L. M. Lomiashvili Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of Omsk State Medical Academy
S. G. Mikhailovsky intern at Omsk State Medical Academy
S. V. Vaits postgraduate student of the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of Omsk State Medical Academy
“Going there, I don’t know where, and doing something, I don’t know what” is a difficult task! This applies to almost all areas of our lives, including dentistry. Even if you imagine the future design of the tooth being restored, your hands do not always reproduce the correctness of its shape and volume.
Students of the Faculty of Art and Graphics are taught that “one hundred still lifes must be written in order for the one hundred and first to turn out correctly”! Unfortunately, in universities, dental students are given limited knowledge about the shapes of teeth, and an insufficient number of hours are devoted to reproducing teeth from available materials (clay, plasticine, plastic). But the correctness of the newly created forms is the path to the solution to harmony!
The ability to correctly restore the shape of missing hard dental tissues in clinical dentistry is of paramount importance.
The dentist's hands are the main tool for modeling teeth! You can develop this skill through artistic modeling classes.
The purpose of the classes: development of visual memory, manual skills, creative thinking and the ability to perceive shapes in space. Anyone who wants to know the stages of recovery can begin the first exercises with a minimum of conditions - material and simple tools.
Dental modeling is a creative process where, in addition to knowledge of anatomy, there must be freedom to choose the material from which models can be created. Before you begin, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic properties of the materials and choose which one suits you best.
When cutting out a form from hard materials: wood, stone and others , the sculptor gradually, step by step, cuts off the material, freeing the form contained in it. This technique is widely used in therapeutic dentistry, for example, at the stage of competition of the filling surface.
Modeling is the making of sculpture from soft materials. For modeling, you can choose any material that has plasticity. It can be plasticine, sculpture clay, plastic, wax.
Hand Soap Basics
Records of the first soap made from tallow and ash date back to 2800 BC. Initially, it was used for medical purposes - they treated various skin diseases and washed wounds, which healed faster after this procedure. In Europe, soap factories appeared only in the 10th century: in France, Spain, Italy. European soap was thin, contained large amounts of olive oil, and was available only to wealthy people. French soap, which included essential oils from Provence, was considered the best.
Indirect modeling steps
First, the dentist takes impressions of the upper and lower jaws. In this case, silicone is used, since it is very important that the material is of high quality. Then the doctor records the habitual closure of the jaws, preparing the bite ridges, and performs registration using a face bow.
The next stage is work in the articulator. This is the name of a special device that allows you to simulate the movement of the lower jaw and debug all chewing movements of the dental apparatus. If the bite decreases, then with the help of special studies, taking into account facial characteristics, they calculate how many millimeters it needs to be raised.
A silicone model of teeth is placed on a plaster base in an articulator and analyzed. At the same time, the dental technician takes into account the functional and aesthetic wishes of the patient and the dentist. He then makes a wax model and shows it to the patient. If necessary, correction is made.
If the patient is satisfied with everything, then a permanent prosthesis is made in the laboratory based on the Wax-up model.
How does forward modeling work?
Mock-up modeling is performed directly in the oral cavity. It allows you to determine the optimal shape of the prosthesis. Direct modeling can be figuratively compared to trying on a dress.
The doctor makes silicone impressions of the teeth. Great importance should be paid to modeling the palatal surface, without which it will not be possible to make a full-fledged cast.
Composite plastic is placed into the silicone impression (it is better to use a material that is different in color from the teeth) and placed on the patient’s teeth. The impression is then removed and excess materials are removed from it. If necessary, increase the size of the teeth and reduce the width of the spaces between them.
Next, the dentist, using special brushes and prophylactic paste, cleans the teeth of plaque. At the same time, no manipulations are performed with the teeth: they are not prepared or sawed, as with conventional prosthetics, which allows maintaining the integrity of the dental apparatus.
The base shade of enamel and layer-by-layer dentine are applied to the template. Next, the doctor restores the structure of the tooth, forming anatomical details on the surface of the model, including mamelons (the so-called protrusions and tubercles on the teeth). Restoration of the dental structure is carried out sequentially, starting from the oral surface and gradually moving to the vestibular surface. Finally, an enamel shade application is made.
Mechanical finishing is carried out after the surface of the model has dried. If the model is even a little wet, it will be difficult to visually control the quality of grinding. Polish the surface carefully using special silicone heads of different shapes. In this case, their rotation frequency should be low.
The teeth are treated with a special fixing glue and the prepared model is attached to them.
