From this article you will learn:
- best toothpaste for bleeding gums,
- selection of toothpastes for periodontal disease,
- Which toothpaste – Parodontax, Lacalut, etc. helps better.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Therapeutic toothpaste for gums should contain special components that will reduce pain and bleeding when brushing your teeth, as well as a number of anti-inflammatory components. There are now a huge number of anti-inflammatory toothpastes on the market, which are very difficult for the average consumer to navigate. For example, despite the fact that all these toothpastes are positioned as “anti-inflammatory”, in fact they will act differently on such a symptom as bleeding gums.
Toothpaste for bleeding gums should first of all contain astringent components such as aluminum lactate or zinc lactate. The effectiveness of which you will notice after 1-2 applications. As for other components, anti-inflammatory toothpastes for periodontal disease usually include antiseptic chlorhexidine (0.05-0.25%), mineral salts, allantoin, bisabolol, thymol and eugenol, phenyl salicylate + medicinal plant extracts.
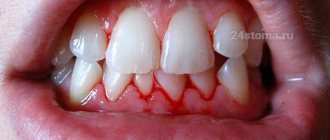
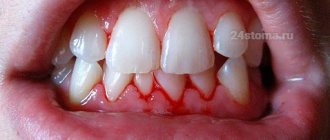
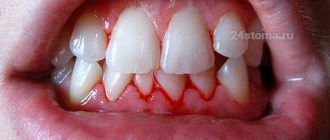
Bleeding gums -
One of the most famous remedies for inflammation and bleeding gums is Parodontax gum toothpaste. Below we will give detailed reviews of it, but in our rating it is far from 1st place. The rating was compiled based on an analysis of the composition of the products, as well as thanks to the 10 years of work experience of the author of the article - a periodontist (documents on advanced training of the state standard in the Periodontology program - can be viewed in the editorial section).
Also in this article we will look at the side effects of long-term use of toothpastes with antiseptics. You will be surprised, but in patients with cardiovascular pathology, they can even lead to increased blood pressure. It is also not unimportant that the use of toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is not compatible with antiseptic rinses with chlorhexidine solution. And we justify all this with references to clinical studies.
Choosing a toothpaste for gums – summary
If the main symptom of gum inflammation is bleeding, it is better to use pastes of the Lacalut and President brands, because they contain components such as aluminum lactate and zinc lactate. The latter very quickly reduce bleeding gums, but keep in mind that such toothpastes (as well as toothpastes with the antiseptic chlorhexidine) are ideally undesirable to use for more than 2 weeks. And after this period, it is worth switching to toothpaste without antiseptics and antibiotics, for example, Paradontax toothpaste.
But precisely during the period of acute manifestations, in order to quickly relieve inflammation in the gums, special gum rinses can be a good addition to anti-inflammatory toothpaste. Many of them contain high concentrations of anti-inflammatory components, which can eliminate bleeding gums even faster (than if you use only one toothpaste). Such rinses are also divided into those that can be used for a short course, and those that can be used on an ongoing basis.
Important: next, a very important point for patients who are going to use anti-inflammatory toothpaste for gums - in parallel with antiseptic mouth rinses with chlorhexidine solution. Clinical studies (source) have shown that chlorhexidine can be inactivated by the oral hygiene component sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), which is present in most toothpastes.
This is of great importance because... rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine solution is usually recommended after oral hygiene (morning and evening). Studies have found that after brushing your teeth with a paste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, ideally 2 hours should pass (at least 30 minutes, but this is not enough) so that lauryl sulfate does not affect the effectiveness of chlorhexidine. Therefore, if you are going to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine at the same time, we recommend buying toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS).
How do the first signs of gum inflammation appear?
The beginning of the inflammatory process of the gums can be recognized by the following signs:
- the presence of swelling or swelling of the gums;
- pain while eating;
- white plaque on the gums and mucous membranes;
- noticeable deposits (plaque) on the surface of the teeth;
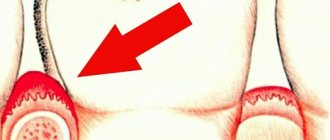
- discoloration of periodontal tissues - slight bluishness or redness;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- temperature increase.
If you have these signs, you should visit your dentist. This will help avoid serious consequences. If inflammation is caused by dental plaque or improper installation of crowns, then you cannot do without the help of a specialist.
Correctly chosen toothpaste will help to quickly alleviate the manifestations of the inflammatory process, as well as ensure the prevention of bleeding.
Side effects of toothpastes with antiseptics -
We urge you to be careful when using toothpastes that contain the antiseptic chlorhexidine (especially if its content is 0.1% or higher). Providing an antimicrobial effect on certain types of pathogenic bacteria, chlorhexidine leads to a total change in the ratio of different types of microorganisms in relation to each other. Scientific studies (source) found that with long-term use of toothpastes with chlorhexidine, the number of bacteria in the oral cavity increased, which were characterized by more active production of lactic acid.
Accordingly, this led to an increase in the content of lactic acid in the oral fluid (saliva), and a shift in pH to the acidic side. At the same time, this led to a decrease in the buffer capacity of saliva, which reduces the ability of saliva to neutralize acids secreted by cariogenic bacteria. This is important because the acidic pH of oral fluid promotes demineralization of tooth enamel (leaching of calcium) and, accordingly, increases the risk of developing caries.
Important for patients with cardiovascular pathology –
Unfortunately, these are not all the side effects of chlorhexidine. The fact is that this antiseptic disrupts the ability of oral bacteria to convert nitrates (contained in foods) into nitrites. This bacterial activity is called “nitrate-reducing,” and it is one of the mechanisms that allows our body to maintain normal blood pressure. Nitrites produced by bacteria enter the blood, helping to lower blood pressure.
