If you suddenly have a severe toothache and the pain is throbbing, sharp, unbearable, then such symptoms may indicate tooth pulpitis. What kind of disease is pulpitis, why does it appear, how can it be cured and the tooth saved? We will answer all these questions in detail in this article. After reading the material, you will learn how tooth pulpitis occurs, what methods of its treatment are used in modern dentistry, and whether it is possible to cure tooth pulpitis at home or not.
Pulpitis of the tooth and its treatment
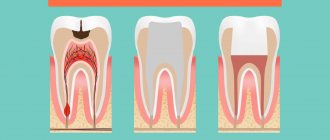
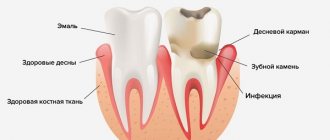
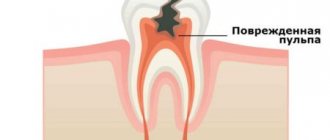
A characteristic sign of this pathology is inflammation in the pulp, which is located inside the tooth cavity, where blood vessels and nerves are concentrated. The cause of inflammation is the penetration of harmful bacteria into the cavity due to damage to the external dental tissues (enamel and dentin). This is the destruction that we most often owe to untimely treatment of deep dental caries: pulpitis becomes a consequence of the carious process. Much less often, it appears due to mechanical damage to the pulp, poor preparation of the tooth for filling, and unprofessional installation of orthopedic structures.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
In dentistry, two main methods are used to treat dental pulpitis in adults and children:
- biological - drug treatment of pulpitis with antibiotics and medications;
- surgical - treatment of pulpitis by amputation (partial removal of the pulp) or extirpation (in which the nerve of the tooth is completely removed).
The choice of technique remains with the dentist. The doctor studies X-ray diagnostic data, interviews and examines the patient. Based on these data, he selects the most rational method of treating pulpitis for a particular case.
Causes
Treatment of the disease primarily depends on the causes of its occurrence. Factors that often lead to inflammation:
- Untreated caries in a timely manner. In a mild form, the disease does not affect the pulp in any way, since the carious lesion extends only to the superficial tissues. As the crown is destroyed, caries affects all cellular structures and reaches the roots.
- Chronic periodontitis (except for mild forms). Deep periodontal pockets that form with this pathology reach the root plexuses. Pathogenic microorganisms that multiply in these cavities spread throughout the tooth and reach the pulp.
- Injury. Impact, bruise and other external influences contribute to the disruption of the established blood supply process and lead to a pathological process.
- Poor quality dental treatment. If the dentist did not clean the tooth cavity well before placing the filling, leaving carious particles, they will spread into deeper layers and reach the neurovascular bundle. Also, due to the fault of the doctor, the patient may receive a thermal burn of the pulp if the specialist neglected the rules while drilling the crown and did not cool it enough with water. The disease is also provoked by overdrying of the dentinal tubules by air flow.
- Exposure to acids, alkalis, medications, toxic filling compounds and other chemicals.
- Blood infection. Infection can penetrate into the pulp not only through carious holes, but also during sepsis.
- The patient's individual predisposition to tooth wear and the formation of mineral deposits in the pulp chamber.
Types of pathology
There are 2 main forms of the disease: acute and chronic. In the first case, a person suddenly experiences a sharp, paroxysmal pain (most often at night), which does not depend on external factors and does not go away when the irritants are eliminated. At first, a dark hole appears on the enamel, which grows over time and affects deep tissues, including reaching the canals.
If the inflammation does not go away after 3 weeks, the disease becomes chronic. Dull aching pains appear with a certain frequency and are disturbing not only at night.
Types of acute pulpitis:
- Focal. It is observed only for a few days. The pain lasts up to 20 minutes, with the intervals between attacks being about 2-3 hours. There is swelling of the gums.
- Diffuse. It extends to the coronal part, nerve endings and root. There is a disruption in the blood supply to tissues. The pain becomes throbbing and lasts much longer than with the focal form.
- Purulent. The cavity of the affected unit fills with pus. A painful pulsation is felt. The patient's condition is constantly deteriorating.
- Serous. Most often, this type is observed in children (pulpitis of temporary teeth). This is a pathology of infectious etiology, which is accompanied by short attacks of pain.
