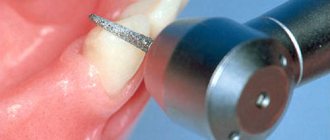
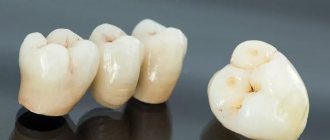
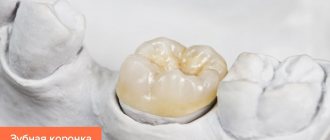
Preparation of a tooth or grinding of a tooth for further installation of a metal-ceramic crown on it means cutting down special hard shells of the tooth, represented by mineralized tissues - dentin and enamel.
Preparation for metal-ceramic crowns
Description of the procedure
Tooth preparation is the removal of hard tissues that are damaged or interfere with the fixation of the crown.
Previously, turning under metal ceramics was long and painful. However, thanks to modern anesthesia drugs and the latest instruments, the duration and pain are significantly reduced.
During the procedure, the doctor strives to preserve healthy organs as much as possible. In this case, it is necessary to create natural forms, which is achieved through the formation of ledges.
For proper preparation, the following criteria must be met:
- the dental organ has retained its natural shape;
- the tooth stump is reduced and slightly tilted;
- the tooth is reduced in size by up to 2 mm;
- There are no unpleasant consequences near the dental organ.
Thanks to the preparation of teeth, the metal-ceramic crown receives the place it needs, so that it does not exceed the neighboring teeth in height and does not protrude outward or inward.
The crown should fit tightly under the gum, which is facilitated by a ledge under the gum.
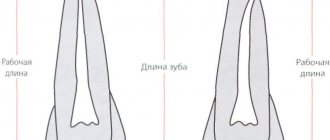
To install a solid crown, up to 0.3 millimeters must be removed from the lateral surface without damaging adjacent teeth. To install a metal-ceramic prosthesis, the tooth is depulped and then 2 millimeters are removed from it. There should be a ledge on each side.
The doctor determines what size layer to remove based on the size of the tooth and the characteristics of its position in the dentition.
Cost of services
If treatment is started on the day of treatment, consultation and treatment plan are free
| Temporary crown (laboratory manufacturing method) | RUR 2,500 |
| Solid crown | RUB 7,900 |
| Metal-ceramic crown with ledge | RUB 13,700 |
| Metal-ceramic crown | RUB 11,500 |
| MK crown using shoulder masses | RUB 15,500 |
| Metal-ceramic crown supported by an implant | 28,000 rub. |
| All-ceramic crown | RUB 16,500 |
| Ceramic crown on a zirconium dioxide frame | 40,000 rub. |
| Core inlay CoCr | 7,000 rub. |
| Stump inlay silver | RUB 8,900 |
| Partial removable denture | 22,000 rub. |
| Complete removable plate denture (1 person) | 25,000 rub. |
| Plate prosthesis reinforced with mesh | RUB 32,500 |
| Removable nylon prosthesis “Quattroti” (1 person) | 55,000 rub. |
| Removable denture with 1-2 teeth | 8,000 rub. |
| Partial removable plate denture made of ImplFcryl plastic (including silicone and imported teeth) (1 person) | 45,000 rub. |
| Complete removable plate denture made of ImplFcryl plastic (including silicone and imported teeth) 1 person. | 55,000 rub. |
| Clasp prosthesis (2-3 clasps) | 35,000 rub. |
| Clasp prosthesis with locking fastenings “Bredent” | 65,000 rub. |
Peculiarities
Grinding teeth for metal ceramics has the following features:
- The need to remove a significant layer of enamel and dentin (up to 2 millimeters).
- The use of anesthesia so that the patient does not feel pain during grinding. The most common methods are infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
- The main goal of specialists is to preserve as much bone tissue as possible and remove all damaged areas.
- After removing the tissue, a truncated cone is obtained, the edges of which are then slightly rounded.
- Grinding should be done intermittently after every 2-3 seconds.
- The tool must be constantly cooled during grinding so as not to cause a burn to the pulp.
- The contact surfaces must be ground with the device at low speeds.
