Many dental clinics offer fillings using several different filling materials. Price lists (including those posted on websites) are also often replete with various commercial names of fillings: Filtek, Spectrum, Aesthetics, Charisma (Karizma), Vines (Venus), Gradia, Estelite, Herculite, Point, Tetrik, Admira, Brilliant, Enamel Plus and others. Patients are asked to make a choice, but this requires dental-level knowledge, which most people, of course, do not possess.
Popular articles on the Internet for the following queries: “which filling is better?”, “which filling material is the best?”, “which filling is better to put?” and so on. – do little to clarify the situation. Most articles (often written by anonymous authors or copywriters) discuss only classes of filling materials: cements, amalgams, glass ionomers, chemical and light-curing composites. After a detailed description of materials that went out of use several decades ago (apparently to give more volume to the text), the conclusion is made that light-curing composites are the best, and if a person has the financial means, then it is advisable to install fillings from them. Either nothing is mentioned about specific brands of heliocomposites, or it is stated that they are all approximately equally good. Or “the latest generation nanocomposites” begin to be advertised.
What fillings do not need to be placed?
The first and most important thing that every patient should understand is that light-curing fillings (photopolymers, heliocomposites) are the only reasonable choice in the 21st century. Even for people on a budget. Other materials are not 10 or 20 percent, but many times worse. Discussing the advantages or price/quality ratio of cement fillings in our time is as stupid as looking for advantages, for example, in reel-to-reel tape recorders. For a long time now, no one has been producing or buying cassette and video recorders, but for some reason some individuals allow themselves to install a 19th-century seal.
Plastic fillings are completely beyond reason. Acrylic oxide and similar anachronisms should have been banned for use a quarter of a century ago, since they are not only unable to stop the further spread of caries, but also provoke its progression. A plastic filling on a tooth is a direct road to pulpitis and periodontitis. You have to hate yourself with a fierce hatred to allow this to happen to you. And clinics that currently use such materials will be deprived of their license.
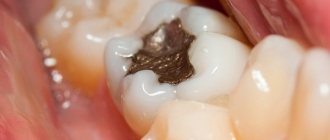
Amalgam fillings are famous for their durability, but due to toxicity (not for the patient, but for the environment and medical staff), dentists themselves refuse them.
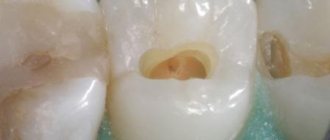
Chemical composites are moderately bad - if a person lives from hand to mouth, then, of course, you can install them (it’s still better than nothing). But for most other people who do not experience urgent need every day, this will not be a justifiable choice. It may happen that such a filling will last for many years, but more often the opposite happens. After 3-5 years (or earlier), caries will develop under the “chemical” filling, and it can either reach pulpitis, or the amount of destruction will become so great that instead of re-installing the filling, the manufacture of an inlay or onlay will be required. As a result, the cost of repeated intervention increases by an order of magnitude due to the savings of thousands of rubles the first time (the approximate difference with the cost of a light-curing composite).
Precautions after filling
After installing a light-curing filling, it is extremely important to follow your dentist’s recommendations for oral care and nutrition during the first time after the procedure. You will be able to eat no earlier than an hour after filling ; food should be of neutral temperature and hardness.
The final polymerization process continues for several more days, so for the next 3–5 days you should refrain from foods and drinks with active pigments: cherries, beets, coffee, pomegranate juice, tomato soups. Such precautions are necessary to maintain the shade of the installed composite.
Light-curing fillings are not uniform
Glass ionomer cements with a light-initiated curing mechanism are available. For example, Fuji 2 (Fuji II LC). Compomers (a hybrid material between composites and glass ionomers) are also cured using a lamp. Their most famous representative is Dyract XP. These materials are more reliable than some heliocomposites, but are still significantly inferior to their best representatives. Due to the misconception about the toxicity of composites, some doctors recommend these materials for filling for children. For pediatric dentistry, Fuji and Direct are acceptable options, but composites are still preferable.
Dental composite materials are divided into universal (suitable for filling any cavities), aesthetic for anterior teeth (excellently convey all the nuances of the color of natural teeth) and packable for chewing teeth (have low shrinkage and abrasion, but also low aesthetic characteristics). There is another class of composites – flowable. Previously, they were recommended for filling wedge-shaped defects due to their high elasticity, however, according to modern data, universal composites give better results even with non-carious lesions.1 Therefore, current composites currently have only an auxiliary value: they are used together with other classes of materials, but the main one the volume of the filling does not make up.
