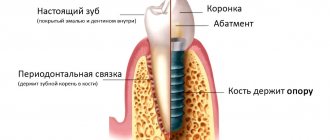
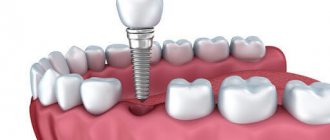
One of the most popular modern technologies for restoring lost teeth is implantation. It appeared more than half a century ago and since then has been continuously improved, offering new materials and components, expanding the range of implants, developing simpler and more effective surgical protocols, increasing efficiency and safety.
Let's look at the pros and cons of dental implants. Today it is a painless and safe procedure that provides a number of advantages over other types of prosthetics:
- wide possibilities of prosthetics – with the help of implantation you can restore one tooth, several, and even the entire dentition,
- preservation of bone tissue - without chewing load, the jaw bone gradually atrophies, and implants, transferring the load to the jaw, stop this process,
- excellent aesthetics - any crowns can be installed on implants and the appearance of artificial teeth will be no different from natural ones,
- careful treatment of natural teeth - implantation does not require grinding down neighboring teeth, it does not affect them at all, and even (preserving the jaw from atrophy) prevents displacement and loosening,
- ease of use – implants feel exactly like your own teeth, you can easily get used to them in 1-2 days and do not cause any discomfort,
- complete restoration of chewing function and diction - there are no restrictions on food intake for implants (except for the period of their engraftment).
Of course, implantation also has some disadvantages, such as pain and discomfort in the first days after surgery, a rather long period of complete engraftment of the material, a small risk of complications (2-3%), as well as high cost, but nevertheless, implantation is becoming more and more is widely used as the cost of this procedure decreases and components become more accessible to the general public.
How are dental implants done today?
Almost all patients who decide to undergo this operation are concerned about the question of how dental implantation works. The procedure involves the following steps.
- An implant is placed in the prepared hole, then it is covered with a gum flap, sutured and wait until it integrates. Healing of the implant takes several months: about two or three - on the lower jaw, from four to five - on the upper jaw.
- A small circular incision is made in the gum and a gum former or abutment is installed on the implant and loaded with a temporary crown.
- Impressions are taken, a permanent crown is made and installed on the implant.
Immediately installing a permanent crown is not recommended, as it puts strong pressure on the implant, which leads to its rejection. The two-stage technique is ideal for smokers and patients who do not take good care of hygiene - bacteria will not be able to penetrate into the closed socket, and the risk of implant rejection will be minimized.
The two-stage method is most often used to restore already missing or traumatically removed teeth, when there is not enough bone tissue in the area where the implant is installed. In these common situations, bone volume needs to be increased. Sometimes this manipulation can be carried out simultaneously with the installation of the implant, but most often it is necessary to postpone the implantation for several months and wait until the required volume of bone tissue is formed.
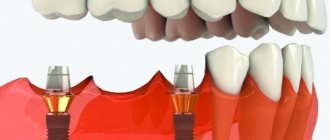
The process of installing a dental implant before and after
Types of implants
Fixed implantable prostheses can be intraosseous or extraosseous.
Intraosseous
If you look at the implant carefully, like an orthodontist, you can distinguish not 2, but 3 parts:
- supporting;
- transgingival;
- the largest is intraosseous.
The intraosseous shape of implants is different, repeating or not repeating the shape of the tooth root. It is by these criteria that the types of dental implants are most often classified.
The shape of the intraosseous part of the prosthesis is usually made in the likeness of a tooth root. Then healing after implantation will be quick, and the chewing load will be distributed evenly in the jaw.
Lamellar
The surface of these implants is textured and (or) corrugated. There is also a macro-relief resembling a snake. To allow bone tissue to grow through the prosthesis after implantation, holes are provided in the structure. Their total area does not exceed a third of the area of the intraosseous part.
There are:
- non-separable;
- collapsible, with internal or external thread for installing the head.
Root-like
Root-shaped (endosseous) implants include:
- cylindrical. The intraosseous part is smooth, with a small surface area. It is characterized by the lowest biomechanical performance in the shear test, so the cylindrical part is made textured (bioactive coating). They are produced only collapsible;
- screw. With different thread profiles, detachable and one-piece. The surface can be smooth or rough;
- basal. Longer, with a thread at the end to secure itself in the deep layers of bone.
Mini-implants that are installed for a limited time are also classified as root-shaped. This is not to say that they are thinner or shorter than regular ones. They have a simplified and slightly lighter design for people with osteogenesis disorders.
If the root-shaped implants are not connected to each other, their rotation can occur even after a period of bone tissue regeneration. The most common causes are medical manipulation and chewing load. Therefore, their design includes anti-rotation locks (anchors, holes, longitudinal grooves, etc.).
