it can become exposed due to certain diseases (periodontal disease, etc.). An x-ray is a kind of photo of the structure of the tooth and will give you an idea of what the state of affairs is in the oral cavity.
Impregnations for threads
During the production process, floss manufacturers add various impregnations and flavors to the threads to make the process of brushing teeth more enjoyable and effective. Impregnations can be flavoring, mineralizing and antiseptic:
- Menthol (or fruit) - have a pleasant aroma and freshen your breath.
In addition to menthol, fruit flavors are also used, for example, lemon, cinnamon, strawberry, etc. Curaprox DF834 waxed dental floss has a pleasant mint taste . Thread length 50 m.
Waxed floss Curaprox DF834, 50 m
Waxed thread Splat Dental Floss with strawberries, 30 m
Waxed thread Splat Dental Floss with bergamot and lime, 30 m
Waxed thread Splat Dental Floss with coconut, 40 m
- Fluoride - provide additional strengthening of teeth due to the mineralization of enamel with fluoride ions.
These flosses are recommended for those who have sensitive teeth. Pierrot Dental floss with aloe vera from the Spanish company Fushima is made of nylon . It contains fluoride and aloe vera juice for anti-inflammatory effects. Thread length 50 m.
Waxed dental floss Pierrot Dental floss EXPANDING, 30 m
Waxed dental floss Pierrot Dental floss with aloe vera, 50 m
Waxed dental floss Pierrot Dental Floss with strawberries, 50 m
- Chlorhexidine - have an additional antiseptic effect, reducing the likelihood of developing inflammatory gum diseases.
When choosing a thread with chlorhexidine, we recommend paying attention to the high-quality tape thread Mirafloss chx-Tape. The thread is unwaxed. Length 20 m.
Tape floss with chlorhexidine miradent Mirafloss chx-Tape, 20 m
Floss Curaprox PTFE floss tape DF820 with chlorhexidine, 35 m
Some threads contain combinations of several of the impregnations described above, and some are made without any impregnations.
Histological structure of the tooth
The special hardness of teeth is due to their structure. The outside of the crown is covered with enamel, the basis of which is hydroxyapatite crystals. 96% of the enamel consists of inorganic substances, which is why it is so hard (which, however, does not mean that experiments can be carried out on teeth, testing their strength). But dentin, which is located under the enamel, has much less inorganic substances - about 70%. It is softer, and therefore is destroyed by caries more than enamel. Inside the tooth there is a cavity filled with a neurovascular bundle, or pulp. The entire rich spectrum of pain during the deepening of the carious process is associated with it. In addition to nerve fibers, the pulp also contains a large number of blood vessels, through which infection from the affected tooth spreads throughout the body. This is why it is so dangerous to leave dental diseases untreated.
Modern dental floss
Teflon dental floss is considered the most durable. They have a low coefficient of friction and high mechanical tensile strength. Does not disintegrate into fibers.
Mirafloss Tape is an unwaxed (not waxed) tape floss that is tear and abrasion resistant due to Teflon fibers. Thread length 20 m.
Pierrot Dental TAPE is a waxed (wax-coated) tape floss made of Teflon. Suitable for those who have narrow interdental spaces. Thread length 20 m.
Revyline PTFE Black Edition is a waxed Teflon dental floss with mint impregnation. Ideal as a first thread. Length 50 m.
Tape floss Miradent Mirafloss Tape 20 m
Waxed Pierrot Dental TAPE with mint, 25 m
Dental floss Revyline PTFE Black Edition, 50 m
Flat, ribbon threads
The thickness of tape threads is usually 0.005-0.007 mm (tens of times smaller than a human hair), which allows them to easily penetrate even the narrowest interdental spaces. These flosses are recommended for those who have teeth that are close to each other.
Oral-B Pro-Expert Clinic Line and Oral-B Satin Floss are wax coated, mint flavored and 25m long.
Miradent Mirafloss chx-Tape is impregnated with chlorhexidine for an antiseptic effect. Thread length 20 m.
