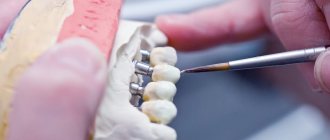
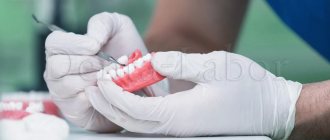
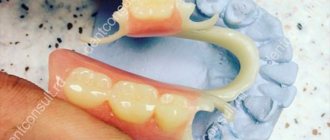
The capabilities of modern orthopedic dentistry have increased significantly. New structures appear, which are sometimes difficult to distinguish from natural teeth and gums. Fixing dentures in the oral cavity also becomes more effective. Various technologies are used today to securely fasten crowns, bridges, and complete removable and fixed structures. The methods used depend mainly on the type of prosthesis.
Fixed dentures - features and advantages
Fixed dentures are considered the most effective and inexpensive solution to restore dentition.
The most common causes of tooth decay and subsequent loss are:
- abundant carious lesions;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- dental cysts, etc.
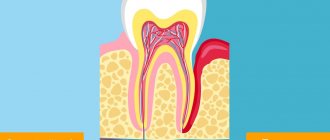
As a result of these dental diseases, tooth crowns and roots are destroyed, teeth fall out on their own, or surgical intervention is required to remove dead hard tissues and roots. For restoration, the dentist recommends permanent dental prosthetics, the basis of which is a bridge and ceramic crowns of the latest generation.
Advantages of fixed dentures:
- Aesthetics. Fixed dentures are difficult to distinguish from your teeth. With proper selection and proper installation, the design looks harmonious in the oral cavity, and the person smiles boldly.
- Comfort. A person quickly gets used to a fixed denture and does not feel discomfort afterwards.
- There is no need to build up bone for high-quality implementation of a fixed denture. When using modern artificial roots, there is often no need to build up bone tissue. This simplifies the entire dental procedure and makes it much more affordable.
- Fast payback. The investment in fixed dentures always pays off in dental health, attractive visual effect and durability.
Why do you need dental prosthetics?
- With the complete loss or severe destruction of one or more teeth, deformation of the WHOLE dentition occurs - neighboring teeth shift towards the gap, tilt, there is a loss of physiological interdental contacts and, as a result, a disruption of the bite and the functioning of the entire dental system. So dental prosthetics is not only desirable, it is necessary, regardless of aesthetic ones - purely for medical reasons.
- Aesthetic indications for the installation of, for example, veneers are a separate issue, and here, of course, the patient’s desire plays the main role.
Advantages
The main advantage of fixed prosthetics is a complete solution to the patient’s problem – “set it and forget it.”
The main types of permanent dental crowns
At the stage of planning treatment with a fixed denture, the dentist, together with the patient, decides which type of fixed dental crown to use for high-quality prosthetics.
Currently, the most common fixed dentures are:
- Teeth crowns
They are used if the hard tissues of your tooth are destroyed by more than 2/3. The implementation of this type of fixed dental prosthetics occurs as follows:
- the tooth is strengthened with a supporting core and a fiberglass dental pin;
- the tooth is ground down;
- the dentist makes impressions of the tooth;
- After a week or two, a ceramic crown or one made of metal ceramics, plastic, zirconium dioxide, etc. “sits” on your tooth.
- a person receives a new healthy tooth that does not differ from his own either visually or in functional characteristics.
- Veneers – as a type of fixed denture
- their teeth are prepared;
- a thin ceramic onlay is fixed on the surface of pre-selected teeth;
- within a few hours the patient receives an impeccable effect - even, snow-white and beautiful teeth.
A veneer is a thin ceramic inlay that perfectly matches the shape, color, and transparency of your tooth. Such a fixed denture “sits” with the help of a special dental glue on the front wall of a previously ground tooth. Recently, super-thin permanent dental veneers have appeared, which practically do not require grinding of their crown, do not stick out, and look organic. As a rule, veneers are placed on the front six to ten teeth of the upper jaw (smile area). If the lower teeth are in good condition, whitening them is enough to achieve the ideal effect.
Installation of fixed dentures and veneers occurs as follows:
The average lifespan of veneers with proper use is up to 10 years.
Restoring ceramic inlays are used when more than ½ of the tooth crown is destroyed. Dental micro dentures are made from individual dental impressions in dental laboratories, fixed using a special dental bond, and prevent the occurrence of recurrent caries on the teeth.