Types of root-shaped implants
Combined
The intraosseous part of the implant can also be a combination of cylindrical and plate-shaped:
- the central part is a cylinder;
- “lateral roots” - 2 asymmetrically or symmetrically located plates.
This type also includes disc, transmandibular (designed with a bracket and 2 pins) implants. Implants of a combined form are usually detachable.
Extraosseous
For osteoporosis or osteonecrosis of the jaw, extraosseous implants are sometimes used for patients in the older age group.
Subperiosteal
These prostheses are used for the rehabilitation of patients with significant atrophy of the jaw bone tissue. They are screwed into the periosteum on the side of the gum.
Intramucosal
They are used when there is a lack of bone tissue, when the patient refuses augmentation, sometimes as a temporary measure. A small, mushroom-shaped magnet is inserted into the gum. In the future, it serves as the basis for removable orthodontic structures.
Stabilization
When implanted, the prosthesis is mounted on the natural root of the tooth, takes root well, but is considered temporary, since the “base” dries out with age, like any bone tissue.
What are the latest dental implant technologies?
One-stage
Today, an implant can be installed in just one day. This modern technology is called one-stage implantation. Do not confuse it with one-stage, these are two fundamentally different methods. Single-stage implantation is carried out immediately after tooth extraction, and during a one-stage procedure, a temporary crown or gum former is installed simultaneously with the implant. The one-stage method is most often used when restoring the frontal group of teeth, so that the patient does not feel embarrassed about his smile. In addition, installing a temporary crown or former at the same time as the implant helps to correct the shape of the gums, which plays an important role in creating an ideal smile.
Together with tooth extraction
Single-stage dental implantation - how does it happen? Such an operation can be carried out only under ideal conditions: if the tooth was removed atraumatically, there are no inflamed hard and soft tissues left in the socket, and there is sufficient bone tissue present. If the conditions are unsatisfactory, bone material is poured into the hole, and after a couple of months, two- or one-stage implantation is performed. Moreover, in some cases, a one-step technique can become a one-stage one. For example, if the implant is installed into the bone with a certain force, and there is no severe inflammation in the patient’s oral cavity.
By template
New technologies for dental implantation, such as surgery using a surgical template, make it possible to correctly position implants in the oral cavity. Before the procedure begins, a special template is made for the patient, which is sent to the computed tomography department, where the template is scanned, and then the patient along with it. Next, the computer models are combined in a special program. The resulting stencil allows you to first work with aesthetics, that is, determine where the crowns or dentures will be placed, and only then place implants under them. This unique technology helps to achieve an excellent visual effect, accurately install implants even in areas with the minimum allowable bone volume, without affecting vessels and other anatomical formations, and also reduce the procedure time. Using a surgical template before dental implants is ideal for patients who are missing all or several teeth in a row.
Important points when choosing superstructures
The patient may refuse to install the former; the technology provides for this option. But in the end, at the final stage, the aesthetics of the smile will suffer when using prosthetic teeth in the frontal zone. Lack of proper gingival contour boundaries will result in incomplete closure of the base of the artificial root. The resulting gap will contribute to the accumulation of bacterial plaque, which is difficult to clean.
When choosing abutments, you need to consider the following factors:
- when using metal-ceramic prosthetics, a titanium superstructure is suitable;
- it is preferable to install a zirconium dioxide crown for the anterior section on an abutment made of the same material to avoid unaesthetic translucency;
- Custom-made abutments are better than standard analogues, since they take into account the anatomy of the patient’s dentofacial apparatus.
The absence of a clearly formed gum contour when refusing a former or choosing an unsuitable abutment is dangerous due to the formation of a deficiency of gingival tissue.
How does implantation proceed from start to finish?
Let’s simulate a situation where the patient has previously undergone an examination and comes to the clinic directly for implantation. How does dental implantation proceed in this case? First, he is given anesthesia, local and not general. Even the longest operation does not take more than two hours and does not require such a serious type of anesthesia as anesthesia for dental implantation. Further, the procedure regulations depend on the type of implantation: if we are talking about a two-stage technique, then first the gum is cut, a hole is made in the bone, an implant is installed in it, which is covered with a flap, and then suturing is done. All of the above manipulations take no more than fifteen minutes. If the operation follows a template, then the installation of each implant takes no more than ten minutes, since no cutting of the gums or suturing is required.
Single-stage and one-stage implantations last a little longer, since they require either tooth extraction or the installation of a crown or gum former.
