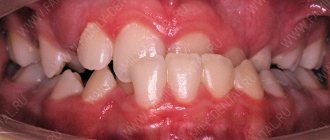
Hypertrophic pharyngitis is one of the varieties of the chronic form of the disease. It usually begins to appear 6-8 months after acute inflammation was diagnosed, which was not properly treated. The hypertrophic form of pathology affects not only the posterior wall of the pharynx, but also its lateral parts.
With pathology, the mucous membrane of the pharynx not only becomes thicker, but its density also increases. These changes are pathological, and as a result, it begins to function incorrectly and becomes inflamed. Also with this disease, the appearance of lymphoid granules is noted, which look like pink grains. The disease can appear in people of any age, but more often affects adults, since they often do not properly treat the acute form of the disease and suffer it on their feet. Gradually, disruption of the pharyngeal mucosa can also spread to the uvula. Hypertrophic pharyngitis symptoms increase as the damage to the mucous membrane progresses.
Causes
The disease develops against the background of the fact that negative factors cause excessive activity of the immune system, due to which it begins to provoke the development of a number of neoplasms on the mucous membrane, associated with the detection of even minor pathogens. As a result, inflammation develops and tissue changes occur. The main factors causing hypertrophic pharyngitis, in addition to its advanced acute form, are the following:
- living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- working in hazardous industries in violation of safety rules;
- long regular stay in a room in which the air is very dry and warm;
- smoking – not only active but also passive smoking has a negative effect on the mucous membrane and the body as a whole;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages - even not strong ones, they irritate and damage the tissues of the pharynx, making them more susceptible to pharyngitis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, in which blood circulation in the tissues of the pharyngeal mucosa is disrupted, as well as those that lead to congestion in the respiratory system;
- serious metabolic disorders, especially against the background of pathologies of the endocrine system;
- regular occurrence of allergies;
- disturbances in the structure of the pharynx;
- constant significant lack of vitamins.
Chronic pathologies of the nasopharynx, such as tonsillitis, sinusitis and rhinitis, can also cause the disease. Pathogenic bacteria will abundantly penetrate the mucous membrane and remain dormant in it until factors unfavorable for the immune system appear. When they develop an exacerbation of the disease.
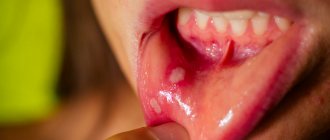
Causes of pimples in the mouth
70% of red, white or pinkish rashes in the oral cavity, including on the tongue, indicate the presence of a serious dental disease. The asymptomatic course of the disease does not mean that the “trouble” will go away on its own. However, prescribing treatment on your own, guided by the advice of friends or recommendations from the Internet, is dangerous.
Important!
In principle, there cannot be acne on the tongue. Purulent skin rashes develop due to inflammation of the sebaceous glands, which are not present in the mouth. Accordingly, we call those pimples that appear in the oral cavity “pimples” by analogy. Just by external similarity.
There are several reasons for the appearance of irritations that visually resemble pimples:
- mechanical damage. A prick with a fish bone, a scratch, a burn from hot coffee can provoke a similar pathology;
- allergy. Not necessarily to foods; a seasonal allergic reaction is possible, manifesting itself in such an unusual way;
- viral and infectious diseases. Herpes, rubella, scarlet fever and ARVI sometimes manifest themselves as rashes in the mouth;
- fungal infection (candidiasis);
- stomatitis. Usually, with stomatitis, pimples first appear on the gums, but sometimes red spots with a whitish halo, which react sharply to touch or spicy/hot food, form over the entire lingual surface.
There is no point in waiting until diseases become chronic. In 98% of cases, such pathologies are treated quickly and inexpensively, if you do not neglect the condition and do not self-medicate.
Kinds
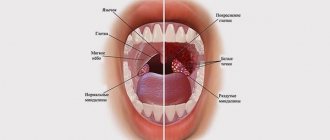
This form of the disease can have two types. Depending on which of them is diagnosed, the exact treatment method is determined. Granular hypertrophic pharyngitis affects only the back wall of the pharynx. With it, tissue swelling is not felt so much at the onset of the disease, which is why not all patients seek medical help in a timely manner.
Lateral hypertrophic pharyngitis is manifested by more acute pain and difficulty breathing. It is extremely difficult to ignore it for a long time, which is why treatment most often begins on time. The diagnosis is made after examining the patient's pharynx.
Locations of acne in the throat
Pimples in the throat in infectious diseases are often located on the back wall. The favorite place of localization of fungi is on the tongue and its root. White pimples in a child's throat are clearly visible on the tonsils.
Widespread hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the soft palate and uvula is observed with inflammation of the nasopharynx. Stomatitis affects the gums.
The rash due to childhood infections is also located on the inner walls of the cheek, the tonsils. Diseases of the ENT organs are accompanied by pimples in the throat on the back wall.
Forecast
With timely, complete and systematic treatment of the disease, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. In this case, it is possible to stop pathological changes in the mucosal tissues. After quality therapy, exacerbations of the disease are extremely rare.
If treatment is started late, when the throat lesion is already quite serious, then the prognosis for the patient is relatively positive, since it will not be possible to ensure a long remission, but at the same time the risk of complications will be eliminated.
Treatment of pimples on the tongue
Carrying out an examination of the mucous membrane of the tip, side, and root of the tongue, the doctor examines the red pimples and growths. Based on laboratory tests, examination and medical history, the specialist makes a diagnosis, finds out why the disease appeared, and determines the therapeutic direction. The classic method of treatment is medication:
- Antibiotics are used to destroy bacteriological pathogens
. Effective drugs for local action: Bioparox, Fuzafyungin. As well as medications for systemic treatment: Amoxicillin, Cefadroxil. - To prevent the rashes from becoming inflamed, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Stomatidin, Ingalipt, Lugol.