Universal heliocomposites are the most widely used type of filling materials in the world. The commercial names of fillings offered to the patient to choose from mostly refer to these materials. They also differ in quality. The percentage of inorganic filler, its chemical composition and the shape of the granules determine the mechanical properties of the filling: polymerization shrinkage, mechanical strength, hardness and wear resistance, polishability and surface smoothness. Some of these parameters antagonize each other. For example, for good polishability, the granules of non-limiting filler (oxides of silicon, zirconium, aluminum, etc.) should be as small as possible, and to increase strength, on the contrary, as large as possible. Therefore, materials advertised as “nanocomposites” cause a wry smile among professionals - the prefix “nano-” attracts illiterate dentists and patients who blindly associate it with high technology. However, for the sake of fairness, quite good material can be presented. For example, Filtek Ultimate.
Indications for installation
Permanent fillings are placed when necessary to eliminate carious or non-carious defects. Due to the variety of fillers that can be included in light-curing composite fillings, they can be placed if there are any indications for installing permanent fillings.
Specific indications for which light-curing filling material is not only desirable, but necessary, are:
- pathological change in crown size;
- injuries, fractures and chipped teeth requiring restoration;
- pathological mobility grade 1–3;
- the presence of scattered carious cavities on the entire surface of the tooth;
- elimination of defects in the front teeth;
- defects of the root or dental neck;
- the presence of pigmentation that cannot be eliminated by other methods;
- defects in a small area of enamel, where other filling compounds will not hold.
The best filling materials (as of 2022)
In the dental world, the greatest authority in the assessment of restorative materials currently belongs to the American publication The Dental Advisor. For the last 12 years (from 2010 to 2022), the highest award in the “universal composites” category has been awarded to the Japanese filling material Estelite Sigma Quick. Selection criteria: percentage of inorganic filler, amount of shrinkage, correspondence of shades to the natural color of the tooth, ease of use, radiopacity, polishability. A survey of dentists showed that they switch to Estelite more often than to other filling materials. Clinical success of Estelite is 99%.2
Among aesthetic composites in 2015, 2016, 2022, according to the same publication, the filling material from Germany, Venus Pearl, took the highest position. Its clinical effectiveness is 91%.3 In 2021, it received the title of “preferred product”. It can also be used for chewing teeth.
In 2022 and 2022, first place in the category of aesthetic composites was taken by the Harmonize material of the American manufacturer Kerr Restorative.4
Other good quality filling materials should also be mentioned. These include those who received awards in 2016-2019: Omnichroma, Brilliant EverGlow, Admira Fusion, Filtek Supreme Plus and Filtek Supreme Ultra.
Service life of the light seal
If you follow medical recommendations, the service life of a light filling installed on a tooth will be 5–6 years. The patient must observe the rules of oral hygiene, undergo preventive examinations every six months and adhere to proper nutrition, especially in the first week after he received a filling.
The diet should contain a balanced amount of hard and soft foods, a sufficient amount of fruit and dairy products. Most dentists insist on the need to stop smoking for at least the first two weeks after filling, otherwise the preservation of the composite shade is not guaranteed. Natural dental tissue and photopolymer are colored differently, so the artificial material will stand out noticeably against the background of the dentition.
Rating of filling materials:
| Filling material | Manufacturer | Rated by The Dental Advisor | Year of last assessment |
| Estelite Sigma Quick | Tokuyama Dental (Japan) | 99% | 2021 |
| Herculite Ultra | Kerr (USA) | 98% | 2016 |
| Tetric EvoCeram | Ivoclar Vivadent (Liechtenstein) | 97% | 2017 |
| Harmonize | Kerr (USA) | 96% | 2019 |
| Filtek Supreme Universal Restorative | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2019 |
| Filtek Supreme Plus | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2018 |
| Filtek Supreme Ultra | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2018 |
| Brilliant EverGlow | Coltene (Switzerland) | 96% | 2018 |
| Beautiful II LS | Shofu (Japan) | 96% | 2018 |
| Grandio SO | VOCO (Germany) | 96% | 2012 |
| Gradia | GC (Japan) | 96% | 2007 |
| Omnichroma | Tokuyama Dental (Japan) | 94% | 2020 |
| Beautiful II | Shofu (Japan) | 94% | 2009 |
| Admira Fusion | VOCO (Germany) | 93% | 2019 |
| Venus Pearl | Kulzer (Germany) | 91% | 2021 |
| Premise | Kerr (USA) | 91% | 2005 |
Aesthetic and artistic restoration of teeth
- Work examples
- Questions and answers
- Stock
- Reviews
Painlessness and good results are the advantages of the “Aesthetic Dental Restoration” procedure. Dental service allows you to make a Hollywood smile by eliminating imperfections. Not only the color, but also the shape can be adjusted.
