Causes of bad taste in mouth
There can be many reasons for a strange taste in the mouth, but the most common are:
Read also: Why do I love nature?
- Poor oral hygiene. Lack of or poor oral hygiene can cause food debris to remain on and under the tongue, teeth and cheeks, which feed bacteria, causing an unpleasant taste.
- Nutrition. What we eat directly affects the taste in our mouth.
- Hormonal disbalance. Fluctuations in hormone levels or other hormonal changes can cause unusual tastes because hormones, in addition to their main functions, also affect taste buds.
- Medicines. The use of medications can have a negative impact on the taste in the mouth. For example, some types of medications change the sensation of taste or contribute to its absence altogether.
- Bad habits. Excessive drinking and smoking are obvious causes of a strange, unpleasant taste. When you overeat, it is difficult for the intestines to do their job; as a result, pathogenic bacteria multiply in it, which causes certain taste sensations.
- Various diseases. A number of diseases, from infectious to chronic, can cause a specific taste in the mouth.
To understand why there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth, it is necessary to determine its taste sensation and origin.
How does a lump in the esophagus manifest itself?
A lump in the esophagus is a very unpleasant sensation
A description of this symptom is found in the works of the great ancient physician Hippocrates. He considered a lump in the esophagus to be a manifestation of hysterical natures. Since then, the idea of a coma in the esophagus has changed somewhat. It is characterized by the following signs:
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the area of the esophagus.
- Constant desire to cough, to swallow obstruction.
- Feeling of lack of air, suffocation.
- Fear of suffocation, choking (especially in sleep).
- Hoarseness, pain when talking or eating.
Such sensations are not always permanent; they can manifest themselves after taking a certain body position, or after eating, mental stress, or the appearance of strong emotions.
Diseases of the nervous system and blood vessels
In rare cases, the appearance of a salty taste in the mouth can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system and blood circulation, namely:
- cerebral ischemia;
- epilepsy;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis;
- high blood pressure;
- hemorrhagic stroke.
The development of a benign or malignant tumor in the brain or near nerve endings and roots often leads to disruption of the sense of touch and taste buds, which can result in an unusual taste in the mouth. Only a doctor can identify the exact cause through an extensive examination of the patient’s body.
Possible complications
The symptom itself does not cause complications, but diseases that manifest themselves in this way can.
The most common causes and their complications :
- Plaque – caries;
- Periodontal inflammation – osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- Injuries and inflammations of the mucous membrane, inflammation of the pharynx - abscess;
- Sinusitis – spread of purulent focus, sepsis;
- Mumps – abscess of the salivary gland, inflammation of other exocrine glands;
- Inflammation of the lacrimal canal – spread of inflammation, conjunctivitis;
- Dehydration – increased dehydration, arrhythmia, death;
- Kidney pathologies – renal failure;
- Allergy – anaphylactic shock;
- Hormonal disorders – increased hormonal disorders;
- Gastritis and ulcers - perforation of the ulcer, rough scars, narrowing of the pylorus;
- Diabetes mellitus – pathologies of blood vessels, retina, kidneys.
Most of them do not develop instantly - the patient and doctor have time to notice alarming symptoms and take action in time. These conditions are life-threatening when left untreated or treated incorrectly.
Causes and treatment of unpleasant taste in the mouth:
Hydrogen sulfide taste
Such an unpleasant taste, like the taste of a rotten egg, suggests the presence of gastritis or a peptic ulcer caused by Helicobacter in your stomach, which can be detected by probing.
This can also signal stagnation of food in the stomach and the process of fermentation and rotting. Another taste of hydrogen sulfide may indicate a narrowing of the outlet of the stomach in the event of post-ulcer scars and tumors.
Therefore, in isolated cases, you can take an enzyme tablet to improve the digestion process, but in case of repeated signals, you cannot do without a doctor. And the sooner you meet him, the better.
Read also: Actors of the series 13 Reasons Why
Dumping syndrome
Poor condition after eating may be due to dumping syndrome.
This pathology develops after surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract. It consists of excessively rapid evacuation of food from the stomach to the intestines. Develops in 30% of cases as a complication after resection. The main symptoms of dumping syndrome develop either immediately after a meal or during a meal:
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach
- Weakness, decreased vision
- Pain, burning in the epigastrium
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache
- Noise in the ears, sudden surges in pressure
- Increased gas formation
- In severe cases - up to the development of coma
The degree of severity depends on the time factor. The more time passes after the intervention, the less pronounced the symptoms become.
