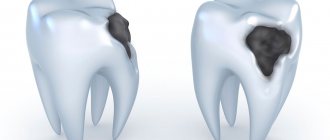
Malocclusion in a child is a pathology in which one row of teeth deviates relative to another, which violates the anatomical norm, and occlusion is disrupted (the teeth do not close correctly when the jaws are brought together). Malocclusion is not considered to be the curvature of the dentition due to the incorrect position of individual teeth.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis of malocclusion in children
- Treatment
- Correction
- Prevention of malocclusion in children
- Prognosis of malocclusion in a child
Causes
A child's malocclusion may have hereditary roots. If parents' jaws are anatomically incorrect, most likely their child will experience the same thing. Bite abnormalities appear gradually. In infants, the jaws consist mainly of the alveolar process, and their basal parts are still underdeveloped. At the same time, the bones of the upper jaw grow faster than the lower jaw, and the lower jaw has two halves that fuse when the child turns 1 year old (on average).
The jaws change, which is reflected in the bones and muscles, including the temporal, chewing and pterygoid. The most developed muscle in babies is the chewing muscle, because they need it to suck on their mother's breast. But the lateral and medial pterygoid, as well as the temporal muscles, thanks to which the lower jaw moves up and down and back and forth, are poorly developed during this period. And after the first teeth have erupted, they begin to actively develop. A child from 1 year of age begins to experience malocclusion.
Factors that influence bite problems in children:
- artificial feeding of a newborn (sucking a bottle is easier than extracting milk from the mother’s breast, therefore the muscles of the jaw and face develop less than they should at this age)
- use of a pacifier up to 1.5-2 years (during this period the baby is teething)
- after the eruption of primary molars, the child’s diet lacks food that must be chewed before swallowing
- baby's habit of holding and sucking fingers or toys
From 5-7 months of life, the child’s upper central incisors are also cut. This is the beginning of the formation of the baby rows of teeth. In cases where the upper jaw is more developed than the lower jaw, or the teeth are small, the spaces between the teeth (three teeth) can be more than 1 mm in size. This is a signal of future problems with the child's bite.
When a baby turns 3-4 years old, the bone structures of his teeth and jaws are actively forming. From the age of 5, the gradual resorption of the roots of baby teeth and the growth of the alveolar processes of the jaws begin. From the age of six, baby teeth fall out and molars grow in their place.
Orthodontists call replacement teeth those that a child has until the age of 13-14 years. During the same period, the size of the jaws also changes, because their basal part is actively growing. If deviations occur during this period, they may precede a malocclusion. The twisting of individual teeth relative to their axis or erupting them in the wrong place is almost a guarantee that the child will develop a malocclusion. Violation of occlusion in children has a main cause - an anomaly in the shape of the dental arches.
The cause of malocclusion may be hidden in the syndrome of chronic difficulty in nasal breathing in various diseases of the ENT organs or congenital pathologies of the nasopharynx and nasal septum:
- enlarged adenoids
- polypous rhinosinusitis
- sinusitis
- rhinitis
With such pathologies, the child breathes through his mouth, even in his sleep. Therefore, the muscles responsible for lowering the lower jaw do not relax at night, the upper jaw is pulled forward, and therefore the bite is disturbed. The proportions of the face change, which is called the adenoid type of the child’s face.
Endocrinologists say that bite defects can be a consequence of functional disorders of the thyroid and parathyroid glands. In particular, due to a lack of production of thyroxine and thyrocalcitonin, bone growth is delayed. The maxillofacial bones also grow poorly, and the child’s baby teeth are cut slowly and belatedly. When the parathyroid glands are underdeveloped or diseased, the production of parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium levels in the body, is disrupted. Impaired calcium metabolism causes demineralization of bone tissue, which can cause the jaws to lose their normal anatomical shape and location.
Ways to correct a bite
Today there are four ways to correct a bite and one way to carefully disguise the problem.
- Aligners
- Trainers
- Bracket systems
- Surgical intervention
We have listed these methods in order from easiest to most difficult. You must understand that each case is individual, and depending on this, the doctor will select the optimal bite correction system. You can hide an unaesthetic bite with the help of veneers - we will also talk about them.
Aligners
Removable aligners that are created from dental impressions. The most modern way to correct a bite, which is suitable for the treatment of simple disorders.