Classification of chronic dental pulpitis:
- Fibrous. Is a consequence of acute. It can proceed latently for several months with periodic periods of exacerbation. The gums are not swollen, the pain is aching and occurs infrequently.
- Gangrenous. This is a complication of acute fibrotic disease, in which the death of pulp tissue and destruction of the coronal part occurs.
- Hypertrophic. In the carious cavity, tissues of a bright red hue are clearly visible, which constantly bleed, especially when pressed.
Symptoms
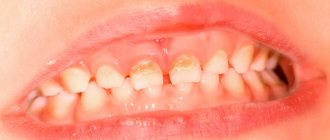
Despite the fact that each type of disease has its own distinctive features, there is a list of symptoms characteristic of all forms of pathology. At the initial stage of the disease, the tooth begins to react painfully to cold and hot, as well as to other irritants. Then a sharp throbbing pain appears, which intensifies at night and when lying down. Soreness occurs spontaneously or under the influence of irritating factors.
External manifestations of the disease, regardless of its type:
- darkening of the enamel;
- tooth mobility;
- bleeding;
- redness of the gums;
- swelling of the tissues around the diseased tooth;
The chronic form of pulpitis can be asymptomatic. It is characterized by a putrid odor from the mouth and aching pain.
Important! Very often the patient cannot understand which tooth hurts. The pain may radiate to the neck or ears. To determine the location of inflammation, a doctor’s examination and additional diagnostic tests are necessary.
Diagnostic methods
To make an accurate diagnosis, the dentist conducts and prescribes the following studies:
- inspection of the damaged cavity using a mirror and probe;
- checking the tooth’s reaction to temperature fluctuations (thermometry);
- exposure of the crown to a weak electric current (electroodontodiagnosis), with the help of which one can distinguish the disease from deep caries and determine in what form it occurs;
- X-ray.
Features of treatment
The therapeutic regimen directly depends on the stage of the disease and the location of inflammation. Treatment methods for pulpitis used in dentistry:
- Biological. Only the source of infection is eliminated, the progression of the disease is stopped, and the inflammation gradually goes away. Medicines are introduced into the cavity, which stop the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora and help eliminate inflammation.
- Conservative (vitalization). The doctor preserves the living pulp, but removes its coronal part. The tooth is completely preserved, while its functioning is restored.
- Devitalization. A special paste is placed into the drilled hole, which promotes the complete death of the pulp. The neurovascular bundle is removed, then the specialist places a temporary filling. When tissue inflammation completely disappears, the filling material is replaced with a permanent one. Devitalizing paste is used by pediatric dentists for tooth pulpitis in a child.
- Surgical. Surgical removal is divided into amputation (partial removal of pulp tissue) and extirpation (the pulp is completely removed).
Attention! The sooner the patient contacts the dentist, the higher the likelihood that the tooth can be saved. A qualified doctor will be able not only to cope with swelling and inflammation, but also to restore the integrity of the crown and restore the lost whiteness of the enamel.
Is it possible to cure a disease with folk remedies?
Pulpitis requires qualified medical care and cannot be treated on its own. Home methods for relieving pain and reducing inflammation can only temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. Without timely conservative or surgical treatment, severe complications are possible.
Possible complications
If you do not receive treatment on time or do it incorrectly, the risk of complications increases, such as:
- periodontitis (damage to hard tissues around the tooth root with pulpitis);
- periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum, or flux);
- abscess (purulent inflammation accompanied by intoxication of the body);
- sepsis (blood poisoning);
- chronic pathologies of internal organs and systems.
Preventive measures
In order to avoid long-term treatment and surgical intervention, you need to take care of the prevention of pulpitis by adhering to the following rules:
- brush your teeth 2 times a day, rinse your mouth after eating, remove plaque and tartar in a timely manner;
- visit the dentist for preventive examinations at least once every six months;
- do not use toothpicks or other traumatic devices;
- eat a balanced diet, ensure that the body receives a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals;
- give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol), large amounts of sugar and junk food;
- treat caries and other dental pathologies in a timely manner, without bringing them to severe stages.
Sharp pain radiating to the neck, temples or ears is a reason to urgently visit a dental clinic. If treatment is not started in time, serious complications are possible, including complete tooth loss and a septic process.
By following preventive measures, you can protect yourself from the occurrence of pulpitis and other oral diseases.
