Causes
A cystic formation in the form of a capsule isolating the inflammatory focus develops against the background of the following diseases:
– pulpitis, periodontitis;
– extensive carious lesions;
– respiratory tract infections (otitis media, inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, tonsillitis);
– weakened immunity;
– difficult teething;
– bite defects;
– chronic stomatitis;
– cracks, chips of tooth enamel, mechanical injuries to teeth.
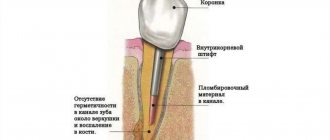
Tooth cyst (radicular cyst) - symptoms and treatment
Types of treatment for radicular cysts can be divided into conservative, surgical and conservative-surgical.
Conservative treatment
The conservative method is aimed at removing the necrotic neurovascular bundle of the tooth (pulp) and eliminating pathological changes in the bone behind the root apex.
The decayed pulp is removed with special endodontic instruments. Then the root canal is expanded and antiseptic treatment is carried out. Medicinal pastes are introduced into the root canal, which eliminate the microbial flora and restore the affected bone tissue. These pastes are administered for a period from several days to 1–1.5 months. Usually this process is well tolerated, but sometimes the pastes cause an exacerbation of the process with severe pain. To prevent the paste from getting into the mouth, the tooth cavity is hermetically sealed with a temporary filling.
If the inflammation of the bone tissue is eliminated, the root canals are filled with permanent material, and the defect in the hard tissues of the tooth is closed with a filling.
The fact is that there are no microorganisms in the cyst cavity itself. This is a response to a high concentration of microorganisms in infected root canals. After proper treatment of the canals, the number of microbes decreases and the body, with the help of cellular immunity, copes with a small number of microorganisms in the area of the root apex. The “barrier” in the form of a thin connective tissue membrane of the cyst becomes unnecessary, and macrophages completely destroy the membrane. With a small size of the cyst, rational treatment and the body’s ability to resist the disease, conservative treatment gives a good result - the shell of the radicular cyst is completely resorbed, the alveolar fascicle bone is restored.
After final treatment of the canals, it is recommended to do a CT scan after 6 and 12 months. If the cyst is completely resolved, there is no need to fear relapses, since the cause (bacterial infection of the canals) has been completely eliminated.
After root canal treatment, the tooth does not receive adequate nutrition, so it may deteriorate over time. To prevent this, it is recommended to cover pulpless teeth with artificial crowns.
If the conservative method is ineffective and the focus of destruction remains, surgical removal of the cyst is performed. This combination of methods is called conservative-surgical treatment.
Surgery
The surgical method involves removing a cyst from a previously pulpless tooth, and often the apex of the tooth root is cut off. The operation is carried out strictly according to indications: in case of a broken instrument, poor-quality treatment of the measles canal, or if the root protrudes into the cavity of the cyst. The extent of surgical intervention is determined during diagnosis.
To improve the prognosis after surgical treatment, bone defects are more often replaced with osteoplastic materials [15][16]. Such materials restore lost bone tissue and stimulate the formation of new one.
One of the main directions in modern reconstructive surgery is the use of biotechnologies, which allow accelerating the processes of regeneration of damaged tissues [17]. We are talking about platelet-derived growth factors obtained from the patient’s own blood. First, venous blood is taken from the patient. Then, using a centrifuge, the blood is separated into fractions. The platelet-rich fraction is used to restore bone tissue defects. This method is available almost everywhere.
There are two main surgical methods for treating radicular cysts: cystectomy and cystotomy.
1. Cystectomy is an operation in which the fibrous membrane of the cyst is completely removed. Usually performed in an outpatient setting under local anesthesia. If the cyst is large and affects the nasal cavity, maxillary sinus or mandibular canal, the operation is performed in a maxillofacial surgery hospital.
Surgical technique:
- Under local or general anesthesia, a section of the jaw bone in the projection of the cyst is skeletonized (exposed).