Oral hygiene
A common cause of a salty taste in the mouth is poor oral hygiene. If a person does not brush his teeth well enough, if plaque forms, all this contributes to the development of pathological microflora, the waste products of which will give this unpleasant salty taste.
Also, the appearance of taste is influenced by the presence of an infectious process in the oral cavity - the formation of tartar, fistulas, chronic tonsillitis.
Taste of illness. How to determine your diagnosis by the taste in your mouth Read more
Read also: It’s very difficult for me to live
Weakness after eating
Weakness after eating can cause hypoglycemia.
Feeling bad after lunch or dinner? This can be a symptom of various pathological conditions. Causes of discomfort:
- Hypoglycemia – a sharp drop in blood glucose
- Hyperglycemia – elevated blood glucose levels
- Dumping syndrome
- Thyroid diseases
- Pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, ulcers, enteritis
All these conditions require examination, treatment and follow-up by a doctor.
Reason: dehydration
If you have a salty taste in your mouth, then it’s time to calculate how much clean water you drink per day. Because it is the imbalance of fluid in the body that often becomes the answer to the question of why the salty taste bothers us. Our saliva contains sodium chloride, in other words, it is ordinary salt. When fluid is lost in the body, blood and saliva thicken, causing dry mouth. Saliva undergoes a process of dehydration, causing it to contain more salt and less liquid and other useful minerals. The more severe the dehydration, the more clearly the unpleasant symptom appears.
The cause of dehydration could be a low-carbohydrate diet, taking diuretics, poisoning and indigestion, drinking alcoholic beverages, drinking too much strong coffee or soda, or smoking a large number of cigarettes. Dehydration can develop during intense physical activity, after spending a long time in the scorching sun or in hot, stuffy rooms.
An imbalance of fluid in the body often causes a bothersome salty taste.
When dehydrated, the taste of salt may be accompanied by other alarming symptoms: weakness, dizziness, thirst, rare urination, diarrhea. The first thing to do in such a condition is to drink as much liquid as possible, in particular clean water. It’s better to generally make it a rule to drink at least one and a half or two liters of water a day every day. This is approximately 8 glasses. However, in cases where the body suffers from dehydration, this figure can be safely increased. For example, lovers of strong coffee drinks who drink up to 5 mugs of coffee a day should regulate the balance of healthy fluids in the body by taking 2-3 glasses of clean water more than those who are not fond of coffee.
Chest trauma and esophagus
When a coma appears in the esophagus, a cause such as chest injury cannot be ruled out. This could be a bruised sternum, fracture or cracked rib. Soft tissues suffer during a fracture, their trophism is disrupted, and swelling appears, which is positioned as a lump in the esophagus. In case of a chest contusion, a dangerous complication may initially be unnoticed internal bleeding.
If the feeling of a coma in the esophagus is accompanied by a symptom such as the appearance of bruises under the skin or a deterioration in the general condition, it is necessary to urgently consult a traumatologist and call an emergency ambulance.
A lump in the esophagus can be a symptom of a variety of diseases and conditions, both dangerous and those that do not require significant medical care. Only a doctor can correctly assess the condition, prescribe examination and treatment, and you should contact him if these sensations appear.
The reason is tears
Another interesting reason may be related to the pathology of the tear ducts. It would seem, how are the eyes and the salty taste in the mouth connected? In fact, if there is a disruption in the functioning of the tear ducts, increased secretion of tears may occur; on the other hand, the normal passage of this tear content is also disrupted. As a result, the tear enters the nose, then it flows down the back wall of the throat, and a feeling of saltiness occurs in the mouth. Pathology of the lacrimal glands (ducts) can provoke a salty taste in the mouth.
Why does a metallic taste appear in the mouth? More details
Diagnostics
If a salty taste in the mouth appears against the background of relative health, treatment should begin by contacting a dentist .