The patient can walk around with temporary teeth, which will allow him to observe his sensations and determine what exactly needs to be corrected. The doctor will also have the opportunity to study the reaction of the mandibular joint.
The technician can produce several models so that the client can make the best choice.
If the patient no longer has any complaints, then the resulting model is sent to the laboratory, where permanent dentures are made based on it.
It is especially recommended to use Mock-up models for patients who need to improve their bite, as well as for those whose teeth are severely worn out. The models are also irreplaceable when performing prosthetics on implants.
How to make soap at home for ov
1. Melt the soap base. Prepare all the necessary ingredients and tools so that you have them at hand at the right time. Cut the soap base into small pieces, place in a container and place in a large saucepan in a water bath. Wait until the base is completely dissolved, while making sure that its temperature does not exceed 60 degrees. When boiling, bubbles form in the mass, which will spoil the appearance of the soap, especially transparent ones.
2. Add base oil. If you are using a ready-made base or baby soap, add base oil at the rate of one tablespoon per 100 g of soap. If you are making soap from scratch, follow the recipes. You can add one oil or several at once. With palm oil, the soap turns out to be as hard as possible, castor oil gives excellent foam, and coconut oil is responsible for the quality of cleansing. Olive oil is suitable for creating baby and hypoallergenic soap. Avoid sunflower, flaxseed and corn oils - they quickly go rancid and the soap spoils.
3. Add dye. For soap making from the base, professionals recommend choosing food colorings that do not cloud the mass and do not precipitate. 5 drops per 100 g of base is enough to give the soap a bright, rich color. When making natural soap from scratch, it is better to use mineral pigments: for example, titanium dioxide for whitening, chromium oxide for green, iron oxide for red.
4. Add essential oil. The concentration of essential oil in soap base is usually 1-4%. In made-from-scratch soap, the oil content varies depending on its volatility. Heavy oil - cedar, neroli, cinnamon - up to 1%. Light oil - orange, tea tree, eucalyptus - up to 10%.
5. Give the desired shape. Spray the selected mold with alcohol from a spray bottle. Carefully fill it with liquid soap and place it in a cool place for a couple of hours or in the refrigerator for five minutes. The packaging of the soap base usually indicates the hardening time. After the soap has hardened, dip the mold into hot water and remove it. Place on paper and leave to dry for two days.
Modeling tooth 36 from plasticine: main steps
Plasticine is perhaps the most common material; it is easily accessible and does not require special preparation for work. Having taken the required amount, just warm it up, knead it in your hands, and you can start working. Having no experience working with this material, in the first stages it is better to work without tools to feel its properties, and then create shapes using tools. After kneading, the plasticine is ready for modeling, but it does not need to be heated for long, as it becomes too soft and sticky and will not hold its shape well.
Let's consider the main stages of modeling the 36th tooth from plasticine. We give the plasticine the shape of a ball (Fig. 23).
Rice. 23. Giving the material a ball shape
Having outlined the main surfaces and tops of the tubercles of the future model, we deepen the first-order fissure of the F-shape. As a result, five tubercles are formed on the chewing surface (Fig. 24) (1 - anterior lingual, 2 - posterior lingual, 3 - anterior buccal, 4 - posterior buccal, 5 - distal).
Rice. 24. Formation of the overall outlines, the tops of the main cusps: anterior lingual (1), posterior lingual (2), anterior buccal (3), posterior buccal (4) and distal (5). Surfaces: M - mesial, D - distal, V - vestibular, L - lingual
Using the tool (Fig. 25), modeling of the distal ridge (B), longitudinal ridge (A), medial ridge (C), anterior lingual tubercle (1) and modeling (Fig. 26) of the medial ridge (B), longitudinal ridge ( A), distal ridge (C), posterior lingual tubercle (2).
Rice. 25. Modeling of the distal ridge (B), longitudinal ridge (A), medial ridge (C), anterior lingual tubercle (1). (2) posterior lingual cusp, (3) anterior buccal cusp, (4) posterior buccal cusp, (5) distal cusp
Rice. 26. Modeling of the medial ridge (B), longitudinal ridge (A), distal ridge (C), posterior lingual tubercle (2). Modeling is carried out with a spatula
Rice. 27. The final result, the model of the lower jaw molar is made of plasticine
Modeling from plastic
Plastic is another material from which you can create a beautiful tooth model. This is a fairly dense, non-sticky material that does not require special preparation for work, but it is necessary to observe the conditions for its storage: temperature changes at which the material is stored can have a negative impact on its properties. Plastic is convenient because you can work with it for an unlimited amount of time, it does not harden, which makes it possible to work out the microrelief of the future model in more detail and clearly, and make the necessary adjustments during the work.