Features of composite restoration of anterior and chewing teeth
Speaking specifically about veneers, aesthetic restoration with composite material is used exclusively for front teeth. The primary task of overlays is to hide cosmetic and anatomical problems, as well as mechanical damage. This is why composite restoration of anterior teeth costs much more than a conventional filling, and many experts even consider the process of making veneers an art.
In the case of chewing teeth, the issue of aesthetics is already less significant: functionality comes to the fore. However, restoration of chewing teeth with composite material makes it possible to restore damaged dental tissues at a high aesthetic level. In this case, it is almost impossible to notice the filling on the tooth. Typically, dentists use macrophilic and hybrid composite materials when filling molars because they are considered stronger and more durable.
vote
Article rating
What is a composite restoration and when is it used?
Many patients believe that the use of composites is a new technology. In fact, composite materials have been used in dentistry since the middle of the last century. However, at that time they had a lot of disadvantages - they were not strong enough, had poor adhesion, and were toxic. Modern dentists use new, higher quality, durable and completely safe materials. This allows you to achieve the desired effect.
It is advisable to resort to composite restoration when the tooth is damaged to a maximum of 50%. It is not always possible to use these materials when restoring chewing teeth, since they are subject to significant loads - it is necessary to select other restoration techniques.
Composites have proven themselves to be excellent materials that can effectively eliminate relatively small defects - uneven dental surfaces, scratches, cracks.
Advantages of composite restoration
The restoration method involving the use of composites is relatively complex. It requires increased attention from the doctor. Nevertheless, this technique has many positive aspects:
- the technology is extremely gentle. The tooth is ground down to a maximum of 0.2 mm (for comparison, installing veneers involves grinding one or more millimeters, and installing crowns requires even deeper grinding);
- The restorative procedure requires just one visit to the dentist. Thus, there is no need to use temporary overlays, as well as experience some inconvenience and waste your time;
- even if the composite part is damaged, it will not be difficult to solve this problem. It can be quickly adjusted or even a new one installed – also in just one visit;
- accessibility is a huge plus. Restoration using composites is cheaper than restoration using ceramics.
And of course, one cannot fail to note the high efficiency. If you want to understand what results composite dental restoration can produce, before and after photos will allow you to be convinced that this procedure really returns your teeth to their former aesthetics.
How are composite materials selected?
The restoration procedure is necessarily preceded by the selection of material. It should be suitable for damaged dental units, and also be completely safe for the body as a whole.
Materials are always selected individually for each patient. To do this, the dentist needs to carry out initial familiarization work, during which the composition and quantity of the composite are determined. When selecting, the following factors will be of greatest importance:
- location of a dental unit with defects;
- condition of the tooth and its layers;
- general features of the patient’s dentition.
How is a composite restoration performed?
Restoration is carried out in several stages. The first one is preparatory. At this stage the following activities are carried out:
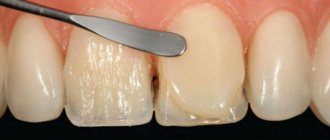
- professional cleaning, which allows you to accurately determine the shade of tooth enamel;
- selection of composite shade according to the Vita scale.
Then follows the main, most difficult and lengthy stage:
- carious areas are drilled out;
- the tooth is isolated from saliva using a rubber dam;
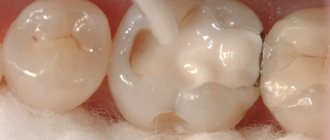
- layers of composite are applied layer by layer.
For the highest quality restoration, composites with different characteristics regarding shade and light transmission are used. This allows you to achieve just such a combination of layers, thanks to which the restored dental unit will look natural.
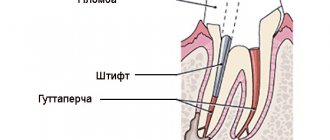
In case of large damage, this stage may be preceded by the installation of a pin. It is necessary to strengthen the structure.
The final stage involves grinding and polishing. This makes it possible to make the result even better.
If you need dental restoration using composite material, use the services of our specialists. In dentistry, the cost of this procedure depends on various factors. The main one is the severity of the defect. However, in any case, we can guarantee the best prices and excellent results with which you will be completely satisfied!
| Service | Price |
| Initial consultation with a specialist | from 1,100 rub. |
| Restoration of anterior tooth with composite veneer | from 19,900 rub. |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth with a light-curing composite using the direct method with a pin | from 26,000 rub. |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth with a light-curing composite using the direct method | from 22,500 rub. |
To avoid possible misunderstandings, please clarify the cost of services in clinics with the administrator or during a consultation with a doctor. Prices on the website are not a public offer.
Restoration with composite materials: technology review
Precise recreation of the shape, optical and mechanical properties of teeth using photopolymer materials is the essence and goal of composite restoration, sometimes called artistic.