Biorepair Filo Non Cerato Ultrapiatto floss is ideal for cleaning narrow interdental spaces and sensitive teeth. The flat part helps remove food debris even in the most difficult to reach places. Thread length 30 m.
Revyline PTFE Black Edition dental floss is made of Teflon, has a jet black color and is impregnated with menthol. Thread length 50 m.
Waxed thread Oral-B Pro-Expert Clinic Line Cool mint, 25m
Tape floss with chlorhexidine miradent Mirafloss chx-Tape, 20 m
Ultra-flat thread Biorepair Filo Non Cerato Ultrapiatto, 30 m
Waxed thread Oral-B SatinFloss mint, 25 m
Expanding threads
The peculiarity of such threads is that they swell (expand) under the influence of saliva and become thicker than 1 mm in diameter. This allows them to thoroughly clean the wide interdental spaces from food debris and plaque.
Biorepair Espandibile dental floss is an ultra-soft, expanding floss infused with hyaluronic acid to relieve gum inflammation. Thread length 30 m.
GUM Expanding Floss is a waxed expanding floss, ideal for sensitive teeth. Length 30 m.
Swiss Smile waxed dental tape penetrates the interdental space slightly expanding, thereby providing excellent cleansing without damaging soft tissues. The tape refreshes the oral cavity well due to its mint impregnation. Available in two colors: blue and black. Thread length 70 m.
Waxed Splat Dental Floss expands with use, providing more effective cleaning of the surface of the teeth. The antibacterial component Biosol stops the proliferation of bacteria. Thread length 30 m.
Waxed dental tape Swiss Smile, 70 m
Waxed thread Splat Dental Floss mint with silver fibers, 30 m
Waxed thread GUM Expanding Floss, 30m
Waxed expanding thread Biorepair Filo Cerato Espandibile, 30 m
Superflosses
Superflosses are special threads consisting of several types of alternating fibers for effective cleaning of braces, bridges and implants.
Most superflosses consist of two parts:
— a rigid tip necessary for threading under an orthodontic structure or a bridge;
— the spongy part (a wide unwaxed thread resembling a sponge), necessary for cleaning orthopedic and orthodontic structures, as well as interdental spaces.
Superfloss brand Oral-B Superfloss differs from classic superfloss: firstly, it has a fixed length (the package contains 50 pieces of 60 cm in length), and secondly, it consists of three parts (hard tip, spongy part and regular waxed thread) .
Mirafloss Implant chx is a practical box of 50 threads, 15 cm long, for cleaning braces and implants. The middle part of the superfloss is impregnated with chlorhexidine for an antiseptic effect. Available in two versions: thin threads (diameter 1.8 mm) or medium thickness (diameter 2.2 mm). Thread length 50 m.
GUM Access Floss superfloss is no less effective in cleaning braces, implants and wide interdental spaces . There are 50 threads in a package. The total length of the thread is 30 m.
Dental floss Oral-B Superfloss, 50 pcs.
Floss miradent Mirafloss Implant chx 1.8 mm for implants/braces
Floss miradent Mirafloss Implant chx 2.2 mm for implants/braces
GUM Access Floss for implants/braces, 30m
Waxed threads
Waxed threads are those that are coated with wax on top. They need such a coating in order to easily slide into the interdental spaces of dense or crowded teeth. This type of thread is atraumatic and does not cause discomfort when used, so it is more often recommended than others for those who are just beginning their acquaintance with threads.
Emmi-dent Dental Floss is made from high quality nylon and has a refreshing mint flavor. Suitable for sensitive teeth. Thread length 50 m.
The voluminous waxed floss of the Italian production Splat Dental Floss glides easily between the teeth, contains essential oils (cardamom, strawberry or bergamot) and the antibacterial component Biosol, which provides effective protection for the oral cavity. Thread length 30 m.
Waxed dental floss Pierrot Dental floss is made of nylon and impregnated with wax for better glide. Fluoride, which is included in the composition, restores and protects enamel from caries in places inaccessible to a brush, and aloe vera has an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect. Thread length 50 m.