Advantages of ceramic inlays (mini dentures) compared to composite fillings:
- high strength;
- durability of teeth (on average, from 3 years);
- ceramic systems do not absorb pigments and do not darken;
- retain their qualities throughout the entire period of validity.
Medical Internet conferences
Karpenko G.V.
Scientific supervisors: Ph.D. Perunov A.Yu., Krechetov S.A.
Karpenko G.V.
Karpenko G.V.
Scientific supervisors: Ph.D. Perunov A.Yu., Krechetov S.A.
Karpenko G.V.
Scientific supervisors: Ph.D. Perunov A.Yu., Ph.D. Krechetov S.A.
GBOU VPO Saratov State Medical University named after. IN AND. Razumovsky Ministry of Health of Russia
Department of Orthopedic Dentistry
Goal of the work
To study the advantages and disadvantages of each method of fixation of fixed orthopedic structures supported by implants.
Job Objectives
1) Describe various methods of fixation of fixed orthopedic structures supported by implants.
2) Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each method in various clinical situations
3) Analysis of the examination of patients
Research materials
The analysis was carried out in 32 patients during a preventive examination who had orthopedic structures in the oral cavity supported by implants, which were installed from 1 to 10 years ago.
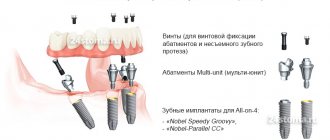
Implant-supported prosthetics, depending on the type of connection between the superstructure and the implant, can be divided into:
- cemented prostheses
- screw-fixed prostheses
-combined type of fixation of prostheses - cement-screw (Screw & Cement Retained Protheses-SCRP).
These types of fixation have their own exceptional advantages and disadvantages.
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of different types of fixation.
Biomechanical criteria.
In terms of biomechanical aspects, cemented and CV orthopedic designs are relatively better. When installing screw prostheses, it is generally very difficult to achieve passive fit and adhesion, especially when prosthetics are used with long-length structures. This is due to the fact that the creation of these structures requires additional clinical and laboratory stages, at each of which errors are possible. The presence of small technological gaps is the main criterion that complicates the passive fit of the structure, which is almost impossible to achieve even using laser welding techniques, the spark erosion method and connecting the cut parts of the prosthesis by soft soldering.
During the day, during the operation of the masticatory apparatus, reversible cyclic deformation of the bone tissue of the upper and lower jaw occurs. Hobkirk and Schwab showed in their study that osseointegrated implants in edentulous patients move relative to each other during mandibular movements. The displacement can reach 420 microns, and the pressure of the connected implants on each other is -16 N. These indicators can vary depending on the distance between the implants and the thickness of the bone tissue.
All the disadvantages of screw structures lead to the fact that under the influence of occlusal load there is a possibility of weakening or fracture of the screw. And even an implant. Also, excess stress that occurs in screw-retained prostheses can be transferred to the bone tissue surrounding the implant.
In cemented and cement-screw prostheses, given the presence of a gap of 25-30 microns for cement, it is possible to achieve an ideal fit. Filling the gaps between the indirect restoration and the abutment with cement material after the passive connection of the abutment and the implant reduces or completely compensates for the presence of inaccuracies, eliminating preload and more evenly distributing the load on the implant, and accordingly, on the bone tissue.
Retention and occlusal relationships.
Retention is the leading criterion that affects the long-term functioning of the structure.
Retention depends on several factors:
-convergence of axial surfaces
-height and area of contacting surfaces
-microrelief of surfaces.
Jorgensen has proven that a convergence of 6 degrees is ideal for the preparation of natural teeth, and the same figure is also true for implant-supported prosthetics. Most implant systems have this taper on standard abutments. When using individual abutments in cemented CV structures, a 6-degree taper is also recreated during the milling process. The height of the walls of standard abutments is greater than the walls of the tooth, but the surface area is less. A custom abutment can be manufactured with criteria that replicate the morphology of the natural tooth.
In a number of studies, it has been observed that a rougher surface creates better retention. It is possible to achieve greater surface roughness by sandblasting the abutment and the internal surface of the structure. However, provided that the taper is maintained and the axial walls are of sufficient height, there is no need to create greater roughness.
Occlusion is another factor influencing the choice of type of structure fixation. The problem of insufficient interocclusal height during prosthetics can be solved through the use of screw structures. The advantage of screw-retained prostheses is the ability to reduce the height of the clinical crown without loss of retention.