After drawing up a treatment plan, the patient receives 3–5 sets of aligners of varying stiffness. The mouth guard is designed to last for two weeks, and then it needs to be changed to the next one, and so on until the final result. The course of treatment lasts on average 4–8 weeks.
Aligners need to be worn 24 hours a day, and this may not be comfortable for everyone. They are not suitable for deep bites. The mouthguard is designed so that it is “one step” ahead of the current position of the teeth in the dentition. Therefore, after putting it on, pressure is felt, which is evenly distributed throughout the jaw. Aligners consist of an elastic transparent material, so they are invisible to others, unlike braces.
Trainers
Removable silicone mouth guards for two jaws, which help correct a simple bite or consolidate the result. You need to wear the trainer during sleep and during the day for up to 4 hours.
Veneers
The characteristics are similar to crowns, but they are installed only on the front surface of the tooth in the form of a thin plate on a special dental glue.
Veneers can be composite, ceramic or zirconium. The first two types last about 10 years. Products made of zirconium dioxide with external porcelain coating - up to 15 years.
Veneers eliminate defects that arise as a result of cracks or damage to the integrity of teeth. A visually straight dentition is formed.
For the patient, the result of orthodontic treatment is aesthetics, and for the doctor, it is functionality. If your teeth are just crooked and your bite is perfect, you can get veneers or crowns. In other cases, you cannot do without braces: veneers do not correct the position of the teeth, but only mask their external imperfections.
Bracket system
Braces are small clasps that are attached to the teeth with a special composite glue. A metal arch is placed in the grooves of the braces - the most important element of the braces system. The arch has the shape of a regular dentition. She pulls her teeth, setting them in the correct position. In order for the bracket system to successfully complete its work, it is important to periodically change the arches to more elastic ones.
The doctor fixes the arch on the braces with special rubber bands - ligatures. Depending on the task at hand and the required force that will act on each tooth and jaw as a whole, the orthodontist can choose metal or elastic ligatures. The latter have a clear advantage - when they are changed, you can get rid of the bacteria accumulated under them.
Increased salivation in the first days after installation is a good reaction of the body. The tongue contains sensory neurons that, when food appears in the mouth, send signals to the brain to turn it into a food bolus. When braces are put on your teeth, at first the brain perceives them as food. This is the body’s reflex that there is something in the mouth, which means it needs to be treated with saliva in order to then swallow it. After some time, the salivary glands will get used to it.
Does it hurt to wear braces?
The first days are unusual, but not painful. But if braces scratch your lips and cheeks, you shouldn’t tolerate it. “ Make an appointment with your orthodontist. Sharp elements can be corrected with special materials and filled with special wax
“, our expert advises.
The same applies to tooth sensitivity: sign up for a diagnosis. It is possible that areas of demineralization have appeared. Depending on what the teeth react to, further treatment will depend.
Types of braces
Braces are classified according to the following criteria:
- material (metal, plastic, ceramic and sapphire);
- technique (classical and self-ligating, without ligatures);
- Place of installation (on the outer surface of the teeth - vestibular, on the inner surface - lingual).
Metal braces
Despite the fact that these are the oldest braces systems, they are still popular, and not only because they are the cheapest. Their main advantage is the minimal friction force between the groove and the arc, the magnitude of which largely determines the duration of the entire treatment.
The only negative is that such braces are noticeable on the teeth. However, modern designs differ from their ancestors - they are smaller and more convenient.
Plastic braces
Second after metal ones in the price range. Since plastic itself is not strong enough, the design has metal grooves. Their disadvantage is that such braces are stained by coffee, tea and other coloring products. They are also more fragile than others. However, plastic braces come in a variety of colors and shapes and are therefore popular in pediatric orthodontics.
Ceramic braces
More expensive, but stronger than plastic ones. The color matches the color of the teeth, which makes them almost invisible. Their disadvantage is higher friction between the arch and the bracket slot, which can increase the duration of treatment.
Sapphire braces
Artificial sapphires are used to make them. They are transparent and shimmer beautifully in certain lighting. This design will appeal to those who are sensitive to aesthetics.
Combined braces
Consist of several materials. In the smile area it can be ceramics or sapphires, and in the chewing area it can be metal.
Lingual braces
They are attached to the inside of the teeth and are invisible to others. Their main disadvantage is their high cost. Also, at first they may interfere with diction, but after 2-3 weeks the language adapts and the problem goes away.