A preventive examination is free in most clinics, and it is this procedure that will help identify dental problems. The doctor will see tartar deposits, periodontal disease, and mucosal injuries. If they are the cause, then he will prescribe treatment; if not, then he will have to continue visiting doctors. If the problem definitely does not lie in the oral cavity, or there are symptoms pointing to other organs - for example, a nasal voice or lacrimation, then you need to continue the examination with a therapist. The doctor will begin the diagnostic process with a detailed interview and examination of the patient. A mandatory procedure is palpation of the salivary glands and nasal sinuses.
This allows you to identify or exclude mumps and sinusitis. You should prepare for the fact that the diagnosis will take more than one day - this symptom is too multifaceted for the pathology to be easily identified. The result of an examination by a therapist is a referral for tests and to a specialized specialist (or several doctors).
Tests needed to determine the causes of salty taste in the mouth:
- General and biochemical blood tests - detect dehydration, disruption of the supply of any substances, inflammatory processes, allow you to indirectly assess the functioning of the kidneys, liver, and digestive system;
- General urine analysis - helps to determine dehydration, impaired renal function, including diabetes;
- X-ray and ultrasound of the sinuses and salivary glands - allows you to exclude or confirm the inflammatory process;
- Blood test for hormones - identifies the cause if it lies in the area of hormonal imbalances;
- If kidney pathology is suspected - kidney ultrasound, contrast radiography, scintigraphy;
- Blood test for glucose and ketone bodies if diabetes is suspected;
- CT scan of the head if sinusitis is suspected; the same analysis can reveal tumors of the nervous system;
- FGDS for suspected gastric pathology.
The doctor may supplement the examination if there is not enough information to make a diagnosis.
If the patient already has any chronic disease associated with hormonal levels, impaired immunity, the gastrointestinal tract, or the urinary system, then he should contact his doctor. The examination algorithm is similar in both cases.
If a salty taste appears while taking medications, then you need to contact the doctor who prescribed the medicine.
3 signs in your mouth that warrant a trip to the doctor:
Reason: ENT diseases
The salty taste sometimes has rather trivial causes: for example, bacterial sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis or a cold. During inflammation, mucus appears in the sinuses, which consists of mucin protein, salt, nucleic acids and water. In the acute course of the disease, snot flows down the walls of the nasopharynx into the throat, and accordingly, a feeling of salt occurs. With sluggish inflammation of the ENT organs, mucus is also constantly disturbing by its appearance in the mouth.
ENT diseases also contribute to the appearance of a salty taste
Lump in the esophagus as a symptom of digestive system disease
Most often, a lump in the esophagus is a gastrointestinal problem
This reason for the appearance of a coma in the esophagus is the most common among other pathological conditions. Problems with the muscle sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach can cause stomach contents to back up into the esophagus. The acidic environment of gastric juice, which contains half-digested food, is irritating to the walls of the esophagus, which is not adapted to such contents.
This pathology is called a symptom of reflux exophagitis, it is accompanied by heartburn, and if repeated frequently, it can lead to the development of a malignant tumor of the esophagus. To clarify the diagnosis, a gastroscopy and consultation with a gastroenterologist will be required. If the treatment prescribed to them does not lead to positive results, it is possible to perform surgery on the muscle sphincter.
A hiatal hernia can cause a lump in the esophagus. It is accompanied by heartburn, chest pain and frequent, uncontrollable hiccups. The physiological reason for this condition is displacement of the diaphragm muscles due to prolonged coughing, frequent constipation, excess weight, hereditary predisposition, and mental stress.
The hernia must be distinguished from disorders of the cardiovascular system and qualified treatment must be carried out. An untreated hernia can cause reflux esophagitis.
Dehydration
When the body loses too much fluid, such as after severe diarrhea or vomiting, saliva thickens and becomes salty due to the increased concentration of mineral salts in it.
What to do?
To prevent dehydration, doctors recommend drinking 1.5 to 2 liters of fluid per day. In case of severe dehydration, special solutions are prescribed to restore the water-salt balance.
Treatment of stomach discomfort
What to do if you have stomach discomfort?
To alleviate the condition you may need:
- diet;
- assistance with medicines.
To learn more
If discomfort or heaviness in the abdomen is associated with a lack of digestive enzymes, then taking enzyme preparations may be necessary. These drugs support digestion by delivering the same enzymes from the outside. Creon® is available in capsule form and is suitable for this task. The Creon® capsule quickly dissolves in the stomach, releasing hundreds of small particles - minimicrospheres1. Due to their small size, they evenly cover the food in the stomach to help in the digestion of its volume. This helps the body obtain the necessary nutrients from food and cope with symptoms such as heaviness and discomfort in the abdomen, bloating, and gurgling. This mechanism of action distinguishes Creon® from similar drugs in tablet form.