However, screw and cement-screw fixation presupposes the presence of a hole on the occlusal surface of the implant - the exit of the screw shaft, which can occupy from 1/3 to ½ of the entire occlusal surface of the crown. This hole must be closed for aesthetic purposes in various ways, which in turn complicates the concept of correct interocclusal contacts achieved by the dental technician in the articulator. The area of occlusal surface occupied by the screw shaft hole is very important for creating correct occlusion, especially in the molar area. Often, a composite material is used to eliminate an aesthetic defect and close the screw shaft hole, however, according to Ekfeldt and Oilo, the resulting occlusal contacts do not remain stable due to abrasion of the composite material by the opposing tooth, especially when it comes to ceramic restorations. With true cement fixation, it is possible to achieve ideal occlusal contacts that will be stable for a long time.
Correction of implant angulation.
One of the main problems when eliminating defects in the dentition by installing implants is their parallelism. For one reason or another, a dental surgeon cannot always achieve parallel placement of implants, which complicates the task of prosthetics for an orthopedic dentist. When using structures with cement-screw and screw fixation, it is possible to adjust the angle of inclination of the implant axis through the use of standard angular and individual abutments. In screw-retained prostheses, this possibility is limited.
Aesthetic criterion.
The aesthetic appearance of the structure is an integral part of competent and complete orthopedic treatment, and often takes precedence after the functional aspect.
In prostheses with screw and cement-screw fixation, a solution to the problem of correcting the aesthetic component is required, especially if the exit of the screw shaft is located on the vestibular surface of the crown. These aesthetic defects can be eliminated in several ways.
Closing the defect with filling material is the simplest and cheapest way. This method makes it possible to achieve acceptable aesthetic results without special costs and complex manipulations, however, the composite material cannot boast of stability over a long period of time, and it is also quite difficult to select a color shade for the existing orthopedic restoration, without using a special set of dyes for composite materials.
The most acceptable in aesthetic and functional terms is the use of specially manufactured inlays using e.max press technology. These inlay or onlay inlays are made directly by the dental technician, which allows you to achieve not only excellent aesthetic results, but also helps create precise occlusal contacts.
Installation and maintenance of the structure.
Most modern implantation systems have an internal conical type of connection between the implant and abutment, which allows achieving excellent functional and hygienic results. However, this type of connection requires precise fit of all components of the prosthesis, which requires X-ray control after installation of the structure, both with screw and cement-screw and cement fixation.
Another feature when installing prostheses with the SCRP fixation type on implants with an internal fixation type is the limitation of the “path of insertion” due to the wide and long contact surface between the implant and the abutment.
Structures with screw and cement-screw fixation can be easily removed if necessary. This need arises when: replacing orthopedic components of the structure; fracture of the screw or abutment; various modifications and repairs of the prosthesis; periodontal diseases requiring periodic treatment. The possibility of removing the structure significantly increases the safety of treatment and is an advantage of these types of fixation over cement.
Presence of residual fixing material.
For a long-term prognosis of the functioning of prostheses with a screw type of fixation, an X-ray image is sufficient to confirm the correct fit of the superstructure to the implant.
Restorations that have a cement type of fixation, in addition to X-ray examination, require, after installation, careful removal of excess cement, which affects the condition of the tissues around the implant and can cause iatrogenic inflammation. In addition, the very procedure of removing excess cement with various instruments, in particular a probe, leads to the formation of scratches on the ceramic surface of the prosthesis. Scratches contribute to the formation of plaque on the surface of artificial crowns, which also leads to deterioration of the soft tissues. Therefore, the edge of a cemented fixed structure should be located within no more than 1 mm apical to the gingival margin.
Prostheses with cement-screw fixation have the advantage that they can be cemented onto the abutment directly on the plaster model, then the excess fixing material can be removed, polished and transferred into the oral cavity, fixed to the implants.
Analysis of the examination of patients.
Of the 32 patients with orthopedic structures supported by implants: 12 patients with cement fixation, 10 patients with screw and 11 with cement-screw type of fixation.
During a routine examination of patients with a cement type of fixation, 2 patients were found to have remains of the fixing material and inflammation of the soft periodontal tissues. Excess cement was removed and anti-inflammatory therapy was prescribed. In 7 patients with screw and cement-screw type of fixation, who received prosthetics more than 5 years ago, failure of the filling material used to close the hole in the abutment screw shaft was revealed. There was a change in the color of the filling, abrasion and a violation of the marginal seal. The filling material was replaced with new one.
