Statistical studies based on the results of diagnostic procedures performed in clinical settings show that occlusal deviations occur in the majority of people. Quite often, patients are unaware of the presence of a problem, turning to orthodontists solely out of a desire to improve the aesthetics of their smile, but in fact, the pathological condition can provoke more serious consequences. The correct ratio of the upper and lower rows is characterized by close contact of the antagonists, a small (no more than a third of the height of the crowns) overlap, as well as a natural anatomical arrangement of the elements. Malocclusion, the types of which are classified based on characteristic symptoms, requires proper treatment.
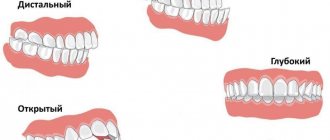
Open bite
An overbite is called this way if, during central occlusion, the dentition, it is important to note, not the extreme ones, but the frontal ones, do not close. The cause is shortened central teeth and dentoalveolar long teeth on the sides. This bite can also be horizontal.
Externally it manifests itself in lengthening and tension of the face, increasing the length of the chin and lower section of the face. Usually there is no closure of the lips or closure is difficult and is given with effort. The gap between the teeth obscures the large tongue.
Pathogenesis
In orthodontics, there are five stages in the formation of the natural anatomical structure of the dentofacial apparatus, and at each of them there is a possibility of the formation of deviations from the norm:
- 0-6 months - manifestation of sucking skill, providing sufficient stimulating load on the tissues.
- From 6 to 36 months. — eruption of milk units that make up the temporary dentition.
- 3-6 years - the preparatory stage, during which the active development of the jaws takes place, necessary for a change in completeness.
- 6-12 years - mixed period, gradual renewal of elements along the entire length of the rows.
- Up to 16 years of age inclusive is the final stage, following which permanent occlusion is formed.
It is worth noting that the formation of anomalies is possible even at the stage of intrauterine stay, being provoked by infectious or chronic diseases, toxic poisoning and other factors affecting the initial characteristics of the rudiments.
Deep bite
Expressed in the relative position of the lower and upper jaw rows along the anterior segment so that the upper teeth protrude in front of the lower ones by at least a third of the length of the crowns of the latter. During anterior occlusion, the cutting parts of the lower anterior incisors pass the dental cusps of the upper anterior teeth and touch their palatal parts at the base.
The most advanced forms manifest themselves painfully - the lower central incisors come into contact with the mucous membrane of the palate and, as a result, damage it (this is the degree of deep and traumatic interaction).
General overview
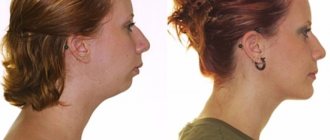
In dentistry, it is customary to distinguish between dental and skeletal forms of abnormal development of the dentofacial apparatus. In the first case, we are talking about pathological closure caused by incorrect teething, insufficiency or excessive completeness, unnatural dimensions of individual crowns, as well as defects in the formation of the alveolar process. The second category includes problems associated with deviations in the anatomical structure and position of the jaws - their correction requires the use of more radical medical techniques, which is determined by the complexity of the pathology.
Crossbite
Characterized by atypical (reverse) closure of the anterior or lateral or both the first and second teeth together with simultaneous deviation of closure in the left or right area of the bite. A double form of this bite is possible.
If professional treatment and care are not provided, patients with transverse bite experience facial distortions and serious changes in appearance, as the jaw bones develop asymmetrically. Characterized by chewing dysfunction and difficulties with pronunciation. Often patients with this bite suffer from biting the mucous membranes of the cheeks, tongue, and lips.
Possible consequences
Malocclusion is a cosmetic defect; a person with a violation of the position of the teeth may experience psychological discomfort and embarrassment, and difficulties with communication. In addition, it can cause facial asymmetry and changes in a person’s profile.
However, psycho-emotional consequences are not all that can be fraught with the pathology of the development of the dental system. Bite defects affect your health as follows:
- there is a risk of developing periodontal diseases (periodontitis, periodontal disease);
- there is a high probability of inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity - this is associated with the risk of injury from the edges of incorrectly positioned teeth;
- the incidence of caries increases - a broken bite makes hygiene difficult, a large amount of plaque and tartar are formed, caries occurs;
- tooth decay may be non-carious, improper distribution of the chewing load leads to increased abrasion of the enamel of certain groups of teeth, a high risk of chips and cracks due to mechanical loads;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract develop due to poor quality of chewing food;
- speech defects, speech therapy problems occur, sound pronunciation is disrupted;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint are formed;
- Chronic headaches occur due to impaired tone of the masticatory muscles due to improper, uneven distribution of the load.
That is why the main indication for correcting malocclusion is taking care of your health, although the aesthetics of a smile cannot be discounted.
Treatment methods
The first thing that needs to be done is preparation from a dentist-therapist in the form of sanitation of the oral cavity. Before installing orthodontic structures, it is important to treat carious and gingival pathological processes and remove tartar using an ultrasonic tip.
Next, surgical preparation may be necessary - extraction of units, removal of excess soft tissue structures, plastic surgery of the labial frenulum. Removal of destroyed or supernumerary units may be required. It happens that further treatment tactics force the extraction of healthy teeth that interfere with the orthodontic process.
What to do if specialists discover an incorrect bite? - be sure to treat. Treatment is divided into 2 periods - active and retention.
Taking into account all the nuances of the clinical situation, at the active stage it is possible to use various correction options:
Aligners (transparent aligners).
