Intra-canal teeth whitening is a modern method of lightening tooth enamel. You will often hear this whitening method referred to as endodontic whitening or endobleaching . These names are equivalent and are synonyms. The essence of the intra-canal whitening method is to place a special whitening gel inside the tooth, under the influence of which the tooth enamel is lightened from the inside.
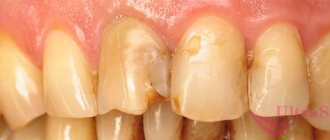
Intra-canal whitening is indispensable when tooth enamel darkens from the inside. Such darkening may occur due to damage to its internal tissues and their inflammation. The main cause of darkening is the death of the dental nerve (pulp). This can occur due to dental diseases such as pulpitis and periodontitis. First, damage to the pulp occurs, and then its complete death, which entails a gradual darkening of the dental tissues. In such cases, various home whitening methods using pastes and special strips, as well as modern teeth whitening methods such as Zoom whitening, are ineffective.
If you notice that the tooth is darkening from the inside, then whitening should be done from the inside. By applying for endodontic bleaching as early as possible, you will not only save your time, but also reduce treatment costs.
When to use
Teeth take on an unsightly gray tint when their internal structure becomes damaged. Most often this occurs due to the destruction of pulp tissue, progressive chronic pulpitis, and periodontitis. Then the metabolic processes required for normal nutrition of the crown and roots become impossible. The enamel becomes thinner and cracks. It does not receive enough minerals and darkens.
Among the reasons for changes in the natural color of a smile that can be corrected by intracanal whitening are:
- Mechanical injuries of the jaw. Very often, patients whose problem with dark teeth appeared in childhood come to see a dentist. People put off making a decision, but at some point they still make an appointment with the doctor. Whitening the crown by targeting the canals is an excellent option.
- Age-related changes. With age, tissues are less well supplied with blood. The risk of smile changes is especially high if depulpation has been performed.
- Increased abrasion of enamel. This is a pathological condition that needs to be treated. As it develops, microcracks form on the outer surface. This is what leads to a change in shade.
- Depulpation performed for medical reasons. After this procedure, proper nutrition of the dental tissues becomes impossible; the nerves are removed. In the absence of a neurovascular bundle, the unit darkens.
- Installation of a filling containing silver impurities. Fortunately, today dentists no longer use such materials. But there are still people who have such fillings. They must be replaced after performing intracanal bleaching.
- Use of resorcinol-formalin mixture in canal treatment. In this case, the coronal part becomes pink. It looks quite strange.
- Incompetent endodontic therapy. In case of incomplete removal of the damaged nerve, poor-quality cleaning of the canals, or leaving a fragment of the instrument inside the root, undesirable consequences arise.
All of the above situations are a reason to consult a dentist and perform intracanal bleaching.
Side effects of endobleaching
The fact is that any teeth whitening involves chemical destruction of protein dyes. When endobleaching, you have to deal with chemical dyes contained in filling materials. Therefore, initially there is a risk that the effectiveness of the procedure will be quite low. In addition, internal bleaching of a pulpless tooth seriously weakens its strength, since post-bleaching lesions in a non-vital tooth are not restored. Because of this, the risk of dental crown fracture increases significantly. Therefore, endobleaching cannot be performed more than four times.
Preparation for the procedure
The technique can be used exclusively on pulpless units, that is, the canals must be cleaned and treated, and darkened pulp should not remain inside the crown.
If the roots were filled long ago, you have to clean them of material and re-treat them. In this case, special protapers are used, which are ultra-flexible nickel-titanium files. They are inserted into the sealed canal in order to extract the mass located in it.
The doctor then disinfects the walls using a chelating agent and sodium hypochlorite . At the end of the preparatory stage, the treated canal is obturated, that is, its lumen is closed.
Clinical researches
Clinical experiments with the use of the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia) have proven that the use of Asepta line products results in a decrease in complaints of discomfort, but bleeding persists when brushing teeth.