The main stages of modeling the 16th tooth from sculptural clay
Sculpture clay has long been used in art to recreate shapes. This inexpensive material is ideal for sculpting teeth; working with clay is pleasant in its own way, it is soft, does not stick to your hands, and hardens gradually. Sculpting clay requires longer preparation for work than plasticine, which is most often used for modeling teeth. If the clay is dry, then first you need to mix it with water to the consistency of sour cream, leave for some time until it dries and forms a plastic mass. After this, the clay becomes hard only after a few hours, this time is quite enough to successfully complete the work. The smaller the volume of available material, the faster it hardens. When the desired consistency is obtained, the clay is shaped into a ball (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The material has the necessary plasticity and is ready for use. Giving the future model a ball shape
Let's consider modeling the first right molar of the upper jaw (16th tooth). The overall outlines of the model of the 16th tooth are set (Fig. 2, 3), the location of the main surfaces is outlined: medial contact (M), distal contact (D), vestibular (V) and palatal (P).
Rice. 2. Giving the overall outline of the model
Rice. 3. Modeling the tops of the main tubercles.
The tops of the main hillocks are determined. Markings are applied on the chewing surface (Fig. 4), corresponding to a first-order H-shaped fissure.
Rice. 4. Applying markings corresponding to the first-order fissure, H-shaped, on the occlusal surface
Completion of the formation of the external contours of the model and the equator (Fig. 5) is done by hand.
Rice. 5. Smoothing out irregularities and shaping the equator
Before this stage, all actions were performed by hand (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Working with your hands allows you to better feel the basic properties of the material
To model the chewing surface of the tooth, it is better to use tools. The first-order fissure is deepened with a spatula (Fig. 7, 8).
Rice. 7. Deepening of the fissure of the first order, separating the anterior buccal tubercle (2) from the posterior buccal (1) and anterior palatine (4). Posterior palatine tubercle (3)
Rice. 8. 1 - posterior buccal tubercle, 2 - anterior buccal tubercle, 3 - posterior palatine tubercle
When modeling, there is no need to draw fissures, but it is necessary to divide the main tubercles so that an H-shaped fissure appears between them (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9. Completing the modeling of the first-order H-shaped fissure
Tools for work are chosen that are more convenient to work with: it can be a spatula, a smoothing iron. A fissure shaping tool, such as a probe, is required. 2-3 tools are enough.
After completing the work, the model can always be corrected by cutting off excess with a scalpel or spatula. The resulting tooth model can be stored for a long time, reminding of the results of the work.
Rice. 10. Modeling of the longitudinal (2), medial (1), distal (3) ridges of the anterior buccal tubercle
Rice. 11. Second-order fissures are formed on the anterior buccal tubercle
Rice. 12. Modeling of the main (2) and additional (1, 3) ridges of the anterior palatine tubercle
Rice. 13. Final view of the 16th tooth model
Rice. 14. Appearance of the 16 tooth model. Occlusal surface
Rice. 15. Appearance of the 16 tooth model. Palatal and chewing surfaces
Useful properties of soap
Any hand soap recipe includes base and essential oils. Its beneficial properties largely depend on them. Let's figure out how to make handmade soap so that it brings exactly the result you need.
First, let's look at the base oils. Olive is a universal option for all skin types, including dry and sensitive. Coconut heals and whitens the skin, creates a protective film from ultraviolet radiation. Castor oil is ideal for sensitive skin.
A good solution for creating moisturizing soap is grape seed oil. It contains fatty acids that easily penetrate skin cells and nourish it. In addition, it regulates the functioning of the sebaceous glands and helps maintain good condition of oily skin.
Avocado, mango, apricot kernel, and wheat germ oils effectively fight signs of aging. Sea buckthorn accelerates wound healing and is used to get rid of acne. Cocoa butter tones and softens the skin at the same time.
Let's look at what effect you can expect from the most popular essential oils:
- Sweet orange. Rejuvenates, eliminates comedones, tightens and stimulates collagen production.
- Verbena. Works as an antiseptic and antidepressant, calming and improving mood.
- Cedar. It has a deodorizing effect and treats skin diseases.
- Lavender. Prevents the appearance of the first signs of aging and blackheads, removes irritation and restores the elasticity of blood vessels.