- Access to the cyst cavity is created, all affected bone tissue and the cyst shell are removed.
- According to indications, the root apex or part of it is cut off and retrograde filling of the root canal is performed (filling through the root apex) and filling of the apical openings of the canals with special cement intended for these purposes.
- The surgical wound is treated with antiseptic solutions, filled with osteoplastic material and sutured.
- Postoperative material is sent for pathohistological examination.
A dental microscope is used for treatment. It allows you to minimize the volume of removal of the root apex and effectively close the root canals.
You must visit the doctor the next day after the operation, then if the course is calm after 10–14 days, to remove the stitches. The patient should be under the supervision of the attending physician until the postoperative wound is completely healed, then return every six months to monitor the restoration of bone tissue and exclude relapse. As practice shows, relapses are rare; they are usually detected in the first year after surgery.
Types of material for filling a bone tissue defect after surgery:
- Autogenous material is obtained from another area of the patient’s bone tissue (branch of the jaw, chin, etc.). Due to its complete biological compatibility, such material is rarely rejected and quickly restores the defect. However, when the patient’s tissue is taken, the operation time increases, the intervention becomes more traumatic, which negatively affects the patient’s recovery.
- Xenogeneic material is obtained after special processing of mammalian bone tissue. The most commonly used bones are ox and pork. Processing removes substances that can cause immune and allergic reactions.
- The synthetic material contains calcium salts. For better compatibility it is often used in combination with autogenous material.
2. Cystotomy is an operation during which the cyst shell is not removed, but only its anterior wall is excised, which allows the contents of the cyst to be evacuated. With cystotomy, the scope of surgical intervention is smaller, but recovery after such an operation lasts longer (about a month). The resulting bone defect is filled with turunda with iodoform, then dressings are made with a certain frequency, replacing the turunda. This method is used less and less due to protracted recovery, the introduction of new techniques and the improvement of the material and technical base.
Oronasal (between the mouth and nose) cystectomy and oronasal cystotomy are performed if the cyst penetrates into the maxillary sinus or pushes it aside.
Surgical methods using laser technology are increasingly used in modern dentistry. Laser techniques are less traumatic. In addition, the laser has a bactericidal property, which reduces the likelihood of developing purulent-inflammatory complications [18][19][20].
Removal of a tooth. A tooth is removed only if saving it is not practical. Indications for removal:
- complete destruction of the crown part of the tooth;
- destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth below the level of the gingival margin by more than 2 mm, when it is not possible to advance the root orthodontically or when the root of the tooth is too short, which will complicate further prosthetics;
- lack of lumen in the root canal (due to structural features or previous treatment).
In all other cases, tooth-preserving operations described above are performed.
Complications after treatment
Complications after cyst removal occur infrequently. These include perforation of the maxillary sinus, damage to the inferior alveolar nerve, as well as the formation of a residual cyst, which is formed during incomplete excision of the radicular cyst.
Causes of maxillary sinus cysts
Predisposing factors for the formation of a maxillary sinus cyst are:
- Individual anatomical and topographical features of the structure of the nasal cavity, which impede the free movement of air through the nasal canals (congenital deformities, deviated septum).
- Blockage of the excretory duct of the glands located in the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinus. This happens with frequent rhinitis, sinusitis, allergic rhinitis and polyposis.
- Inflammatory dental diseases with infection spreading to the root canals. The paranasal sinuses are separated from the roots of the molars and premolars by a thin septum, so infection from pulpitic or periodontitis teeth often causes an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinus.
- The formation of a dental cyst, which grows into the maxillary sinus and continues to grow inside it.
The maxillary cyst gradually grows larger, filling the sinus without pronounced clinical symptoms. The presence of a formation can be suspected during exacerbations caused by colds, acute respiratory viral infections, local hypothermia, and decreased immunity.