Technology for installing dental implants in pictures
Implants should be installed in a sanitized oral cavity, so visiting a therapist and hygienist will not be a bad idea. Consulting doctors are also competent in how dental implantation proceeds; they will treat caries and remove all dental plaque, thereby minimizing the risk of implant rejection.
Vertical and inclined installation
Most implants require exclusively vertical installation. And if several of them are placed, then the doctor must observe the principle of parallelism. But in some situations, implants can also be implanted into the bone at an angle of up to 45 degrees. Here, the main indication for inclined installation is a lack of bone height or low density due to atrophy or inflammatory processes. Angled placement allows for a larger area of bone to be used for contact with the implant surface. And also bypass areas of atrophy and anatomical structures (nerves or sinuses), and exclude additional bone grafting surgery[1]. True, not all implants are designed for this – and this must be taken into account.
How many implants are needed and which ones to choose?
Installing ten implants on each jaw is an ideal solution for patients suffering from complete edentia. However, a good result can be achieved with eight or even six implants. More economical options are removable dentures on four implants. The most budget-friendly alternative is a removable denture on two implants. Some patients believe that two or four implants will not be able to withstand the load placed on them during jaw work and will be rejected. In fact, the pressure during chewing is distributed throughout the entire prosthesis and falls not only on the implants, but also on the bone and gum, so there is no need to fear rejection.
The choice of product depends, firstly, on the volume of bone tissue. If there is a lot of bone, then any implant can be installed, and if not, then only a certain size. Secondly, from the methodology. Thus, it is possible to carry out one-stage implantation only if the implant is tightly fixed in the bone. To do this, either its rod or thread must be of large diameter. Not all companies produce such aggressive implants, so the patient has not much choice. And thirdly, from the budget.
How much does it cost on average in Moscow?
Many clinics do not calculate the cost by stages and estimate the costs of implantation on a “turnkey” basis.
| Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| Dental prosthetics | |
| With metal-ceramic crown | 39100 |
| With all-ceramic crown | 50200 |
| With a ceramic crown on a special alloy | 60000 |
| Prosthetics with removable dentures | |
| With ball mount | 54700 |
| With beam fastening | 160000 |
| Prosthetics for a toothless jaw | |
| on 4 implants | 350000 |
| on 6 implants | 450000 |
Do I need to follow certain rules after surgery?
After the procedure, you must follow all the specialist’s recommendations. In the first two to three days, you should not rinse your mouth in the area of the implant, since blood cells that promote its healing are washed out from the operated area. However, it is still necessary to clean the implant installation area, although very carefully. To do this, you can use special brushes with soft bristles and a paste with an antiseptic effect. For three to four days after the operation, you should not exercise, carry weights, or visit a sauna, bathhouse or solarium. And - most importantly - if any unpleasant or abnormal sensations occur, you must immediately contact your dentist. If you carefully care for the implant and follow all recommendations, it will last you a lifetime.
Stage four: gum formation
Duration - 1 week
This stage is relevant only for the classical implantation method, in which implants, after installation, take root within several months, covered with gums. 1-2 months after implantation, the gums open and a special device is fixed on the implant - the gum former. It is necessary to adjust the gingival contour so that after installing dentures, the gums in the area of the artificial tooth are smooth, beautiful and uniform throughout the entire dentition. In some cases, plastic surgery may be required, which involves surgically adjusting the position of the gums.
Who can undergo implantation and who cannot?
Implants cannot be installed in girls under eighteen years of age, and in boys under twenty-one years of age, since during this period the bone is still forming, and implantation can disrupt this complex process. As for the upper age limit, there is no upper age limit for installing implants. Absolute contraindications include disorders of blood clotting and bone regeneration. It is prohibited to perform the operation on pregnant women and people with an unbalanced psyche. In all other cases, implantation is possible.
Contraindications
| Absolute (operation impossible) | Relative (the operation is temporarily postponed) |
|
|
What is the cost of dental implants?
The process of dental implantation is quite complex, with many subtleties and nuances. Therefore, its price is appropriate. In dentistry, the minimum cost of a South Korean implant and its installation is 18,000 rubles. It comes with a five-year warranty, but with adequate care it will last you a lifetime. German implants are more expensive - from 30,000 rubles, but they have a lifetime guarantee. The cost of implants for a one-step technique is 36,000 rubles. The price list of premium level products starts from 42,000 rubles. Additional manipulations, such as bone grafting, are paid separately. Bone tissue augmentation costs from 18,000 rubles to 40,000 rubles, depending on the complexity of the operation. The cost of a temporary crown is 12,000 rubles, a permanent one - from 18,000 to 34,000 rubles. Dentures on implants cost from 64,000 to 190,000 rubles.