- Neroli. Removes rosacea, comedones and the appearance of cellulite.
- Patchouli. Perfectly softens the skin, preventing cracks. Facilitates the course of dermatoses and makes scars less noticeable.
- Tea tree. Thanks to its bactericidal, antiviral and antifungal properties, it is indispensable for frequent herpes, fungal infections, acne, eczema and other skin diseases
If you use handmade soap, only beneficial substances penetrate into your skin, and not complex chemical compounds. Natural vitamins, fatty acids and other microelements are bioactive, promoting accelerated cell regeneration. The skin retains its freshness, elasticity and firmness for a long time.
The truth about periodontitis: if you want to keep your teeth and health
The lack of competent information from the patient regarding gum disease and timely professional treatment unfortunately leads to very sad consequences - loss of teeth, and can also threaten a person’s overall health. To prevent them, we talked with the leading periodontist, therapist and surgeon at the Elite Center Clinic, Marina Mikhailovna Shakirova.
Periodontal disease is a disease of the gums and bone surrounding the tooth.
The following stages of gum disease are distinguished:
- Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums caused by plaque.
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of not only the gums, tooth ligament, but also the bone tissue surrounding the tooth.
- Mild periodontitis (I)
- Average degree of periodontitis (II)
- Severe periodontitis (III)
Tab. 1. Signs of the disease
| Gingivitis | I Art. Periodontitis | II Art. Periodontitis | III Art. Periodontitis |
| Blue-red gum color. Swelling and bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth and eating solid foods. Smell from the mouth. Pain (itching, burning) in the gums. | Bleeding gums. The space between the roots of the teeth and the gum (gum pocket). Bad breath. Sore gums. Hypersensitivity of teeth. | ||
| The depth of the gum pockets does not exceed 4-5 mm. | The depth of the gum pockets is 5-6 mm. Exposure of the tooth root. Mobility of teeth. | The depth of the gum pocket is more than 6 mm. Severe tooth mobility and exposed roots. | |
How does the disease occur? After each meal, a small amount of food debris remains on the teeth and between the teeth, which forms a soft plaque. This plaque is difficult to see; oral microorganisms immediately settle in it. Microbes and their metabolic products are deposited on the surface of the tooth and lead to gum inflammation. Gradually accumulating, plaque becomes hard, turning into tartar, which increases inflammation.
So, what every person, especially those suffering from periodontitis, needs to know:
1.100% OF DENTAL CLIENTS HAVE GUM DISEASES.
In 98-100% of patients who come to the clinic with oral problems (caries, etc.), we detect varying degrees of periodontal disease. In addition, 100% of people who smoke suffer from periodontitis!
2.PERIODONTITIS IS A MORE INSANE AND DANGEROUS DISEASE THAN DENTAL CARIES.
There can be no healthy teeth without healthy gums! The teeth may not be affected by caries, but we will lose them because the bone has left the interdental spaces.
3.PERIODONTITIS CAN SIGNAL ABOUT HIDDEN DIABETES!
Of course, the main cause of gum disease is improper and irregular oral hygiene!
BUT! You need to know that PERIODONTITIS is an autoimmune disease (autoimmune diseases are diseases associated with dysfunction of the human immune system, which begins to perceive its own tissues as foreign and damage them).
And diseases such as diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, systemic osteoporosis, blood diseases, etc. lead to changes in the periodontium. A patient suffering from periodontitis may not even be aware of the hidden course of these diseases.
And for patients with these diseases, it is imperative to see a periodontist.
But! It is useless to treat periodontitis if the patient does not treat the underlying disease (diabetes mellitus, hormonal problems, blood diseases).
4.PERIODONTITIS CAN CAUSE ARTHRITIS, GASTRITIS AND OTHER DISEASES!!!
Periodontal pockets are a source of chronic infection. It has been proven that the long-term presence of infection in the periodontal pocket leads to the development of diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, endocarditis, gastritis, etc.
5. PERIODONTITIS MAY NOT MANIFEST FOR LONG YEARS - IT CAN ONLY BE DIAGNOSED BY A DOCTOR!
The insidiousness of the disease is that it does not manifest itself for many years. Only a doctor can make a timely diagnosis and prescribe treatment by examining the oral cavity and x-ray examination (orthopantomogram or computed tomogram (CT)). In addition, we definitely prescribe an additional examination if we see an aggressive course of the disease, exacerbation, mobility, halitosis (bad breath) and, according to X-ray data, significant loss of bone tissue.