One of the patients with a screw type of fixation complained of mobility of the crown during the act of chewing; during the examination, a weakening of the screw connection was revealed. In this patient, the following was performed: 1) removal of the composite material covering the hole in the screw shaft; 2) replacing the screw with a new one; 3) tighten it with a force of 30 Ncm, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations; 3) closing the hole with a composite filling material.
In the remaining patients, the examination did not reveal any violations, the orthopedic structures were sound, and there were no changes in the periodontal tissues.
Conclusion.
There is no single “best” way to install a prosthesis on implants, and each individual clinical case requires careful planning and selection of the optimal method that will solve a particular clinical problem.
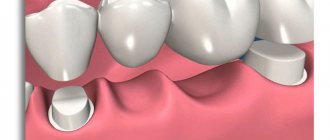
Classic dental bridge or fixed dental bridge
A classic bridge is a one-piece denture structure consisting of a base, as well as functional and supporting crowns. Functional crowns replace lost teeth, and abutment crowns serve as the basis for securely holding a fixed denture in the oral cavity.
Why do patients choose dental bridges?
- Deadlines. Prompt production of individual impressions in a dental laboratory - up to 14 working hours. days. With additional payment and comfortable conditions, it is possible to produce a fixed denture in 3–5 days.
- Indications for implantation. A fixed dental prosthesis is an excellent replacement system for diagnoses where there are restrictions on the implementation of titanium dental implants and the installation of crowns on these artificial roots.
- Price. The cost of a classic bridge is several times cheaper than the price of a titanium implant and a metal-ceramic or zirconium dioxide crown.
- No age restrictions. Bridges are often staged for both older people and middle-aged audiences.
The nuances of using a dental bridge with pre-implantation:
- You have to grind down your supporting teeth, albeit a little;
- It is often necessary to first remove the roots of the teeth before implantation.
Four, six... or maybe three?
Nobel Biocare is rightfully considered a leader in the field of implantological innovations, although some of the solutions they offer are, to put it mildly, widely discussed in the professional community. So, most recently, she proposed the Trefoil concept, which allows the use of only three (!) implants to support a fixed prosthesis:
It is also worth noting that the All-On-4 scheme, i.e. “all-on-four” was also proposed by specialists from Nobel Biocare, and the rest, it seems, turn out to be “repetitive pigs”:
Of course, this does not mean that this concept cannot be implemented with other implants - of course it can, and we do it all the time:
The point is different:
Trefoil, like All-On-4, were developed and offered by Nobel with a lot of reservations regarding indications and contraindications; they are compromise schemes and, therefore, cannot be applied to all clinical cases.
The relative cheapness and apparent simplicity have led to the fact that some doctors have significantly expanded the indications for prosthetics using these methods - as a result, now we see not just a large, but a gigantic number of problems in the near and distant future. In fact, now we are seeing the same picture as with basal implantation, when a specific and extremely compromise method was turned into almost a panacea, “used” in absolutely all clinical cases. With predictable consequences, of course.
To prevent this from happening with four implants installed to support a fixed prosthesis, you should know that:
– the cheapness of such a design is a myth. The angled multifunctional abutments used in it are sometimes more expensive than two additional implants.
– for All-On-4 and especially for Trefoil, only original components of implantation systems can be used. Which is also reflected in the price, which is not at all positive. The use of counterfeit, counterfeit and incorrect spare parts is one of the main causes of complications, and very serious ones, such as fractures and loss of implants.
– the main reason why implants are placed at an angle is the desire to avoid expensive osteoplasty or sinus lifting in the lateral areas. You have to pay for this with an uneven and very compromise distribution of the load, in the vector decomposition of which a nonspecific component appears that sets the torque. Simply put, when the implant is placed in this way, the load on it is transferred and distributed in a way that is not at all how it should be distributed.
That is why such prosthetic schemes are recommended for patients with long-term absence of teeth and significant, at least 10-15 years, experience in using complete removable dentures. If we implement the “all-on-four” technique for prosthetics for a healthy man who lost all his teeth two months ago due to periodontitis, then with a high degree of probability we will end up with a lot of problems.