Stages of the procedure
Let's take a step-by-step look at how teeth are ground for a metal-ceramic crown:
- Creating grooves. The doctor makes peculiar incisions that will show how much hard tissue needs to be removed. These grooves subsequently contribute to uniform grinding. Creation of notches can be done with a bur or a shaped head in the form of a wheel. They are carried out from the vestibular side to a depth of 1.5 millimeters. The ledges on the palatal and vestibular sides are removed.
- Removing tissue from the vestibular and oral sides. Maximum caution is important at this stage. Diamond burs directed parallel to the tooth remove the required layer. When working on the palatal side, the palatal tubercle is preserved.
- Preparation from the occlusal surface. This stage consists of preparing one and a half to two millimeters, while not disturbing the anatomy of the chewing surface. The living crown of the anterior dental units is thus shortened by 25%.
- Separation of the contact side. It is important to separate the medial surface from the distal one and then remove the tissue. A diamond bur with flame-shaped or needle heads is used. 0.5 millimeters are left above the gum. To prevent periodontal injury, a dental matrix and an interdental wedge are used.
- Gum retraction. If it is necessary to immerse the bur deeply, you need to protect the gums. Therefore, it is moved away with the help of special threads, rubber rings and a spatula. This stage is important for taking an impression so that a high-quality model can be easily made.
- Formation of the ledge. The width of the ledge can be 0.5-1.5 millimeters, depending on the anatomy of the dental organ. It is made with a face bur.
- The final stage of processing. The dental stump should be in the form of a uniform cone. At this stage, irregularities are cut off, protruding edges are removed, and the stump is rounded.
Laser processing
Thanks to laser pulses, a thermal effect occurs on the fluids contained in the teeth. In this case, the structure of the material is microscopically destroyed. Unnecessary tissue is then cooled with an aqueous solution or air, and then removed without hindrance.
Laser preparation has the following advantages:
- no noise when the tool operates;
- safety of the procedure due to the absence of tips in the device that rotate at high speed;
- the frame for the future crown is obtained quickly and without pain;
- infection during the procedure is excluded, since the instrument does not touch the tissues.
Are there any complications?
In most cases, complications are temporary and completely reversible:
- Damage to the gums due to improper processing. Collapse of the gum line may occur, leading to pain, inflammation, and gradual atrophy of the soft tissue. The problem requires surgical treatment. When an infection occurs, gingivitis can develop.
- Tooth opening during grinding. The doctor will accumulate (restore) the destroyed fragment or remove the pulp and install a pin.
- Inflammation of the pulp after the procedure. It is characterized by swelling and discomfort and is temporary.
Tunnel preparation
Tunnel turning is carried out using turbine units with diamond or metal tips. At the same time, it is important that the equipment is new, since a worn-out instrument can cause overheating of the tissues and their destruction.
Note: With this method, it is possible to save as much material as possible for future crown installation. The result of removal can be predicted in advance, and during the procedure it is easy to control the volume of the removed layer.
This type of preparation is used today more often than other methods.
Preparation with abrasives
An alternative to a drill with its rotating drills is also the supply under pressure of air mixtures containing an abrasive powdery substance. By acting on the enamel, this mixture gradually removes hard tooth tissue.
Features of preparation with abrasives are as follows:
- speed of the procedure;
- absence of tissue overheating and painful sensations;
- gentle effect on the dental shell;
- careful grinding, which allows you to obtain the necessary stump while preserving a significant amount of healthy tissue.
Is dissection painful?
Removing hard tissue is a painful procedure. But with high-quality anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain at all. However, there are situations when, after the anesthesia wears off, the tooth or gums around it begin to hurt.
The main cause of pain in this case is the removal of a large amount of tissue from the vital dental organ. In this case, the tooth, the pulp of which is located under the remaining thin layer of hard tissue, hurts when touched, as well as when exposed to cold or sour food. In such a situation, it is better to consult a doctor so that he can install a temporary crown to protect the ground tooth or cement the thinned area.