Symptoms
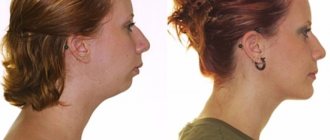
An incorrect bite is always visible visually. And the symptoms depend on the type of dental anomaly. Malocclusion in children can be distal: maxillary and alveolar prognathia. The first of these is manifested by a strongly developed upper jaw protruding forward. In this case, the upper dental arch is expanded, and the upper teeth overlap the crowns of the lower dentition by more than a third.
The alveolar leaf bite is special in that only that part of the bone where the tooth sockets are located protrudes forward. When a child with such a defect smiles, not only the upper teeth are visible, but also to a large extent the alveolar zone of the gum. With a mesial bite, the lower jaw, which is more developed than normal, protrudes forward, so the lower row of teeth “overlaps” the upper one. When a child has such a pathology, it is difficult for him to bite off food, and there may also be incorrect articulation to a greater or lesser extent.
Vertical incisal disocclusion (or deep bite) is visible visually and also audible. The upper jaw may be too narrow and the middle of the lower jaw too flat. This explains the short lower part of the face. The child pronounces hissing sounds incorrectly because the upper incisors deeply overlap the central part of the lower jaw. There are also problems with biting.
An open bite is diagnosed if several chewing teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not close together and there is a large gap between their surfaces. These children's mouths are slightly open almost all the time; they have difficulty biting when eating because the front teeth do not close together. The lower labial fold is absent in almost all cases. It is difficult for a child to hold his tongue in an anatomically normal position, and therefore his speech is distorted.
Crossbite in children is manifested by the following symptoms:
- unilateral underdevelopment of the lower jaw
- difficulty moving the lower jaw to the left and right
- biting the soft tissue of the cheeks
- violation of facial symmetry with strong displacement of the lower jaw from the anatomically normal position
When does a child need to have their bite corrected?
You can be of any age to correct your bite. Treatment can begin at 3-4 months. You can notice a malocclusion in an infant by abnormal breathing: it is often difficult. During feeding, you need to pay attention to the position of the baby's head: it should not be thrown back or pressed with the chin to the chest.
In children under 2 years of age, the facial muscles are poorly developed, so it is impossible to recognize an incorrect bite without consulting a specialist. In this case, hardware techniques are not used; the child can be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures and massage.
In children over 5 years of age, disorders are clearly visible. The child's speech may be impaired, as well as chewing function. The defect can be seen upon visual inspection: the teeth grow incorrectly (displaced, crowded). The child has asymmetry of the jaw or face (partial closure, protruded lower or upper jaw).
If the molars grow incorrectly, the child may complain of headaches, constant biting on the inside of the cheeks and clicking in the temples.
Diagnosis of malocclusion in children
For diagnosis, the child must be taken to an orthodontist. He performs an oral examination. The doctor takes into account the proportions of the face, for which the width of the dental arches, the angle of the occlusal plane and other indicators are determined. If a child has trouble breathing through the nose, an ENT consultation is needed to treat diseases of the paranasal sinuses, nose and adenoids to restore normal breathing.
To accurately determine the number of teeth and their location in the dentition, as well as the location of the jaws relative to each other, the characteristics of muscle tissue and the condition of the temporomandibular joint, computer 3D cephalometry and a panoramic x-ray of the dental system, which is also known as an orthopantomogram, are performed.
The examination must be comprehensive so that the specialist can establish the relationship between the width of the upper and lower dental, alveolar and basal arches. Normal anatomy is that the maxillary dental arch should be wider than the alveolar arch. Normally, the alveolar arch should be wider than the basal arch. And for the lower jaw it’s the other way around. After determining the size characteristics of all elements of the jaw in each case, the doctor creates a diagnostic model of the jaws, which is used to determine the type of deviation of the maxillofacial structures and the type of occlusion disorder in the child.
Treatment and correction of distal bite
Treatment methods for prognathia depend on its degree, the form of the disorder and are selected only after diagnosis.
What is prescribed to the patient:
- radiography;
- teleradiography;
- CT;
- MRI;
- rheography;
- electromyography.
These diagnostic procedures allow you to determine the correct shape of the jaw, as well as identify any complications caused by the distal anomaly. During the examination, the entire temporomandibular joint and masticatory muscles are checked.