Biological method of treating pulpitis
If the disease has become chronic, a biological method or conservative treatment of pulpitis with calcium is used. The process involves applying therapeutic pads containing calcium preparations. The technique is also used in the following cases:
- if the pulp was accidentally exposed during the caries treatment procedure;
- when you need to strengthen the bone partition between tooth enamel and pulp.
The specialist applies a drug for the treatment of pulpitis to the site of thinning bone tissue and thereby strengthens it. Next, the tooth is filled and monitored over time, conducting X-ray examinations at certain time intervals. The method is suitable:
- children with baby teeth;
- patients under 30 years of age during the treatment of reversible pulpitis;
- everyone who takes special care of their oral cavity.
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth aches, hurts when pressed or bitten, and the pain remains for a long time, intensifies at night, and becomes long-lasting, you must return to the clinic. Aching pain during the treatment of pulpitis indicates that more radical, that is, surgical, methods are needed.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
How is pulpitis treated surgically?
As we have already noted, there are two possible options for surgical intervention:
- treatment of pulpitis using the amputation method with partial preservation of the pulp;
- treatment with complete removal of soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves.
If there is an objective possibility, the doctor will remove only the top of the pulp - from the crown, leaving the root part. The blood supply and sensitivity (innervation) of the tooth will be preserved. The technique is used in the treatment of children - for milk or permanent teeth that have not yet fully grown. This allows them to form normally in the future. Treatment for pulpitis can be carried out in one visit.
Eliminate cannot be deleted
A term that patients in all fields of medicine fear is chronic disease. Let's see what the consequences are in our case. Inflammation of the dental nerve with chronic pulpitis lasts from a month to several years. The pain syndrome remains, but becomes less pronounced. Seizures occur periodically. The patient can no longer chew on the side of the diseased tooth. The affected nerve begins to bleed and dentin continues to deteriorate. Chronic pulpitis is also characterized by several phases:
- Fibrous. Relatively “easy” stage. It occurs when carious tissues are not located close to the dental nerve. Unpleasant sensations occur only when you press on the tooth.
- Gangrenous. The pulp tissue is completely infected. The nerve changes color. The pain becomes more noticeable. The tooth is deeply affected by caries.
- Hypertrophic. Bacteria destroy the tooth down to the pulp chamber, connecting both cavities. A polyp grows in the vacated space, causing the nerve to bleed. The pain syndrome persists.
- Exacerbation. The final stage of the disease, when the patient is attacked by periodic attacks of pain, combined with constant aching unpleasant sensations. Pus appears in the tooth cavity, inflammation spreads to the tooth root, and periodontitis develops.
In 90% of cases, doctors treat fibrous pulpitis, less often - the second stage. In general, chronic inflammation is an irreversible process. The only solution is to remove the damaged dental nerve.
Treatment of acute pulpitis
The above methods are ineffective in treating exacerbations of chronic pulpitis, an acute disease when the tooth becomes a source of unbearable pain radiating to the ear, temple, and back of the head. With these symptoms, endodontic treatment of pulpitis is carried out - with cleaning of the root canals and complete removal of the pulp.
In dentistry, two modern methods of treating tooth canals for pulpitis are used: devital and vital.
- Treatment of pulpitis using the vital amputation method is carried out by removing the nerve, washing, cleaning and filling the canal.
- Devital treatment of pulpitis involves the use of medicinal pastes and requires several sessions.
These treatment methods are most often used for pulpitis on permanent teeth.
First visit:
Anesthesia or is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth?
How painful is it to treat pulpitis: It is definitely very painful if you decide to do it without anesthesia. Fortunately, modern anesthetics can completely solve this problem. If you still feel pain after anesthesia, this may be due to the anesthetic not being strong enough or the anesthesia technique being used incorrectly. The latter usually happens when the doctor tries to anesthetize large molars in the lower jaw (mandibular anesthesia, which is complex in technique, is performed there).
An example of anesthesia (video) –
Drilling out all carious tissues with a drill -
Firstly, at this stage all carious tissue is removed. Secondly, healthy tooth tissues are also partially removed, namely all tooth tissues above the pulp chamber and the mouths of the root canals. This is necessary to ensure visualization of the root canal orifices and ease of their processing with instruments. In Fig. 6-7 you can see the boundaries of excision of hard tooth tissues in the treatment of pulpitis. Figure 8 shows a view of the root canal mouths after they have drilled into the required amount of tooth tissue.