Curaprox Dental Floss waxed interdental floss with mint flavor. Thread length 50 m.
Waxed thread Emmi-dent Dental Floss mint, 50 m
Waxed dental floss Pierrot Dental floss with aloe vera, 50 m
Waxed floss Curaprox DF834, 50 m
Waxed thread Splat Dental Floss with cardamom, 30 m
Unwaxed threads
Unwaxed threads are threads that do not have a wax coating. Due to this, the threads do not slip into the interdental spaces, but gently “rub the enamel,” thereby cleaning it much better from plaque and food debris.
ROCS Black Edition unwaxed expanding floss with mint flavor helps prevent gum inflammation, keeps teeth healthy and white, and freshens breath. Length 40 m.
The Biorepair line includes two types of unwaxed floss: Biorepair Spugnoso - a sponge floss (unwaxed, sponge-like) for cleaning wide interdental spaces, and Biorepair Ultrapiatto - an ultra-flat unwaxed floss for cleaning narrow interdental spaces. Both threads contain unique MicroRepair crystals that promote mineralization of tooth enamel. The length of the threads is 30 m.
Tape floss with chlorhexidine Miradent Mirafloss , impregnated with a chlorhexidine solution, has an antibacterial effect and reduces the formation of plaque. The surface of the tape is unwaxed, made of PET (Teflon), thanks to which it glides easily when inserted into dense interdental spaces.
Dental floss ROCS Black Edition (black), 40 m
Sponge dental floss Biorepair Filo Non Cerato Spugnoso, 30 m
Tape floss with chlorhexidine miradent Mirafloss chx-Tape, 20 m
Ultra-flat thread Biorepair Filo Non Cerato Ultrapiatto, 30 m
The structure of baby teeth
A temporary bite differs from a permanent bite not only in the number of teeth (in a temporary bite there are 20). Baby teeth have a bluish tint to the crown, which is also much wider than the root. Children have less enamel mineralization, so caries affects them very quickly, and the pulp takes up more space compared to permanent teeth. The canals of baby teeth are wider, easier to pass for instrumentation, and the roots themselves have a rounded shape. The structural features of baby teeth determine their rapid destruction in case of infection penetration and very severe pain in the child, so in childhood, visit the dentist in a timely manner.
Knowing the structure of teeth will help you quickly find a common language with the dentist and feel more confident when discussing treatment issues.
You will be able to better navigate the manipulations performed by the doctor and clarify all the points that interest you with an understanding of the essence of what is happening. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
History of dental floss
The word “floss” comes to us from the English language and is literally translated as “dental floss”. It was first mentioned in the book A Practical Guide to Dental Care, written by American dentist Levi Spear Parmley in 1819. He suggested to his patients and readers to use silk dental floss to remove food debris from the interdental spaces.
During World War II, when Japan stopped supplying silk to America and Europe, silk dental floss was replaced by nylon floss, developed by DuPont. Nylon was thinner, stronger and cheaper. It was produced in large quantities, and therefore became very popular in the mass market.
The principle of installing a crown on a chewing tooth
This is a step-by-step process, where each step takes a different amount of time and procedures preceding the placement of the prosthesis.
- Initial consultation with a dentist – examination, diagnosis of problem areas of the oral cavity. Drawing up a prosthetic plan and choosing material for making crowns;
- Preparatory measures consist of absolute sanitation of the dental system. If required, the pulp is removed and a support pin is prepared.
- Preparation of the tooth, production and transfer of a plaster model of the tooth to the denture laboratory, where a crown for the tooth or implant is created.
- Installation of a temporary metal-plastic structure.
- Fitting and temporary fastening of an element to be worn by the patient for a certain period. After the trial period (one month), if the patient has no complaints, the doctor removes the prosthesis and cleans it thoroughly. Then he places it on the support again, having previously treated it with a special medical composition.
The method of installing crowns is the same for both upper and lower chewing teeth.
How are tooth sizes determined?