Correction of prognathism in adult patients takes several years. Sanitation of the oral cavity is first required, that is, complete cure of diseases of the gums and teeth, for example, caries.
Correction of distal occlusion without surgery is possible if the deformation affects only the dentition. In this case, braces are effective, after which you will have to wear retainers or mouth guards for a long time or constantly to keep the teeth in the desired, correct position. Complex therapy includes special myogymnastics.
In more complex cases, special devices are used to correct the bite or surgery is performed. During treatment, all consequences obtained during the development of the deformity are eliminated.
Application of braces
Correction of distal pathology using braces in adult patients requires at least 2 years. They are selected individually, which depends on the degree of deformation, the reasons that caused the development of the pathology, and financial capabilities.
To correct the bite, braces are used:
- metal;
- ceramic;
- sapphire.
Such materials do not harm the body and do not provoke the development of allergic reactions.
Some people prefer lingual braces when correcting distal occlusion. These are devices that are fixed on the inner surface of the teeth and are invisible to others. But they are not suitable for correcting all forms of prognathic deformity.
With the help of a braces system, not only the bite is corrected, but also the function of proper chewing is normalized. To do this, it is necessary to perform special gymnastics.
When using braces on your teeth, you must constantly visit your doctor, follow all his recommendations and take the most careful care of your oral cavity. The duration of wearing braces is determined by the degree of prognathism.
Myogymnastics
If a distal bite is corrected using braces, correction after them or while wearing them involves performing myogymnastics. This is a special set of exercises for developing facial muscles.
What effect does regular exercise have?
- secures the jaws in the desired position;
- eliminates tooth alignment disorders;
- corrects the position of the upper and lower lips;
- develops tongue and chewing muscles.
Devices for correcting bite
In severe forms of deformation, treatment is carried out with the fixation of frame devices; they help move the first molars to normal. For this purpose, non-removable devices Forsus and Powerscope are used, which must be worn for up to six months.
A facebow with palatal traction helps eliminate deformation of the upper jaw. This device is worn for about 10 hours every day.
To bring the lower jaw into a normal position, intermaxillary elastics are used. With their help, the lower bone moves forward over a period of 3 to 4 months.
Alternative Methods
Orthodontists also use alternative methods to correct bite:
- Veneers. Only minor deformations of the dentition are hidden.
- Aligners. They are removable plastic mouth guards. In case of distal damage, they are ineffective, so they will have to be changed every month.
- Trainers. Removable silicone structures to correct malocclusion. At the beginning of therapy, soft ones are used, at the end - more stringent ones.
Treatment
Treatment of malocclusion is called orthodontic treatment, and it takes a long time. The treatment method depends on the type of malocclusion in the child. The younger the child is, the easier it will be to correct bite defects. In most cases, removable pre-orthodontic trainers, plates, mouth guards or elasto-aligners are used. Soft and hard trainers should be worn during the daytime and at night for 1-1.5 hours. They help wean children two to five years old from bad habits (sucking the tongue and sticking it between the teeth or biting the lower lip). Trainers help teeth erupt correctly and straighten the front incisors when they grow crookedly.
Custom-made removable dental guards made from polycarbonate are called dental trays or aligners (elasto-aligners). They are used mainly to correct the bite in children from 6 to 12 years old, if the forearms are twisted, excessively tilted forward or into the oral cavity. Mouthguards are worn 2-3 hours a day or more.
Braces are non-removable structures that are attached to a child’s permanent teeth. They must straighten the teeth and dentition due to constant pressure on the alveolar arches of the jaw from special arches that are fixed in the grooves of the braces. Braces are worn from 12 to 26 months (depending on how crooked the child’s teeth are). When braces are removed, retention plates are installed to help keep the teeth where they are when straightened. The period of wearing these plates can be up to 3 years. For alveolar prognathia, braces are used for treatment, but they are not relevant if the child has other types of occlusion disorders.
Care and hygiene rules
One of the advantages of aligners is their ease of care. To keep them clean and effective throughout the correction, follow these simple rules:
- aligners must be worn up to 22 hours a day, depending on the orthodontist's indications, removing them only for eating or oral hygiene;
- The aligner must be cleaned regularly by rinsing the inner surface with warm running water and brushing with a toothbrush;
- You should avoid too hot water so that the polymer does not deform due to temperature changes.