On examination, hyperemia and bleeding of the gingival papillae are noted. On the 7th day, complaints of gum bleeding persisted in 4 patients. Upon examination, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted, but bleeding persisted upon probing. On day 14, 2 patients continued to complain of bleeding gums when brushing their teeth; upon examination, a significant decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted. After the final application of the gel with propolis, normalization of clinical manifestations was revealed, which is manifested by the absence of bleeding during brushing and probing.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
Endodontic bleaching technique
Before putting a whitening compound inside, the doctor needs to understand what led to the darkening of the enamel. If the cause of the problem is not established, the likelihood of relapse will remain very high. During the diagnosis, the specialist examines the condition of the roots, looks at the results of x-ray diagnostics, and draws up a detailed anamnesis.
The next preparatory stage is the formation of an expanded cavity for laying the gel inside . If necessary, the pulp area is first cleaned and low-quality fillings are removed.
The gel is poured into the dental canal using a syringe applicator. Neighboring teeth that do not need whitening are isolated. It is important that the brightening solution does not get on their surface. When the gel is in the designated place, it is covered with a thick cotton ball and fixed with a cement temporary filling.
The dentist always decides how many days the patient has to wait for a second appointment on an individual basis. It all depends on:
- unit state;
- degree of destruction of the coronal part;
- the presence of concomitant dental diseases;
- expected effect.
It is important that the client comes for a follow-up appointment exactly on the day indicated by the doctor. Some people find that it is better to take longer with the bleaching medicine, since they want to lighten one unit by a large number of tones in one procedure. Doctors never tire of repeating: you should never do this.
The solution inside the channel is quite aggressive. If you overexpose it, the already weakened walls of the tooth after depulpation will become even more fragile. Negative reactions will begin to occur inside the dental cavity. This may result in the loss of a unit. Then only prosthetics will help.
During the re-examination, the doctor checks whether the expected result is obtained. If not, remove the drug, treat the channels and use a second portion of the gel. The maximum number of such bookmarks should not exceed four.
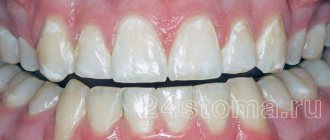
When the expected effect is achieved, the canals are washed, sealed and a permanent filling is installed. From this moment on, the patient can freely use his renewed tooth and enjoy a beautiful smile.
Why does a dead tooth turn dark?
Teeth that lack nerves inside are considered dead. The surface of such processes is characterized by a tendency to change color and the appearance of dark spots. The reasons for the darkening of a pulpless tooth are as follows:
- lack of food. After the nerve is removed, the power to the tooth stops. Moisture leaves the enamel, nutrients are not supplied by the nerve endings, which leads to darkening;
- increased vulnerability. Without regular feeding, the tooth becomes very vulnerable. Pores form on the surface of the enamel, through which various coloring substances from the food consumed penetrate into the internal tissues. These dyes change the color of the enamel.
These are the most common reasons why tooth enamel darkens. In such cases, superficial bleaching of the dead tooth will help restore whiteness. But there are also often cases where a tooth has lost its original color due to bleeding during pulp removal. As a result, the enamel becomes reddish or purple. Classic whitening will not provide results in such situations; a more complex procedure will be required.
When not to use in-canal bleaching
The procedure has medical contraindications. So, it is forbidden to resort to her help if:
- there is untreated caries, periodontal disease, pulpitis;
- the client is under sixteen years of age;
- a woman is pregnant, breastfeeding;
- diagnosed with increased tooth sensitivity;
- the crown is very fragile and crumbles, there are a large number of cracks on its surface.
All of the above situations can be solved. In the case of dental diseases, you must first treat them. During pregnancy and lactation, you should wait until these periods are over. In case of high sensitivity, attention should be paid to restoring the enamel and only then lightening it. When painting the crown, prosthetics will help.
There are no unsolvable problems. Modern dentistry successfully solves problems of any level of complexity. The most important thing for a patient is to get an appointment with an experienced doctor in a good clinic.
Is it possible to guarantee 100% results?
At the first consultation, the doctor must warn the patient that it is impossible to accurately predict the result of whitening. The order of lightening of hard tissues is a strictly individual value, as it is determined by the age of the patient and the initial degree of staining, the thickness of the tooth enamel and the structural features of the dental tissue.