A tablet is an indivisible form of release that cannot be properly mixed with food in the stomach, and therefore cannot help in its complete digestion. The idea that a tablet can be crushed is erroneous, since this will lead to a breakdown of the protective coating of the drug, and the enzyme will simply die in the stomach.
You can find out more about the differences between Creon® and other drugs here.
In the fight against heaviness or discomfort, as a rule, 1 capsule of Creon® 100001 helps. Creon® capsules are easy to use: if necessary, you can open them and mix minimicrospheres with food or juice1. This way you can individually select the dose, which is especially important for young children, for whom Creon® is approved from birth1.
How to treat loss of taste
To quickly restore your sense of taste, you should consult a specialist to diagnose the cause of the disease. Depending on the factor contributing to the loss of taste, appropriate treatment is prescribed:
- Dryness in the mouth, accompanied by insufficient secretion of saliva, will be eliminated by drugs that help moisturize the oral mucosa. For this purpose, artificial saliva preparations are prescribed - Salivart, Mouth Kote.
- In addition to medications, you can use mouth rinses . They not only moisturize the mucous membrane, but also have an antibacterial effect.
- If the loss of taste is associated with fungal infections of the mouth , drugs for candidiasis are prescribed - Clotrimazole solution, Decamine ointment.
- When diagnosing a lack of Zinc and vitamin B12 in the body, Zincteral, Berocca, and intramuscular injections of cyanocobalamin are prescribed. Additionally, multivitamin complexes may be prescribed.
- restore taste perception . The leaves of peppermint, lemon balm and motherwort have a sedative effect and eliminate the main cause of pathology - neurosis. When the oral cavity is infected with a bacterial or fungal nature, rinses made from chamomile flowers, calendula and oak bark are used.
- To increase the spiciness, you need to add spices to your food such as cloves, cinnamon, mustard and lemon.
Photo 2: Regular cleaning of the surface of the tongue reduces the risk of loss of taste. Source: flickr (Gabriella Yazickr).
Associated symptoms and what they indicate
By looking at various accompanying symptoms, you can understand what is happening to the body and how serious it is. It should be remembered that self-diagnosis does not provide a comprehensive result - its task is to determine how urgently you need to see a doctor, or whether the problem can be solved on your own. In any case, in emergency conditions, an unpleasant taste is the last thing the patient pays attention to.
If this symptom worries the patient, it means there is time for self-diagnosis.
| Symptom | What is he talking about? |
| The taste is constant | This situation occurs when there are problems in the oral cavity or neighboring organs, and the process is chronic. The constant flow of blood, mucus, tear fluid or pus creates unpleasant sensations. The same situation occurs with abuse of salty foods, alcohol and dehydration. |
| Taste appears in the morning after eating | This is due to the characteristics of the products. Smoked meats and pickles for breakfast create a lasting aftertaste for a long time. Coffee or strong tea can have the same effect due to dehydration. |
| Taste in the morning | This may be a reaction to dental care products. More serious causes are stomach pathologies that cause reflux of contents, belching, and heartburn. In this case, the symptom appears in the early morning when the patient wakes up. |
| Salty saliva | This symptom is observed with dehydration, excess salty foods, pathologies of the salivary glands, kidney diseases, and diabetes. |
| The taste of salt on my lips | Associated with inflammation, damage to the lip mucosa, excessive sweating, allergies, and lacrimation. |
| Salty teeth feeling | Occurs when hygiene standards are violated - this is the taste of mineralized plaque. |
| Sweet-salty taste | Appears with dehydration, pregnancy, chronic inflammatory processes, and sometimes bleeding. Often not related to the sugar content of substances that enter saliva. |
| Bitter salty taste | Occurs with pathologies of the salivary glands, pyloric diseases, gastritis, gastric ulcers, kidney diseases, diabetes, poisoning. |
| Sour-salty taste | Associated with GERD, damage to the esophagus, poor hygiene, and dehydration. |
| Food seems salty | This effect occurs with a combination of dehydration and insufficiently moist food, and mental illness. |
| A cough appears | A sign of an inflammatory process in the throat, severe dehydration (cough when swallowing). |
Taking medications can cause any shade of salty taste - this is an individual reaction. If the discomfort is very disturbing, or other symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor - you may need to find another remedy or change the dosage.