This technique cannot compensate for significant bone atrophy. Why? Because in this case, the massive base of a fixed prosthesis will create hygiene difficulties. In this case, it would be more correct to consider a removable denture supported by a beam fixed on implants, which we talked about a little earlier.
– immediate loading, such as “teeth in one day”, when implementing the “all-on-four” method is rare. It is not always possible to do this; this is rather the exception than the rule. All dentists are happy when this happens; they immediately run to post these works on their pages on social networks.
Why? Because of course it is possible to make a denture supported by installed implants, but to make a correct and functional denture is, unfortunately, almost impossible. Therefore, if you have the opportunity to avoid immediate prosthetics on implants, it is better to do so. If you hurry, you will make people laugh.
Therefore, we try not to load the implants immediately after installation, using the remaining teeth as support for the prosthesis:
If there are opportunities (namely, the remains of natural teeth), we use this approach quite often. Yes, it turns out to be more expensive than “all at once,” but it carries much fewer risks than immediate prosthetics itself. In particular, this applies to the “all-on-four” scheme.
And yet, when is “all-on-four” a good, usable technique? Frankly, we do not consider it a good and suitable technique even for the small number of clinical cases for which it is intended.
Those whales on which its popularity, speed, cheapness, simplicity rest, turn out to be not whales at all, but, at most, minnows.
Therefore, the only fixed structure that has the qualities we need is a bridge supported by six or more implants:
This technique can be considered a proven classic, because it is manufactured according to the same principles as implant-supported bridges.
The only difference is that often, very often, imitation gums are used to compensate for bone tissue atrophy (and increase interalveolar height):
Rarely, very rarely, usually with immediate implantation, we can do without artificial gum:
We classify such clinical situations as “LUCKY!”, because most often, in order to create teeth of the desired shape and height, the prosthesis needs some kind of base to compensate for the loss of bone.
Again, the type of prosthetics, removable or fixed, will depend on its thickness. If there is significant loss of bone tissue and the need for a thick base, it is better to consider the option of a removable denture supported by a bar. Then it will be much easier for the patient to care for it, therefore, we will not worsen the quality of life and will not reduce the service life of the structure itself.
The same goes for more implants - seven, eight, ten, twelve... Increasing the number does not improve aesthetics, will not get rid of artificial gums and will not improve your life if bone atrophy has gone too far. A simple example is basal implants, which are installed in dozens, but patients still remain dissatisfied.
And the quality of implantation and, especially, prosthetics means, first of all, a satisfied patient.
Unexpectedly for ourselves, we realized that it is impossible to talk about all the nuances of prosthetics in two or three articles. Having simplified some concepts, removed terms, made huge assumptions and adapted the text for ordinary people, we have not been able to present even half of what we consider necessary. No matter how much information there is about prosthetics, it will always be not enough. And there is an explanation for this.
With implants, everything is very simple - in fact, we have several dozen implantation systems and several hundred standard sizes. Whatever the implant, neither its brand, nor its shape, and especially the country of origin, determine the quality of the treatment performed.
At the same time, a denture, an aesthetic and functional imitation of a natural tooth, is individual and unique. Just as there are no two absolutely identical teeth in the world, there will never be two identical dentures. Dental prosthetics is always handmade, delicate and delicate, taking into account a thousand nuances and little details.
No matter what they say, no matter what marketers write about, a scanner-computer-milling machine will never replace a qualified dental technician and prosthetist. Not a single, even the most advanced computer program that operates with standard libraries of tooth shapes and sizes will reduce the relevance of the experience, competence, vision and simply aesthetic taste of the right doctor.
Suddenly a terrible event happened - a man lost all his teeth. If earlier it automatically transferred an active and young person to the category of an old man, now we have learned to restore entire rows of teeth with a high degree of reliability and an increase in the quality of life. For this purpose, we use dental implants as supports for dentures.
No matter what the advertising tells you, dental prosthetics is a long, complex and, unfortunately, very expensive treatment process.
The type of prosthetics (removable or fixed), as well as the number of implants (four, six or more) are selected based on the clinical picture and take into account a huge number of factors. Of course, we take into account all the “patients’ wishes,” but only if they do not contradict common sense and do not negatively affect the quality of prosthetics.
Therefore, when we talk about planning such treatment, its timing and, especially, cost, we need to act wisely and consider each case individually. The best option is an in-person consultation with a specialist doctor. All you need to do is call us, write to any of the instant messengers, leave a message on our social network page or simply fill out a form on the website, and then choose a convenient time to meet with the doctor.