Transparent soft silicone or polyurethane plates, individually manufactured according to a 3D print. They are worn constantly, removing them only for meals and hygiene. They are not visible in the mouth and do not cause discomfort. It is necessary to meet with an orthodontist once every few months to control the movement of units and receive a new batch of aligners, which are independently changed every 2 weeks. Aligners achieve effective results in cases of crowded units, narrow or wide dentition, or correction of previous treatment with braces.
Trainers
Silicone massive mouth guards with sides for wearing at night, and during the day for no more than a few hours. Suitable for treating children under 12 years of age, and at older ages they are used for correction or prevention.
Removable plate-devices.
They are used during the period of primary occlusion to reduce the period of further treatment with braces and improve sound pronunciation. The best results are achieved when interacting with a speech therapist.
Braces
Prescribed for the correction of various bite pathologies. Specialized buttons are attached to the coronal surface of the units with medical glue and connected with an arc. Thanks to the shape memory arch, the alignment of the dental units occurs.
Braces are classified according to:
- Places of attachment - vestibular (external) and lingual (internal).
- The method of attachment to the arch is ligature and self-ligating.
- Materials: plastic, metal, ceramics, titanium, sapphire, silicone.
The cost of a braces system varies depending on its type and the material used. They also need careful home care - special brushes, brushes, pastes, floss.
With age, restrictions on the use of certain systems and materials appear. The older the patient, the longer (more than a year) and more difficult it will be to change the location of the units due to the intractability of the bone tissue. Therefore, you should start correcting your bite as early as possible.
In the final retention period (preservation of the result), the patient has a retainer attached to the inner surface from canine to canine, and it is recommended to wear night guards. This period continues throughout the life of the teeth.
Surgery
Radical orthodontic surgery is considered when there is severe maxillofacial deformity, and all of the above correction methods will not be effective. An incision is made in the gum tissue and the jaw bones are shifted to an anatomical position. It is also possible to use implantation to restore missing units; implants add a fulcrum for the correction of individual areas. To speed up the treatment time, the orthodontist may additionally need mini-implants, which can be unscrewed after their work. They will allow in some cases to avoid surgical intervention and move an entire group of teeth.
Orthopedics
At the end of orthodontic treatment, to achieve the best aesthetic result, it is recommended to perform prosthetic treatment of the frontal group of units with veneers or crowns. This way, the optimal size of the crown parts of the teeth is achieved, suitable for facial characteristics.
Reasons for appearance
Due to the structural features of the maxillofacial bones, newborns have a disproportion in the size of the jaws - the upper one is always slightly larger than the lower one. With normal development of the baby, the feature disappears during growth, but this does not always happen. As a result, the child develops an incorrect bite or incorrect position of the teeth, which causes physical and psychological discomfort. In addition, anomalies arise due to the influence of a number of external factors.
Among the main reasons are the following:
- Artificial feeding. Refusal to breastfeed does not always lead to jaw abnormalities, but the risk of developing such pathologies increases significantly. If the nipple on the bottle is not shaped correctly, the baby’s lower jaw practically does not work, and as a result does not develop as it should.
- Finger sucking habit. This habit is often observed in preschool age. It can lead to the cessation of jaw growth, as a result of which the closure of the dentition is disrupted.
- Habit of lip biting. Also often observed in children, it leads to forward deviation of the upper incisors.
- Mouth breathing. When breathing through the nose, the tongue is in the palate and presses from the inside on the upper row of teeth. From the outside, pressure is exerted on the teeth by the cheeks, as a result of which the correct shape of the upper dental arch is formed. However, when breathing through the mouth, the tongue moves down, causing the upper jaw to become wider.
- Poor posture. This problem leads to changes in body posture and head position. In this case, the center of gravity shifts forward, which often provokes dental anomalies of varying severity.
- Congenital causes. These include birth injuries, bad habits of the mother during pregnancy (for example, smoking), etc.
- Heredity. Some people have a genetic tendency for jaw misalignment, which can lead to complex abnormalities.
- Early removal of baby teeth. This can cause acquired malocclusion. With premature loss of teeth, the entire row is displaced, which leads to narrowing and shortening of the dental arch.
What is the importance of orthodontic treatment for children?
Some parents believe that baby teeth do not need any treatment or correction of their position. Why put your child through additional stress if the temporary teeth are going to fall out anyway? This is a deep misconception, due to which the health of the permanent dentition often suffers. If a child has had certain anomalies in the structure of the jaw apparatus and the position of the teeth since childhood, treatment should be started immediately. Age plays an important role in orthodontics and bite correction, because it is in childhood that bones are more plastic, due to which correction is easier and much faster.
The importance of orthodontic treatment in childhood is due to the following reasons:
- timely correction will help prevent many problems with teeth and the child’s health in general,
- at an early age, correction of defects takes much less time, while for an adult, treatment of similar anomalies requires twice as much time, despite the fact that the guarantees of the result will be very vague,
- The specialist gets the opportunity to control the direction of growth and the process of tooth formation, and make the necessary adjustments in a timely manner.
If you notice that your child’s teeth are overlapping each other or, for example, one of the jaws is protruding forward, be sure to make an appointment with the orthodontist. After a visual examination, the specialist will be able to identify a specific problem, assess its severity and prescribe timely treatment.
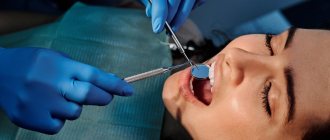
Orthodontic diagnostic process
Before correcting the bite, the orthodontist organizes a step-by-step diagnosis:
- conducts an examination of the oral cavity;
- Visiographic photographs are taken;
- takes impressions and makes diagnostic models;
- takes a photo of the patient’s teeth, face and smile (determines the appearance, symmetry of the face or the influence of identified bite pathologies on these factors).