Pain may also be a consequence of pushing back the gums with a special thread in order to see the working area when grinding. The floss puts pressure on the soft tissue between the tooth and gum, creating swelling and pain. This pain should go away within two days. If it occurs after a longer period of time, it is better to consult a doctor, as this may be a signal of nerve inflammation or the development of periodontitis.
Anesthesia
In order to numb the desired area, modern dentistry uses several methods of anesthesia, as well as some types of anesthetics. The method of anesthesia that is carried out along the nerve trunk, as well as by injecting an anesthetic with a special needle into the mucous parts of the gums, is very popular.
Anesthesia
These types of anesthesia require close attention from a specialist, as well as strict adherence to all necessary precautions. This is necessary in order not to infect the patient, as well as to prevent infection with various types of viral infections transmitted through blood - hepatitis viruses or immunodeficiency viruses.
When carrying out pain relief measures, several types of solutions are used:
- "Lidocaine";
- "Xylocytin";
- "Artikain";
- "Ubistezin";
- "Ultracaine".
"Lidocaine" solution
The most effective among the above-mentioned medicinal anesthetics is Ultracaine. This drug perfectly freezes the part of the gum that needs to be treated and keeps it frozen for a long time.
- Grinding of teeth for metal-ceramics
It also happens that the patient feels anxious and cannot pull himself together before the procedures. For this purpose, premedication is provided, which consists of administering small doses of tranquilizers to the patient to relieve anxiety symptoms. Premedication is given 30-45 minutes before anesthesia.
Premedication in dentistry
For premedication, some drugs from the following list are given:
- "Phenibut";
- "Mebicar";
- "Tazepam";
- "Elenium";
- "Diazepam."
"Elenium"
In modern techniques, in order to significantly increase the effect of anesthetics, the addition of vasoconstrictor drugs is used. These substances are capable of spasmodic vessels along the bloodstream, which are located in the periphery. This leads to local oxygen starvation in the tissues at the injection site. This reduces the excitability and conductivity of nerve fibers.
It has been proven that the use of vasoconstrictors in modern methods of dental procedures leads to a decrease in the effect of toxic substances contained in the anesthetic. And the painkiller itself is required several times less.
Vasoconstrictors
Vasoconstrictor drugs used in dental practice are:
- a hormone produced by the adrenal cortex - adrenaline;
- a hormone produced by the pituitary gland - vasopressin.
It also happens that total general anesthesia is necessary. This technique is used quite rarely and is necessary for the following indications:
- patient intolerance to local anesthesia or complete lack of pain relief effect;
- diseases associated with the nervous system, leading to convulsive contractions (chorea, hyperkinesis).
General anesthesia
To use general anesthesia, the drug “Rotilan” is used; it has a fairly pronounced, but at the same time mild effect. It is also important that the specialist does not lose contact with the patient.
Treatment under general anesthesia
In order to avoid touching soft tissue when grinding hard parts of a tooth, the specialist must know well what depth is maximum for a certain part of each tooth.
Purpose of installing temporary crowns
After grinding down the tooth, a temporary crown made of plastic is placed on it, which will remain in the oral cavity for two or three weeks while the permanent prosthesis is made.
For some patients, the fact that a doctor makes and places a temporary crown is incomprehensible and even seems meaningless.
But this procedure is simply necessary. Since temporary crowns protect teeth from external influences, and also correctly distribute the load when chewing.
The advantages of using temporary crowns are as follows:
- Teeth ground for a crown are not protected from the harmful effects of pathogenic bacteria, which can cause inflammation of the teeth under a permanent crown, and temporary products protect them from infection.
- When biting, a ground tooth can be displaced by the opposite dental organ, which can lead to unwanted errors during prosthetics.
- Temporary dentures give the oral cavity an aesthetic appearance, and with it the patient’s self-confidence. They operate in the same way as permanent ones, only they are made from budget material.
Rules for grinding on a living tooth
- Dissection is carried out under anesthesia, slowly, intermittently, and with sufficient water.
- For turning it is necessary to use a new bur and a special tip.
- Application of a special coating that prevents infection from entering the nerve and further development of the inflammatory process.
- Immediately, immediately after the procedure, temporary crowns must be installed on the ground teeth, which are fixed with special cement containing an antiseptic.