To determine the size of a person’s permanent teeth, the calculation tables of Wetzel and V.L. Ustimenko with average standards and permissible deviations are used. However, an experienced dentist is able to independently identify the anomaly during a visual examination or by applying the formula for the ratio of the height and width of the natural crown. During diagnosis, the specialist takes into account the patient’s face shape and height. For example, with a wide jaw, the size of teeth exceeding the norm is not a pathology.
To determine the size of the root canal, there are also tables that indicate the average distance from its apex to the cutting edge or cusp of the tooth surface. The longest is the root of the canines - about 26 millimeters, the root canal of the incisors is 21 - 23 millimeters, and the size of the roots of the chewing zone and premolar teeth ranges from 19 to 22 millimeters.
Normal and deviations in tooth sizes
All dental units of the same name have approximately the same height and width, except for the central (medial) incisors. The size of the front teeth of the upper jaw is normally slightly larger than that of the lower jaw. The height of the crown of the upper central incisors varies from 9 to 12 millimeters, width - from 8 to 9 millimeters. The lower teeth are similar in height, but are about 5 millimeters wide. The size of a person's wisdom teeth does not differ from the parameters of other molars. The table below shows the average width of dental crowns in millimeters.
| Upper jaw | Lower jaw | |
| Medial incisor | 8.5 mm | 5.3 mm |
| Lateral incisor | 6.5 mm | 6 mm |
| Fang | 7.6 mm | 6.7 mm |
| First premolar | 6.7 mm | 6.8 mm |
| Second premolar | 6.4 mm | 7 mm |
| First molar | 9.4 mm | 10 mm |
| Second molar | 9.4 mm | 10.2 mm |
Anomalies in the size of human teeth can be congenital or acquired and are accompanied by malocclusion, impaired chewing functions and an unaesthetic appearance of a smile. The most common deviations are macrodentia and microdentia.
Oral hygiene in children
There is a tradition of giving a silver spoon for the first tooth that erupts. We would add a toothbrush to this tradition. We recommend that you teach your child how to brush their teeth in a playful way from the moment the first tooth appears.
Doctors note that up to the age of 10, it is necessary to help children brush their teeth, since at a younger age children find it boring and do not understand why they should do it at all. There are also special liquids or tablets that allow you to check the remaining plaque on your teeth using contrast staining.
There are modern toothbrushes that can be synchronized with a tablet, then brushing your teeth turns into a game.
It is important to remember that the sooner you start brushing your child’s teeth properly, the healthier his teeth will be!
Lengthening the upper teeth using crowns to raise the bite
The orthodontic method of crown lengthening is preferable when it is necessary to preserve the gingival contour between adjacent teeth and “stretch” only one tooth. The disadvantages of this approach include the mandatory installation of braces or
removable denture, as well as a long treatment period. It may take at least three months, and after that the patient will also have to wear a retainer to consolidate the results of previous procedures. In this case, braces can be fixed to several teeth or to the entire jaw, which depends on the specific clinical case.
In addition, the concept of “teeth lengthening” includes a number of other procedures, such as:
- veneering,
- composite dental restoration,
- veneering and prosthetics with crowns.
Lengthening teeth using a composite material is advisable for minor damage to the coronal part. The front teeth are usually lengthened with Hollywood veneers or Lumineers. If the tooth is seriously damaged (more than 70%), then a crown is used.
Patients with increased wear often need a complex of orthopedic measures, which involves lengthening all teeth at once, and not just one. The upper and lower teeth are lengthened using crowns, which are used to raise the bite and change the shape of the dentition.
Indications for prosthetics
- Chipped crown (when the defect cannot be corrected by installing a filling);
- multiple cracks in the enamel;
- pathological abrasion of enamel;
- fluorosis;
- tetracycline teeth;
- color change (darkening, yellowing);
- destruction of the supragingival part of the tooth more than 70% with preservation of the root;
- thin, weakened enamel;
- replacement of an old restoration.