Tooth isolation from saliva –
This is done using a rubber dam. Isolation is necessary to prevent infection from the oral cavity from getting into the root canals along with saliva. This is standard international practice, but in Russia a rubber dam can often be seen only when a doctor fills a tooth. Normally, any work with root canals should be carried out using a rubber dam.
Removal of pulp from the tooth crown and root canals –
It is carried out with special tools designed to work in canals.
In Fig. 9 you can see tooth pulp wound around such a tool. By the way, video 1, which we posted above, shows the process of pulp removal. The video below clearly shows the moment when the tooth pulp is removed from the root canal (time – 1 minute 5 seconds). Treatment of pulpitis: video of nerve removal from a tooth
Measuring the length of root canals in a tooth –
This is one of the most important stages, because... if the length of each channel is determined incorrectly, it will cause -
- or underfilling of the canals, which will lead to complications after the end of treatment,
- or refilling the canals, which can lead to long-term pain and injury to the mandibular nerve.
Measuring the length of the canals is ideally carried out using a combination of the x-ray method and the use of an “apex locator”. In this case, first, special K-file instruments are introduced into each root canal in turn (Fig. 10), which are connected to the apex locator using a thin electrode (Fig. 12). The K-files are gradually advanced deeper into the root canal until there is a signal on the apex locator screen that the tip of the instrument has reached the apex of the tooth root.
It is necessary to measure each channel in turn, because The length of each channel is unique and there are no exact standards. After the measurements are completed and the data are recorded, K-files are simultaneously inserted into all channels (each to its own depth), and a control x-ray is taken (Fig. 11). The apex locator sometimes makes mistakes, so the x-ray will show how accurately the length of the canal was measured and whether adjustments are needed.
Mechanical processing of channels –
A budget option for mechanical treatment of root canals involves the use of manual files (K-files or reamers) - in Fig. 13 you can see a K-file in the root canal. The dentist rotates this instrument by the handle with his fingertips, and the cutting edges of the instrument excise chips from the walls of the canal, expanding it. The purpose of mechanical treatment is to widen the canal so that later it can be properly filled.
A better and more expensive processing option involves the use of an endodontic micromotor and special nickel-titanium files with shape memory. Mechanical processing of each channel is carried out to the depth determined at the previous stage. This is necessary to ensure that each root canal is filled exactly to the root apex. During the expansion process, it is very important to constantly rinse the canals with antiseptics, which is necessary for disinfection, but first of all, to wash out the shavings from the canal (24stoma.ru).
Mechanical treatment of root canals:
In video 1, you can see in detail how the expansion of root canals is carried out with ordinary hand instruments (for this, hand-held K-files of different diameters are used - from smaller to larger). In video 2, the dentist processes root canals using an endodontic micromotor and ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium profiles.
Placing a temporary filling –
After the canals are washed and dried to remove excess moisture, turundas soaked in antiseptic are left in them, and a temporary filling is applied to the tooth. The cost of treatment is calculated based on the number of root canals in the tooth.
Stages and stages of tooth treatment for pulpitis using the devital method
- Stage I.
The tooth is anesthetized and the carious cavity is cleaned. The pulp cavity is opened. - Stage II.
A devitalizing paste is placed into the exposed pulp and the tooth is filled for 3 to 7 days. People still call the paste “arsenic,” although it has nothing to do with this substance. - Stage III.
During your next visit, your dentist will clean the root canals according to medical protocol. - Stage IV.
If there is a risk that the tooth will crack, it is covered with a crown. If the hard tissues are well preserved or only slightly damaged, they are restored. The tooth is strengthened with a fiberglass or metal anchor pin and securely filled with photopolymer material.
The treatment time for pulpitis depends on how damaged the tooth is, the age of the patient, whether there are complications, and how many root canals should be treated.
Prerequisites
The most common cause of inflammation of the dental nerve (pulp) is the presence of caries. And in a deep stage. The infection reaches the soft tissues through the destroyed tooth tissue, provoking an inflammatory process. A similar situation occurs when a filling falls out or is damaged, when the pulp is “exposed.”
Bacteria can enter the tooth cavity from another source of infection in the body. Inflammation also occurs when a tooth is injured, minerals accumulate in the pulp, or low-quality components are used when filling canals.