Aligners do not require special solutions. If you remove them, then put them in a special clean and sealed box, protected from dust and moisture.
Oral hygiene when wearing aligners also remains the same - brush, paste, mouth rinse solutions and dental floss. The latter is also suitable for effectively removing food particles.
Let us note the contraindications under which aligners cannot be installed:
- periodontal disease. Like other methods of orthodontic treatment, aligners are not prescribed for periodontal disease due to the high risk of losing teeth due to destruction of periodontal tissue;
- severe deformation of the jaw. Aligners work well for minor malocclusions. However, serious defects require surgery;
- in the presence of impacted teeth. Often this problem occurs with molars that do not erupt and remain in the gum or even in the jaw bone. Having an aligner can interfere with their development and lead to problems in the future;
- if 4 or more teeth have been lost.
In other cases, aligners are equally effective for all ages - from children to adults.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Pokrovskaya Natalya Sergeevna
Head of the Department of Orthodontics
Specialization: Invisalign bite correction, neuromuscular diagnostics, pediatric orthodontics.
Free consultation
Correction
With a distal bite, the development of the apical points of the alveolar and basal arches of the upper jaw is restrained, and the growth of the child’s lower jaw is activated. For this purpose, during the period of loss of baby teeth, the following devices can be used:
- Andresen activator
- Engle's arc apparatus
- Ainsworth arc apparatus
- Herbst arc apparatus
- functional Frenkel apparatus of the first or second type
Removable plates are placed on the teeth, and a vestibular retraction arch helps reduce tremors. Also, the goal of treatment is to give the desired direction to the growth of the maxillofacial bones. To do this, a facebow is installed outside, which the child wears at home; there is no need to wear it to school.
Prognosis and prevention
The most effective results in correcting malocclusion are achieved during the mixed or primary dentition. If you choose the right treatment method, it is possible to achieve high-quality jaw alignment in adulthood, but it will take more time.
The formation of the bite in infancy plays an important role. It is important to monitor the correctness of breastfeeding, the position of the child during sleep, and prevent the formation of bad oral habits. Timely treatment of disorders that slow down or impair the growth of jaw bones and dental correction is also required.
Correction of mesial bite
The goal of treating such a malocclusion is to correct the protrusion of the lower jaw or promote the development of the upper jaw. For this purpose the following devices are used:
- Frenkel activator type III
- removable Andresen-Goipl apparatus
- Klammt activator
- Wunderer or Delaire apparatus
- orthodontic cap with chin sling bandage
- Adams, Nord or Schwartz records
- single-jaw stationary Angle arch
In order to inhibit the growth of the bone structures of the lower jaw, children 13-14 years old can undergo dental surgery. During this procedure, the buds of the lower eighth teeth, the so-called wisdom teeth, which begin to grow when the child is between the ages of 6 and 14, are removed.
Correction of deep bite
It takes a lot of effort to correct this effect when a child has baby teeth. In practice, it turns out that improper closure occurs again in a child after the appearance of permanent teeth. Treatment of deep bite involves preschool children performing special exercises, the purpose of which is to develop the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles, which push the lower jaw forward. To coordinate pressure on the teeth of the lower row, the following devices are used:
- Andresen's plate apparatus
- bite blocks
- Klammt activator
- fixed orthodontic devices of various designs
Open bite correction
If a child has an open bite, in most cases the upper jaw is narrowed. For this reason, removable expansion plates of various modifications are used, equipped with a spring or screw for children whose permanent teeth have just begun to emerge. They are used for treatment and construction to increase the anterior parts of the upper alveolar arch, to reduce the lateral parts of the alveolar zones, which is selected individually in each case.
If the discrepancy between the incisors and canines is large, for children over 12 years of age, intermaxillary traction techniques using Angle orthodontic devices with additional traction can be used. The second way of correction is the use of plastic mouth guards, which are placed on both jaws (front teeth).
Crossbite correction
The purpose of treatment: to establish the most correct arrangement of teeth in the row and the position of the child’s lower jaw. If a child with baby teeth has a crossbite, it is necessary to separate the dentition. To do this, crowns or trays are installed on the molars, as well as on the lateral teeth - plate devices with bite plates.
In cases of cross occlusion and severe lateral displacement of the lower jaw, a chin sling is sometimes used. Plate devices, adjustable with screws and springs, are suitable for expanding the dental, alveolar and basal arches of the child’s jaws.