A general examination includes blood biochemistry, a complete blood count, an analysis for latent hemoglobin, and the laboratory data obtained very often reveals latent and already progressive forms of diabetes mellitus (in young people). Very often a blood disease is detected.
“REJUVENATION” OF DISEASES – EVEN 16 YEAR OLD PEOPLE ARE SICK.
A feature of the current situation with gum disease is the “rejuvenation” of this process. If earlier this disease was detected after 45-50 years, now we can detect it at 16 and 18. This is usually associated with poor hygiene and crowded teeth. Especially if orthodontic problems are not treated. Moreover, the younger the patient, the more aggressive the course of the disease!
IF A PERSON IS SICK WITH PERIODONTITIS – IT IS FOREVER!
Periodontitis is an autoimmune disease; we can only bring it into remission and prevent further progression. A 100% cure occurs only with gingivitis (if the patient follows the recommendations).
If periodontitis is simply treated once, the effect is lost instantly. Any periodontal disease requires dynamic observation, that is, the so-called dispensary observation, supportive treatment and an invitation to attend MPT (maintenance periodontal treatment). The first examination is after 1 month, the 2nd procedure is after 3 months, then every 4 months. At the Elite Center Clinic, we keep a mandatory journal in which we record the schedule of visits the patient needs and invite him in advance.
GINGIVIT IS 100% ACCOMPANYING PREGNANCY.
Since during pregnancy, hormonal levels change, which leads to changes in the composition of plaque. It is believed that all patients with periodontitis have an increased risk of having a low-birth-weight child, and the source of infection can lead to the early development of caries in babies, and bacteria contained in the discharge from periodontal pockets can provoke miscarriage. This is a proven fact. Therefore, if pregnancy is planned, then it is necessary to undergo treatment by a periodontist and be observed by a periodontist during the 1st and last trimester of pregnancy.
SO HOW TO CORRECTLY TREAT GUM DISEASES?
Traditionally, there are 3 STAGES in periodontal treatment:
STAGE 1 OF TREATMENT:
This is the stage of PROFESSIONAL HYGIENE or otherwise – the closed curettage procedure.
Closed curettage includes:
- professional removal of plaque, tartar (using ultrasound and air-flow)
- root cleaning and polishing.
At the Elite Center Clinic, our patients also have access to the most modern hardware treatment for periodontitis, which often allows us not to proceed to the 2nd stage - surgical treatment:
1) FotoSan device (manufactured by CMS Dental, Denmark) As a result of light photoactivation, oxygen is released, which destroys pathologically altered cells and inflammatory microflora in periodontal pockets. Active oxygen acts instantly, safely, without side effects and eliminates the need for antibiotics.
2) Prozone device (W&H Dentalwerk Burmoos GmbH, Austria) In periodontics, the effectiveness of the Prozone device can hardly be overestimated, because it destroys bacteria in the gingival pocket, which are very difficult to reach, since they are in a biofilm. Bacteria become coked and live there in colonies. With Prozone, ozone penetrates into any place to be disinfected and completely destroys pathogenic microflora, minimizing the risk of re-infection.
3) Vector device (Durr Dental, Germany) The use of ultrasonic energy simultaneously with a jet of highly dispersed suspension of hydroxypatite powder allows you to remove infected granulation tissue, biofilm, plaques, and tartar. At the same time, waste products of microorganisms are washed out. This gives a powerful regenerating impulse and anti-inflammatory effect.
This same stage includes active rinsing with antiseptics and medicinal dressings. With these methods we can stop not only mild, but also moderate periodontitis!
STAGE 2 – SURGICAL TREATMENT
Classical periodontics recommends the use of surgical treatment methods if the pocket is more than 5-6 mm. But how are we doing at the Elite Center Clinic? If the use of all stage 1 treatment methods and laser technologies leads to stabilization, then we do not resort to surgical treatment. That is, if 3 months after the 1st stage of treatment the patient is not exacerbating, then we conduct a course of maintenance periodontal treatment even with a severe form, if it is in a stable phase.
But in any case, severe and aggressive periodontitis requires ONLY COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT!!! Together with an orthopedist, together with an odontist, together with an endocrinologist, a therapist, a cardiologist.
General somatic diseases are contraindications for surgical treatment.
Before surgery, tooth mobility is prevented - the splinting method is used: we cannot operate on mobile teeth (otherwise they may take the wrong position).