Characteristic features and materials used
The physical properties of composites and the conditions for their curing determine the working methods, equipment and results of dental restoration. The composite composition is a polymer (usually a dimethacrylate resin) filled with a microdispersed inorganic composition of high hardness.
Dental composites differ from technical dimethacrylate composites in their biological compatibility and balance of mechanical properties. Their abrasive resistance, strength, elasticity and thermal expansion coefficient are close to the parameters of dental tissue. Polymerization of such materials occurs, as a rule, under the influence of light with a wavelength of 427 - 491 nm.
Shrinkage of the material during polymerization does not allow the formation of elements with a large cross-section. Therefore, the dentist has to apply many layers, alternately working with a brush and an ultraviolet lamp.
Today in aesthetic dentistry they use:
- Microcomposites are resins filled with salts/oxides of barium, lithium, aluminum, quartz with particle sizes of 0.1 - 1.0 microns.
- Nanocomposites are resins filled with silicon dioxide with particle sizes of 0.01–0.1 microns.
- Hybrid composites - contain microfractions (0.6 - 1.0 microns) and nanofractions (silicon dioxide 0.04 microns).
- Flowable matrices - with low filler concentration. Provide high adhesion with high shrinkage.
- Concentrated matrices - with a high concentration of filler. Provide minimal shrinkage with relatively reduced adhesion.
- Adhesive systems - include phosphoric acid, conditioners, primers, bonds. Serve to form a strong bond between dentin and enamel with composites.
- Toners are dyes for selecting the natural color of dental products.
- Opaques - for adjusting the optical properties of the restoration.
Despite the long list of expensive materials, the price of composite dental restoration is significantly lower than the cost of ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns.
Direct method
Conducted in one clinic visit. The dentist shapes the missing areas of the tooth using several layers of composite with different physical parameters. The technology makes it possible to recreate the internal structure of the crown of the tooth, giving the necessary shades to the layer that imitates dentin and the layer that imitates enamel. This is how composite fillings and veneers are made.
Indirect restorations
They provide for laboratory production of veneers, inserts, bridges or crowns from composite materials. This method requires more time and at least 2 visits to the clinic by the patient.
Dental restoration price
The cost of work can vary greatly depending on its type and volume.
Aesthetic dental restoration performed with veneers, and even more so, lumineers, costs significantly more than photopolymer.
The price of dental restoration can increase if it is necessary to restore several units and when treating deep caries.
Therefore, only the doctor on the spot can finally name the amount, after assessing the amount of work.
Varieties
Dentists have many ways to restore a patient’s beautiful smile; they are conventionally divided into two types:
direct restoration method, when restoration is carried out directly in the patient’s mouth (it is also called artistic restoration);
an indirect restoration method in which the preparatory work is partially carried out outside the oral cavity.
Make an appointment
Direct tooth restoration
This method involves building up the missing part of the tooth using a light-curing composite or other materials. Such manipulations, as a rule, do not take much time, and the price for aesthetic dental restoration using the direct method is low.
Filling is the most common procedure that is well known to patients, during which a doctor, under local anesthesia, drills out damaged areas (for example, if a tooth is affected by caries) and fills the cavity with a composite. Then the filling is polished. An important condition when filling a tooth is its isolation from saliva: previously this was done with cotton swabs, but now rubber dams made of latex are used.
Repairing chips is similar to filling, the only difference is that chips do not require drilling out the affected tissue. When restoring chipped front teeth, it is especially important to choose a composite that matches the color of the enamel so that the restored area does not stand out.
Inlays are also similar to fillings, but instead of light-curing materials, the dentist uses metal, ceramic, or zirconia inserts to fill the drilled-out cavities of the tooth. They are much stronger and more durable, but the price of cosmetic restoration of teeth of this type is higher.
Pins. If the tooth is severely damaged, the doctor will restore it using pin structures. A pin - a strong rod made of titanium or fiberglass - is fixed in the root part of the tooth using dental cement, and on its basis, dental tissue is restored from composites.
Indirect tooth restoration
Indirect restoration is more often called dental prosthetics and is performed by an orthopedic surgeon. The procedure for preparing for restoration partially takes place without the participation of the patient, and treatment time, as a rule, is required. There are three types of indirect dental restoration.
Crowns. - artificial teeth, which are made of ceramics (with or without a metal frame) or zirconium dioxide. Modern technologies make it possible to make dentures that are no different from the patient’s own teeth. First, the damaged tooth is prepared and ground in a special way, and then the crown is fixed with dental cement.
Dental bridges are structures consisting of several crowns that can restore significant defects in the dentition. Along the edges, the bridge rests on adjacent teeth, which are prepared in the same way as when installing single crowns.