Thank you for reading to the end.
As always, we are ready to answer all your questions in the comments under this article.
Best regards, CLINIC IN
What else can you read about dental prosthetics at CLINIC IN?
A whole section about dental prosthetics
You are planning dental prosthetics. What do you need to know about this before consulting a dentist?
Implant-supported prosthetics – how is it done?
A whole section on dental implants
Orthopedic implant platform – cones, hexagons and screws
About the quality of implantation
Adhesive fixed bridge prosthesis
An adhesive fixed denture got its name due to the peculiarities of fixation on the supporting teeth. To connect it with living tooth tissues, adhesion is used, that is, “sticking” technology. For reliable bonding, the prosthetist uses a dental primer, bond, some types of acids (for example, phosphoric acid), chemical or light-curing cement.
Adhesion helps to secure the ceramic tooth and onlay processes to the supporting teeth without removing the roots and grinding away a large layer of its enamel.
Structure of an adhesive dental bridge:
- main abutment tooth;
- side linings in the form of processes (petals), onto which a fixing compound is applied.
The average lifespan of an adhesive dental bridge is up to five years.
What types of fixed prosthetics and when are they used?
In modern dentistry, there are the following technologies of fixed prosthetics:
- Microprosthetics
:
- installation of veneers/lumineers – used primarily for aesthetic reasons to correct chipped enamel, small defects in the front wall of the tooth, eliminate gaps, irreversible changes in enamel color, etc.
- Prosthetics with ceramic inlays help to reliably restore even a badly damaged tooth with a large cavity.
- Prosthetics using a crown
. This type of permanent prosthetics is used to restore a single tooth crown, even after its complete destruction, provided that the tooth root is preserved. - metal-ceramic
- metal-free
- zirconium.
. This type of fixed prosthetics is used when it is necessary to restore 1-2 lost teeth in the presence of neighboring ones and is often recommended as temporary.
Dentures on implants are indicated in the absence of a large number of teeth.
- Single implantation is the most reliable and aesthetic way to restore a tooth lost by the roots.
- Prosthetics of one jaw on 4, 6 implants
Prosthetics of the jaw or part of it on implants is the most modern, natural and reliable method of restoring dentition.
Video: interview with the head physician and orthopedist of the clinic R.Z. Babaev
Watch a video about how the entire process of high-quality dental restoration takes place - from the first visit, planning and to the implementation of the plan into a real smile. Watch an interview with Roman Zakirovich’s patient, Svetlana, and find out the main principle of a good doctor’s work.
Fixed denture on titanium implants
Fixed dentures on dental implants are one of the most common systems for restoring lost teeth.
The main advantages of such solutions:
- titanium implants installed in deep bone layers preserve hard tissue around them;
- healthy supporting teeth do not require preliminary grinding and root removal;
- the average shelf life of such dentures on artificial roots is twenty years;
- the method of restoring teeth with fixed dentures is considered the most gentle and natural;
- ready-made solution for restoring edentulous teeth;
- attractive dental aesthetics.
The only caveat when installing a fixed dental structure on implants is the considerable cost of the solution.
If we compare all the existing options for fixed dental prosthetics, it is the fixed prosthesis on a dental implant that is the best solution - in terms of quality, aesthetics, reliability and durability of the teeth.
Types of structures
Due to the variety of dental cases characterized by the need for prosthetics, various technologies and materials are used to create prostheses. From the point of view of design specifics, there are:
- Veneers and lumineers are thin plates made of ceramics used to hide visually noticeable defects in the frontal units;
- Crowns and inlays are products used as a protective cover that imitates the natural structure of the tooth and are placed on top of the damaged unit;
- Bridges are structures designed to replace several successively located units fixed on implants or healthy teeth;
- Implants are permanent prostheses used in cases of complete destruction of not only teeth, but also root areas, completely restoring the structure.
The choice of material for manufacturing is determined by technology and also depends on the financial capabilities of the patient. The most common materials include:
- Ceramics - used to create artificial crowns and veneers that are externally indistinguishable from natural tooth enamel. Fixed dentures made from solid ceramics allow you to create an attractive smile, but are not very durable and affordable;
- Metal alloys - the use of precious and ordinary alloys makes it possible to achieve operational reliability and durability of replacement elements, but reduces aesthetic qualities;
- Metal-ceramics is a technology that combines the advantages and hides the disadvantages of the two above-mentioned materials, highly appreciated by dentists and patients.