Surgical treatment involves detaching the gum, cleaning the root from subgingival stone, polishing the root, filling this space with a protein-matrix complex or artificial bone, putting the flap back and suturing it. The roots are exposed.
At the Elite Center Clinic, surgical treatment is mandatory with the Emdogain protein-matrix complex.
Emdogain is a drug with a biological composition that promotes predictable restoration of both hard and soft tissues. But! It leads to an increase in bone tissue volume by only 0.5 - 1 mm. The process of bone destruction stops, but new bone does not grow. When applied to the surface of the tooth root, after cleaning it, emdogain begins to imitate biological processes, stimulating the restoration of tissue around the tooth.
Upon completion of the operation, we prescribe dressings, antibiotics, immunocorrective therapy, antihistamines, rinses, and a certain hygienic regimen.
We can carry out all periodontal treatment procedures (quite painful) for our people under sedation and anesthesia!
TAKING SOME DRUGS CAUSE PERIODONTAL DISEASE.
Periodontitis can be detected as a result of taking certain medications, they cause the phenomenon of gum overgrowth. For example: Cyclosparins, drugs that reduce blood clotting, all hormonal drugs. Patients taking hormones should definitely be seen by a periodontist.
Very often we detect periodontitis after suffering severe diseases, for the treatment of which antibiotics were taken. After this, the plaque becomes viscous and easily adheres to the surface of the teeth, which leads to aggravation.
Periodontitis is always present with orthodontic problems.
HYGIENE, HYGIENE AND MORE HYGIENE!!!
The lack of DAILY proper oral hygiene in patients with periodontitis leads to an immediate aggravation - after 12 hours the plaque is fixed and ALL treatment comes to naught.
YOU MUST REMOVE PLATE AND FOOD REMAINS EVERY 12 HOURS!!!
The patient’s task is to come for examinations not in a state of exacerbation, but in a state of remission to a maintenance complex, because each episode of exacerbation leads to loss of bone tissue. We must not allow this to worsen!
During the appointment, we select individually for our patients, based on the indications: what toothpaste should be, what brush, what rinse, in what mode to use, when to replace, what medications to take.
When a patient is sick with acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract, the viscosity of saliva increases and local corrective immune factors decrease (their level decreases in the oral cavity). This leads to the fixation of a more sticky plaque. Therefore, after almost all acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, we note an exacerbation of processes in patients. During illness, hygiene should be increased. After (during) an illness, you should contact your doctor for corrections in the treatment program (changes in the cleaning regimen are possible, additional antiseptics are prescribed), and additional professional cleaning.
PROSTHETICS AND IMPLANTATION FOR PERIODONTITIS
It is mandatory to undergo periodontal treatment before prosthetics and implantation. Implantation for periodontitis - can be carried out only when periodontitis is in a stable phase; there should be no presence of supra- and subgingival deposits.
BE HEALTHY AND VISIT YOUR DENTIST ON TIME - THIS IS A GUARANTEE OF A HEALTHY AND BEAUTIFUL SMILE!
Sign up online
Registration Online
Causes
The cause of pain in the teeth can be both dental and non-dental reasons.
Dental include:
- caries or its more severe form pulpitis;
- gingivitis or periodontitis, when the gums or tissue around the tooth root become inflamed;
- periostitis, in which rotting of the alveolar processes occurs in the upper or lower jaw;
- postoperative complications or errors during filling.
Also, toothache can be a concomitant symptom of other diseases, for example:
- migraine and other types of headaches;
- maxillofacial neuralgia, including inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- diseases of the ENT organs;
- oncology;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Attention! Only a dentist can determine the exact diagnosis. At home, you can only try to get rid of toothache, easing your condition before visiting a doctor.
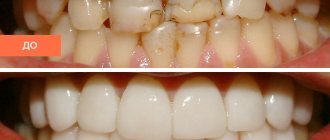
What is caries and why is it dangerous?
Caries is a sluggish pathological process in the oral cavity. It progresses in the hard tissues of teeth.
The disease occurs due to the complex effects of unfavorable factors, which we will discuss below.
If you do not remove caries from your teeth, they will gradually begin to decay. But the negative consequences do not end there. There may be a constant bad breath, as well as inflammatory processes that can result in purulent formations and even blood poisoning.
Caries can provoke the appearance of diseases such as pulpitis, gumboil, periodontitis, and cysts.
Therefore, it is important to cure caries as early as possible, and for this you need to identify it in time - independently examine the oral cavity and visit the dentist annually for a preventive examination.