Infections
Caries, gingivitis - each such infection without proper treatment can progress and lead to serious complications and consequences that affect many organs and systems.
With serious gum diseases such as periodontitis, patients are concerned about the following symptoms:
- tooth mobility;
- the formation of pathological gum pockets and purulent discharge from them;
- pain, burning and other unpleasant sensations in the gums;
- persistent bad breath;
- formation of massive dental plaque.
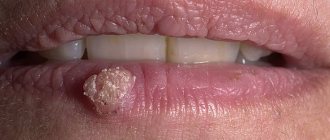
A fungal infection, which is characterized by the appearance of a white cheesy coating on the mucous membrane, can also provoke a salty taste in the mouth. With moderate and severe infection, patients may complain of a change in the taste of their usual food and the appearance of off-flavors.
HPV, the human papillomavirus, can infect the mouth and cause a strange taste in the mouth. If the diagnosis was not carried out on time and there is no treatment, this can cause a metallic and salty taste in the mouth.
Treatment depending on the identified cause
Treatment depends entirely on what is causing the salty taste in your mouth. There is no point in fighting the symptom - it will constantly return. Moreover, such actions are dangerous, since the pathological process continues if it is not stopped.
If the cause is tartar, the dentist will prescribe its removal or professional cleaning. This is not only a way to whiten your teeth, but also solve hygiene problems. It is recommended to repeat this procedure only at certain intervals, and it does not replace proper dental care. If the problem is something else, then appropriate means are used.
Medicines (tablets, ointments, solutions, injections)
Etiotropic ones are used, i.e.
affecting the cause, and pathogenetic agents that stop the pathological process. Medicines for the actual salty taste in the mouth are not used - this is impractical. Antibiotics are prescribed if there is a bacterial infection and the causative agent is identified. Used for sinusitis, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, mumps, inflammation of the lacrimal canal.
Dosage forms:
- Local – dental ointments, solutions for rinsing the mouth and throat, eye drops, nasal drops;
- Tablets - used when there is a high risk of complications and spread of infection;
- Injections - most often inside the sinuses. In severe cases, intramuscular or intravenous administration of antibiotics.
The same rule applies to all antimicrobial and antifungal agents - the course of treatment should be at least 5 and no more than 10 days . Broad-spectrum agents are usually prescribed.
Antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs are prescribed for allergies . Depending on the type of irritant, medications can be taken in advance before contact with the allergen, in courses during a dangerous period, or urgently when symptoms appear.
In case of hormonal imbalances, medications are prescribed that return hormonal levels to normal. Selecting an appropriate treatment regimen will take time, since the body's reaction is individual.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are classified as pathogenetic. They are prescribed for bacterial, fungal and viral infections, allergic reactions . Their task is to stop the pathological process. Effective in combination with etiotropic drugs. The forms of administration are varied - these are dental ointments, rinses, throat sprays, eye drops, nasal drops, oral powders, tablets, etc.
For chronic diseases, medications are prescribed to slow down the pathological process. The complete list of medications can be very extensive and depends on the course of the disease in a particular patient. Among the chronic diseases manifested by a salty taste are diabetes mellitus, gastritis and peptic ulcers, GERD, and chronic renal failure. Their treatment regimens are completely different.
In case of early stage dehydration, the patient is recommended to normalize the drinking regime. To normalize fluid metabolism, rehydron is prescribed - a drug with electrolytes in powder form. It is advisable to drink mineral water, limit tea and coffee. If these measures do not help and the pathological process develops, hospitalization and intravenous fluid administration are required.
Folk recipes
These are symptomatic remedies that will help temporarily get rid of the problem, but will not help cure it.
Traditional medicine recommends various herbal rinses that will restore normal sense of taste. Among the popular recipes:
- Chamomile;
- Sage;
- Eucalyptus;
- Oak bark;
- Calendula.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth with an infusion of these plants (separately or in a mixture) every 2-3 hours. Doctors do not recommend combining traditional methods with treatment with sprays and dental ointments - this reduces the effectiveness of the drugs. Traditional rinses are useful for patients with chronic diseases, for whom the salty taste is not the main, but unpleasant symptom. In pregnant women, unless a more serious cause is identified, the use of rinses will also be effective.