In addition, the implantation procedure recommended for severe destruction of individual units or complete edentia involves the use of titanium pins. Titanium is durable and reliable, and is fully compatible with body tissues, which makes it possible to integrate and engraft prostheses.
How to care for fixed dentures?
Basic rules for proper care of fixed dentures at home:
- brushing teeth with a brush and dental floss;
- using a dental irrigator (preferably after every meal);
- hygienic cleaning of the tongue.
- preventive visits to the dentist’s office (at least twice a year) to control the quality, reliability of fastening and aesthetics of a fixed dental prosthesis (bridge);
Don't forget to clean the surface of your tongue, where just as many bacteria accumulate as on your teeth and gums. These organisms provoke the development of caries. To clean your tongue at home, use a hygienic scraper with a rough surface, which can be purchased at a clinic or any pharmacy.
If the patient wears fixed dental prostheses made of metal-ceramics or ceramic crowns, experts recommend checking the so-called supercontacts (heightened areas of the bridge) at least 2 times a year and grinding them to avoid chips and mechanical damage to the dental bridge.
If you feel that the bridge or individual teeth have begun to loosen, you should urgently consult a dentist. In case of mechanical damage to a fixed denture, the defects can be eliminated without replacing the structure with a new one. If you lose time, you will have to resort to dental prosthetics again using a new bridge.
Timing of prosthetics
Depending on the type of prosthetics, the duration of restoration can last from 3-5 days to 1.5-2 weeks. The timing of the work is also influenced by the preparatory stage: if when installing lumineers there is no need to prepare units, then fixed dental prostheses in the form of a bridge require a preparatory stage, which can take about 1-2 months.
Advantages
Fixed structures have a number of advantages:
- long service life (veneers - up to 7 years, stump inlays - up to 20 years);
- strength and reliability of fastening;
- aesthetics (lumineers and ceramic crowns, which are difficult to distinguish from a “natural tooth”);
- performance (the ability to withstand chewing loads on the prosthesis, completely replacing living units);
- do not reduce the sensitivity of taste and thermoreceptors.
Adaptation lasts about 2-3 weeks, after which patients completely forget about the foreign object in their mouth.
Care
Oral hygiene after installation of a prosthesis is almost no different from conventional procedures:
- You should brush your teeth twice a day and rinse with an irrigator;
- buy high-quality paste, do not try to save money on purchasing hygiene products;
- systematically visit the dentist for professional cleaning of the oral cavity and diagnosis of possible pathologies in the early stages;
- do not try to repair a broken prosthesis at home;
- give moderate load on artificial units. If you have a temporary denture installed, avoid temperature changes: prepared teeth are hypersensitive, so pain may occur.
Average price of fixed dentures in Moscow clinics
- Types of dentures
- Efficiency of production
- Qualifications of specialists
- Type of clinic
The price of a fixed denture depends on the following factors:
A budget option is a plastic bridge, which is usually installed as a temporary solution to replace lost teeth. Metal stamped dental bridges are also cheap - from 300 rubles. for one unit. The most expensive are bridges with ceramic crowns, which cost about 30,000 rubles. for 1 tooth.
Fixed dentures are usually made from pre-made impressions in a dental laboratory. The average production time is two weeks, but some services offer to speed up this process for a fixed additional payment (from 1/3 of the cost to double the price, depending on the complexity of the work).
Dental prosthetics requires the help of several specialists: a prosthetist, an implantologist, and a dental technician. The dependence is obvious: the higher the qualifications of the professional, the higher the final price of dental prosthetics.
The price of the same fixed denture in different clinics may differ. If you compare the prices of Moscow dentists, the most favorable prices are from the network of dental clinics “32 Dent”.
How much do fixed dentures cost?
The cost of fixed dentures depends on several factors: the selected material, the volume of bone tissue, the size of the restoration area, and the complexity of installing the structure.
A ceramic inlay for a tooth costs from 20,000 rubles. Dental treatment and professional cleaning before prosthetics are paid separately.
The cost of veneers starts from 15,000 rubles.
When choosing a crown for an implant, you need to take into account that it does not include prices for dental implantation in Moscow. They depend on the brand of the implant, the qualifications of the doctor and the level of the clinic.