Signs of pathology
Incorrect distal bite is conventionally divided into 2 types based on its characteristics. These are facial and intraoral changes. Their most severe severity is observed in adults in the complete absence of treatment.
Facial manifestations of distal occlusion:
- Violation of facial proportions - asymmetrical displacement of the lower jaw back and a small, sloping chin.
- A noticeable state of always half-open mouth.
- Change in the natural shape of the upper lip - reduced in volume, upturned or very short.
- Deformation of the lower lip.
- The teeth of the upper jaw are more developed than the lower jaw, the central upper incisors protrude strongly forward.
- Sharply defined chin fold.
Such changes in the shape of the face negatively affect the appearance, the face becomes bird-like.
Intraoral signs of a distal anomaly are as follows:
- There is no closure between the lower and upper jaw.
- The teeth of the upper frontal group are noticeably moved forward.
- The lateral teeth are located abnormally relative to each other.
In most cases, distal occlusion is formed against the background of other pathologies - diastema, trema, open or crossbite.
Prevention of malocclusion in children
Prevention of malocclusion should begin with breastfeeding a newborn. If this is not possible, it is necessary that the hole in the nipple on the bottle with milk formula is small, and that the nipple itself is in the child’s mouth at a right angle to the nasolabial plane and chin and does not put pressure on the gums. Then the child’s facial muscles will develop normally.
Choose pacifiers of shapes that correspond to the anatomical structure of the baby’s oral cavity. It is better that the child does not suck a pacifier while sleeping. You need to stop sucking a pacifier when you reach 1.5 years of age. Wean your baby from the habit of biting his lips, sucking fingers and toys.
Prevention of open bite is that the baby should sleep so that his head is slightly higher than his body. Children should breathe freely through their nose while sleeping, keeping their mouth closed. If a child does not have a cold, but cannot breathe normally through his nose, it is worth going to an otolaryngologist for an appointment. When a child has already cut 8-10 teeth, you cannot feed him crushed food. For normal development of the maxillofacial muscles, he must bite off and chew food on his own.
Myogymnastics is relevant for children 2.5-3 years old. These are exercises that help develop the muscles of the jaws and face. The orthodontist should tell you about the technique, because each type of malocclusion requires special exercises.
Complications without treatment
In case of malocclusion, treatment is always necessary, since the pathology is not only accompanied by cosmetic defects, but can also cause various complications, which include:
- improper chewing load leads to rapid wear of tooth enamel, which causes increased sensitivity and the risk of premature loss;
- development of periodontal disease against the background of increased periodontal wear;
- problems with the digestive system due to poorly chewed food;
- underdevelopment of individual facial muscles and the appearance of painful sensations in them;
- premature tooth loss;
- difficulties associated with treatment - prosthetics and implantation.
Also, with an abnormal bite, problems with diction, jaw joints, and the rapid occurrence of infections in the oral cavity may occur. With timely and proper treatment, such complications can be completely eliminated.
Prognosis of malocclusion in a child
If measures are not taken to normalize the position of the jaws, it becomes increasingly difficult for the child to bite off food and chew because the teeth do not close as needed. This problem is especially relevant in mesial, open and cross bites. If food is not crushed enough, this can lead to future gastrointestinal diseases.
If a child is diagnosed with a distal bite, the back molars will be overloaded, causing them to wear out prematurely and also damage the enamel. Any malocclusion in children threatens dysfunction of the temporomandibular joints. If your bite is severely misaligned, your nerves can become pinched, causing severe pain. And, of course, an incorrect bite in a child greatly affects articulation; diction can be impaired throughout life.
How to identify distal occlusion: symptoms of occlusion
The most characteristic signs, especially for non-specialists, are facial, caused by improper formation of the skeleton and unbalanced development of the neck muscles. Because of this, the so-called bird profile appears with distorted proportions and retraction of the lower lip.
There are also more specific, but still quite noticeable points:
- protrusion (protrusion) of the frontal incisors;
- insufficient closure of the teeth of the lateral group.
Since the anomaly progresses from a very early age, the child gradually develops infantile swallowing and mouth breathing. The chewing muscles are not strengthened well enough, over time the functions of the TMJ are weakened, and all this provokes the appearance of periodontal and dental diseases.