- Antiseptic agents accelerate wound healing: Chlorhexidine (it is necessary to apply lotions and rinses).
- Dysbacteriosis, which can cause rashes on the mucous membranes, is treated with probiotics: Bifidumbacterin, Acipol, Linex, Bifiform.
- If pimples appear on a baby's tongue, they are often caused by fungal infections; thrush is treated with antifungal drugs
. It is worth doing daily rubbing of the tongue, cheeks and lips with a broad-spectrum solution of Candide. After just 1–2 days, less plaque forms, and after a week, the signs of the disease completely disappear. - Allergic reactions are eliminated with the help of antihistamines: Fenistil, Cetrin, Erius.
What not to do
During the treatment period there are certain restrictions, by violating which the patient risks significantly aggravating his condition. The doctor will not be able to guarantee the patient a positive result of therapy if the following actions are allowed:
- smoking during treatment;
- use of alcohol preparations for gargling;
- eating spicy food;
- staying in a dusty room;
- violation of medical instructions regarding treatment.
If there are no violations in the course of therapy, then it is possible to stop the disease at the beginning of its development without the use of surgical methods of therapy. Treatment of hypertrophic pharyngitis in adults and children is the same.
Candidiasis
The most common cause of candidiasis is decreased immunity. Therefore, thrush often occurs in the mouth of infants. Thrush is characterized by pimples in the throat, covered with a white cheesy coating. The spots are localized on the tongue, behind the arches, tonsils and soft palate.
Important symptom! After removing the top layer, small erosions are visible, from which droplets of blood are released. The rashes cause discomfort to patients.
Signs of thrush:
- pain and dryness in the throat;
- itching and burning;
- tonsil hypertrophy;
- redness of the throat;
- elevated temperature is observed mainly in children;
- decreased appetite.
Untreated thrush becomes more complicated. Ulcers appear in the mouth and fester. The infection spreads to the larynx. Yeast-like fungi Candida are able to penetrate the digestive system.
With the bloodstream they can spread throughout the body, leading a person to sepsis with a fatal outcome.
During treatment, systemic antifungal drugs are prescribed - Fluconazole, Mycostatin, Fucis, Itraconazole. Medicines are prescribed in courses. The doctor selects medications based on the results of the smear, taking into account the severity of the infection.
Gargles with boric acid and oak infusion are prescribed. The oral cavity is lubricated with Lugol's solution, Fukortsin, sea buckthorn oil and antifungal creams. Ultraviolet and laser rays are used in complex treatment.
Diagnostics
Only an external examination of the pharynx is not enough to identify not only the disease itself, but also the causes of its occurrence, as well as the condition of the body. Because of this, the doctor, having identified pharyngitis by eye during the initial examination, necessarily prescribes further tests to the patient, which help to obtain a complete picture of the health condition and select the most effective treatment.
1. A swab from the pharynx followed by inoculation on a nutrient medium. It is necessary to determine the composition of pathogenic microflora and its sensitivity to certain antibiotics.
2. Biochemical blood test. It requires venous blood. The study reveals the presence of antibodies to certain inflammatory agents, hormonal parameters and the presence or absence of malignant cells.
3. Clinical blood test. Blood from a finger is used. Shows the percentage of the ratio of its main components. Deviation of one or another up or down makes it possible to detect a number of pathologies.
4. General urine analysis. The study of the material allows you to accurately assess the severity of inflammation in the body, as well as whether there are any disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys against its background.
5. Biopsy of tissue of the pharyngeal mucosa. Not always prescribed. The procedure is necessary if there is a suspicion of the development of a cancer process. When examining a tissue sample, the presence or absence of malignant (cancerous) cells in the mucosa is determined.
If necessary, an electrocardiogram and x-ray of the sinus area may also be prescribed. These procedures are rarely required. They are usually carried out if complications of the disease begin to develop. In young children, an X-ray of the lungs may also be necessary, since quite often, against the background of inflammation of the larynx, pneumonia or bronchopneumonia appears quickly enough.
Red bumps on the tongue closer to the throat - what are they?
In most cases, bumps at the base of the tongue, pimples on the side, growths on the tip of the tongue are manifestations of the following diseases:
- Diseases of the mucous membrane of an inflammatory nature (glossitis) are accompanied by the formation of painful red rashes on the mucous membrane, in severe form - abscesses, phlegmons.
- Metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiency. Such conditions are characterized by redness and enlargement of the taste buds, which often become inflamed and acquire a red-white color.
- Herpes, characterized by the appearance of painful red pimples and blisters.
If red bumps or nodules appear on the base of the tongue, this may be a symptom of pyogenic granuloma. The formations consist of blood vessels and are localized in the wounded area. Pathology occurs due to injuries and damage to the mucous membrane. When touching the formations, a person feels a sharp pain.
- Digestive disorders (malabsorption). Pimples on the root, all over the surface of the tongue, are one of the symptoms of this pathology.
- Candidiasis (thrush). A disease that often affects newborns. The child's tongue becomes covered with red bumps and a cheesy coating forms. The baby behaves restlessly, cries, and has difficulty swallowing; these symptoms are caused by itchy red-white pimples and dry mouth.
- HPV – human papillomavirus. Formations are localized in any area of the tongue: at the tip, root, side. The bumps on the tongue closer to the larynx cause particular discomfort, as they interfere with swallowing and create the sensation of a foreign object in the mouth.
- Allergic diseases. The rashes do not hurt, but they interfere with swallowing and speaking.
- Diseases common to children: chickenpox, measles.