It is impossible to completely exclude the recurrence of discoloration several years after successful bleaching. A good doctor will definitely warn the patient about this. Fortunately, in this case, when re-applying the bleaching composition, a good result is achieved.
Advantages of the technique
In-canal whitening remains popular, despite the emergence of more progressive programs, because:
- is affordable;
- does not cause pain;
- allows you to work with units located in any area of the oral cavity;
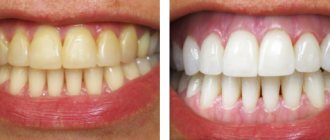
- provides excellent aesthetic results in a short time;
- copes even with complex defects.
Very often, endodontic bleaching helps when other methods fail. The only thing is that the treated tooth does not always remain white. About two to three years after the procedure, it begins to darken again. Then the person again has to turn to an aesthetic dentist for help.
Dentists on Rimskaya
Gneusheva Elena Viktorovna
Dentist-orthodontist, pediatric orthodontist
Experience: 20 years
★ For more than 13 years she worked at the Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics, Ph.D.
Gorokhova Inga Vitalievna
Dentist-therapist
Experience: 14 years of total experience
★ Expertise in restorative dentistry to make your teeth shine
Konstantinov Oleg Nikolaevich
Dental surgeon
Experience: 25 years
★ Virtuoso of painless treatment. Patients fall asleep in the doctor's chair
Nikolaychuk Anna Vladimirovna
Chief physician, dentist-therapist
Experience: 13 years
★ Chief specialist in the treatment of toothache. Masterfully deals with problems quickly and permanently
Frolova Alexandra Ivanovna
Dentist-therapist
Experience: 25 years
★ A brilliant specialist with many years of experience as a manager in public dentistry
Causes of discoloration
Age
This is a change in the color and tone of the teeth, which can be treated with clinical, pharmacy and even home methods. This is due to the fact that the changes are not pathological, due to illness, but occurred due to wear and tear of the enamel caused by solid food, tea, coffee, and excessive consumption of carbonated drinks. Teeth with age-related changes, therefore, can be healthy, but unsightly in appearance: grayish, with a brown or beige tint, yellow.
From pulp necrosis
The pulp dies, and its microscopic particles penetrate into the dentinal canals and, remaining in them, make the tooth gray. They themselves are black, dark gray or brownish in color, but since the enamel and underlying layers are still not completely opaque and allow light to pass through a little, the outside of the tooth itself takes on the shade of the affected pulp and dentin.
From hemorrhage into the pulp
Blood enters the body of the tooth and saturates it from the inside. At first, after such a hemorrhage, the teeth acquire a reddish color, similar to the color of the gums. It is difficult not to notice such organic lesions - they are often accompanied by pain, so that the patient willy-nilly go to the dental office.
If the pulp is not treated, over time it will die, turn black and change the color and tone of the tooth by 3-4 degrees, which is very noticeable. By removing the affected areas, the original color can be restored, and the best way to do this is endobleaching.
Hypercalcification of dentin
Changes in the enamel layer, during which light spots appear in it, which may well be the precursors of caries. In the short term - yellowing of the tooth and loss of rigidity and strength. The most effective treatment method will be root canal cleaning followed by coronal bleaching to restore normal color.
From unqualified treatment
When cleaning the pulp in previous visits to dental offices, the pulp was not completely cleaned. Then its gradual decay will color the tooth dark gray. Aggressive phenol- or iodine-containing medications, as well as outdated filling materials, could have been used.
Thus, intracanal bleaching is indicated in the presence of a previously opened or newly opened dental canal, which has begun to affect the color of the tooth, making it different from others.
Alas, by about the age of 30, it is rare for anyone to have their teeth preserved without any external therapeutic influences. They already have fillings, and this almost always means an invasion of the tooth canals, with possible removal of nerves. It is a dead tooth, retained in the mouth only by supportive medical procedures to stop further decay. The darkening of such a tooth is only a matter of time.
Traditional whitening procedures, even in clinical settings, cannot restore the former whiteness: only the outer layers, such as enamel and, to an even lesser extent, dentin, will be affected. No external procedures in the form of laser, chemical, ultrasound or photobleaching can change the pulp.