Causes
The cyst appears as a tumor under the cheekbone, protruding from the outside. If left untreated, inflammatory processes appear, which can lead to the formation of an abscess or phlegmon. The pathology is a rare formation, usually diagnosed before the age of thirty. Place of development - on the lips, cheeks, palate, less often - in the sublingual ducts. Very rare is the pathology of the glands that develops in the parotid and mandibular areas.
The causes of this pathology are:
- injuries, wounds of the mucous membrane;
- mucus plugs that appear in the ducts;
- stomatitis and other inflammatory processes leading to obstruction;
- formation of salivary stones;
- pressure on the ducts;
- scar type narrowing.
Causes also include developmental defects, genetic predisposition, and damage to certain tissue areas. But more often the problem develops against the background of tissue injury and inflammatory processes. Wounds are formed by frequent biting of the cheek or tongue, due to the abuse of rough, spicy food, and hot dishes. In addition, such injuries can cause gland atrophy, so they cannot be ignored.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
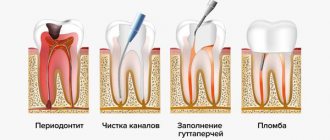
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Signs, diagnosis and treatment
Manifestations of the disease depend on the location of the cyst. Most often, these are rounded formations that slowly increase in size, elastic and soft to the touch. They do not cause pain at first, rarely exceeding 1 cm in diameter. But in the absence of treatment, cysts begin to seriously interfere not only with eating, but also during conversation. The formation may disappear if, due to an accidental breakthrough, the contents come out. However, over time, the cyst forms again; if its size becomes very large, it acquires a characteristic bluish tint.
For diagnosis, methods such as visual inspection, palpation, and a number of hardware studies are used. Ultrasound, sialography to determine the problem with contrast, MRI and CT are more often performed. Additional examination methods may also be prescribed, for example, cystography of the bladder, probing of the salivary ducts, histology. If the diagnosis is questionable, a biopsy and puncture of samples are performed.
Conservative therapy does not bring any effect; when diagnosing a cyst of this type, surgical intervention is recommended. For this, local anesthesia is used, after which the formation is removed along with the affected gland and membrane to prevent relapses. If surgical intervention is refused, the formation often develops into phlegmon, and a tissue abscess develops.
The conservative method provides only temporary results. To do this, the membrane is punctured and the contents of the cyst are sucked out. But in all cases, the formation appears again, that is, this method of therapy is not recommended, as it is ineffective.
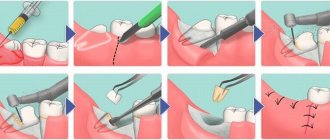
Surgery includes the following steps:
- inspection and surface preparation are carried out;
- local anesthesia methods are used for pain relief;
- the area with the cyst shrinks, which reduces blood flow and ensures stability of the tissue position;
- two oval-shaped incisions are made near the formation, after which the contents are husked;
- the affected lobes of the gland are removed, which helps to avoid complications or relapses in the future;
- the wound is sutured, thin sutures are applied, and self-absorbing sutures are often used.
The contents of the capsule are sent for additional research. This helps to eliminate serious risks, especially if the development of malignant processes is suspected. In case of serious intervention, plastic cystotomy is recommended. Typically, this situation occurs when removing a maxillary-hyoid formation.
Salivary gland cyst
Patients are concerned about a round-shaped formation, small at first, then slowly increasing, not causing pain. Sometimes, when injured by food, it is emptied, then it fills up again. Objectively: a round-shaped formation is determined under the mucous membrane of the lower lip, cheek or in another location; usually the mucous membrane above it is not changed. As the secretion accumulates, the color of the mucous membrane may acquire a blue tint; upon palpation, the consistency of the formation is soft-elastic and moves freely.
Differential diagnosis is made with hemangioma (with hemangioma, after pressing, the formation disappears, if the pressure stops, it fills again).
Surgical treatment: under local anesthesia, two bordering incisions are made in the mucous membrane above the surface of the cyst, then it is peeled off, holding the edges of the mucous membrane, and the wound is sutured with catgut.
A cyst of the sublingual salivary gland (ranula) is most often located in the sublingual area above the mylohyoid muscle and resembles a bubble filled with fluid. With large sizes, it can shift the frenulum of the tongue to the other side. Less commonly, the cyst penetrates into the submandibular region and macroscopically looks like an hourglass, located in the supra- and sub-hyoid muscle, narrowing at the site of its perforation.
Patients complain of a formation under the tongue, which slowly increases, beginning to interfere with eating and talking. It can be periodically emptied and then refilled.