Removal of retention cyst of the lower lip
dentistry teethprostheticsemax high-quality dental prostheticscrownstropedic dentistryveneersceramic inlaysprosthetic crownsHollywood smile white teethpearl teethbeautiful smileimplantationwedge-shaped defectsgingival recessiontreatment of children high-quality dentistry baby teeth colored fillings dental implantation Ankylos implantation high-quality implantation without bone tissue augmentation qualified implantation front teeth prosthetics veneers ceramic crowns Imax e.Max zirconium crowns dental prosthetics with crowns depressurization of composite restoration marginal staining re-polishing of fillings professional examination veneer tooth lightening ceramic veneers exclusive prostheticsgold inlayfront tooth single crownDamon bracesimplantTeeth crowdingOrthognathic surgery Victory bracesMEAW technique multi-loop arch IVD Sato meaw orthodonticSplint therapy wedge-shaped defect treatment of a wedge-shaped defect tooth restorationRestoration of teeth re-polishing fillings artistic restorationExtraction of the inlay remove the inlay from the rootAnchor pin preparation for prostheticsadditional canal cyst treatmentProfessional hygiene clean dental treatmentResection of the root apex Apicotomy Retrograde treatmentSingle-stage implantation Tooth implantation ImplantArtistic restoration treatment of caries Teeth cleaning One-stage implantation Ankyloses Implantation of a tooth with a crack cracked root implantation of a front tooth Ranula retention cyst wound removal save tooth tooth preservation alternative to implantation CCPD SST Ankylos Ankylos FDM implant implant wisdom tooth treatment mock-up mock-up prototyping elastics intermaxillary traction braces hygiene products implantation Astra Astra Tech Panov Mikhail Yurievich dental transplantation dental treatment treatment under a microscope treatment under a microscopeCanal treatmentHollywood smiletooth transplantationTooth extrusionTreatment without preparationTreatment without preparationTreatment tool in the tooth canal Panov Mikhail Yurievich tooth saving treatment of canals filling gum recessionSealing fissure resection of the root apexTeeth preservationIntrusionGum recessiontransplantationDental cariesSST
Retention cyst of the lower lip
It is a common pathology of the oral mucosa. It is a benign neoplasm in the shape of a ball. The pathology usually develops due to blockage of the duct of the minor salivary gland. The reason for this may be the most common injury or inflammatory process.
The cyst occurs equally in both women and men. Its appearance does not depend on age. The cyst is characterized by the ability to very quickly increase in size, which affects a person’s daily lifestyle. That is why doctors recommend removing it.
The main reasons for the appearance of cysts
The neoplasm most often forms as a result of mechanical damage and trauma to the lip. These include burns, blows and biting. As a result of constant trauma to the gland, the excretory canal becomes clogged, the secretion begins to linger, and a small tubercle forms. Gradually it fills with liquid and increases in size. The inflammatory process after injury can also lead to the formation of pathology. A retention cyst of the lower lip can occur in a person at any age. The neoplasm is often a consequence of the congenital development of the germinal components of the so-called glandular cells.
In addition to traumatic effects, the cause of a cyst can be atrophy of the excretory ducts. Typically, such a violation is caused by a tumor that directly compresses the duct, or by a scar. The latter narrows the canal, and the accumulated secretion gradually expands the glandular lobe.
How to recognize pathology?
A retention cyst of the lower lip is a capsule of connective tissue with viscous contents inside. Outwardly, it resembles a small ball. The formation is painless, but may cause discomfort while talking or eating. The cyst tends to grow rapidly and can reach up to 2 cm in diameter. The mucous membrane above it usually does not undergo significant changes. Sometimes it takes on a bluish tint, which is explained by the accumulation of contents. The ball is covered with connective tissue, and inside it there is a clear liquid resembling saliva. On palpation the formation is soft. When eating food, the capsule is easily damaged, causing its internal contents to spill out, but after that the cyst fills up again. As a rule, the formation consists of one chamber, but cases of multi-chamber cysts are known.