Also, treatment of pulpitis may be required if the nerve overheats during preparatory procedures for prosthetics. If there is increased sensitivity, swelling of the pulp can be caused by the use of chemicals during therapy. It is also possible that an infection may accidentally enter the pulp chamber when eliminating a carious cavity.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Many patients believe that treatment for pulpitis is painful. In fact, pain accompanies the disease itself, and not the procedure for its treatment. The pulp tissue and nerves become inflamed, which causes unbearable painful sensations comparable to an electric shock. Pulp removal is absolutely comfortable, because high-quality anesthetics completely relieve the patient of pain while the doctor prepares the canals. During treatment or after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when the internal tissues are severely inflamed. Then safe painkillers are prescribed while healing occurs (1 - 3 days).
Pulpitis in a child
Pulpitis in a child
It is a mistake to believe that treatment of baby teeth is not necessary. Without adequate treatment, caries of a baby tooth in a child, just like caries in an adult, can very quickly turn into pulpitis with all its complications. There are known cases of death after complications of pulpitis due to the development of sepsis, when no more than two days passed from the first pulpitis pain to the development of facial edema and subsequent death.
To avoid any kind of complications, caries of primary teeth in children must be treated on time. And if the moment is missed and pulpitis has already developed, you need to contact the dentist immediately. A competent doctor will do everything possible to ensure that the treatment of a small patient is as painless, comfortable and, most importantly, effective.
Possible complications
If you delay visiting the dentist, inflammation can spread to the bone tissue of the tooth - periodontium. This is how one of the most common and dangerous complications of this disease begins - periodontitis, which can lead to tooth extraction. Periodontitis also occurs due to an unskilled approach to cleaning root canals.
If you are concerned about an elevated temperature after treatment for pulpitis, urgently contact a more reputable dentist, as the inflammation is progressing. Professional clinics use modern methods of canal treatment using microscopes, binoculars, visiographs, endomotors, and apex locators. These instruments prevent the risk of complications.
Unfortunately, pulpitis remains a common occurrence after caries treatment. The reason for its appearance is the same - the unprofessional actions of a doctor who violated medical protocols and made mistakes when filling. Perhaps he accidentally opened the pulp and gave bacteria access to it.
Removal of nerve (pulp)
Before this stage of treatment, the doctor carefully isolates the manipulation area from moisture. It is important to prevent saliva from getting into the canal cavities, because pathogenic microorganisms can also get inside the tooth along with it. Moisture insulation of a tooth can be carried out using different methods, but the most modern and effective method of protection is the installation of a rubber dam - a special lining made of latex material.
Next, the nerve is removed. To do this, the dentist takes a special tool with which he winds and then removes the pulp. The treatment of pulpitis does not end there - the next step in it will be the process of treating the canals, before which the doctor must accurately determine their length and get an idea of the shape. For these purposes, an x-ray is taken, and a specialized tool is used: an apex locator.
How much does tooth treatment for pulpitis cost?
The final cost of pulpitis treatment is influenced by many factors: the degree of destruction of hard tissue, the number of canals in the tooth, the presence of complications, concomitant diseases, and the chosen treatment method. If the tooth is permanent and has one canal, then the procedure in Moscow clinics will cost from 5,000 rubles. This amount includes a full range of services: x-ray diagnostics, application of anesthetic, installation of a rubber dam, treatment of caries, treatment of dental canals with cleaning, installation of a filling. Price may change if multiple sessions are required.
Will we treat him or let him live?
Often the fear of doctors forces us to make do with improvised methods. We take painkillers, fast, endure, in the hope that the sharp pain will go away on its own. Is it really possible to “wait out” an exacerbation, or is it better to get professional help in time? Let's figure it out.
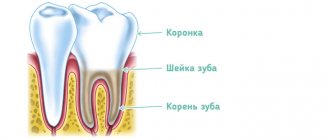
To find the right method of treating a disease, you need to know the origins of its occurrence. The core of the tooth, or pulp, is responsible not only for tooth sensitivity, but also for the production of dentin. The tissue strengthens the tooth from the inside.
The anatomical features of the pulp depend on the type of teeth. In the lateral row, as a rule, there is a chamber with three dental canals. The front row and incisors each have one branch. It is logical that molars are much more difficult to treat than canines or premolars.
Pathological changes in the pulp tissue form swelling, causing unbearable pain. The pain intensifies upon contact with hot food or when pressing on the tooth.