Diet
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that significantly increase the secretion of salt and increase the amount of fluid.
Authorized products:
- Fruits and vegetables – up to 50% of the diet;
- Cereals;
- Coarse bread;
- Meat – chicken or turkey;
- Lean fish;
- For sweets – dried fruits, walnuts, honey (if there is no inflammation in the oral cavity);
- Milk;
- Mineral water;
- Fruit and vegetable juices;
- Compotes, jelly, infusions;
- Vegetable oil.
It is permissible to prepare food in any way, except for salting, marinating and smoking, the main thing is to observe the measure in adding salt. The list of prohibited foods includes salted and pickled vegetables, smoked meats, canned food, sausages, most cheeses, any salty foods, alcohol, tea and coffee. Other products are added as desired, but in small quantities.
If the patient suffers from chronic diseases and has already been prescribed a diet, then the menu is selected based on all the recommendations. The right diet is not decisive in getting rid of an unpleasant symptom if it is not caused by the abuse of salt and alcohol.
Sour-salty taste
This symptom may be a warning of chronic or acute kidney failure, a condition in which the kidneys do not work properly and the body cannot eliminate toxins from the body. In severe cases of renal failure, a taste appears and the smell of the mouth changes. You may smell urine.
In addition to these symptoms, weakness, weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting warn of the development of chronic renal failure and irreversible damage to the body. The person becomes drowsy, headaches and muscle pain occur.
Chronic renal failure
A urologist can diagnose kidney failure. To do this, you will need to take blood and urine tests and examine your kidneys. In some cases, you even need to do a biopsy.
Hypoglycemia after eating, causes and symptoms
Diabetes mellitus can cause hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia is a decrease in blood glucose levels less than 3.33 mmol/l. The condition is critical and requires urgent hospitalization due to the risk of developing coma. This pathology occurs both in patients with various diseases and in completely healthy people. Causes of hypoglycemia that develops after eating:
- Rapid emptying of the stomach and intestines after surgery
- Taking galactose against the background of galactosemia is a metabolic disorder in which galactose is not transformed into glucose
- Long-term intake of fructose
- Excess leucine due to increased sensitivity to this amino acid
- Early stage of diabetes
Other types of hypoglycemia are characterized by gradual development of symptoms and do not depend on food intake. The symptoms of this pathology begin to be felt when the glucose level decreases by only 0.33 mmol/l:
Salty taste in mouth
This is the first sign of dehydration. When a person drinks little water or takes diuretics, the fluid in the body thickens. It’s the same with saliva – salty sodium chloride accumulates in it. Or maybe you're just eating too much salty food - chips, crackers, salty sticks?
If the problem is related to dehydration, drink at least 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day, and in the heat - another 1 liter. At the same time, give up alcohol, including beer. Avoid drinking coffee, tea, energy drinks and weight loss shakes. All of these drinks have diuretic properties.
Very often, a salty taste occurs when the salivary glands are blocked. Then you will need to visit a dentist.
A salty taste in the mouth is a sign of dehydration.
Digesting food is hard work for the body.
Digestion of food
It was tasty and interesting for you, but for the body the process of digesting food is hard work. Although food is crushed in the mouth, it can stick together into a dense lump in the stomach. Blood actively flows to the digestive organs, while other organs begin to experience a lack of oxygen.
Additionally, pressure in the small intestine increases, and the production of catecholamines - mediators and hormones that are involved in metabolism - is activated. This causes weakness and sometimes nausea.
A common occurrence is drowsiness after eating. This effect is associated with changes in blood glucose levels. If you have risen, we are happy, energy is in full swing and we want to live. If it has decreased, then we want to sleep or just lie idle.
Diagnosis and treatment of salty taste in the mouth
The development of prolonged saltiness in the mouth requires contacting a doctor. Remember that this symptom can be either a consequence of eating over-salted foods or a symptom of serious diseases.