Diagnosis confirmation
Recognizing a retention cyst is not difficult for a qualified specialist. When pressed with a finger, the formation disappears, but after a while it appears again. A more accurate diagnosis can be made after an ultrasound examination. During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the structure of the cyst, its size and contents. By probing the canals, the width of the duct and the presence of salivary stone are determined. Only after a complete examination can a specialist recommend treatment for a retention cyst of the lower lip.
The need for differential diagnosis In order to accurately make a diagnosis and subsequently prescribe competent treatment, it is important to be able to recognize this pathology among other neoplasms of a benign nature. The following types of salivary gland cysts are distinguished: ranula; submandibular; parotid; minor salivary gland. The ranula is localized above the hyoid-maxillary muscle. There are known cases of penetration into the submandibular region. This formation is large in size. It can displace the frenulum of the tongue, thereby preventing a person from fully eating and having conversations. The submandibular gland cyst is characterized by slow development. During palpation it is easy to detect a round formation. When this cyst grows, it can involve the upper areas of the mouth. In such a situation, bulging of the formation into the sublingual part is usually observed. Pathology of the parotid gland is quite rare. The main reasons for its formation include mechanical damage, inflammatory processes and blockage of ducts. It is the same factors that provoke the formation of another anomaly of the oral cavity called a retention cyst of the lower lip (photo presented in this article). The development of pathology at the initial stage is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms. As a result of mechanical damage, a so-called extravasal cyst can form. This formation is distinguished by the fact that granulation tissue is formed around it.
What treatment is required?
This pathology is treated by a dentist. After confirming the diagnosis, there are two possible solutions to the problem. The specialist may send the patient home, believing that the formation will resolve on its own. The second option involves surgical removal of the retention cyst of the lower lip.
The operation itself lasts no more than 30 minutes and involves the use of local anesthesia. The physician assistant twists his lower lip and holds it tightly. The dentist makes several cuts along the formation, frees the cyst from its internal contents and applies sutures. According to many patients, the operation itself, under the supervision of an experienced surgeon, is almost painless. The main troubles begin during the rehabilitation period, when the retention cyst of the lower lip begins to gradually heal. The operation can be performed using a laser. However, its help is used extremely rarely due to severe bleeding and a high risk of perforation of the gland membrane.
Postoperative period
After surgery, patients are advised to treat the affected area daily with a special antiseptic solution and monitor their condition. Some note that the first day after surgery is the most difficult. Talking, eating - all these simple actions cause painful discomfort, but after about a month everything returns to normal. It should be noted that the duration of the rehabilitation period directly depends on the size of the formation. Many patients report visual distortion of the lip and slight numbness even months after surgery. To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to remove the pathology at the initial stage of its formation.
Why does a lump form on the lip?
As we said above, a retention cyst forms inside one of the small salivary glands, which are massively scattered throughout the mucous membrane of the entire oral cavity (24stoma.ru). Each such salivary gland has a thin duct that opens on the surface of the mucous membrane and allows the secretion of the salivary gland to enter the oral cavity. When this duct is blocked, the secretion of the salivary gland accumulates in its lumen, stretching the walls of the gland.
The cause of duct blockage is usually mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane. This is why patients note that as soon as they bit their lip, a lump formed. The secretion in the salivary gland is constantly being formed, and therefore the lump on the lip will constantly increase in size - until either spontaneous opening occurs, or you accidentally or deliberately bite through it. If the integrity of the cyst is violated, then you can see how a clear viscous liquid leaks out of it onto the surface of the mucous membrane.
After emptying, the cyst collapses, and for some time you do not notice it. Remember that you cannot deliberately bite or puncture such a cyst (for example, with a needle). The fact is that even if the secretion of the gland comes out, the cyst shell will still remain inside the tissue. This will result in the same cyst forming over and over again.