Upon examination, an oval-shaped formation is detected in the sublingual area, which, if large, can spread to the opposite side. The mucous membrane above it becomes thinner and underneath it it is possible to identify a cavity filled with transparent contents. On palpation, the formation has a soft-elastic consistency, limited from the surrounding tissues by the capsule. Differential diagnosis should be made with a dermoid cyst, salivary stone disease, submandibular salivary gland cyst, lipoma, sialadenitis.
Rarely, a cyst of the sublingual salivary gland becomes infected and then it must be differentiated with an exacerbation of chronic sialadenitis and salivary stone disease with localization of the salivary stone in the excretory ducts. To clarify the diagnosis, a puncture can be performed: a viscous mucous fluid will be obtained from the cyst. To exclude salivary stone disease, a survey radiography is performed. Cystography can be used to diagnose a cyst.
Treatment is surgical. If the cyst is located above the mylohyoid muscle, then the most radical way is to remove the cyst along with the gland. However, its use is limited due to the fact that the cyst shell is very thin and easily damaged. After which the cyst is emptied, the walls of the cyst collapse and it can be very difficult to separate the cyst shell from the underlying tissues.
Therefore, the method of cystostomy proposed by I. G. Lukomsky (1943) has not lost its significance to this day. Under local anesthesia, the protruding part of the mucous membrane and the upper wall of the cyst are excised, the edges of the mucous membrane and the remaining cyst membrane are sutured around the perimeter, an iodoform tampon is loosely placed on the bottom and fixed by tying the ends of the suture material above it. The tampon is changed after 5 days.
If the cyst spreads to the submandibular region, then the operation is performed in two stages (Kabakov B.D., 1978). First, in the submandibular region, retreating 2.0 cm, and parallel to the edge of the lower jaw, an incision is made in the skin with subcutaneous fatty tissue and superficial fascia, the maximally bulging part of the cyst is isolated to the point of narrowing, it is bandaged at this level and cut off, the wound is sutured in layers, leaving a rubber graduate. Then, in the second stage, the sublingual salivary gland with the cyst is removed or a cystostomy-type operation is performed.
A cyst of the parotid salivary gland appears for no apparent reason; facial asymmetry is clinically determined due to swelling of the soft tissues of the parotid region, which gradually increases, the skin on it is not changed. Upon palpation, a formation is determined to be round in shape, soft-elastic consistency, delimited from the surrounding tissues by a membrane, mobile, no pain.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with chronic lymphadenitis and benign tumors. You can use ultrasound, puncture, sialography in combination with cystography (double contrast).
Surgical treatment: the cyst is removed within the membrane with the adjacent tissues of the salivary gland, the branches of the facial nerve are preserved.
A cyst of the submandibular salivary gland is rare; there is an enlargement of the submandibular salivary gland, slowly progressing. By palpation it is sometimes possible to identify a round formation with a soft elastic consistency. Differential diagnosis is carried out with chronic submandibulitis, lymphadenitis, and benign tumors. During puncture, a yellowish liquid with a viscous consistency is obtained, ultrasound is used, and sometimes cystography is performed.
Surgical treatment: the cyst is removed along with the gland. Cysts of the minor salivary glands are more common, and cysts of the sublingual salivary glands are somewhat less common. Parotid and submandibular salivary gland cysts are rare.
It is believed that cysts appear as a result of retention of the excretory duct, as a consequence of its injury or inflammatory process in the salivary gland and adjacent tissues. There is also a theory that cysts are congenital in origin.
Minor salivary gland cysts most often occur in the lower lip area. The cyst has a connective tissue capsule; the contents of the cyst are a viscous translucent liquid, reminiscent of stagnant saliva.
Rehabilitation, expected results
After surgery, there is slight swelling and pain at the operation site for two to three days. The doctor may prescribe medications to eliminate such unpleasant symptoms, for example, analgesics, antibiotics to avoid complications. Oral rinses using special antiseptic solutions are also prescribed.
If the healing process is normal, the sutures are removed after a week, after which a pressure bandage is applied. During recovery, it is recommended to avoid solid, spicy foods, too cold and hot dishes. Oral care also requires care to avoid damaging the operated area.
The prognosis for treatment is favorable; if therapy is carried out correctly and the patient follows all recommendations, there are no problems. But in some cases there are risks of complications. These include relapses, damage to the facial nerve or facial muscles when removing a cyst in the ear area. To reduce risks after completion of the recovery period, it is recommended to correct the shape of the tooth and install new orthodontic structures or dentures. In addition, prevention is needed, protection from injuries to the mucous membrane, and compliance with the rules of oral care.
Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.