To identify the cause of salinity in the mouth, the doctor collects an anamnesis, examines the patient, and prescribes a series of tests and examinations. Depending on the examination results, the patient is prescribed adequate treatment if necessary.
| Cause of salty taste in mouth | Treatment |
| Diseases of teeth and gums | Consultation with a dentist, sanitation of carious cavities, strengthening of gums with physiotherapeutic procedures and herbal medicine |
| Diseases of the nasopharynx | Rinsing the nose with saline sodium chloride solution, instilling vasoconstrictor nasal drops, therapy with antiviral agents. For diseases of the tonsils, gargling, the use of local antiseptics and absorbable tablets are prescribed |
| Upper respiratory tract diseases | Ambroxol-based expectorants, drinking plenty of fluids, chest massage during the recovery process |
| Diseases of the nervous system and blood vessels | Drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain, antipsychotics, injections of B vitamins, fibrinolytics if necessary |
The prognosis is generally favorable, but only if the patient does not self-medicate or ignore symptoms, but immediately consults a doctor
Why does food seem too salty?
Each person has their own taste preferences. Some people like sweets, some like salty, some like bitter. There are times when you want something to such a state that it is impossible to endure.
Why do people have certain preferences? Most often, people are faced with the fact that they want something salty. All food seems under-salted; you want to add salt to any food, even bread. And it’s better not to think about pickles, tomatoes and herring at all. Such whims are not without reason.
If such symptoms occur, the body seems to warn the person that he is missing something.
Why is salt needed?
For some people, salty cravings are associated with pregnancy. Why such a stereotype arose is not difficult to guess. As soon as a woman mentions that she wants something salty, everyone around her looks at her belly. But if the irresistible desire to eat salty foods affects representatives of the stronger half of humanity, then many are at a dead end.
The question may arise: can the human body really need salt? What might he be missing if some people are able to do without it altogether? The answer they will hear will be positive. Salt is responsible for the normal functioning of many important systems of the human body. In the scientific world, salt is better known as sodium chloride.
Why is salt so important for the body?
- It takes part in acid-base metabolism.
- If this element is normally contained in a person’s blood, red blood cells work at full capacity, supplying oxygen to all tissues.
- Together with potassium, sodium promotes the penetration of dextrose and amino acids through cell membranes. In other words, this is what the proper nutrition of the body’s cells depends on.
- This element is also directly involved in the functioning of the nervous system. With its help, the nerve endings receive the necessary information and transmit it further directly to the nerves and muscles.
- Sodium is responsible for the absorption of nutrients by the walls of the intestines and kidneys.
- Normalizes the secretion of gastric juice.
- This may seem strange to many, but salt affects the functioning of the genitourinary system.
- Sodium is one of the most important components of bones, muscles, blood, and intercellular fluid.
Not enough salt or too much? This can cause the body to stop functioning normally. When there is a lack of sodium, the following happens.
- Blocking the passage of nerve impulses to the cerebral cortex, as a result of which the individual begins to gradually become dull.
- Weakening of the effect of electrolytes. Characterized by problems with the perception of information and inappropriate behavior.
- Lack of sleep.
- Weakness.
- Loss of coordination.
- Dehydration.
- Blood thickening.
- There is a risk of developing diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Causes of cravings for salty foods
So why do you want salty foods? Often this desire is pathological. I always want salty food. This problem is provoked by diets, poor nutrition or metabolic disorders. In some cases this may be temporary. The desire for salty foods is especially common in pregnant women.
Pathology
How can you understand that the body is pathologically lacking salty foods? Some symptoms indicate this. In a person who is low in sodium:
- the skin dries out and its elasticity is lost prematurely;
- muscle weakness is felt;
- Nausea begins;
- tachycardia;
- loss of appetite;
- problems appear in the functioning of the nervous system and kidneys.
Here the person's guilt is obvious. Why is this happening? The main reason that there is not enough sodium is strict, often incorrectly selected diets, which can cause metabolic disorders.
Adhering to some diets, a person completely excludes from his diet not only salt, but also all products that contain it. He is forced to give up seafood, cheeses, mineral water, tomatoes, legumes and other products. The result of such diets is problems that arise in the body.
The body craves salty foods due to the following problems:
- accelerated metabolism;
- it lacks some micro- and macroelements;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- some infections affecting the genitourinary system.
People who are constantly stressed can also crave salty foods. Everything around them seems bland - life, work, and food included. A certain drive is missing. A person strives to revive all sensations, trying to add salt to everything.
Source: https://limto.ru/pochemu-eda-kazhetsja-peresolennoj/