Macrodentia
The tooth size exceeds the norm by more than 2 millimeters. Pathology occurs due to the fusion of two rudiments or the main and supernumerary teeth during the period of formation. The cause of macrodentia can be endocrine diseases, metabolic disorders or heredity. There are five types of pathology:
- localized - one or two teeth are significantly larger than the rest;
- generalized - the entire dentition differs in size from the other;
- isolated - enlargement of one medial incisor;
- absolute - the size of the teeth of both jaws exceeds the norm;
- relative - excessive growth of the upper or lower incisors.
What is the cost of a dental crown?
The cost of restoring a lost or defective tooth depends on many factors, the main ones:
1. The status of the dental clinic in general and the treating orthopedist in particular - the higher the doctor’s rating, the more expensive the cost and quality of the services provided.
2. Material for making a crown: the lowest price of metal products, ceramic crowns and products made of zirconium dioxide cost from 27,000 thousand rubles per unit. A crown containing precious metal is the most expensive.
All stages of preparation and treatment: consultation, hardware diagnostics, filling and other procedures that ensure oral health also require certain financial costs. The services of a dental technician are included in the final cost of installing a crown on a tooth.
The main stages of modeling the 16th tooth from sculptural clay
Sculpture clay has long been used in art to recreate shapes. This inexpensive material is ideal for sculpting teeth; working with clay is pleasant in its own way, it is soft, does not stick to your hands, and hardens gradually. Sculpting clay requires longer preparation for work than plasticine, which is most often used for modeling teeth. If the clay is dry, then first you need to mix it with water to the consistency of sour cream, leave for some time until it dries and forms a plastic mass. After this, the clay becomes hard only after a few hours, this time is quite enough to successfully complete the work. The smaller the volume of available material, the faster it hardens. When the desired consistency is obtained, the clay is shaped into a ball (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The material has the necessary plasticity and is ready for use. Giving the future model a ball shape
Let's consider modeling the first right molar of the upper jaw (16th tooth). The overall outlines of the model of the 16th tooth are set (Fig. 2, 3), the location of the main surfaces is outlined: medial contact (M), distal contact (D), vestibular (V) and palatal (P).
Rice. 2. Giving the overall outline of the model
Rice. 3. Modeling the tops of the main tubercles.
The tops of the main hillocks are determined. Markings are applied on the chewing surface (Fig. 4), corresponding to a first-order H-shaped fissure.
Rice. 4. Applying markings corresponding to the first-order fissure, H-shaped, on the occlusal surface
Completion of the formation of the external contours of the model and the equator (Fig. 5) is done by hand.
Rice. 5. Smoothing out irregularities and shaping the equator
Before this stage, all actions were performed by hand (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Working with your hands allows you to better feel the basic properties of the material
To model the chewing surface of the tooth, it is better to use tools. The first-order fissure is deepened with a spatula (Fig. 7, 8).
Rice. 7. Deepening of the fissure of the first order, separating the anterior buccal tubercle (2) from the posterior buccal (1) and anterior palatine (4). Posterior palatine tubercle (3)
Rice. 8. 1 - posterior buccal tubercle, 2 - anterior buccal tubercle, 3 - posterior palatine tubercle
When modeling, there is no need to draw fissures, but it is necessary to divide the main tubercles so that an H-shaped fissure appears between them (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9. Completing the modeling of the first-order H-shaped fissure
Tools for work are chosen that are more convenient to work with: it can be a spatula, a smoothing iron. A fissure shaping tool, such as a probe, is required. 2-3 tools are enough.
After completing the work, the model can always be corrected by cutting off excess with a scalpel or spatula. The resulting tooth model can be stored for a long time, reminding of the results of the work.
Rice. 10. Modeling of the longitudinal (2), medial (1), distal (3) ridges of the anterior buccal tubercle
Rice. 11. Second-order fissures are formed on the anterior buccal tubercle
Rice. 12. Modeling of the main (2) and additional (1, 3) ridges of the anterior palatine tubercle
Rice. 13. Final view of the 16th tooth model
Rice. 14. Appearance of the 16 tooth model. Occlusal surface
Rice. 15. Appearance of the 16 tooth model. Palatal and chewing surfaces