Accordingly, a decrease in the production of nitrites by oral bacteria will lead to an increase in blood pressure, which is especially dangerous for people with existing cardiovascular pathology. These data are confirmed by scientific research - “The increase in plasma nitrite after a dietary nitrate load is markedly attenuated by an antibacterial mouthwash. Nitric Oxide" (2008), authors – Mirco Govoni, Emmelie Å. Jansson, Eddie Weitzberg, Jon O. Lundberg. And if you wish (via the link above), you can familiarize yourself with this study using a browser translator.
Let's sum it up
Pastes for the treatment of gum disease only eliminate some signs of inflammation. If the cause of periodontitis and periodontal disease is tartar, areas of over-occlusion, or any specific type of infection, the disease will not go away. The use of medicinal pastes and self-medication will only blur the clinical picture of the disease and complicate the diagnosis.
The negative point in using such products is that they can mask serious gum diseases, removing symptoms such as redness and swelling. As a result of this use, a person goes to the dentist only at that stage of the disease when the teeth become mobile. You should not fight bleeding gums for a long time only with the help of pastes. When you go to the dentist, treatment may be limited to just removing tartar. No toothpaste will help you treat your gums if you brush your teeth incorrectly and use a low-quality toothbrush. If your gums bleed and hurt when brushing, use a brush with soft bristles, which will make the procedure more comfortable.
Pay attention to the composition of toothpastes; if they contain antiseptics, they should not be used for more than two weeks. Otherwise, dysbacteriosis will occur, against which the fungus grows very well. After completing the cleaning, it is advisable to hold the cleaning solution in the oral cavity for 1-2 minutes and prolong the effect of the active components on the inflamed tissues.
Important instructions for use –
The cause of gum inflammation is soft microbial plaque and hard dental deposits.
If you decide to reduce inflammation in the gums only with the help of toothpaste (without removing plaque from the dentist), you will only get a temporary effect. You should not use toothpastes for inflammation in the gums or for bleeding gums on an ongoing basis, because they only mask the symptoms of inflammation. And in fact, the inflammation will continue, but only imperceptibly, leading to the gradual destruction of the periodontal attachment and the appearance of tooth mobility. Therefore, the best thing you can do for your gums is to have your teeth ultrasonic cleaned by your dentist. This procedure will remove supra- and subgingival dental plaque, which is the cause of gum inflammation. The use of anti-inflammatory toothpastes for periodontal disease (without removing dental plaque) will lead to sluggish chronic inflammation. At first it can only be gingivitis, which over time will certainly turn into chronic generalized periodontitis, in which tooth mobility and suppuration from periodontal pockets are already observed.
Video about gum diseases
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
Consulting specialist
Orlova Elena Vladimirovna
Doctor rating: 9.5 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 33 years
What should you pay attention to when choosing a product?
Toothpastes used for bleeding gums are aimed at eliminating the causes that cause this condition.
This could be a vitamin deficiency, infections, allergic diseases, or poor oral hygiene. To avoid these troubles, you need to choose the right paste.
It is recommended to consider:
- Pastes used for therapeutic purposes from preventive ones differ in the high content of active components of aggressive origin.
Purpose. They can be therapeutic or prophylactic. Pastes used for therapeutic purposes differ from prophylactic ones in the large content of active components of aggressive origin.
- Active ingredients. For long-term use, preference should be given to products containing natural phytocomponents.
Among them, for this pathology, oak bark, aloe, ginseng, eucalyptus, calendula, sage, sea buckthorn, and sanguinaria are considered the most effective.
They are characterized by anti-inflammatory and astringent effects, tone weakened periodontal tissues and act as a natural antioxidant.
Therapeutic pastes contain chemicals that have a high therapeutic effect:
- triclosan;
- chlorhexidine;
- zinc and aluminum compounds;
- fluorine;
- hexetidine;
- bisabolol;
- allantoin.
Their high concentration does not allow long-term use. But at an advanced stage, you cannot do without medicinal pastes.
Anti-caries pastes that restore enamel
Such products are designed to combat enamel demineralization and prevent the development of caries at the white spot stage. Pastes are based on calcium compounds or fluorides. You should not use products that contain both types of compounds. The fact is that fluorine and calcium react and form an insoluble residue, which means that during cleaning no active ions are released and no recovery occurs.
Calcium-containing pastes can be used every day. They are designed to correct mild thinning of the enamel.
Fluoride-containing pastes are designed to restore seriously damaged enamel. They can only be used with the permission of a doctor, as there is a risk of getting excess fluoride in the body. This can lead to brittle bones and teeth. Such products are used no more than twice a week. For greater effectiveness, they can be alternated with calcium-containing pastes.
Pastes against tooth sensitivity
There are special toothpastes for sensitive teeth. They contain potassium chloride, potassium citrate (Twin Lotus Recipe for Sensitive Teeth, Mirasensitive hap+) or strontium chloride. These substances “clog” the dentinal tubules and reduce hyperesthesia. They also saturate the tooth enamel with minerals, the deficiency of which is most often the cause of increased sensitivity of enamel and dentin. But the most progressive substance today is considered to be hydroxyapatite (Sensitivity Control Biorepair). Its crystals are similar in composition to tooth enamel, so they effectively combine with it, restoring the natural protection of teeth. Pastes for sensitive teeth should not contain a drop of chemical bleaches and, instead of coarse calcium carbonate, should contain gentle abrasive substances with a smaller particle diameter, for example, silicon oxide. Such pastes are recommended for hypersensitive teeth, as well as for use during and/or after teeth whitening procedures.
Sensitivity Control Biorepair toothpaste